AP Human Geography Unit 6
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Agglomeration
Clumping together of industries for mutual advantage.

Barriadas
another name for squatter settlements that are residential developments that take place on land that is neither owned nor is rented by its occupants

Bid-rent theory
a geographical economic theory to how the price and demand on real estate changes as the distance towards the CBD increases
Blockbusting
a process by which real estate agents convince white property owners to sell their houses at low prices because of fear that black families will soon move into the neighborhood

CBD (central business district)
The area of a city where retail and office activities are clustered

Census tract
An area delineated by the U.S. Bureau of the Census for which statistics are published
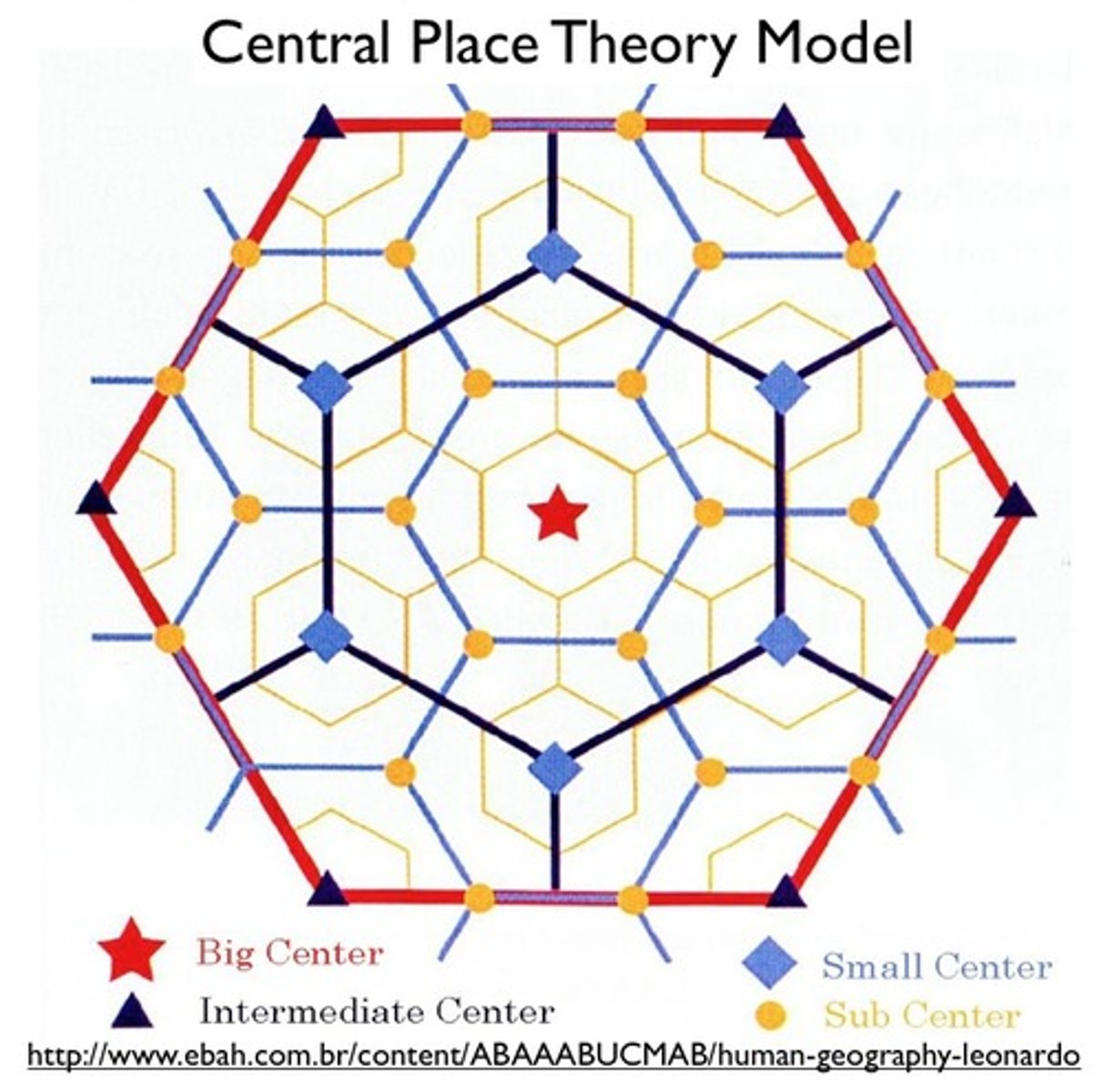
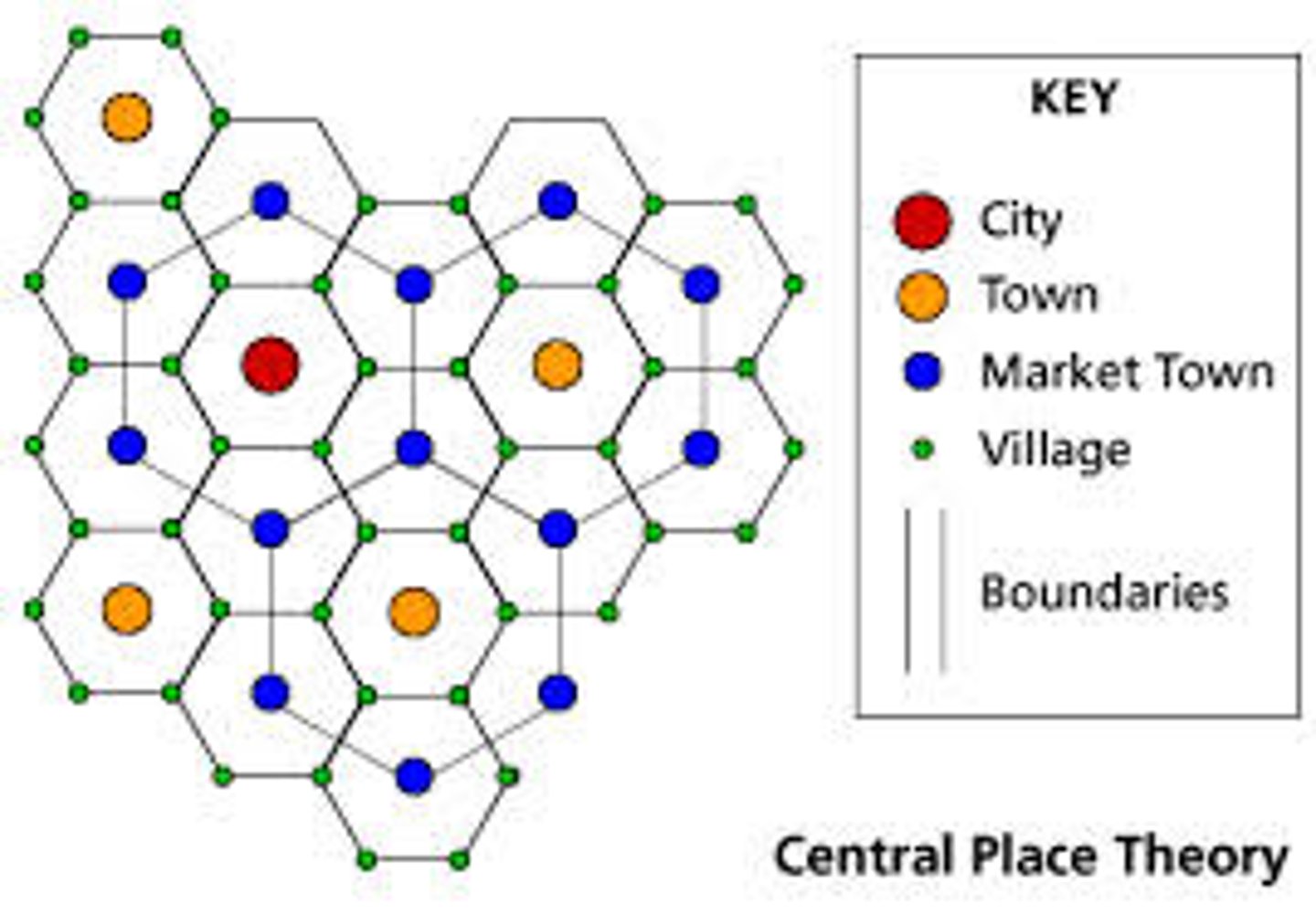
Central-place theory
the distribution of services is based on the fact that settlements serve as market areas for services; larger settlements are fewer and farther apart than smaller settlements and provide services for a larger number of people who are willing to travel farther
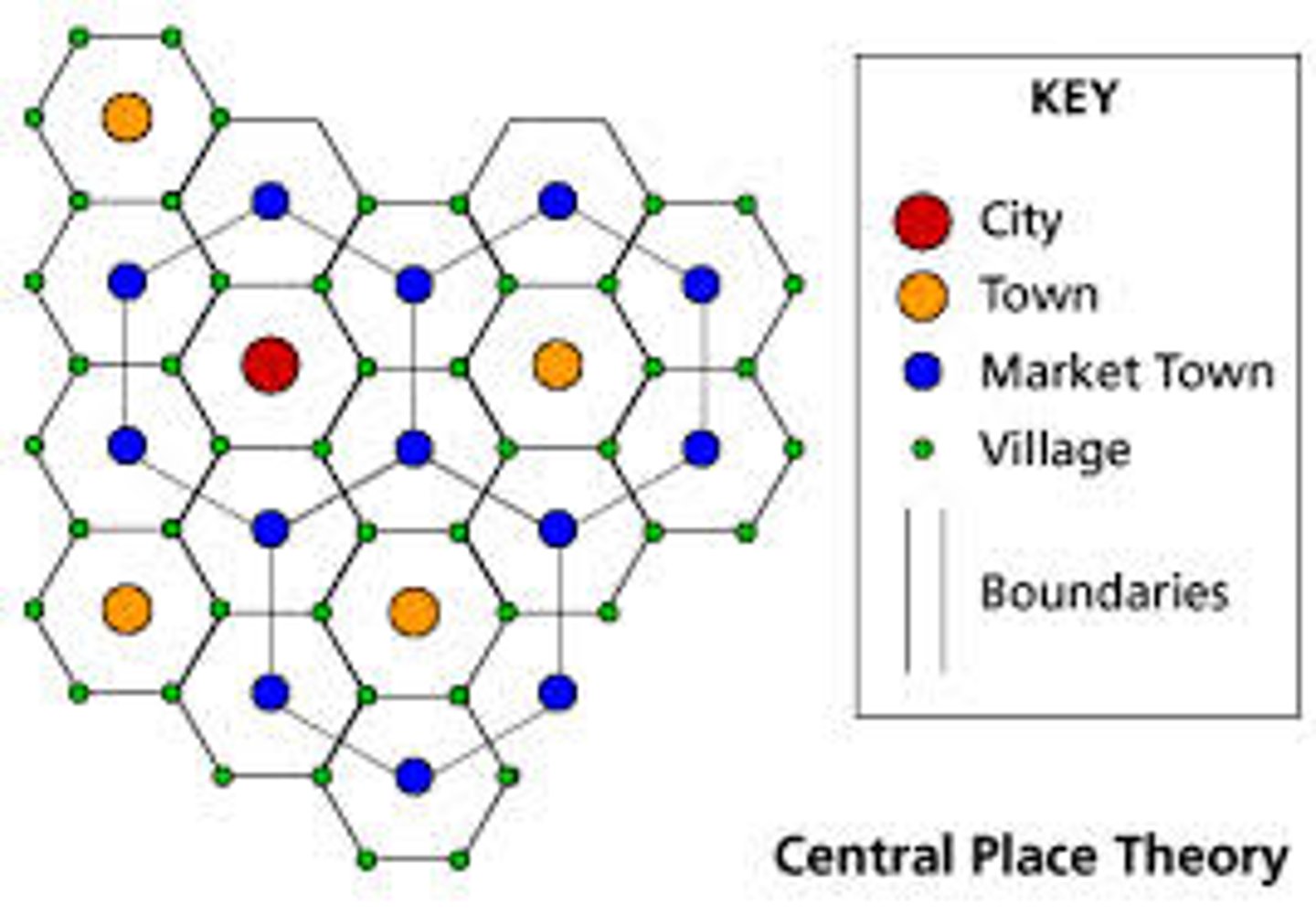
Walter Christaller
created the central place theory which displayed the ideas that central places would provide services and goods to the surrounding areas
City
conglomeration of people and buildings clustered together to serve as a center of politics, culture, and economics.

