CS FINALS REVIEWER
1/131
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
132 Terms
Internet
the go-to place for information, communication, banking, shopping, media and entertainment, and so much more.
History of the Internet (dates)
1957, 1969, 1970s, 1980s, 1990s, 21st century
1957
launch of Sputnik, development of Advanced Research Projects Agency (ARPA)
1969
first ever message sent through ARPANET, UCLA sent “log in” but Stanford only received “lo”. Only four computers were connected to the ARPANET
1970s
Ray Tomlinson created the first electronic mail (email). first computer-to-computer chat happened with Liza and Parry. First use of the term Internet.
1980s
Governments and universities all around the world started researching and implementing their networks.
1990s
ARPANET shut down. Tim Berners-Lee invented World Wide Web. Surfing the internet coined. First item ordered online was a pizza. Yahoo and Google were born
21st century
The 21st Century is known to be the decade when social networking sites emerged.
TCP/IP
Rules of communication for computers.
Packets
small pieces of information transmitted over a network
Transfer Control Protocol (TCP)
Transfer Control Protocol (TCP) breaks large packets into smaller ones.
Internet protocol (IP)
Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and routes packets.
IP Addresses
used by IP to identify destinations
Domain Name System (DNS)
allows the use of alphanumeric characters instead of numbers for IP addresses. (google.com/120.28.5.177)
Servers
machines that hold shared resources and always connected to the network.
Clients
machines for personal use that request a page from the server.
Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (ICANN)
assigns domain names, IP addresses, protocol parameters, and port numbers.
World Wide Web
collection of interconnected documents and other web resources. just a service that runs on the Internet.
Internet vs internet
Internet is an electronic communications network that connects computer networks globally. “internet” is still a computer network, but is not connected to the Internet
ISP
Internet service provider
Types of Internet access technologies
Dial up and broadband
Dial-up
uses a modem and a phone call to connect, one of the slowest methods of accessing the Internet
Broadband
wide bandwidth, most used form of Internet access
Types of broadband
DSL, Cable connection, Fiber optic, Satellite, Mobile broadband
DSL
Digital Subscriber Line, utilizes unused telephone wires.
Cable connection
delivers data over the same cable used to deliver television data.
Fiber Optic
uses light to transmit data signals; fastest
Satellite
uses orbiting satellites to transmit and receive data
Mobile Broadband
wireless broadband technology accessible via smart devices (most used in the Philippines)
Types of Internet browsers
Opera, Safari, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, Internet explorer, Microsoft Edge
The golden rule
Do unto others online as you would have done to you.
Cyberbullying
repeated use of the online platform to embarrass, strip dignity, sow fear, and incite violence against another person.
Not cyberbullying
express thoughts about a person, an incident, or an opinion
Three types of attack
Attack on reputation, attack on appearance, attack on victim’s opinion
Attack on reputation
Attacks on their reputation and branding (Leni Robredo, “Robredo Branding”)
Attack on appearance
Attacks on how someone looks (Nancy Binay, skin color)
Attack on victim’s opinion
Attacks on victim’s views and values (Senator Bong Go, Duterte)
Three manners of attack
Spreading edited images, spreading private videos, spreading lies
Trolling
act of triggering people on the Internet by starting arguments, posting off-topic messages, or provoking negative response.
Personal Information
any and all forms of data that identify an individual
Data Privacy Act 2012
states that the collection of personal data “must be a declared, specified, and legitimate purpose”. Also states such data must be “freely given, specific, and informed”.
