Nucleic acids
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/21
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:39 AM on 1/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms
1
New cards
Nucleotide functions
Energy for metabolism (ATP), enzyme cofactors (NAD+), and signal transduction (cAMP)
2
New cards
Nucleic acid Functions
Storage of genetic info (DNA), Transmission of genetic info (mRNA), Processing of genetic information (ribozymes), and Protein synthesis (tRNA and rRNA)
3
New cards
Nucleobase = Nitrogenous base
• Derivatives of pyrimidine or purine
• Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules (mixed rings)
• Planar or almost-planar structures
• Absorb UV light around 250–270 nm
• Nitrogen-containing heteroaromatic molecules (mixed rings)
• Planar or almost-planar structures
• Absorb UV light around 250–270 nm
4
New cards
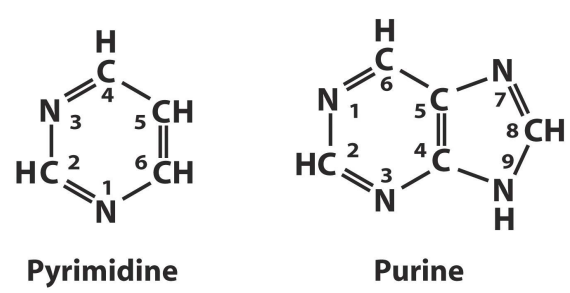
Where do the nucleobases link to the sugars?
Nitrogen 1 on pyrimidine links to the sugar and Nitrogen 9 on the purine links to the sugar (deoxyribose or ribose) at 1’ on the sugar
5
New cards
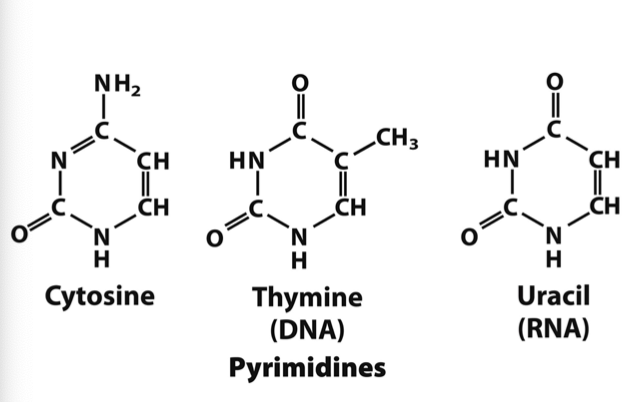
What bases are pyrimidines?
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
loss of methyl group thymine into uracil
loss of methyl group thymine into uracil
6
New cards
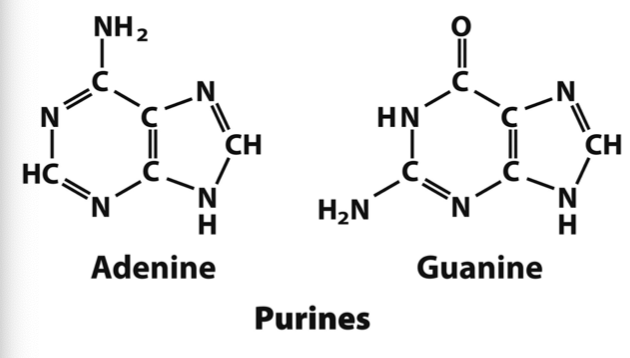
What bases are purines?