Colonial city
compared to older cities , colonial cities typically contain wider streets and public squares, lager houses, surrounded by gardens, and much lower density

Commercialization
the transformation of an area into an area commercially attractive to residents and tourists alike

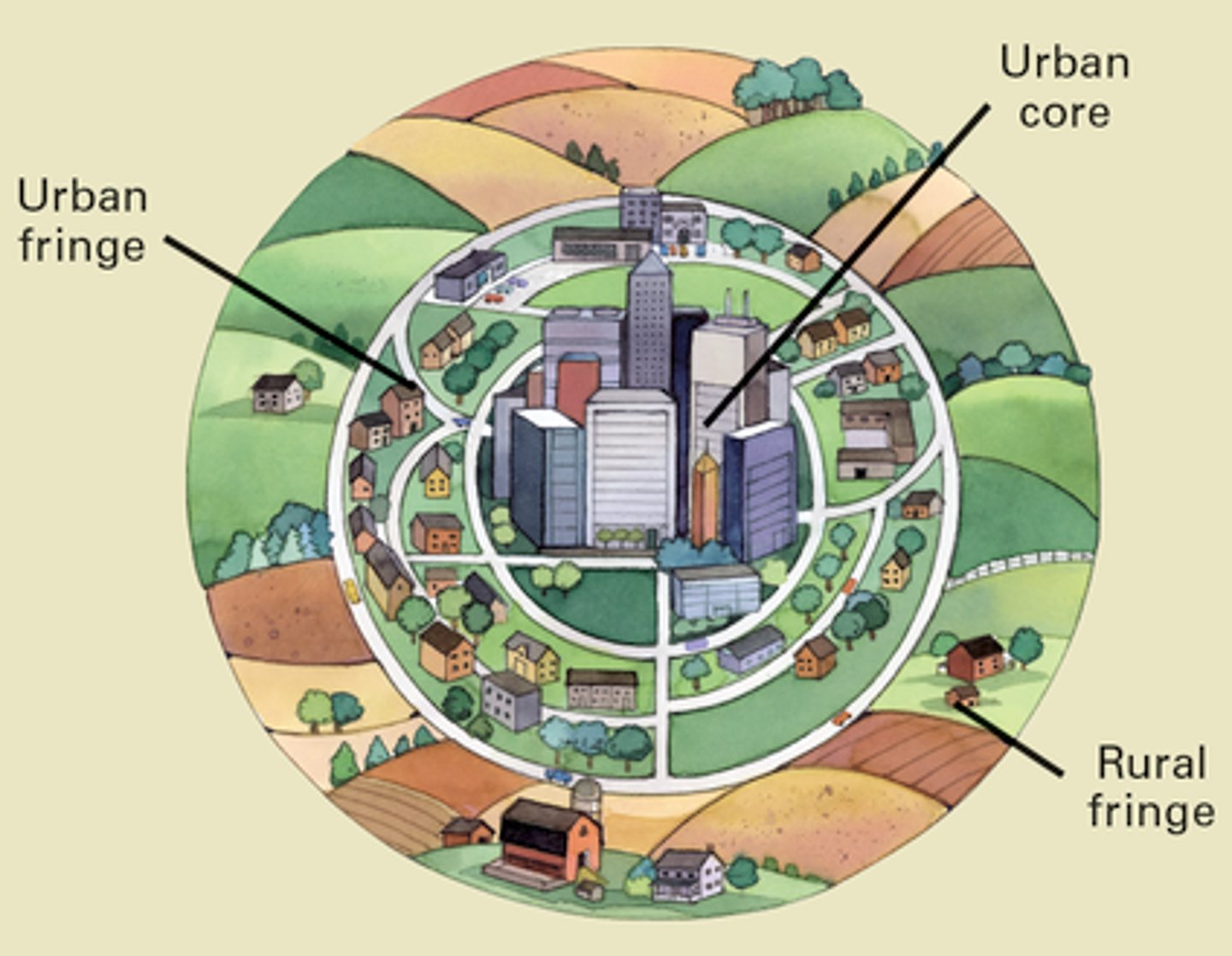
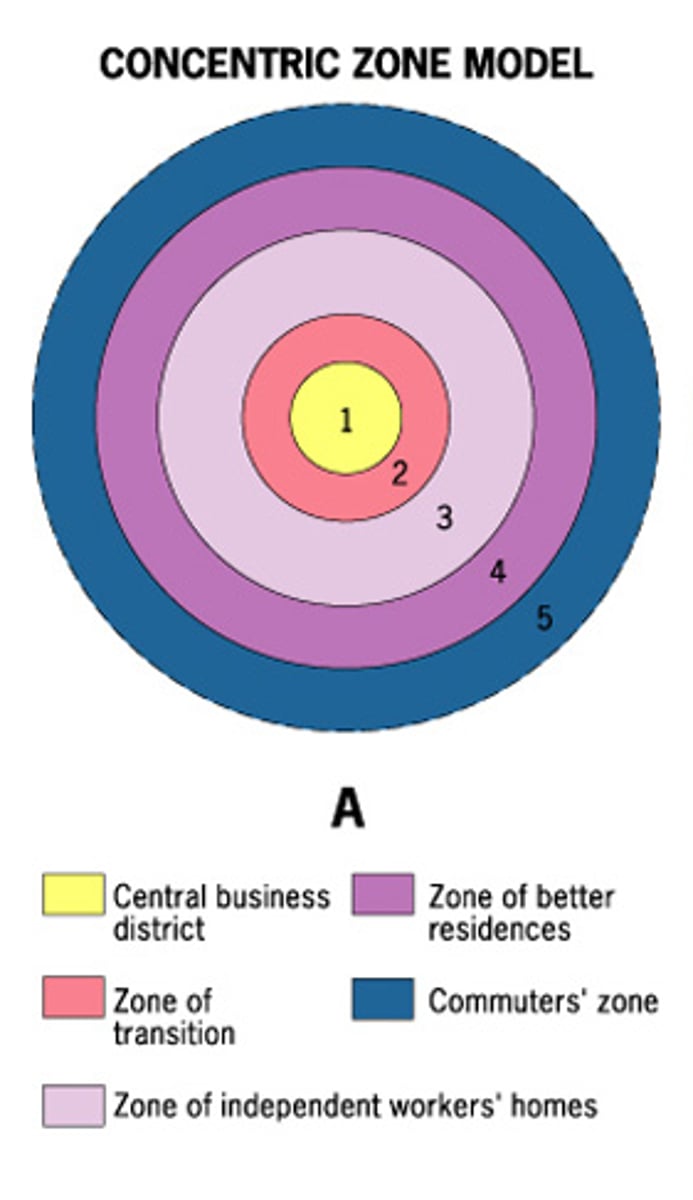
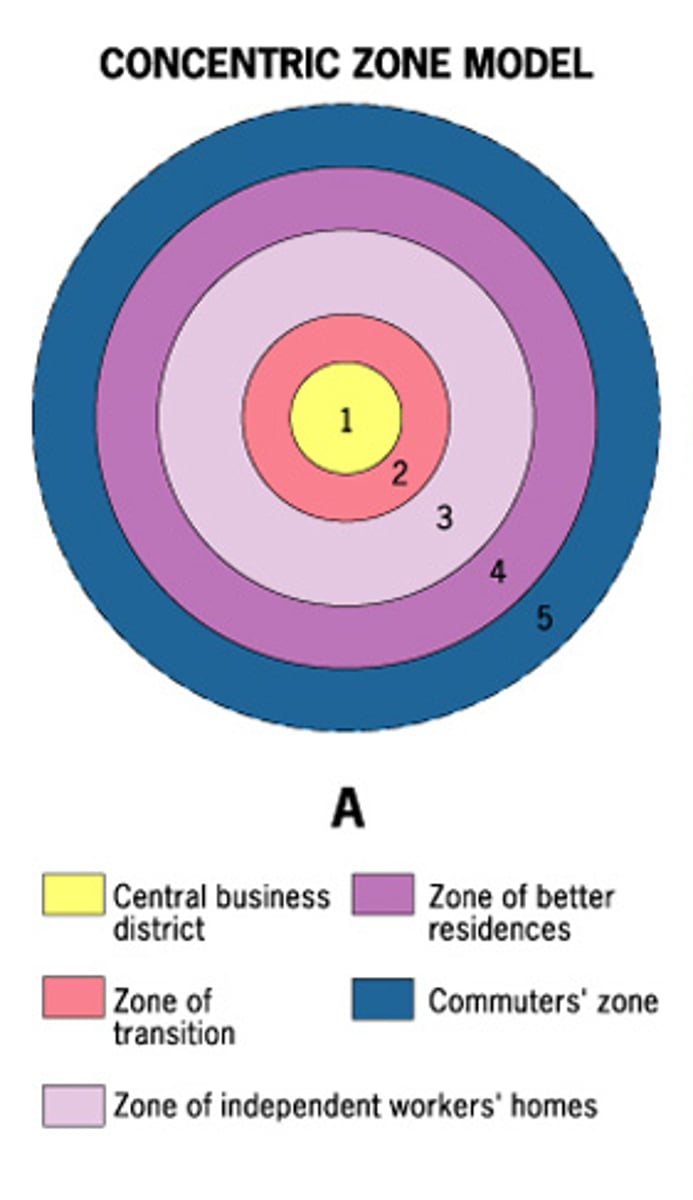
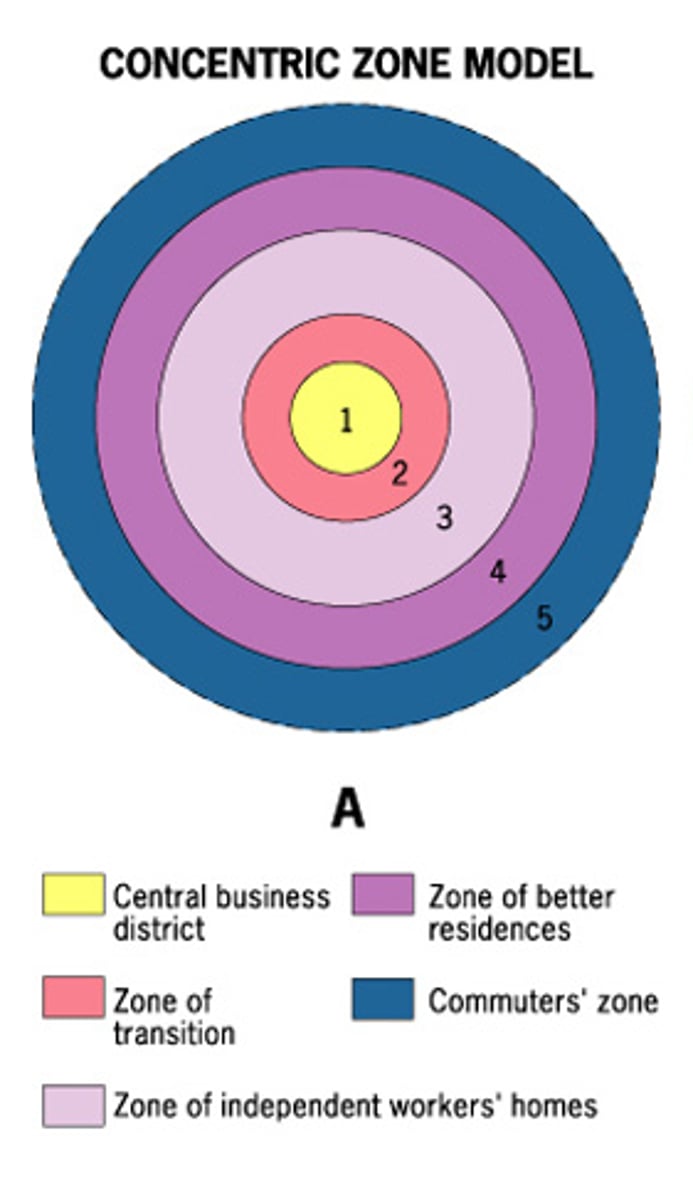
Commuter zone
the fifth ring in the concentric zone model that is beyond the continuous built-up area of the city
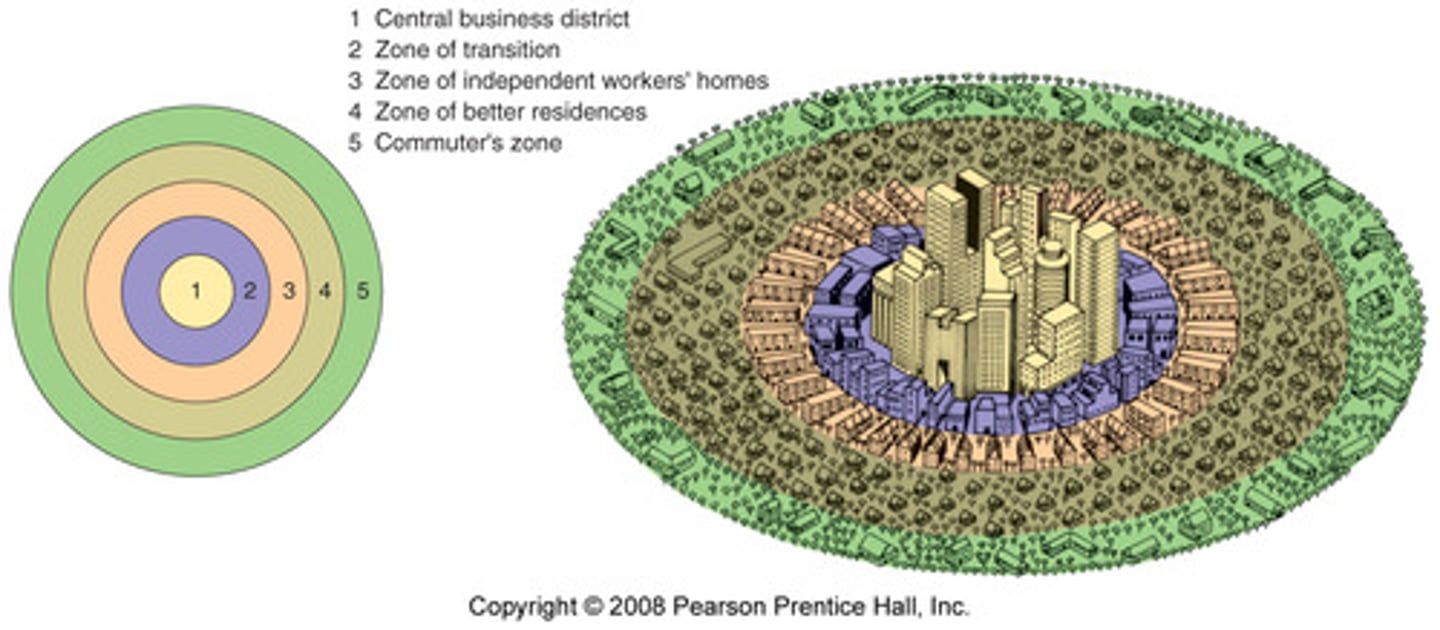
Concentric zone model
a model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are spatially arranged in a series of rings; also called the Burgess Model
Counterurbanization
net migration from urban to rural areas
Deindustrialization
a process of social and economic change caused by the reduction of industrial jobs in a country or region