Online Privacy
ability to control what information you share, who can see what you share, and what others can do with it
Digital Footprint
collected information about an individual across multiple websites
Surfing
go from one website to another in search of information of interest
Website
Set of related web pages served from a single web domain. Websites are accessible through URL
URL
the global address of a website. Consists of protocol, server name, path/filename, and anchors
Protocol
set of rules and formats for information exchange. Consists of HTTP, HTTPS, and FTP
HTTP
hypertext transfer protocol
HTTPS
hypertext transfer protocol secure
FTP
file transfer protocol
Server name
Internet address of the web server, right after protocol
Path/filename
folder and filename, after server name
Anchors
bookmarks within an HTML file (#)
Phishing
act of attempting to acquire information by masquerading as a trustworthy entity
Tags
used to implement html elements
Opening tag
has only brackets <…>
Closing tag
has a bracket followed by a forward slash and closed with another bracket </…>
Self-closing tag
opens and closes with one tag <tagname/>
1990
Tim Berners-Lee created the first Web Browser, the World Wide Web
Tim Berners-Lee
creator of first web browser
Mosiac
first web browser
HTML 1
1993, Tim Berners-Lee linked documents with hypertext; HTML was intended as platform-independent
HTML 5
established guidelines stating the adding of new features based on HTML, CSS, the DOM structure, and JavaScript standards; HTML became device-independent
Creating an HTML document
Decide how your files will be organized
Decide on a naming convention and be consistent with it (kebab-case, CamelCase, snake_case)
Decide on a text editor
Document Object Model (DOM)
provides a common tree-like structure; shows the structure of tags
Document type
<!DOCTYPE html> is written at the start of an HTML document
HTML element
<html> . . . </html> is used to tell the browser uses HTML
– has an attribute lang meaning language
Head element
includes information mostly invisible to the user
> has the metadata, language, title, and supporting files
> metadata tells the used character set/keywords/author/etc
Title element
– declared inside the head
– output is displayed on top of the browser
– uses <title> . . . </title>
Body element
– contains all displayed content on the screen
– anything not on the body will NOT be displayed
Display
– contains the design elements
-either block, inline or inline-block
Inline
only takes up as much space as needed; ex: <span>, <a>, <img>
Block
can take up screen’s whole width and height ex. <div>, <h1>-<h6>, <p>, <header>, <footer>, <section>
Inline-block
formatted like an inline; modifications are allowed
Headings
- subsections; appear nested in the outline
– block elements that create a new line for the next elements
- h1 is the largest, h6 is the smallest
Paragraph
– block element that should only contain inline elements
– body can have multiple paragraphs, but paragraphs cannot be declared inside one another
– uses <p> . . . </p>
Divider
– generic section larger than a paragraph
– multiple dividers can be declared inside dividers
– uses <div> . . . </div>
Horizontal rule
– a partition that indicated a thematic break
– a self-closing tag, uses <hr>
Line breaks
– “breaks” a line and starts a new one
– a self-closing tag, uses <br>
Coding practices
use comment
declare <DOCTYPE! html>
type in lowercase for elements
close all elements
use indentation
Ordered list
– lists whose items are denoted by a number or letter
– uses <ol> . . . </ol>
Unordered list
– lists whose items are denoted by bullet points or icons
– uses <ul> . . . </ul>
Nested list
ordered/unoredered lists inside one another (make sure to use <li> and </li> and close the lists with the one inside going first>
Attributes
– provide additional information about an element
– always specified in the opening tag
- use “type =” and always put the attribute in quotes
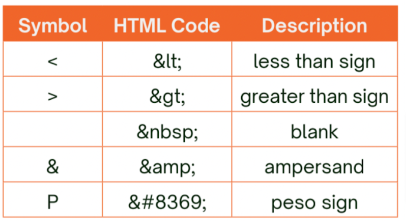
Special entities
typing these out in a paragraph or in <span> will still be okay but code might get confused
Details
– adds a paragraph of information that can be opened
– uses <details> . . . </details>
Summary
– what appears when details is clicked
– uses <summary> . . . </summary>
Span
– inline tag for a plain text
Subscript
– transforms text into a subscript <sub> </sub>
– e.g. O₂
Superscript
– transforms text into a superscript <sup> </sup>
– e.g. 2²
Text-heavy pages
– they are like “lite” versions of websites
– they dwell less on images and visual aids
HTML images
– used to insert images on the screen
– written as <img> (self-closing tag)
– carry two important attributes, src (source) and alt (alternative text)
– support .svg, .gif, .bmp, .png, .jpg, and .jpeg
src
the file name and the file type, displays the SOURCE of the image (the picture)
alt
displays a brief description of the image proper just in case there are any errors or it cant load
Icons
– used instead of texts
– goal is to signify a common object that is universally understandable
– some appear on browser tab or browser’s main body
– e.g. home icon for home page, bell icon for notifications
Favicons
– icons displayed in the browser’s tab
– has attributes rel =“icon” (for relation) and type =“image/png”
– goes between <head> . . . </head>
– not displayed in Trinket
href vs. src
href (hyper-reference) is like the src, but href is generally used for HTML elements, whereas src is for the non-HTML elements
Font Awesome
– a collection of icons used by developers for free
– the icons are recognizable worldwide
To use Font Awesome in your code, the Content Delivery Network (CDN) should be linked in the head and the <i> tag should be declared in the body.
Copyright
“legal protection extended to the owner of the rights in an original work.”
Creative commons
license created for content creators to allow as many people to see, use, and share their work as possible