AP Bio - Unit 1 Review
1/35
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
What is the basic structure of water?
2 hydrogen atoms covalently bonded to 1 oxygen atom
Why is water a polar molecule?
Oxygen is more electronegative, pulling electrons closer and giving water partial positive (H) and negative (O) ends
How does water form hydrogen bonds?
The positive hydrogen of one water molecule is attracted to the negative oxygen of another
Compare adhesion and cohesion.
Cohesion = water sticks to water.
Adhesion = water sticks to other substances
Describe water’s specific heat. Why is this important?
Water resists temperature change (high specific heat), helping regulate Earth’s and organisms’ temperatures
Why is water considered the ultimate solvent?
Its polarity allows it to dissolve many polar and ionic substances by surrounding and separating their molecules
What are some of carbon’s fundamental characteristics?
Can form 4 covalent bonds, bond with many elements, and make large, complex molecules
Why is Carbon found in all living organisms?
It’s the backbone of biological molecules like carbs, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
What types of bonds do carbon atoms often form with other atoms? Explain why.
Forms covalent bonds (single, double, or triple) because it has 4 valence electrons and wants 8
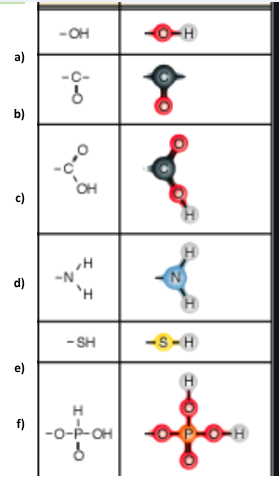
Identify functional group a
Hydroxl
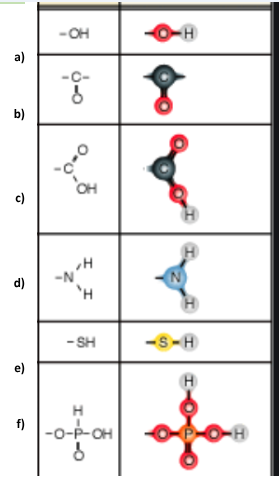
Identify functional group b
Carbonyl
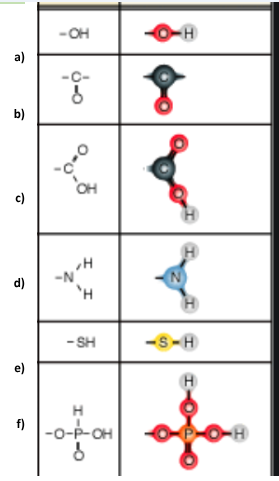
Identify functional group c
Carboxyl
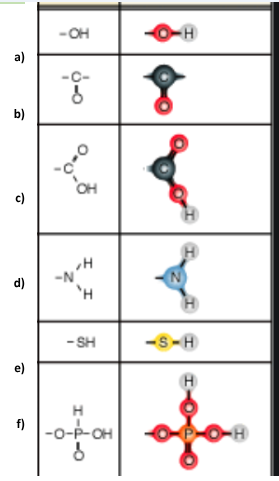
Identify functional group d
Amino
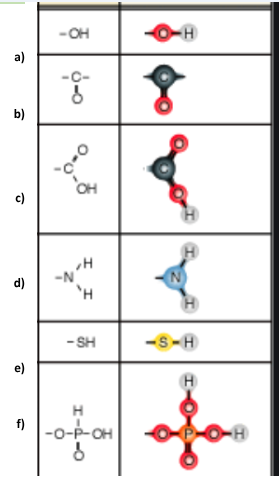
Identify functional group e
Sulfhydryl
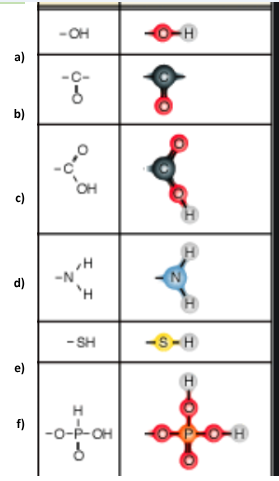
Identify functional group f
Phosphate
Compare dehydration synthesis and hydrolysis. Which process is used to build polymers? Which process is used to break down polymers?
Dehydration synthesis builds polymers by removing water.