Economic Base (basic/nonbasic)
a community's collection of basic industries

Edge city
a large node of office and retail activities on the edge of an urban area

Employment structure
how the workforce is divided up between the three main employment sectors - primary, secondary, and tertiary

Favela
the Brazilian equivalent of a shanty-town, which are generally found on the edge of the city

Gateway city
serves as a link between one country or region and others because of its physical situation.

Gentrification
the invasions of older, centrally located working-class neighborhoods by higher income households seeking the character and convenience of less expensive and well-located residences

Ghetto
during the Middle Ages, a segregated Jewish neighborhood; now the term is used for low-income minority neighborhoods

Great cities
a city with a population of more than 1 million

Hinterland
the area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services, also called the marketplace

In-filling
the use of vacant land and property within a built-up area for further construction or development (like what was done in the Pittsburgh study)
Informal sector
it is the economic activity that is neither taxed nor monitored by a government; and is not included in that government's GNP

Infrastructure
the fundamental facilities and systems serving a country, city, or area, such as transportation and communication systems, power plants, and schools

Inner-city
residental neighborhoods that surround the CBD

Invasion and succession
new immigrants to a city often move to areas occupied by older immigrant groups

Lateral commuting
commuting between two suburbs

Medieval cities
Cities that developed during the Middle Ages that contain narrow buildings, winding streets, an ornate church in the center, and high walls; led to modern European cities

Megacities
a recognized metropolitan area with a total population in excess of 10 million people

Megalopolis/conurbation
an area of an adjacent large metropolitan areas that overlap. BOSNYWASH
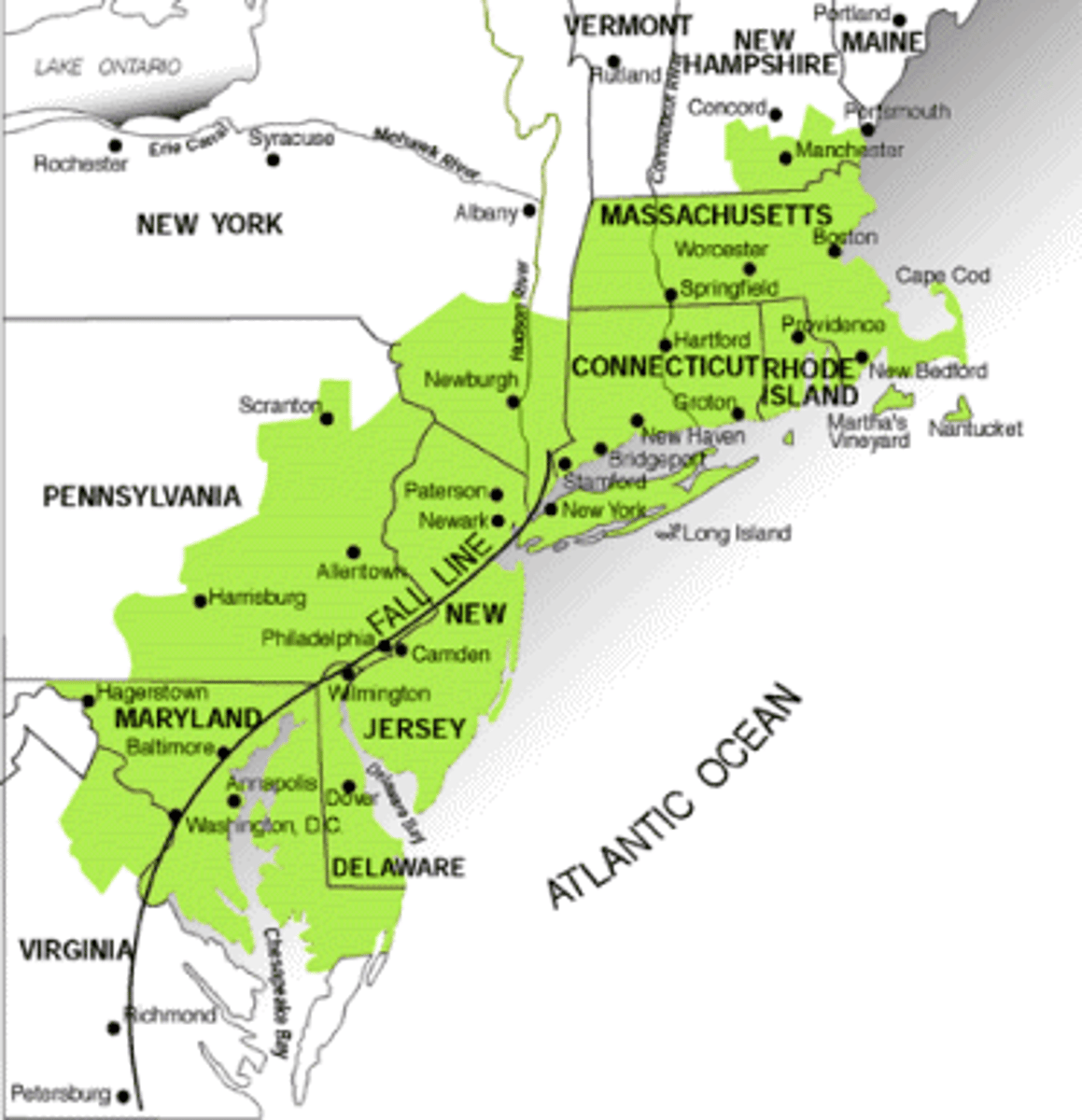
Metropolitan area
a major population center made up of a large city and the smaller suburbs and towns that surround it
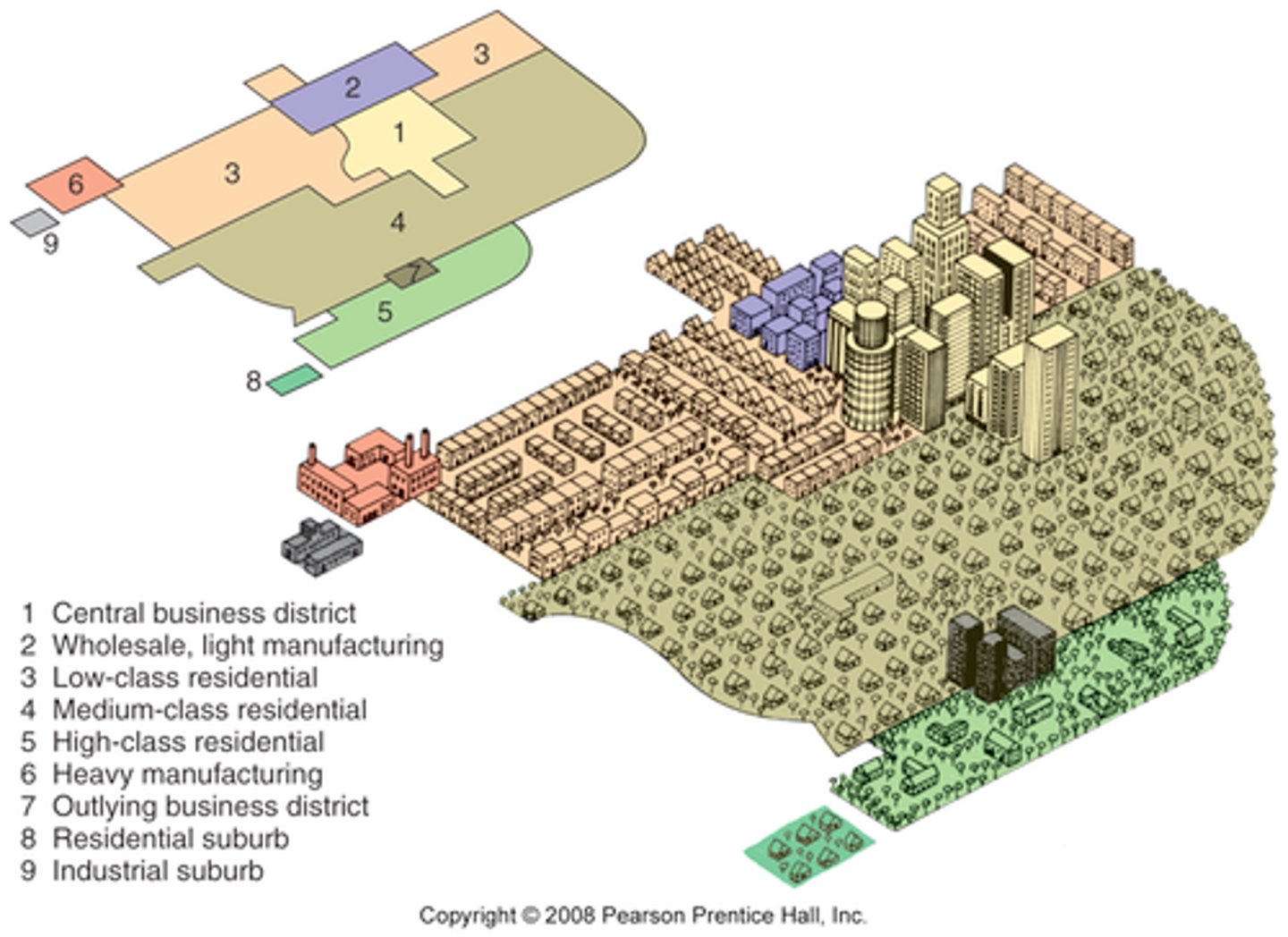
Multiple Nuclei Model
a model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a collection of nodes of activities; also called the Harris Ullman Model
Multiplier Effect
when the basic sector creates more and more nonbasic sector jobs

