SHERPATH | Findings for Chests and Lungs
1/60
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Use this for reviewing the normal and abnormal findings for the chest and lungs!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
what are the expected findings for the following places of the chest via palpation (chest symmetry, rib cage, clavicles, sternum, anterior-posterior and transverse diameter, trachea, spine, and thoracic muscles/skeleton) in adult?
the chest is symmetric
rib cage is elastic
clavicles prominent superiorly (we can see them raised)
sternum is flat and inflexible with no abundance of overlying tissue
anterior-posterior diameter about half the transverse diameter
trachea midline with ‘equal’ space in each side (slight deviation can be expected) with no pulsation or significant tug (meaning no large mass that require tugging)
spine midline with normal curvature with rigid thoracic spine
nontender sensation
variable fremitus
no pulsation on the thoracic muscles and skeleton
what is the expected finding for the skin, mouth, and nail?
skin: dry, warm, and intact
mouth: oral mucosa moist
nail: pink nail beds
what is the expected finding for respiration?
breathing without difficulty
even, regular pattern
rate of (can be low as 10) 12-20 respiration per minute
rate of respiration to heartbeats = 1:4
what is the expected findings for chest movement?
bilateral & symmetric chest expansion
what is the expected quality of percussion tone over these areas: lungs, heart, liver, spleen, heavy muscles or bones, stomach, and viscera (other internal organs)?
lungs: resonance
heart: dull
liver: dull
spleen: dull
heavy muscles or bone: flat
stomach: tympany
diagrammatic excursion, what it measures, and how a student nurse can measure it?
movement of the diaphragm during breathing
to measure how far the diaphragm contract (how flat and obtuse it gets) during inhalation and exhalation
what is the expected finding for a diagrammatic excursion?
3-5 cm
higher on the right side due to placement over the liver
locate diagram by looking for area of the lower chest with dull sounds
DE after full exhalation: patient take deep breath and fully exhale and the student nurse mark the top areas of the diaphragm and marked it
DE after full inhalation: patient take deep breath and hold and the student nurse mark the top area of the diaphragm and marked it
review all of the expected finding when performing an inspection of the infant chest…
chest circumference is about 30-36 cm (usually 2-3 cm smaller than the head circumference)
breathing pattern varies with feeding, sleep, and maturity
30-80 (normal 40-60) breaths/min (expect higher in newborn from C-section)
obligate nose breather (baby can only breath through their nose and only do through mouth when crying)
periodic breathing and brief period of apnea lasting from 10-15 seconds
frequent hiccuping
paradoxical breathing (especially during sleep)
symmetric chest expansion
diaphragmatic breathing
sneezing
intrauterine growth retardation
smaller chest circumference than expected
gestational diabetes
bigger chest circumference than expected
what is the expected finding when performing palpation of the infant chest?
symmetric clavicles, rib cage, sternum
no masses
no crepitus (a crackling, popping, clicking, or grinding sound or sensation that occurs when you move a joint)
xiphoid is more mobile and more prominent than adult
what is the expected finding when auscultating the infant chest?
localization of breath sounds is more difficult
breath sounds easily transmitted from one area to another
gastrointestinal gurgling may be heard
mucus in the upper airway is normal
(immediately after birth) crackles and rhonchi can be heard immediately after birth due to fetal fluid in lung
true or false: percussion may be unreliable on infant as the examiner’s finger may be too large
true
what is the normal breathing rate for a 3 years old?
20-30 breaths/min
what is the normal breathing rate for newborn?
30-80 (normal 40-60) breaths/min
what is the normal breathing rate for a 3 year old?
20-30 breaths/min
what is the normal breathing rate for 10 year olds?
16-20 breaths/min
what is the normal breathing rate for 17 years and most adult excluding the elderly?
12-20 breaths/min
breaths sounds in adult vs pediatric
pediatric breathing sounds is usually more resonant, harsher, louder and more bronchial and bronchovesicular breaths sound can be heard throughout the chest
review the possible causes of decreased chest expansion in the elderly population…
respiratory muscle weakness
physical disability
sedentary lifestyle
calcification of rib articulation
increased use of accessory muscles
decline in lung elasticity
illness
what are some of the common finding when inspecting the chest of an elderly individual?
increased anteroposterior diameter (caused by calcification of rib articulation and kyphosis
kyphosis with flattening lumbar curse
hyperresonance
which is considered a normal finding during respiratory assessment of a newborn?