Hydrolysis breaks down polymers by adding water
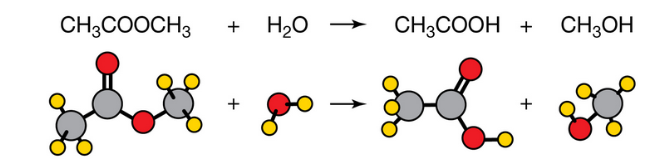
Which process is illustrated
hydrolysis
Compare a simple carbohydrate to a complex carbohydrate.
Simple = one or two sugars (quick energy).
Complex = many sugars linked (long-term energy storage)
What are the main components of a carbohydrate?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
What are lipids composed of?
Carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen; made of glycerol and fatty acids
Compare saturated to unsaturated fats
Saturated = no double bonds, solid at room temp.
Unsaturated = double bonds, liquid at room temp
What are the basic components of a protein?
Amino acids made of a central carbon, amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen, and R-group
Describe the steps to protein folding: Primary
Sequence of amino acids
Describe the steps to protein folding: Secondary
Coils or folds
Describe the steps to protein folding: Tertiary
3D shape formed by R-group interactions
Describe the steps to protein folding: Quaternary
Multiple polypeptides combine
How do enzymes work?
They lower activation energy by binding substrates at their active site and speeding up reactions
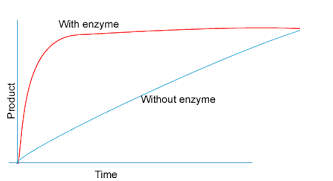
Describe the trends observed in the enzyme graph to the right. Why does the line with an enzyme level off?
With the enzyme production increases rapidly until it levels off because the enzyme is working at maximum capacity. Without the enzyme the production remains consistent.
How could you speed up an enzyme catalyzed reaction? Slow down?
Speed up = increase temperature (to a point) or substrate concentration.
Slow down = lower temperature, change pH, or add inhibitors
What causes enzymes to become denatured?
Extreme temperature or pH changes alter their shape, stopping function
Compare a cofactor to a coenzyme
Cofactor = inorganic helper (like metal ions).
Coenzyme = organic helper (like vitamins).
Compare an allosteric to competitive inhibitors. What do these both do to a reaction?
Competitive = block active site.
Allosteric = bind elsewhere, changing enzyme shape.
Both slow or stop reactions
Compare DNA to RNA. You should have at least 3 differences.
DNA = double-stranded; RNA = single-stranded.
DNA has deoxyribose; RNA has ribose.
DNA uses thymine (T); RNA uses uracil (U).
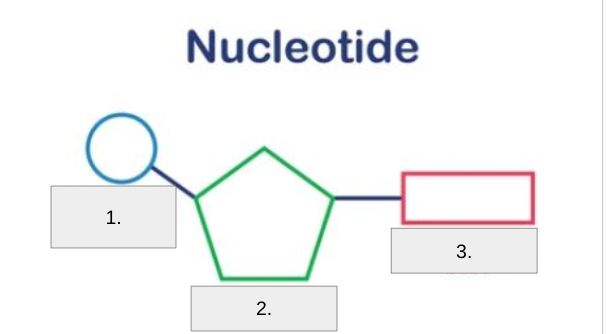
Label #1
Phosphote Group
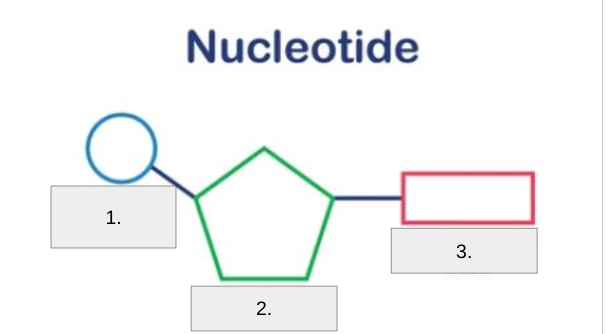
Label #2
Pentose Sugar
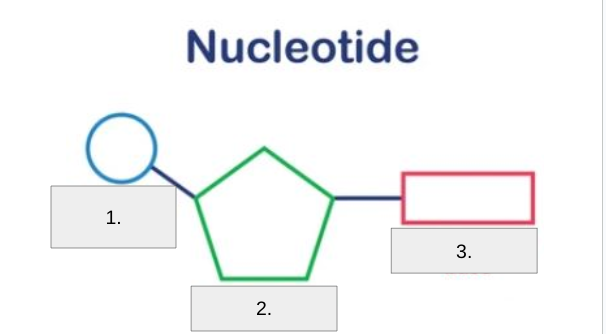
Label #3
Nitrogenous Base