Office Park
is an area of land in which many office buildings are grouped together (business suburb)

Planned Communities
any community that was carefully designed beforehand and often built in a previously undeveloped area
Postindustrial city
a city in which an economic transition has moved most jobs away from a secondary into a service-based economy

Primate City
the largest settlement in a country with more than twice as many people as the second ranking settlement

Racial Steering
refers to the practice in which real estate brokers guide prospective home buyers towards or away from certain neighborhoods based on their race

Rank-size rule
A pattern of settlements in a country, such that the nth largest settlement is 1/n the population of the largest settlement.
Redlining
a process by which banks draw lines on a map and refuse to lend money to purchase or improve property within boundaries
Restrictive Covenants
provision in a property deed preventing sale to a person of a particular race or religion; loan discrimination; ruled unconstitutional

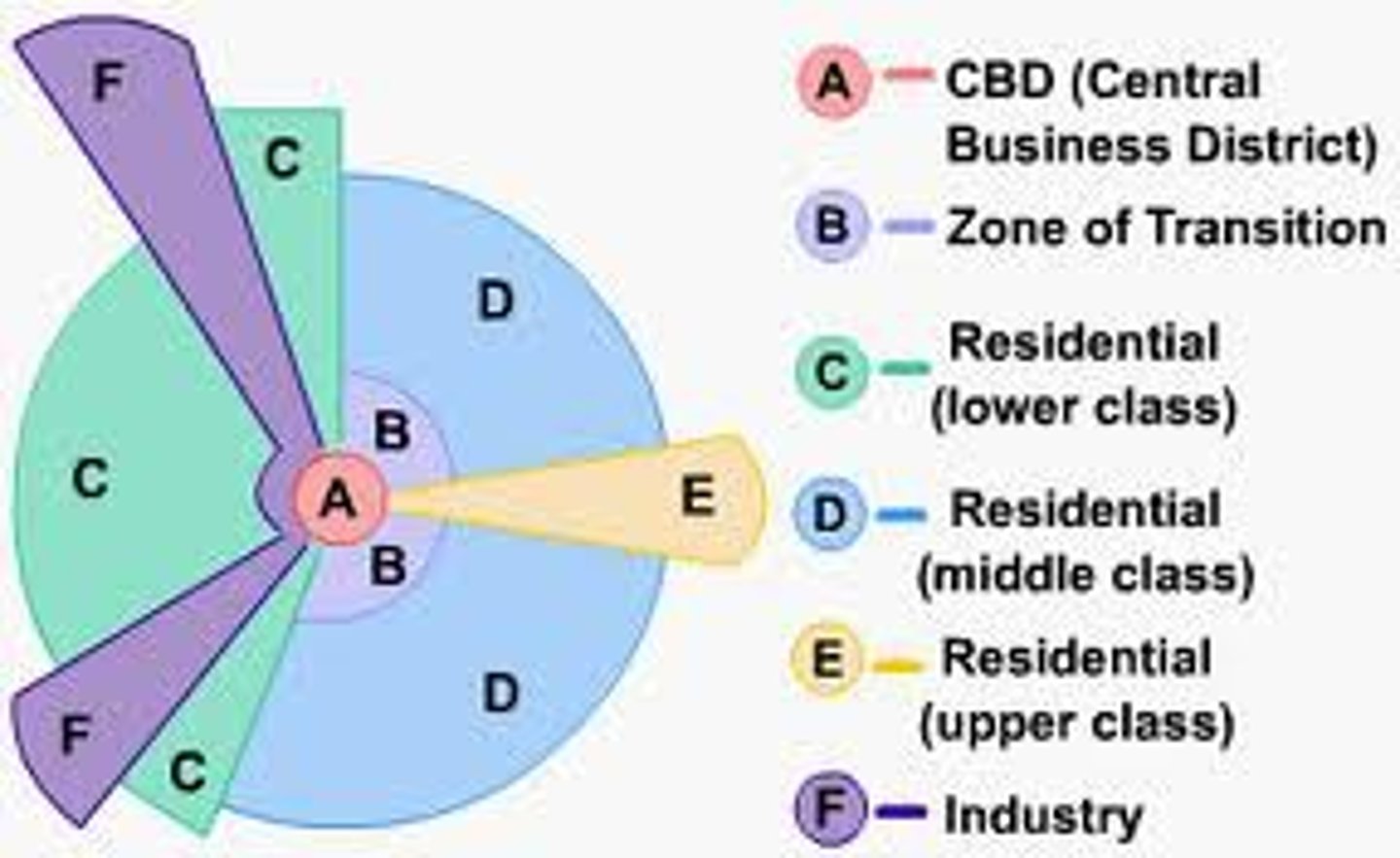
Sector Model
A model of the internal structure of cities in which social groups are arranged around a series of sectors, or wedges, radiating out from the CBD; also called the Hoyt Model
Segregation
the separation or isolation of a race, class, or group
Slum
a heavily populated urban area characterized by substandard housing and squalor

Specialization
separation of tasks within a system

Squatter settlement
An area within a city in a less developed country in which people illegally establish residences on land they do not own or rent and erect homemade structures.

Suburb
residential areas on the outskirts of a city or large town

Suburbanization
a term used to describe the growth of areas on the fringes of major cities

Threshold
The minimum number of people needed to support the service.

Town
an urban area with a fixed boundary that is smaller than a city

Underclass
a group in society prevented from participating in the material benefits of a more developed society because of a variety of social and economic characteristics.

