Genetics Mendel
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Genetics
study of genes and how they are inherited
determined by parents
Genes
como in alleles
encode phenotypes
located in chromosomes
Locus
specific physical location of a gene
Loci
plural of locus
Homozygote
tow same alleles
Heterozygote
two different alleles for same gene
Genotype
individual’s complete set of genes they have inherited from parents
Phenotype
physically observable
Missense mutation
encodes for different aminoacidq
Nonsense mutation
Encodes for stop codon
Frameshift mutation
changes some codons
Mutations
result in gain or loss of function
Gain of function
seen in dominant diseases
Loss of function
seen in recessive diseases
Monogenic diseases
produced by mutations in a single gene
Multifactorial diseases
produced by interaction between group of genes and environmental factors
ie Diabetes II
Chromosomal rearrangements
produced by alteration in number of chromosomes or by their structure
Segregation law
Every individual organism contains 2 alleles for each trait such as when they separate each gamete contains one of them
Mendel’s first law
Two members of a gene pair segregate from each other into the gametes
Mendel’s second law
different gene pairs assort independently in gamete formation
Independent assortment
genes at different loci are transmitted independently
Pedigree structure
No color
3 generations at least
Name age dob
Diseases

Male, Female, Unspecified
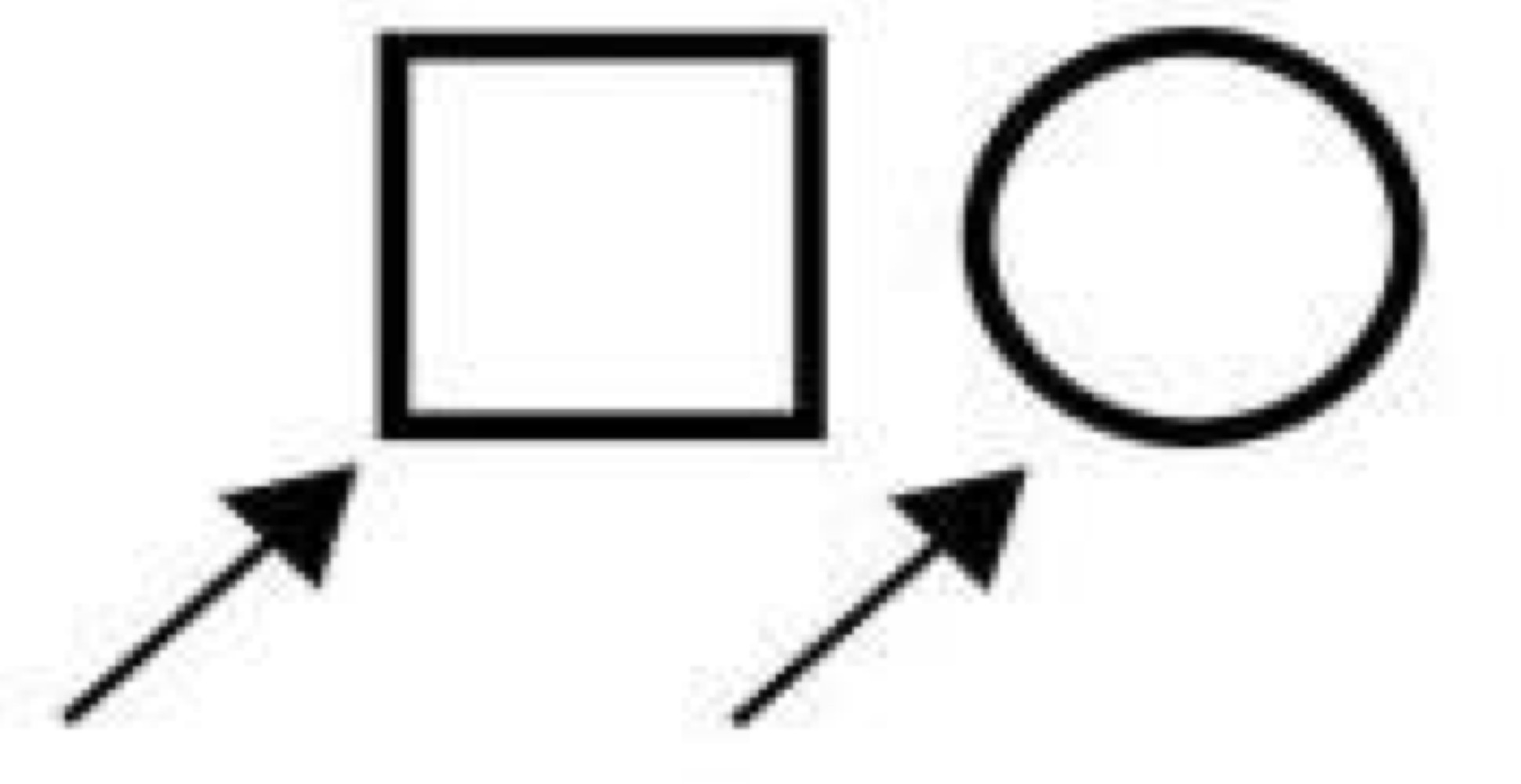
Proband (consultand)
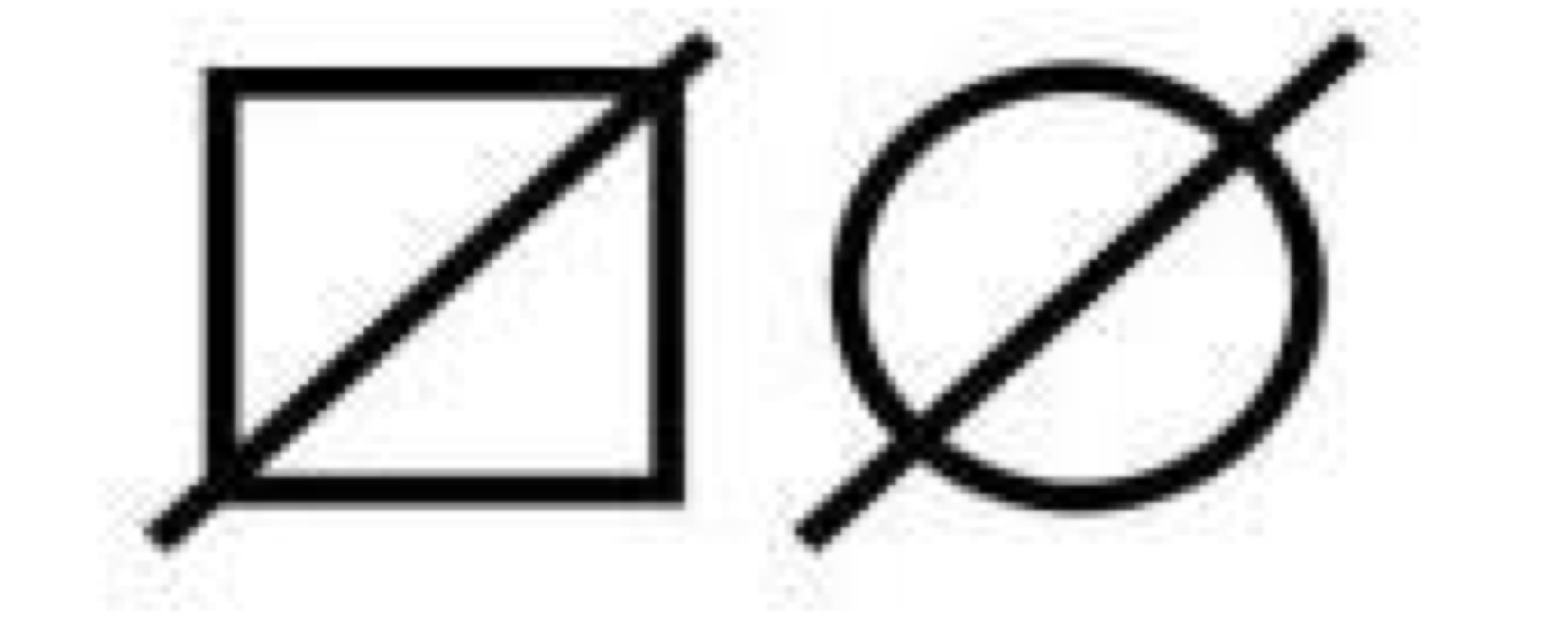
Deceased
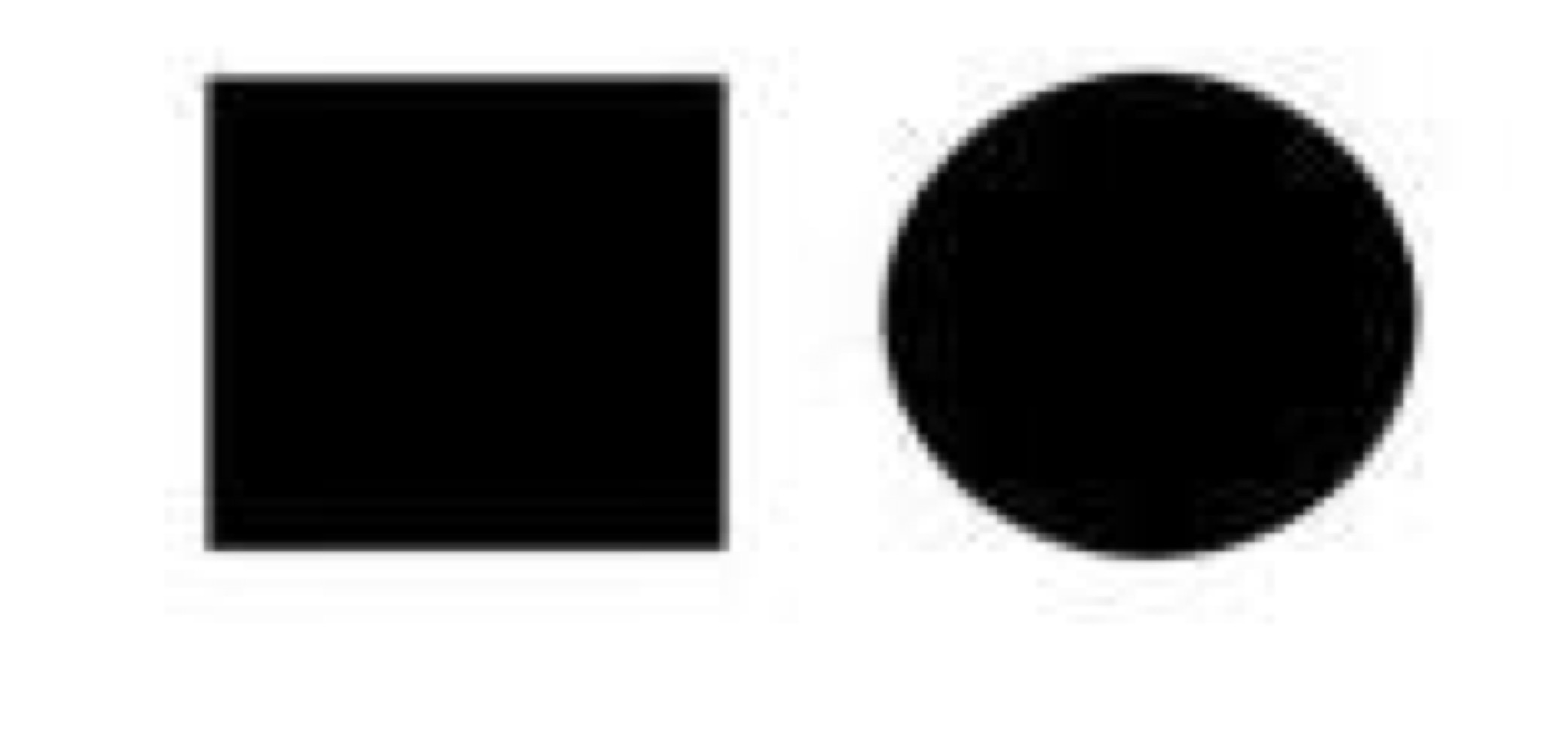
