16/17 Hemostasis
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
Definition of homeostasis
• Control of bleeding following injury
• Dissolution of clot following tissue repair
• If balance is not maintained bleeding or clotting to death can occur
• Excess bleeding- trauma, major surgery, hemophilia
• Clotting- stroke, MI, thrombosis
Major systems involved in hemostasis
• Vascular- lumen is lined with flattened endothelial cells which become thrombogenic when damaged
• Platelets- part of primary haemostatic plug
• Coagulation- cascade of enzymes that enable formation of fibrin clot
• Fibrinolytic- clot dissolution
Minor systems involved in hemostasis
• Kinin- family of plasma proteins that activate vasodilation, blood coagulation and fibrinolysis
• Complement- activates inflammation, opsonisation, direct killing of microbes by lysis
• Serine protease inhibitors- serine proteases cleave peptide bonds, inhibitors regulate coagulation cascade e.g. anti-thrombin
Four main processes in coagulation
• Constriction of blood vessels which limits blood flow to area
• Platelet activation by thrombin leads to formation of platelet plug
• Formation of fibrin clot
• Dissolution of clot by plasmin (fibrinolysis)
Primary hemostasis
• Constriction of injured vessels
• Exposure of subendothelial collagen
• Adhesion and aggregation of blood platelets on damaged surface
• Formation of hemostatic plug
Secondary and tertiary hemostasis
• Formation of thrombin catalysed by the surface of activated platelets
• Formation of thrombin via activation of factor 7 by tissue factor (3)
• Conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin catalysed by thrombin
• Formation and stabilisation of fibrin clot
• Tertiary- clot dissolution
Structure of blood vessels
• Smooth muscle - vasoconstriction
• Connective tissue contains collagen for platelet activation, more in veins
• Walls have a thin layer of endothelium that is non-thrombogenic to ensure smooth blood flow and stop unwanted thrombosis
• Lumen inside where blood flows
Role of blood vessels in hemostasis
• Vasoconstriction minimises blood loss
• Diverts blood from injured vessel to intact ones
• Collagen fibers become exposed when endothelium is damaged which causes thromboplastin and von Willebrand factor to leak from the cells
• Platelets activate after coming into contact with collagen fibers and vWF
• Coagulation system activated when blood proteins contact thromboplastin (tissue factor / F3)
Structural functions of platelets
• Cellular fragments of megakaryocytes
• Alpha granules contain adhesive proteins, coagulation and fibrinolytic factors, growth factors, cytokines, chemokines (recruit to damaged area)
• Dense granules contain ADP/ATP for recruitment of more platelets, Ca++ for platelet activation and fibrinogen attachment, serotonin for vasoconstriction, histamine for platelet aggregation
• Surface connected tubular system for secretion of coagulation factors and rapid uptake of calcium
• Surface receptors specific for vWF and fibrinogen
Role of platelets in hemostasis
• Adhesion by exposure to subendothelial connective tissue which contains collagen fibers and vWF, platelets adhere to damaged endothelium
• Shape changes from normal round / oval shape to irregular with many projection after encountering collagen fibres, irreversible once prolonged stimulation causes degranulation
• Release of alpha and dense granules via tubular system
• Aggregation once fibrinogen binds to platelet receptors, also induced by ADP, collagen, thrombin, vWF
• Results in primary hemostatic plug which is fragile, conversion of fibrinogen to fibrin stabilises it (facilitated by thrombin)
Coagulation cascade
• Generates thrombin, converts soluble fibrinogen to fibrin
• Enmeshes platelet aggregates at the site of vascular injury which creates a more stable hemostatic plug
• Reaction occur on exposed collagen
Coagulation factors
• Plasma proteins - most are serine proteases except fibrinogen, F5, F8
• Synthesised in the liver, vWF made by endothelial cells and megakaryocytes
• Vitamin K is necessary for y-carboxylation of some factors (2, 7, 9, 10) which is a post-translational modification that converts the factors to their functional form
• If vitamin K is deficient, the proteins cannot bind calcium and are non-functional
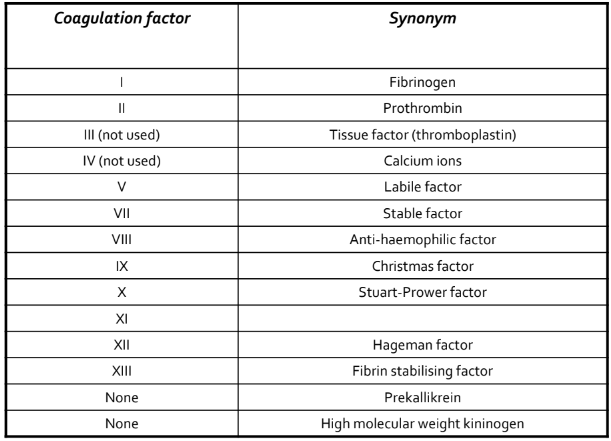
Coagulation factor names
Intrinsic pathway
• Initiated by contact of flowing blood with foreign surface e.g. collagen, phospholiipid
• This activates F12 to F12a which also links intothe fibrinolytic, complement and kinin systems
• Prekallikrein and HMWK enhance activation
• F11 is activated by F12a, F9 is activated by F11a
• F9a combines with F8 in the presense of calcium and phospholipid to activate F10
Extrinsic pathway
• Tissue factor (F3) released from injured cell wall activates F7 to form F7a in presence of calcium
• F3a and TF complex which activates F10 and F9 (both commmon and intrinsic pathways)
• TF pathway inhibitor regulates this complex
• This system allows for quick fibrin production on the surface of injured cells and accelaration of intrinsic pathway
• Both pathways always work together in vivo
Common pathway
• Once factor 10 is activated (F10a) it forms a complex with F5, prothromin (F2), calcium and phospholipid
• This complex assembles on the surface of activated platelets and converts prothrombin to thrombin F2a
• Thrombin converts fibrin to fibrinogen which allows the fibrin strands to polymerise, it also regulates factors 5 and 8
• Thrombin activates F13 to F13a which catalyses the formation of crosslinks between fibrin molecules to stabilise the clot
Fibrinolytic system
• Plasminogen is an inactive form of plasmin which has a high affinity for fibrinogen and fibrin
• Plasminogen activators like tissue plasminogen activator are found in tissues and secretions
• Once plasmin is activated, it digests the clot from the inside to outside
• Fibrinolytic inhibitors e.g. a1-antiplasmin prevent uncontrolled proteolytic activity
Regulatory proteins
• Serine protease inhibitors (serpins) regulate coagulation activity
• Antithrombin is present in plasma and neutralises F10a and thrombin as well as most active serine proteases of the system
• Protein C is a plasma protein that is activated by thrombin and inactivates F5 and F8
• Thrombomodulin is a membrane bound glycoprotein lining vascular endothelium which binds to thrombin and converts it to a less active form, also activates protein C
• Others include heparin co-factor 2, a2-macroglobulin, a1-proteinase inhibitor