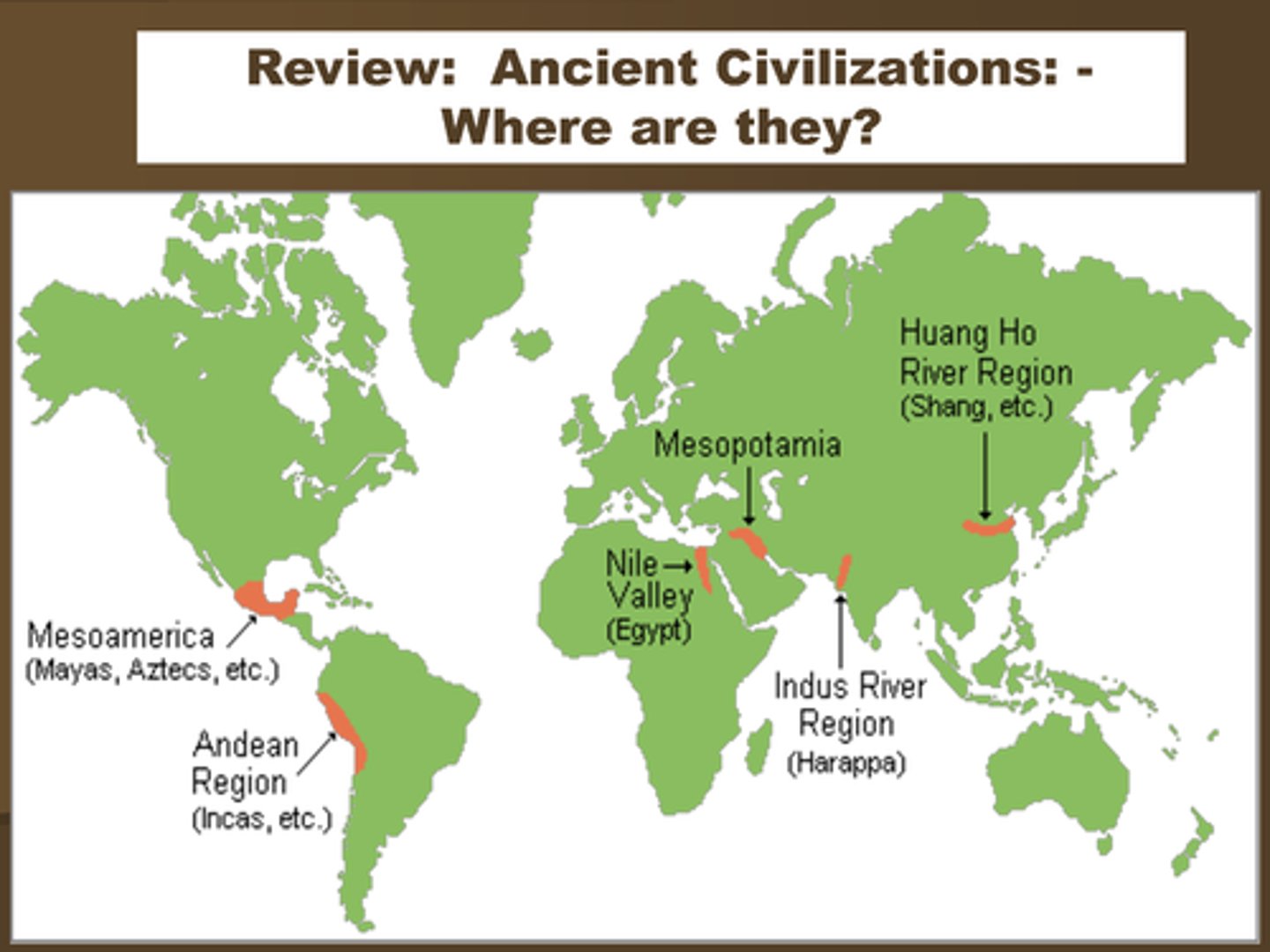
Urban Hearth
An area like Mesopotamia, China, India, or the Nile Valley where large cities first existed.
Urban hierarchy
A ranking of settlements according to their size and economic functions.
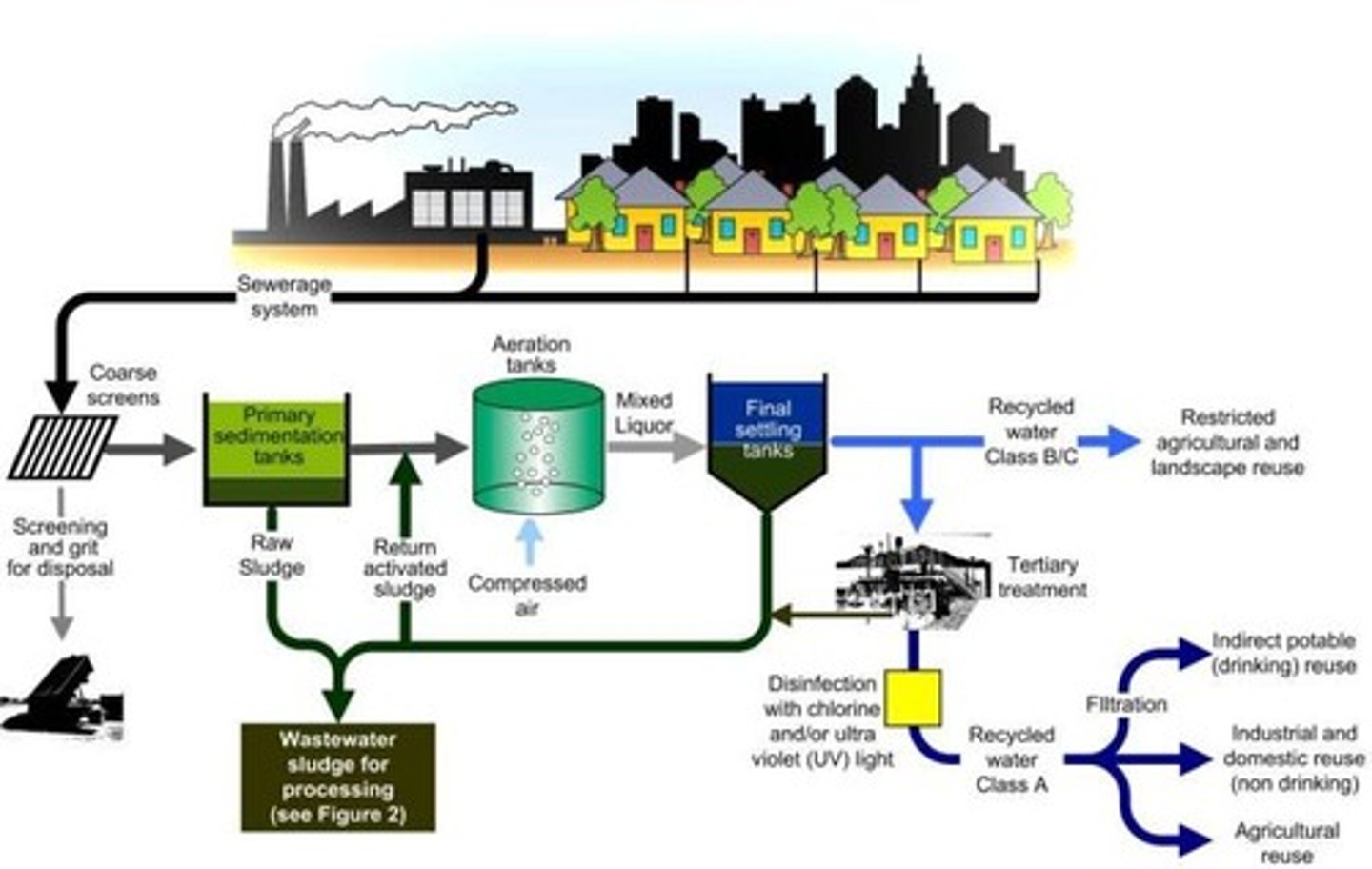
Urban hydrology
Study of water in urban areas and how to treat it. (Pollution)
Urban Morphology
The study of the physical form and structure of urban places.
Urbanization
The process by which the population of cities grow.

World City
Most important centers of economic power and wealth; also called global cities
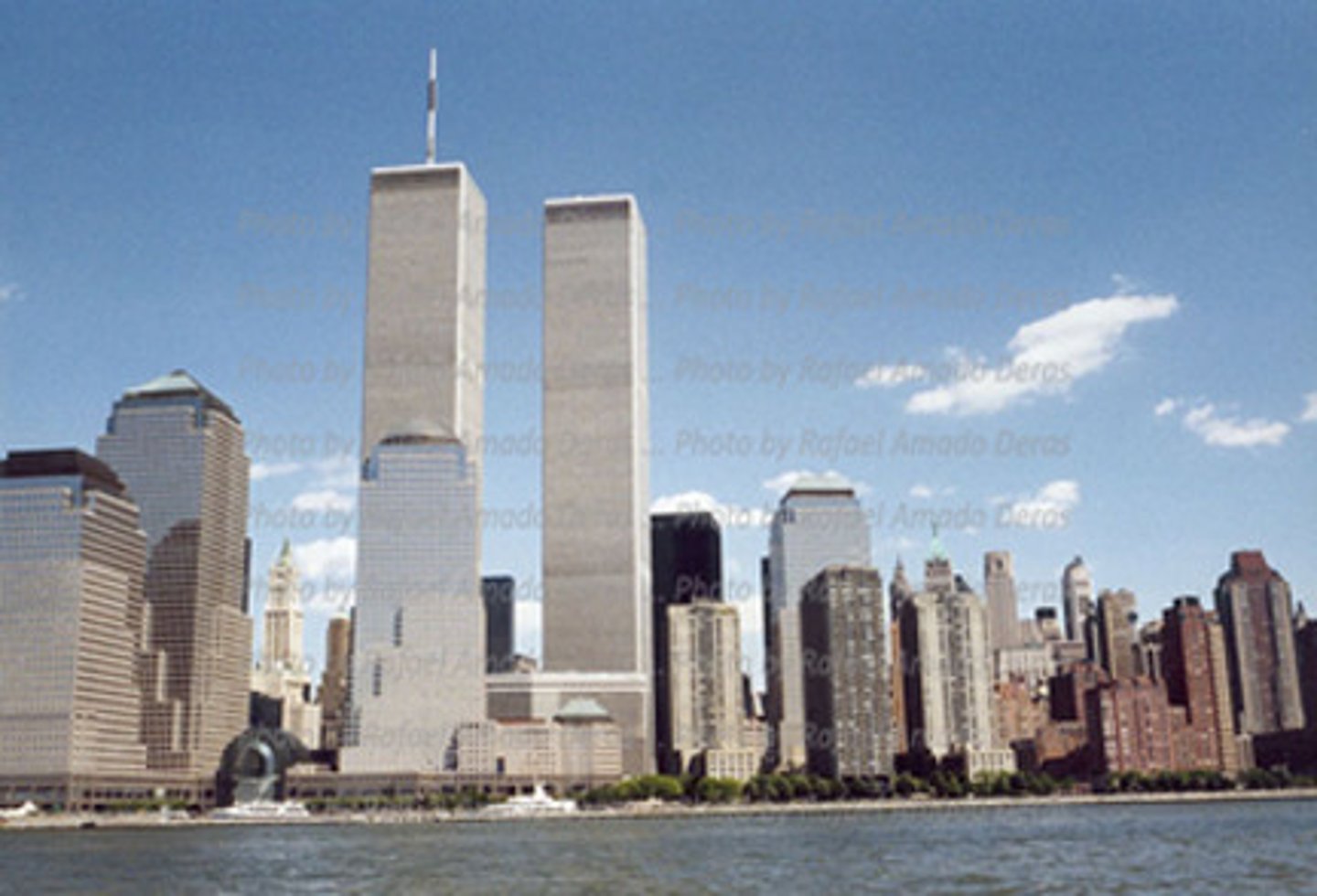

Zone in Transition
area of mixed commercial and residential land uses surrounding the CBD; mixture of growth, change, and decline
Zoning
dividing an area into zones or sections reserved for different purposes such as residential, commercial, and industrial
Range
The maximum distance people are willing to travel to use a service.
Urban Geography
focuses on how cities function, their internal systems and structures, and the external influences on them
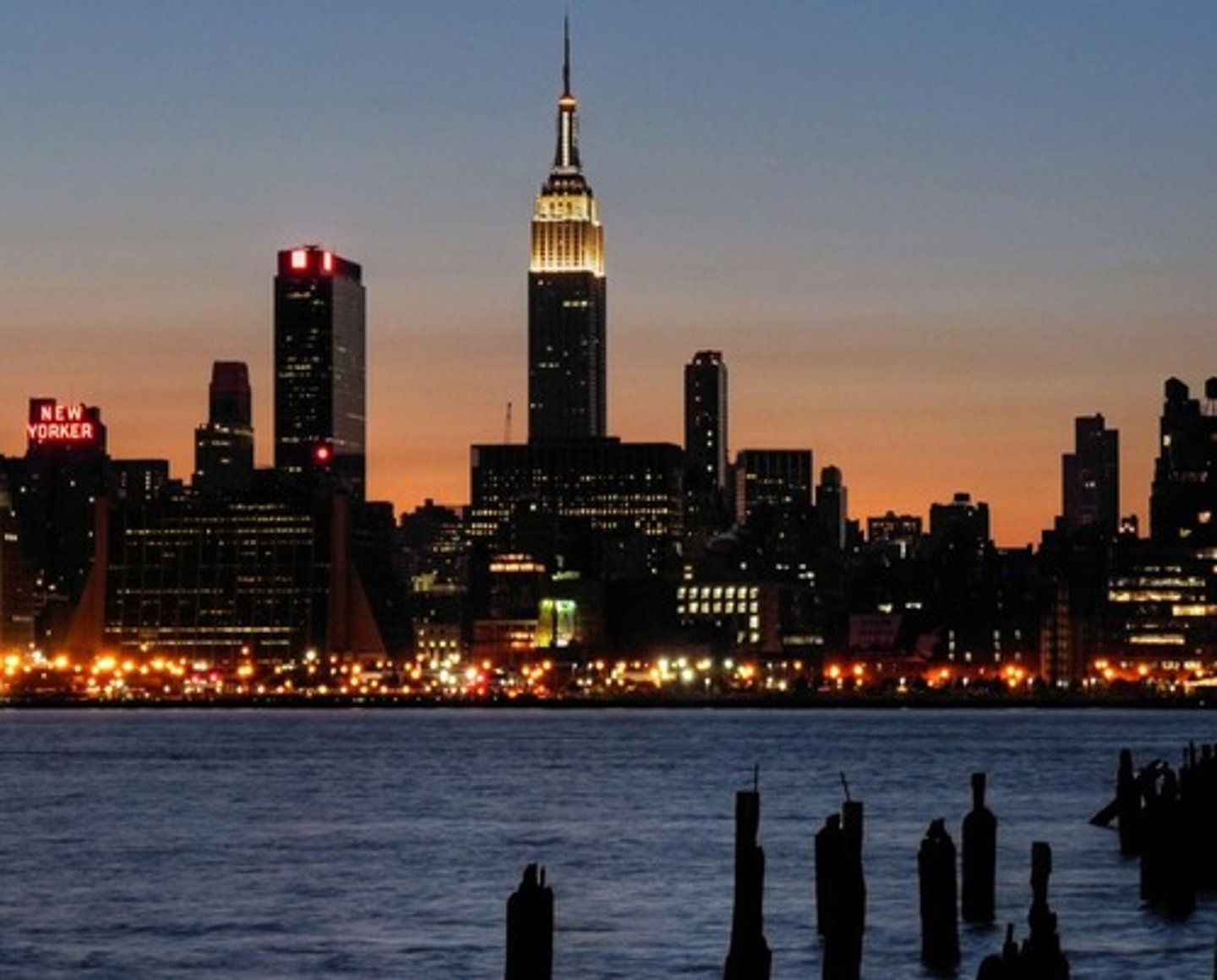