Adenine and Guanine
7
New cards
Nucleotide
Nitrogenous base + Pentose sugar + Phosphate
• beta-D-ribofuranose in RNA
• beta-2’-deoxy-D-ribofuranose in DNA
• Different puckered conformations of the sugar ring are possible - sugars don’t fold flat like bases, prefer ring formation
* 2’ absence or presense of oxygen
* 3’ and 5’ continue chain links
• beta-D-ribofuranose in RNA
• beta-2’-deoxy-D-ribofuranose in DNA
• Different puckered conformations of the sugar ring are possible - sugars don’t fold flat like bases, prefer ring formation
* 2’ absence or presense of oxygen
* 3’ and 5’ continue chain links
8
New cards
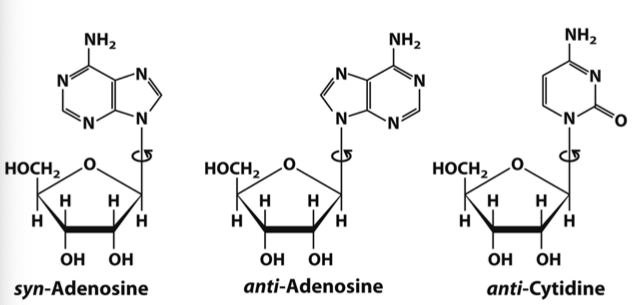
Nucleoside
Nitrogenous base + Pentose sugar
• In nucleosides the pentose ring is attached to the nucleobase via an N-glycosidic bond
• The bond is formed to the anomeric 1’ carbon of the sugar in a β configuration
• The bond is formed between position N1 in pyrimidines and position N9 in purines
• It is a single (not double) bond - rotates and no bond restriction
• In nucleosides the pentose ring is attached to the nucleobase via an N-glycosidic bond
• The bond is formed to the anomeric 1’ carbon of the sugar in a β configuration
• The bond is formed between position N1 in pyrimidines and position N9 in purines
• It is a single (not double) bond - rotates and no bond restriction
9
New cards
Phosphate Group
• Negatively charged at neutral pH
• Typically attached to 5’ position
– Nucleic acids are built using 5’-triphosphates
• ATP, GTP, TTP, CTP
– Nucleic acids contain one phosphate per nucleotide
alpha - closest, then beta, then gamma, then delta
• Typically attached to 5’ position
– Nucleic acids are built using 5’-triphosphates
• ATP, GTP, TTP, CTP
– Nucleic acids contain one phosphate per nucleotide
alpha - closest, then beta, then gamma, then delta
10
New cards
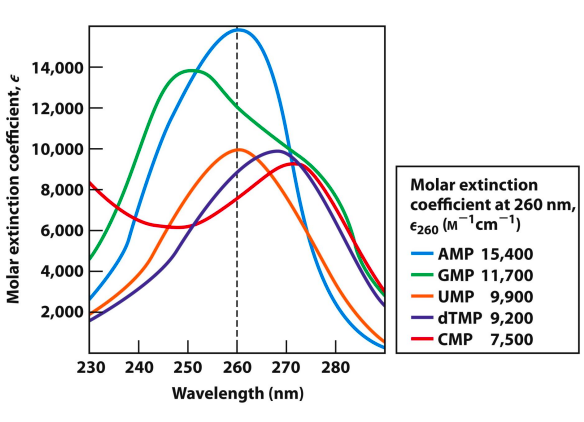
UV Absorption of Nucleotides
* Absorption of UV light at 250–270 nm is due to pi to pi electronic transitions.
* Excited states of common nucleobases decay rapidly via radiationless transitions.
– Effective photoprotection of genetic material
– No fluorescence from nucleic acids
* Excited states of common nucleobases decay rapidly via radiationless transitions.
– Effective photoprotection of genetic material
– No fluorescence from nucleic acids
11
New cards
Polynucleotides
Covalent bonds formed via phosphodiester linkages
* negatively charged backbone
DNA backbone is fairly stable
* Ancient DNA (mammoths, dinosaurs..)
* Hydrolysis accelerated by enzymes (DNAses)
RNA backbone is unstable Linear polymers
* In water, RNA lasts for a few years
* In cells, mRNA is degraded in few hours
Linear polymers
* No branching or cross-links
Directionality
* – 5’ end is different from 3’ end
* – We read the sequence from 5’ to 3’
**Only enzymes make and break phosphodiester bonds**
* negatively charged backbone
DNA backbone is fairly stable
* Ancient DNA (mammoths, dinosaurs..)
* Hydrolysis accelerated by enzymes (DNAses)
RNA backbone is unstable Linear polymers
* In water, RNA lasts for a few years
* In cells, mRNA is degraded in few hours
Linear polymers
* No branching or cross-links
Directionality
* – 5’ end is different from 3’ end
* – We read the sequence from 5’ to 3’
**Only enzymes make and break phosphodiester bonds**
12
New cards
Hydrolysis of RNA
RNA is unstable under alkaline conditions
• Hydrolysis is also catalyzed by enzymes (RNase ribonucleases) • RNase enzymes are abundant around us:
– S-RNase in plants prevents inbreeding
– RNase P is a ribozyme (enzyme made of RNA) that processes tRNA precursors
– Dicer is an enzyme that cleaves double-stranded RNA into oligonucleotides
• protection from viral genomes • RNA interference technology
Can make RNA an enzyme allowing it to cut itself
• Hydrolysis is also catalyzed by enzymes (RNase ribonucleases) • RNase enzymes are abundant around us:
– S-RNase in plants prevents inbreeding
– RNase P is a ribozyme (enzyme made of RNA) that processes tRNA precursors
– Dicer is an enzyme that cleaves double-stranded RNA into oligonucleotides
• protection from viral genomes • RNA interference technology
Can make RNA an enzyme allowing it to cut itself
13
New cards
Hydrogen-Bonding Interactions
* Two bases can hydrogen bond to form a base pair
* For monomers, large number of base pairs is possible
* In polynucleotide, only a few possibilities exist
* Watson-Crick base pairs predominate in double-stranded DNA: A pairs with T (2 hydrogen bonds), C pairs with G (3 hydrogen bonds), and generally a purine pairs with a pyrimidine
* pi - pi stacking between dna ring systems
* For monomers, large number of base pairs is possible
* In polynucleotide, only a few possibilities exist
* Watson-Crick base pairs predominate in double-stranded DNA: A pairs with T (2 hydrogen bonds), C pairs with G (3 hydrogen bonds), and generally a purine pairs with a pyrimidine
* pi - pi stacking between dna ring systems
14
New cards
Aromatic hetrocycle
An organic compound in which one or more of the carbon atoms in the backbone of the molecule has been replaced by an atom other than carbon. Typical hetero atoms include nitrogen, oxygen, and sulfur.