grunting
bradypnea
central cyanosis
acrocyanosis
acrocyanosis (blue color to the hand and feet and should disappear within a few hours or days) - a type of cyanosis
barrel chest
abnormal configurations of the thorax
increased anteroposterior diameter
kyphosis
abnormal configurations of the thorax
excessive outward curvature of the thoracic spine, leading to a hunched posture
scoliosis
abnormal configurations of the thorax
lateral curvature of the spine, causing uneven shoulders or hips
pigeon chest (pectus carinatum)
abnormal configurations of the thorax
forward protrusion of the sternum (pigeon chest)
funnel chest (pectus excavatum)
abnormal configurations of the thorax
sunken sternum and adjacent ribs (funnel chest)
review the possible causes of asymmetrical chest movement during breathing…
pneumothorax (collapsed lung)
pleural effusion (fluid in the pleural space)
fractured ribs or chest trauma
unilateral lung diseases (e.g., pneumonia, atelectasis)
unilateral or bilateral bulging
protrusion of the chest wall on one or both sides of the chest
unilateral: localized pleural effusion, pneumothorax, or mass
bilateral: COPD or obesity
bulging on expiration
conditions of the lungs like hyperinflated lungs, tracheal collapse, intercostal bulging, neck bulging, and palatal prolapse that cause bulging when exhaling
review the abnormal palpation findings of the thoracic muscles and skeleton/thoracic expansion..
pulsation
tenderness
bulges
depressions
unusual movement
unusual positions
asymmetric expansion
rib rigidity
review the abnormal palpation sensation and fremitus for the chest and lung…
crepitus - crackly, crinkly sensation with gentle, bubbly feeling
grating - palpable and coarse feeling/sound
decreased or absent fremitus - coarser and rougher
gentle or tremulous (significantly increased vibration) fremitus
variation between similar positions on right and left thorax
true or false: it is not abnormal for the trachea to have significant deviation or tug and can have present pulsation
FALSE; trachea with pulsation and positions with significant deviation or tug are ABNORMAL
true or false: a diaphragmatic excursion less than 3 cm indicates an abnormality
true
what one cause may dullness over the lung tissues indicates?
denser than normal lung tissues which can ultimately cause diminished air exchange
hyperresonance and absent breath sounds may indicate _________________ due to ____________
hyperinflation; pneumothorax; (the lung tries to push against the air but the lung can still inflate even hyperinflate not like atelectasis)
dullness and absent breath sounds may indicate ___________ due to _____________
hypoinflation; atelectasis (the lung cannot inflate properly due to blockage)
true or false: the student nurse should always note an abnormality when hearing vesicular, bronchial, or bronchovesicular sounds out of their expected lung area
true
vesicular breath sounds (description, expected area)
description: soft and low pitched
expected area: over most of the peripheral lung fields (the smaller airways and alveoli)
bronchial breath sounds (description, expected area)
description: loud and high-pitched
expected area: over the trachea and large airways (e.g., near the sternum or over the manubrium)
indicate con
bronchovesicular breath sounds (description, expected area)
description: medium-pitched and moderate
expected area: heard over the mid-chest anteriorly (around the 1st and 2nd intercostal spaces) and between the scapulae posteriorly
what does the diminished or absent bronchial, bronchovesicular, and/or vesicular lung sounds possibly indicates?
obstruction of the airway
pleural effusion
pneumothorax
ateletacsis (collapsed lung)
severe emphysema (loss of lung tissues and overinflation of alveoli)
thickened pleura
basically conditions that limits breathing
adventitious lung sounds and the types
abnormal lung sounds
crackles (rales): short, popping sounds commonly heard in pt with pneumonia or heart failures
wheezes (rhonchi): high-pitched whistling sounds or low-pitched snoring sounds common heard in pt with narrowed airways (e.g., asthma, bronchitis, etc)
atelectatic crackles: temporary crackling sounds - fine crackles that are not caused by a disease and go away after the person take a few deep breath
fine crackles (discontinuous/continuous. cause, what it sounds like, and significance)
discontinuous
cause: usually due to fluid in the alveoli or small airway (e.g., pneumonia, heart failure)
what it sounds like: short, high-pitched popping sounds (e.g., rubbing hair between fingers near the ear)
significance: common in pulmonary edema or atelectasis
using youtube to review the sound
course crackles (discontinuous/continuous, cause, what it sounds like, and significance)
discontinuous
cause: larger airways or more significant fluid (e.g., chronic bronchitis, COPD)
what it sounds like: low-pitched, moist, bubbling sounds
significance: indicates excess mucus or secretions in the airway
use youtube to review the sound
atelectatic crackles (discontinuous/continuous, cause, what it sounds like, anf significance)
discontinuous
cause: collapse of small airway in the lungs (e..g., after sleep or in bedridden)
what it sounds like: short, fine crackles similar to normal crackles but resolve after a few deep breath
significance: typically not pathologic and resolves after a few deep breath
use youtube to review sound (go to 0:50)
wheeze (sibilant) (discontinuous/continuous, cause, what it sounds like, anf significance)
continuous
cause: narrowing of the smaller airways (e.g., asthma, bronchitis)
what it sounds like: high-pitched, whistling sounds
significance: indicates airway constriction and obstruction
wheeze (sonorous - how is rhonchi similar?) (discontinuous/continuous, cause, what it sounds like, anf significance)
continuous
cause: larger airway obstruction (e.g., secretions or bronchitis) - rhonchi is similar as it also affect larger airway but instead of inflammation it is secretion accumulation causing gurgling sounds
what it sounds like: low-pitched, snoring or gurgling sounds, often heard during exhalation
significance: suggests mucus in larger airways or obstruction
use youtube to review the sound
pleural friction rub (discontinuous/continuous, cause, what it sounds like, anf significance)
discontinuous
cause: inflammation of the pleural surfaces rubbing together (e.g., pleuritis)
what it sounds like: a dry, grating sound, like walking on fresh snow
significance: suggest pleural inflammation or pleuritis
use youtube to review the sound (go to 0:32)
malodorous breath is an indication of a ________________
pulmonary infection
flaring of the alae nasi is an indication of __________________
air hunger
which terms identifies a fast, deep breathing pattern?