Urban Area
A dense core of census tracts, densely settled suburbs, and low-density land that links the dense suburbs with the core
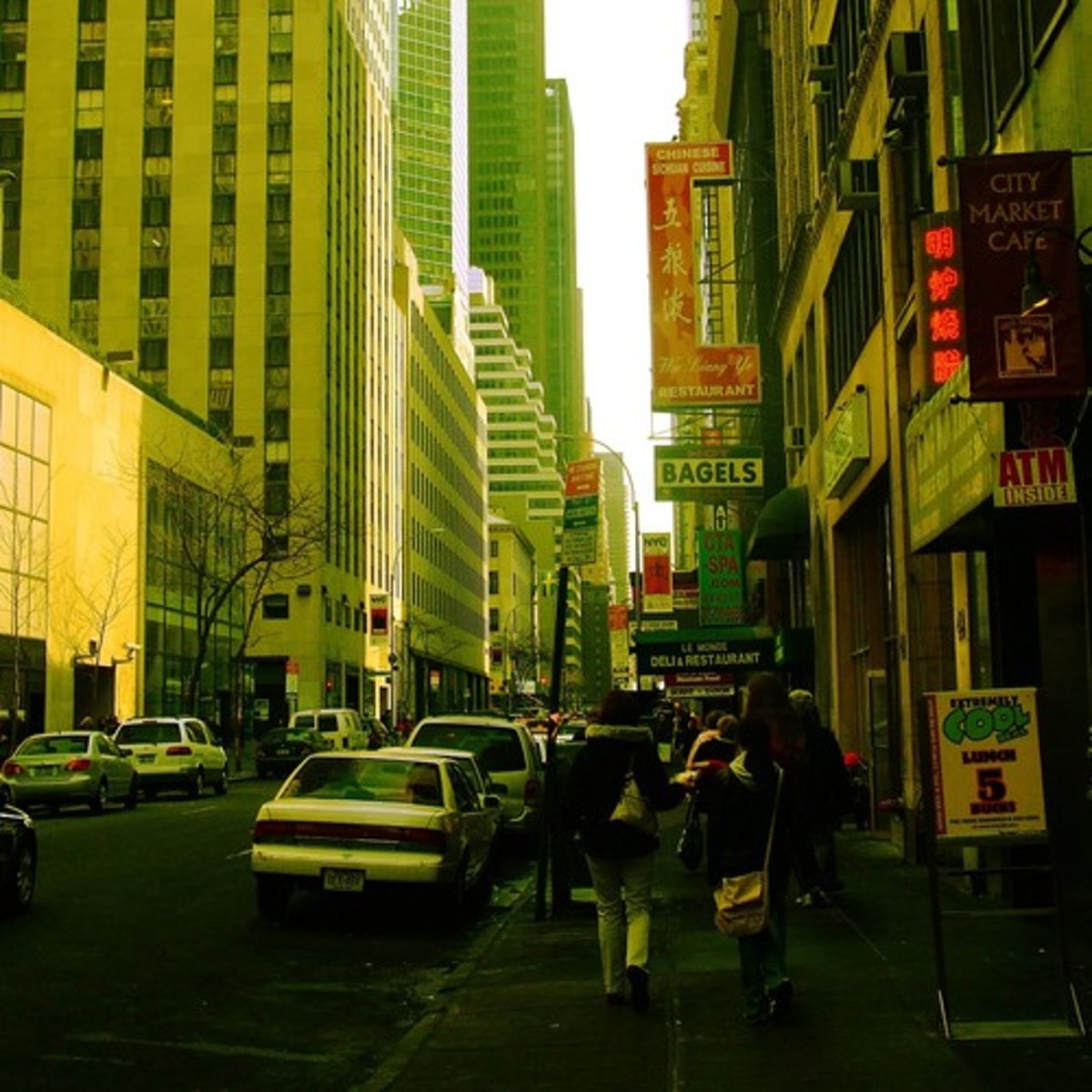

Nucleated Settlement
a compact closely packed settlement sharply demarcated from adjoining farmland; also called a clustered settlement
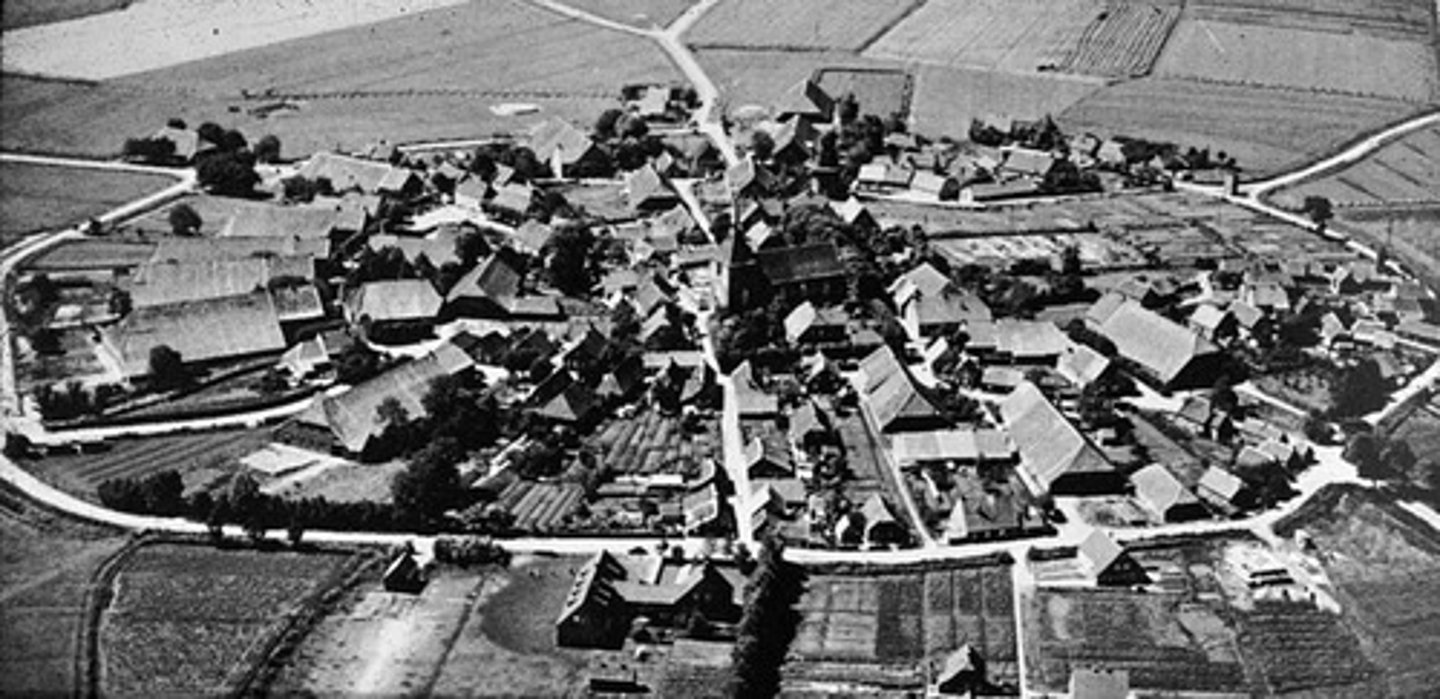

Dispersed Rural Settlement
characterized by farmers living on individual farms isolated from neighbors rather than alongside other farmers in settlements

Metropolitan Statistical Area
In the United States, a central city of at least 50,000 population, the county within which the city is located, and adjacent counties with a functional connection to the central city.
Micropolitan Statistical Area
An urbanized area of between 10,000 and 50,000 inhabitants, the county in which it is found, and adjacent counties tied to the city.
Hamlet
small village

Village
a community of people smaller than a town

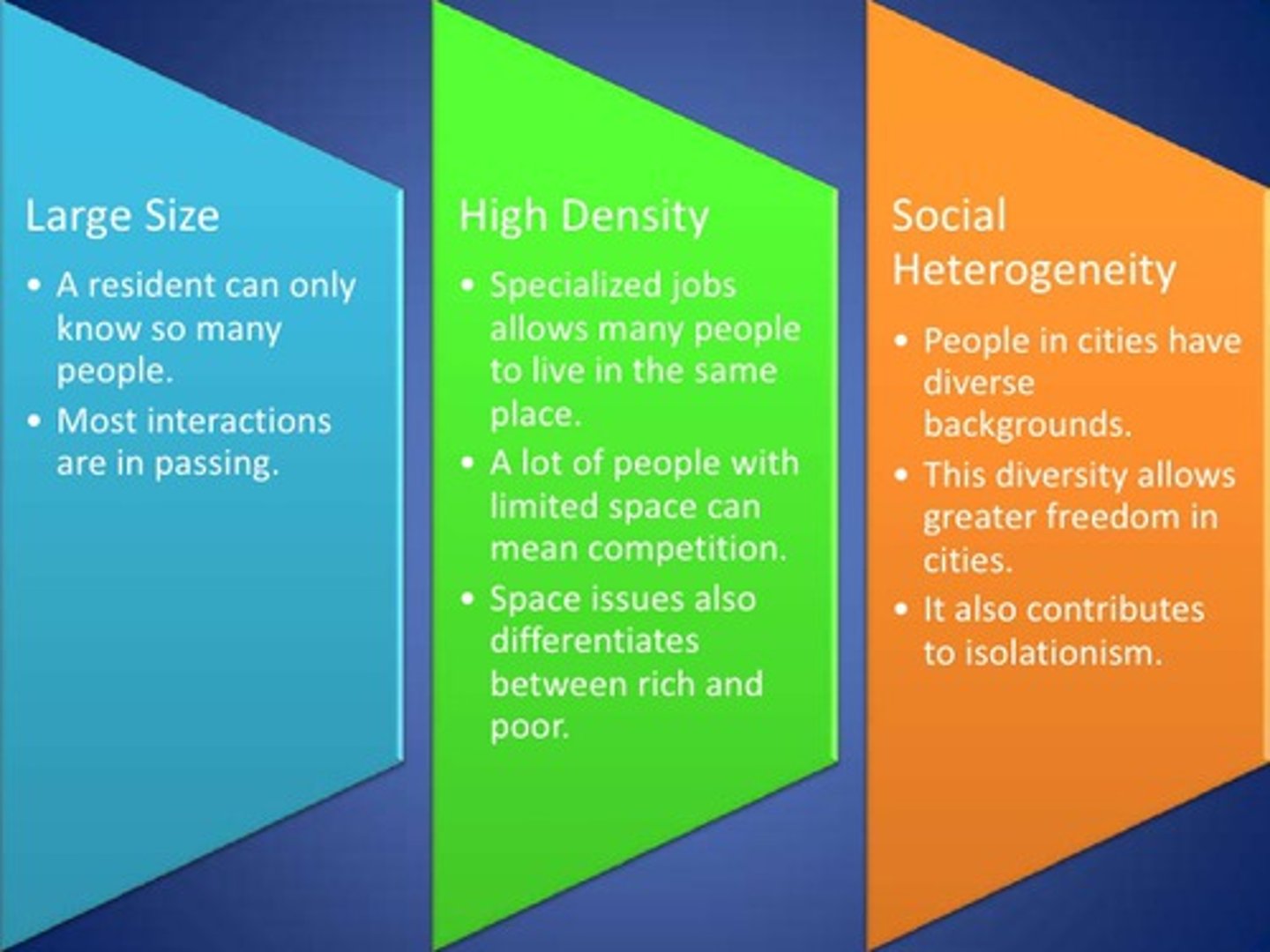
Louis Wirth
said a city has large size, high density, and social heterogeneity
Feminization of Poverty
The increasing concentration of poverty among unmarried women and their children in inner cities