15
New cards
DNA strands
Distance between carbon 1 prime is identical between adenine & thymine and cytosine & guanine
* DNA has a minor and a major groove
* Two chains differ in sequence (sequence is read from 5’ to 3’)
* Two chains are complementary
* Two chains run antiparallel
* DNA has a minor and a major groove
* Two chains differ in sequence (sequence is read from 5’ to 3’)
* Two chains are complementary
* Two chains run antiparallel
16
New cards
Replication of Genetic code
• Strand separation occurs first
• Each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand • Synthesis is catalyzed by enzymes known as DNA polymerases
• Newly made DNA molecule has one daughter strand and one parent strand.
• Each strand serves as a template for the synthesis of a new strand • Synthesis is catalyzed by enzymes known as DNA polymerases
• Newly made DNA molecule has one daughter strand and one parent strand.
17
New cards
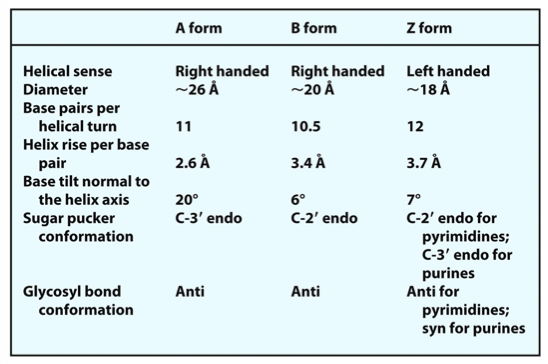
What are the forms of DNA?
A, B (B is normal) and Z (left handed helix)
18
New cards
Tetraplexes / quadraplexes
occur naturally at the end of chromosomes to prevent abnormal shortening of DNA
19
New cards
Palindromes
words or phases that are the same when read backward or forward: can use palindromes to form big hair pin loops and cruciforms
20
New cards
Ribozyme
RNA that cuts RNA
21
New cards
DNA and RNA Denaturation
Covalent bonds remain intact – Genetic code remains intact
Hydrogen bonds between strands are broken – Two strands separate
Base stacking is lost – UV absorbance increases
Denaturation can be induced by high temperature, or change in pH - Denaturation may be reversible: annealing
Denaturation of large DNA molecules is not uniform - AT rich regions melt at a lower temperature than GC-rich regions. This allows you to figure out how much the sample has denatured.
Hydrogen bonds between strands are broken – Two strands separate
Base stacking is lost – UV absorbance increases
Denaturation can be induced by high temperature, or change in pH - Denaturation may be reversible: annealing
Denaturation of large DNA molecules is not uniform - AT rich regions melt at a lower temperature than GC-rich regions. This allows you to figure out how much the sample has denatured.
22
New cards
Damage to nucleic acids
UV light induces dimerisation of pyrimidines; this may be the main mechanism for skin cancers.
Ionising radiation (X-rays and gamma-rays) causes ring opening and strand breaking. These are difficult to fix.
Cells can repair some of these modifications, but others cause mutations. Accumulation of mutations is linked to ageing and carcinogenesis.
If expose two thymines next to each other in DNA under UV light can bind to each other to make a dimer
Ionising radiation (X-rays and gamma-rays) causes ring opening and strand breaking. These are difficult to fix.
Cells can repair some of these modifications, but others cause mutations. Accumulation of mutations is linked to ageing and carcinogenesis.
If expose two thymines next to each other in DNA under UV light can bind to each other to make a dimer