bradypnea
sighing
air trapping
kussmaul breathing
kussmaul breathin
Which breath sounds would be classified as abnormal on auscultation of the peripheral lung tissue in a healthy adult?
Select all that apply.
Tracheal
Bronchial
Vesicular
Wheezing
Bronchovesicular
tracheal, bronchial, wheezing, and bronchovesicular (any other breaths sounds heard besides from vesicular in the peripheral lung tissues ARE ABNORMAL)
During the respiratory assessment, the nurse percusses hyperresonance over the lungs and notes absent breath sounds, precordial clicks, and crackling. Of which condition are these abnormal findings indicative?
Atelectasis
Bronchiectasis
Pneumothorax
Pneumonia consolidation
pneumothorax
which finding regarding the quality of tactile fremitus is considered normal on palpation of the chest?
absent
coarse/rough
bilateral symmetry
tremulous and gentle
bilateral symmetry
which is a normal finding on palpation of the ribs?
elasticity
crepitus
rigidity
tenderness
elasticity
what is a normal finding on palpation of the sternum?
inflexibility
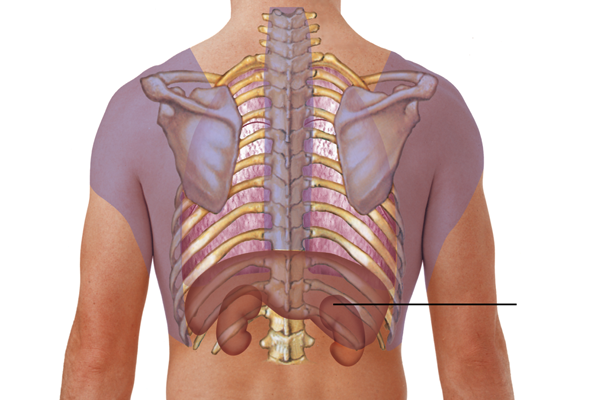
Which tone would the nurse expect to hear when percussing the indicated area?
Dullness
Flatness
Resonance
Tympany
dullness
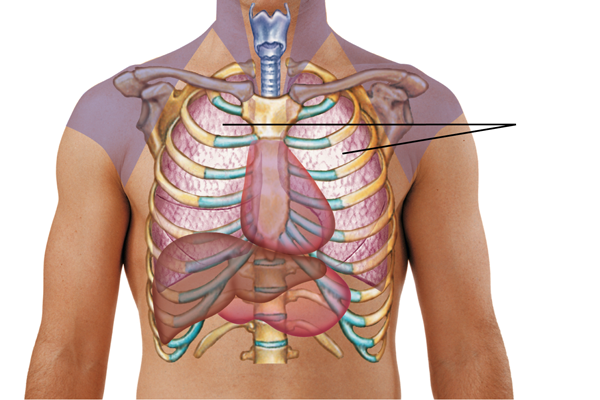
which tone would the nurse expect to hear when percussing the indicated area?
dullness
flatness
resonance
tympany
resonance
When comparing the diaphragmatic excursion of the left and right sides of the body, what is the expected finding?
Equal distance on left and right sides
Diaphragm higher on left side
Diaphragm higher on right side
Excursion typically not measurable on right side
higher on the right side due to the placement of the liver
which breath sounds would be expected on auscultation of the bronchi?
vesicular
bronchovesicular
bronchial/tracheal
tubular
bronchovesicular