Ghettoization
The concentration of a residents in a low-cost residential areas against their will through legal means or social discrimination

Zoning Ordinance
Law that specifies how and for what purpose each parcel of private real estate may be used. They usually separate single-family houses from apartments, industrial from commercial areas, etc.
Urban Renewal
Program in which cities identify blighted inner-city neighborhoods, acquire the properties from private members, relocate the residents and businesses, clear the site, build new roads and utilities, and turn the land over to private developers.

Public Housing
Housing owned by the government; in the United States, it is rented to low-income residents, and the rents are set at 30 percent of the families' incomes.

Megastore/Superstore
huge stores with a wide variety of products

Galactic City Model
edge cities are connected by beltways or highways; also called the Urban Peripheral Model, created by Chauncy Harris
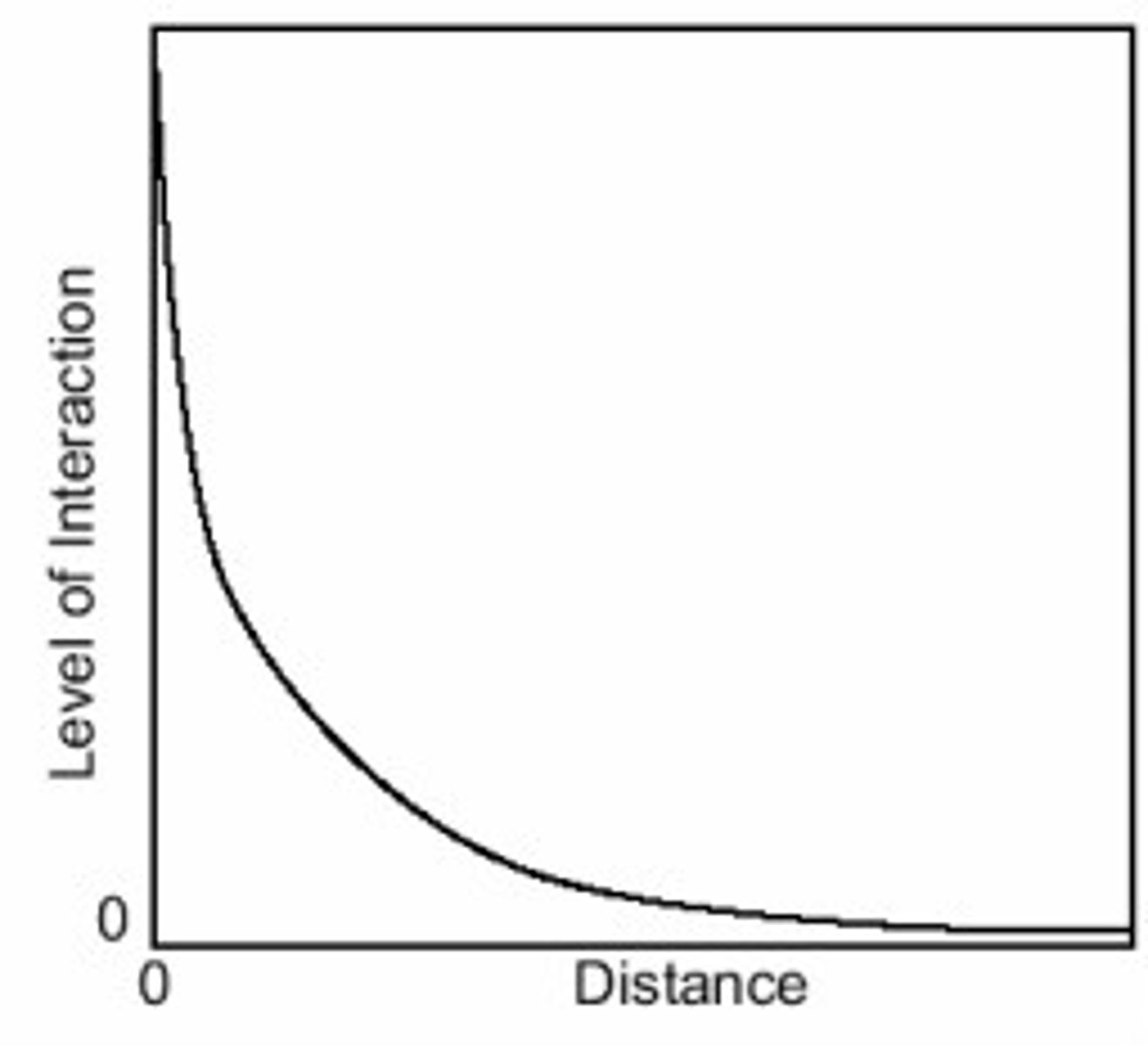
Density Gradient
A change in density of people over distance.
Urban Sprawl
The process of urban areas expanding outwards, usually in the form of suburbs, and developing over fertile agricultural land.

Greenbelt
A ring of land maintained as parks, agriculture, or other types of open space to limit the sprawl of an urban area.

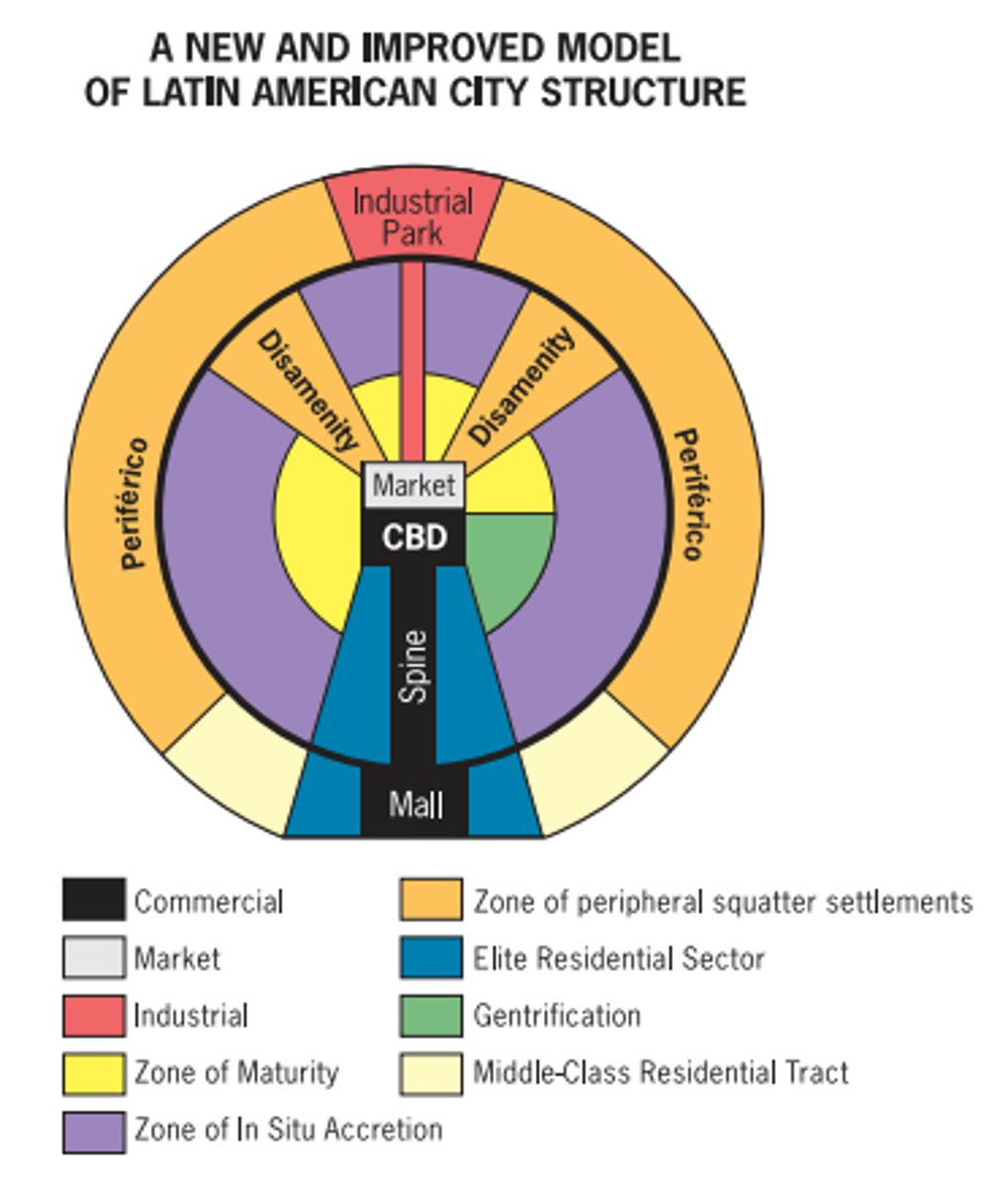
Griffin-Ford Model
a model of the Latin American city showing a blend of traditional elements of Latin American culture with the forces of globalization that are reshaping the urban scene
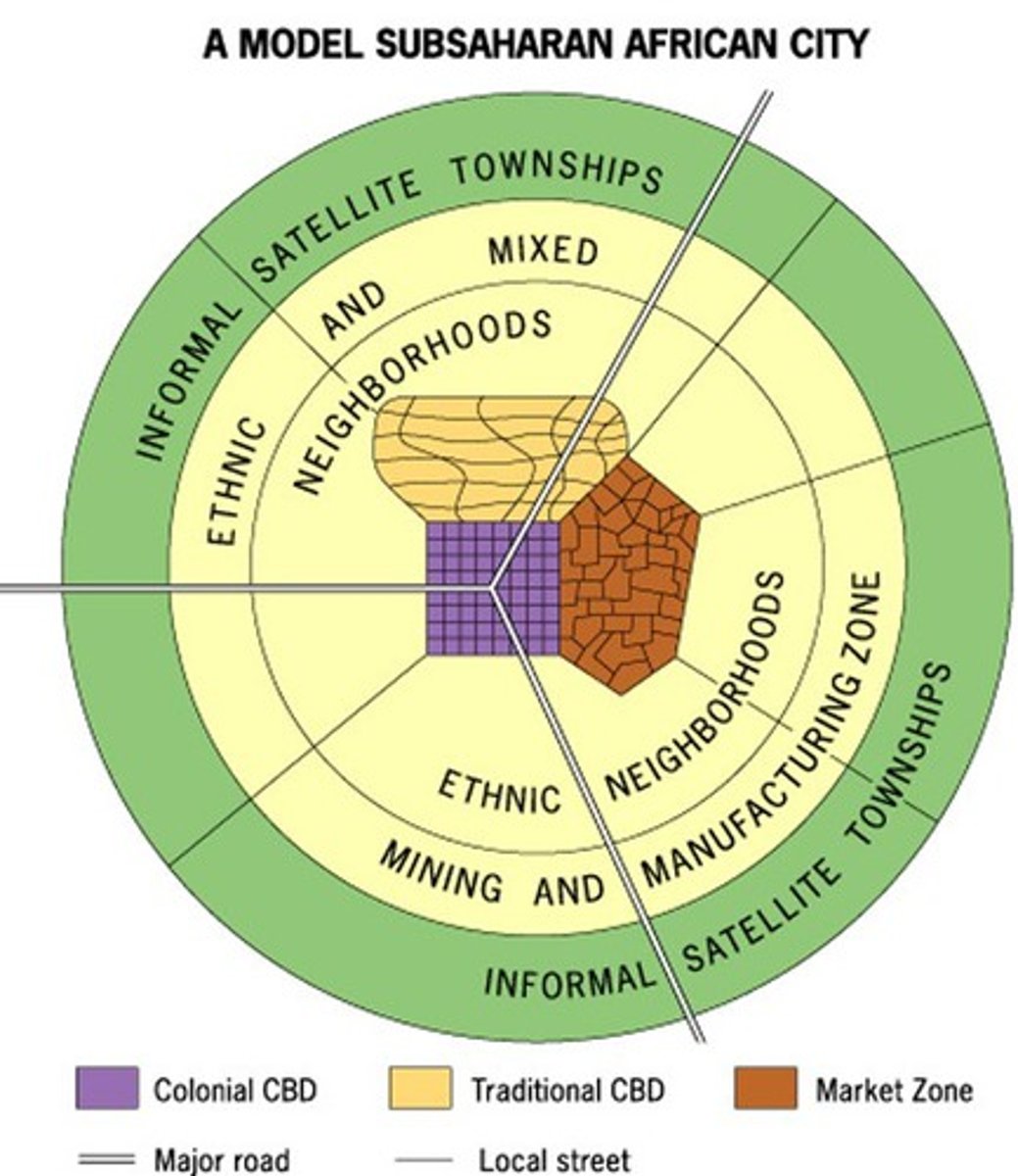
African City Model
Sub-Saharan model that suggests that many cities have more than one CBD with residential rings surrounding each, squatter settlements are on the outside
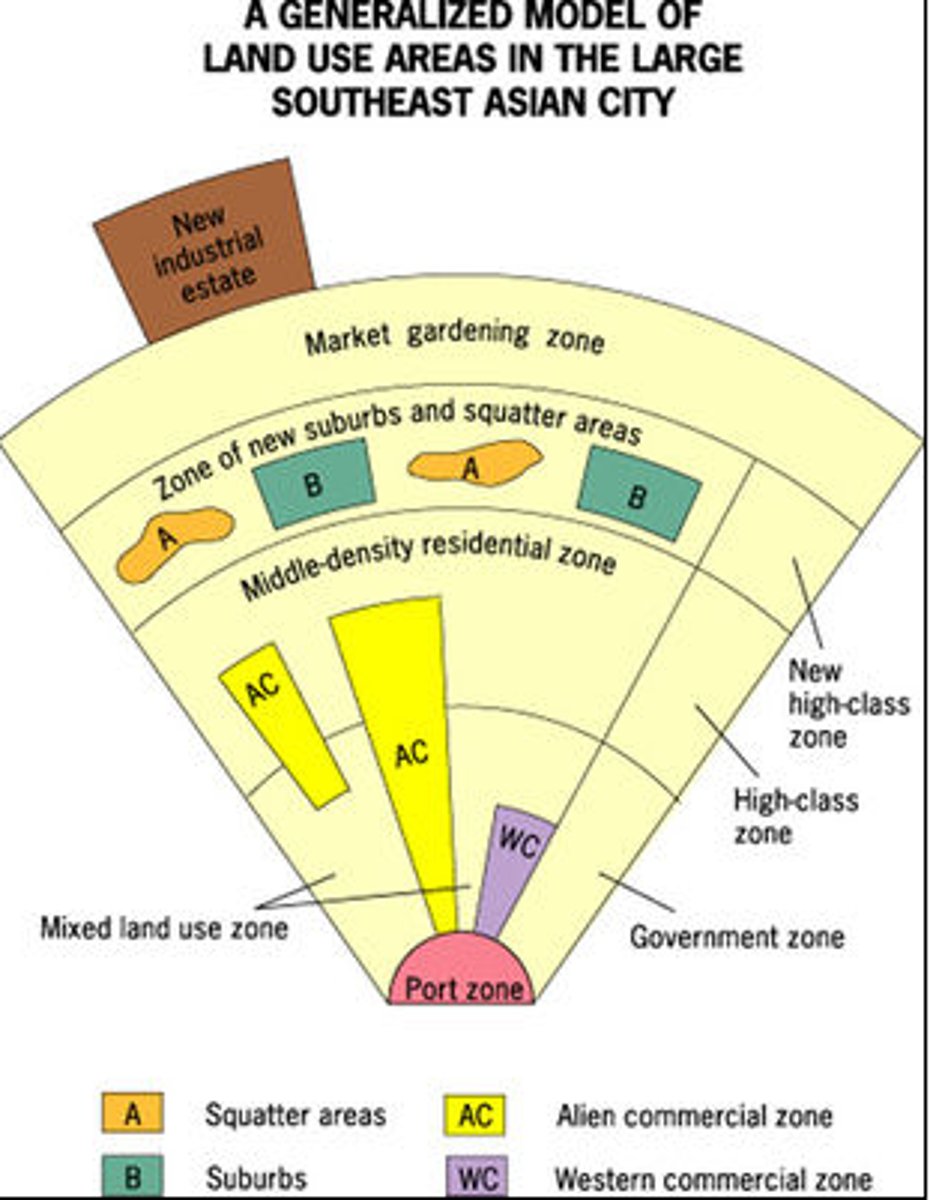
Asian City Model
The focal point is the port and surrounding commercial district. McGee found no formal CBD but noticed a government zone, a Western commercial zone, and a Chinese (alien) commercial zone.
DINKS (double income, no kids)
couples with high incomes, no kids, demanding careers, and a desire to work, vacation, and focus on their marriage

SINKS
An acronym that represents unmarried young professionals

Manufacturing City
A city overrun with factories, supply facilities, transport systems, and the construction of tenements for a growing labor force.

Eminent Domain
Power of a government to take private property for public use.

Filtering
a process of change in the use of a house, from single-family ownership , to multifamily dwelling, to eventual abandonment

City Beautiful Movement
Movement in design that drew directly from the Beaux Arts School. Architects imparted order on hectic, industrial centers by creating urban spaces that conveyed a sense of morality and civic pride, which many feared was absent from the frenzied new industrial world.

Scattered Site Housing
dispersing public housing throughout the city
Shadow Economy
illicit economic activity (such as black market transactions and undeclared work) existing alongside a country's official economy.
Urban Canyons
Streets lined with tall buildings can channel and intensify wind. They also prevent natural sunlight form reaching the ground.

New Urbanism
A city design that calls for development, urban revitalization, and suburban reforms that create walkable neighborhoods with a diversity of housing and jobs; a form of smart growth

Exurbanite
Person who has left the inner city and moved to outlying suburbs or rural areas.

Market Area
The area surrounding a central place, from which people are attracted to use the place's goods and services; also called the Hinterland
White Flight
working and middle-class white people move away from racial-minority suburbs or inner-city neighborhoods to white suburbs and exurbs

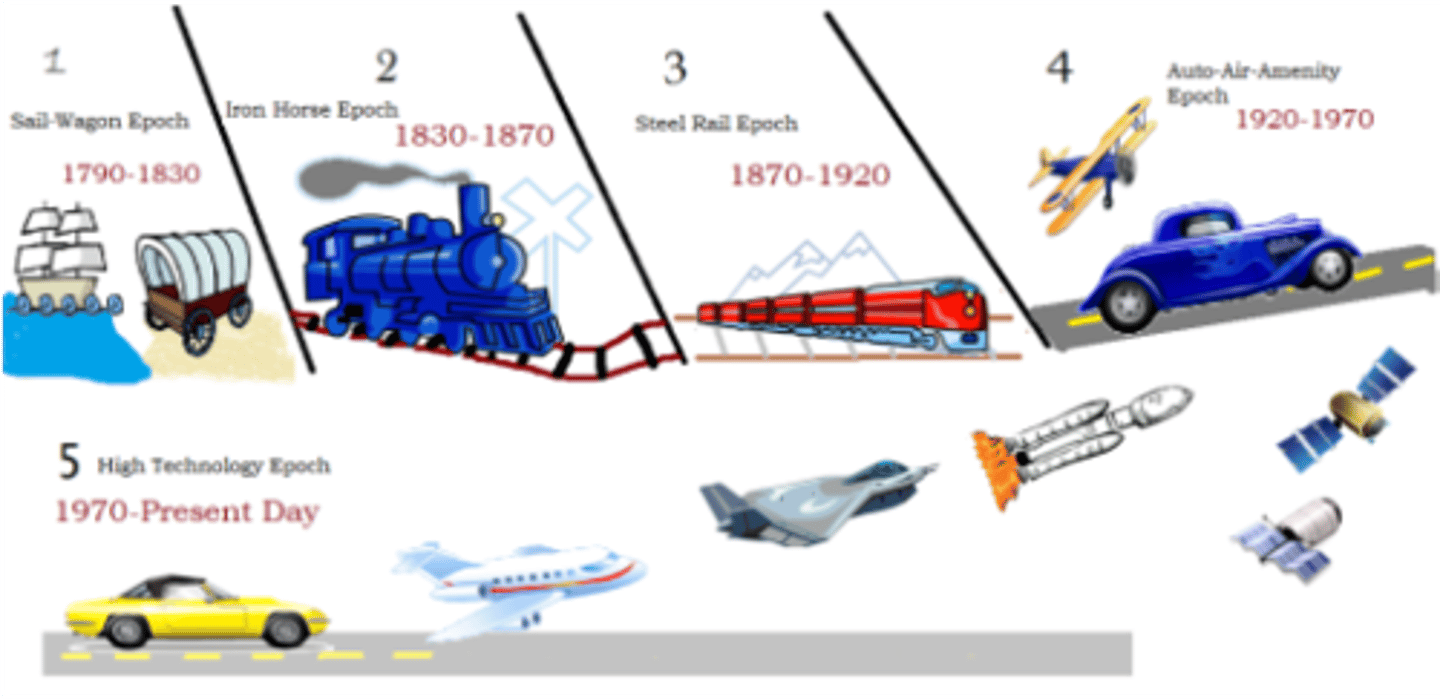
Borchert's Model of Urban Evolution
created in the 1960s to predict and explain the growth of cities in four phases of transportation history: stage 1, the "sail wagon" era of 1790-1830; stage 2, the "iron horse" era of 1830-1870; stage 3, the "steel rail" epoch of 1870-1920; and stage 4, the current era of car and air travel that began after 1920.
Urban/Rural
By the census of 1920, for the first time, more Americans lived in urban areas than in rural areas.