Affected with trait
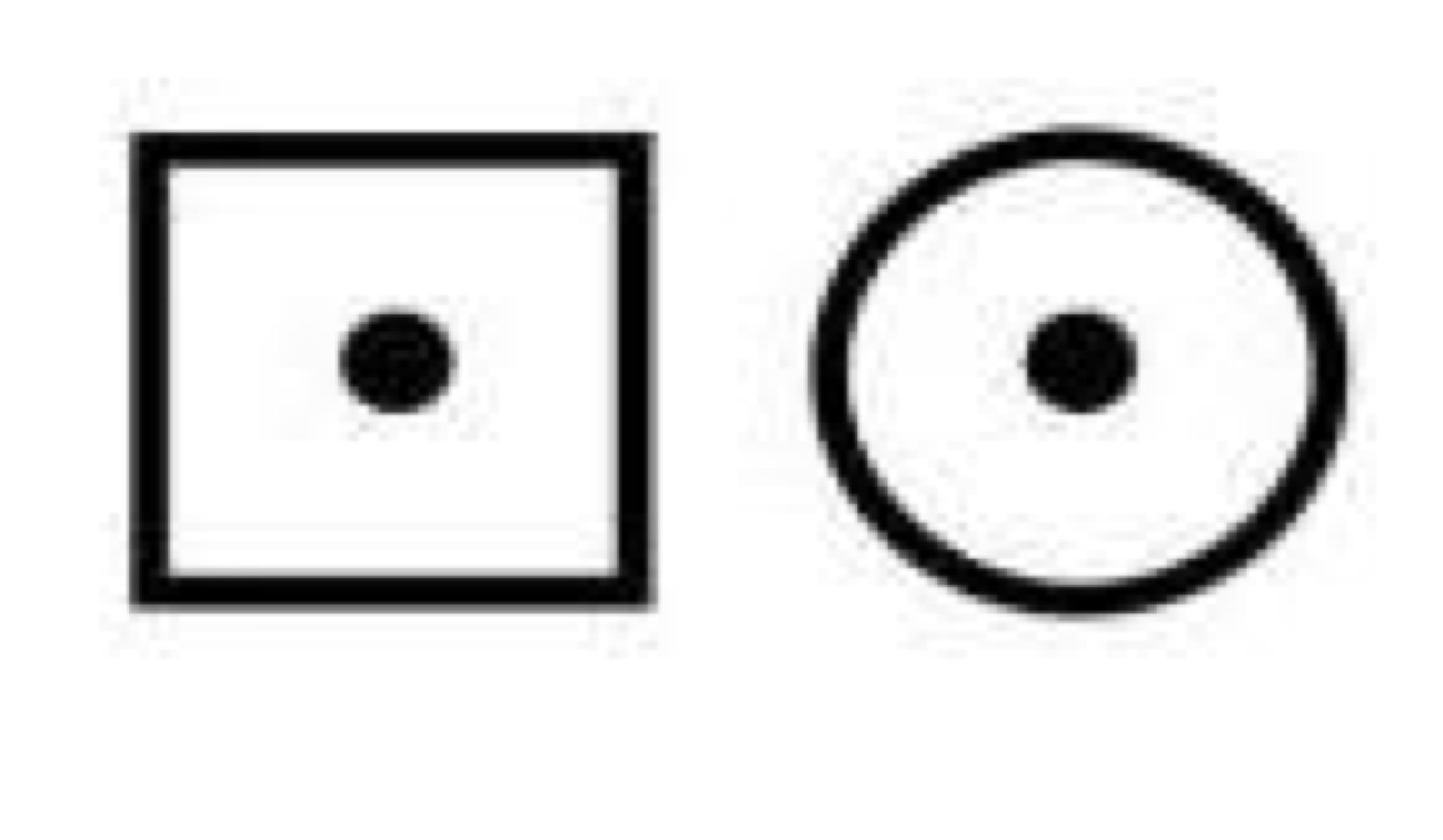
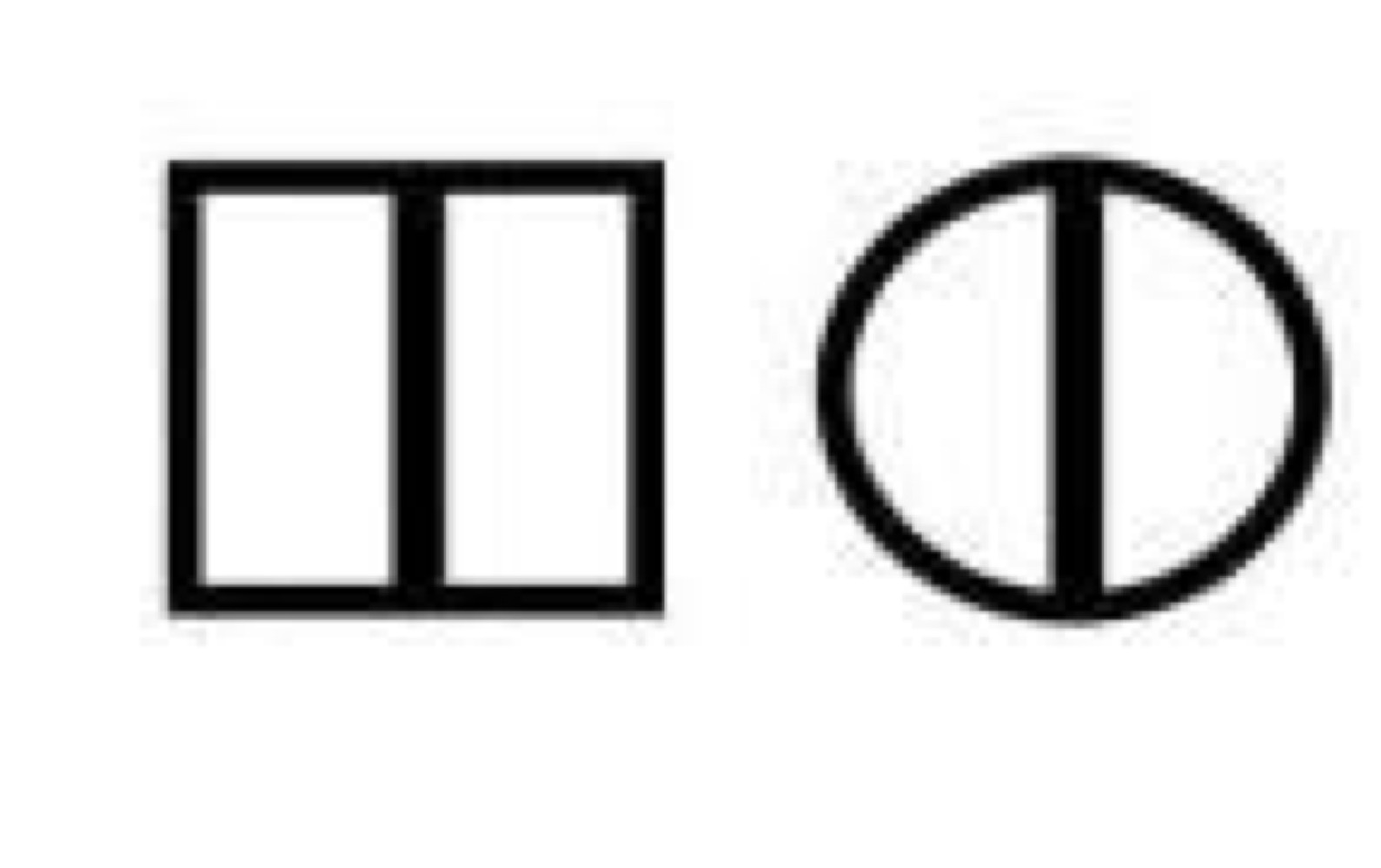
Carrier (autosomal or x-linked recessive)
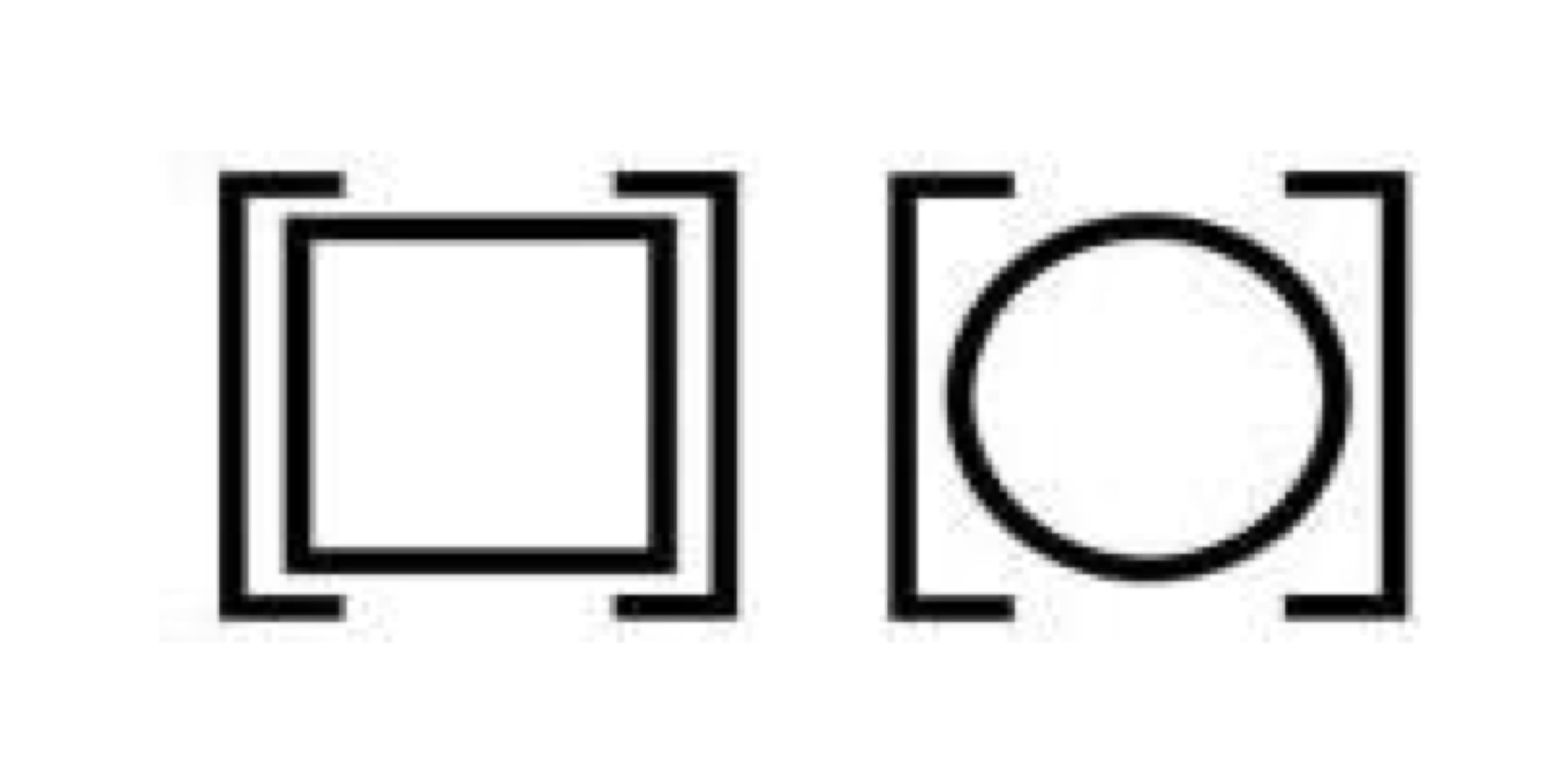
Asymptomatic (autosomal dominant)
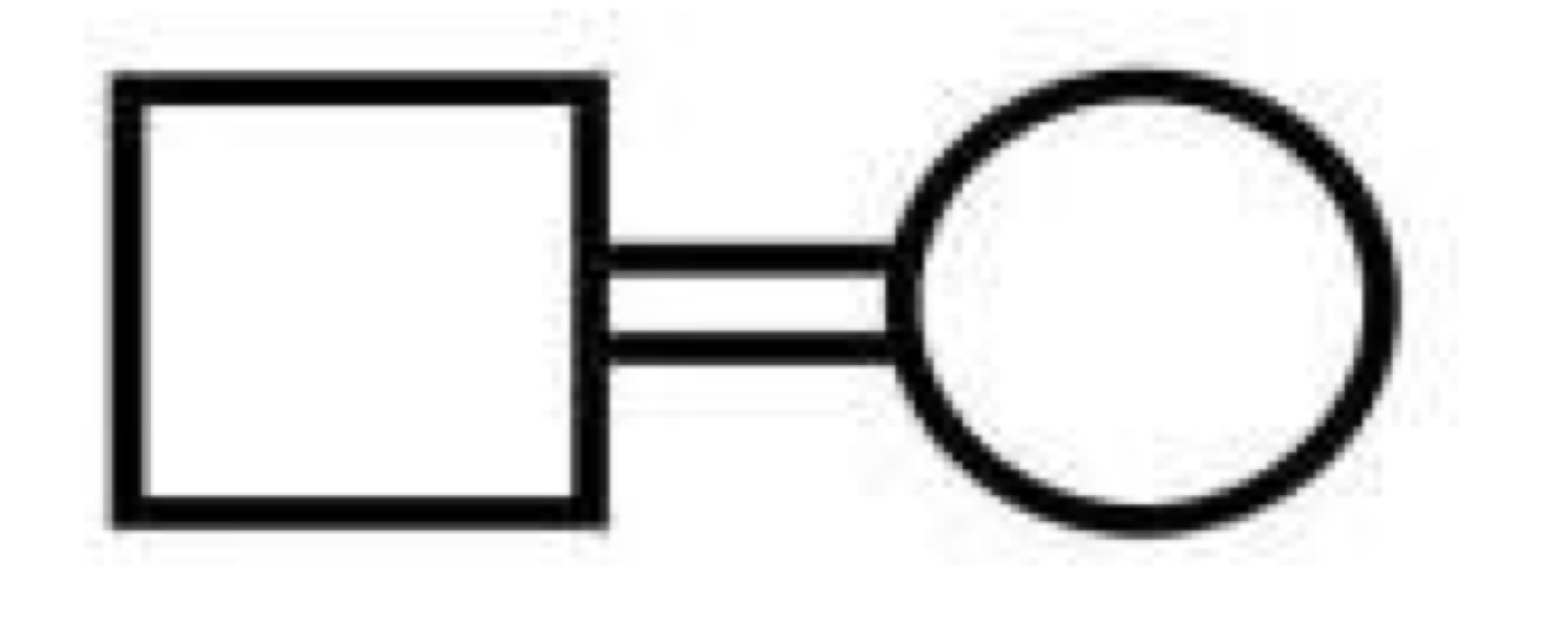
Adopted
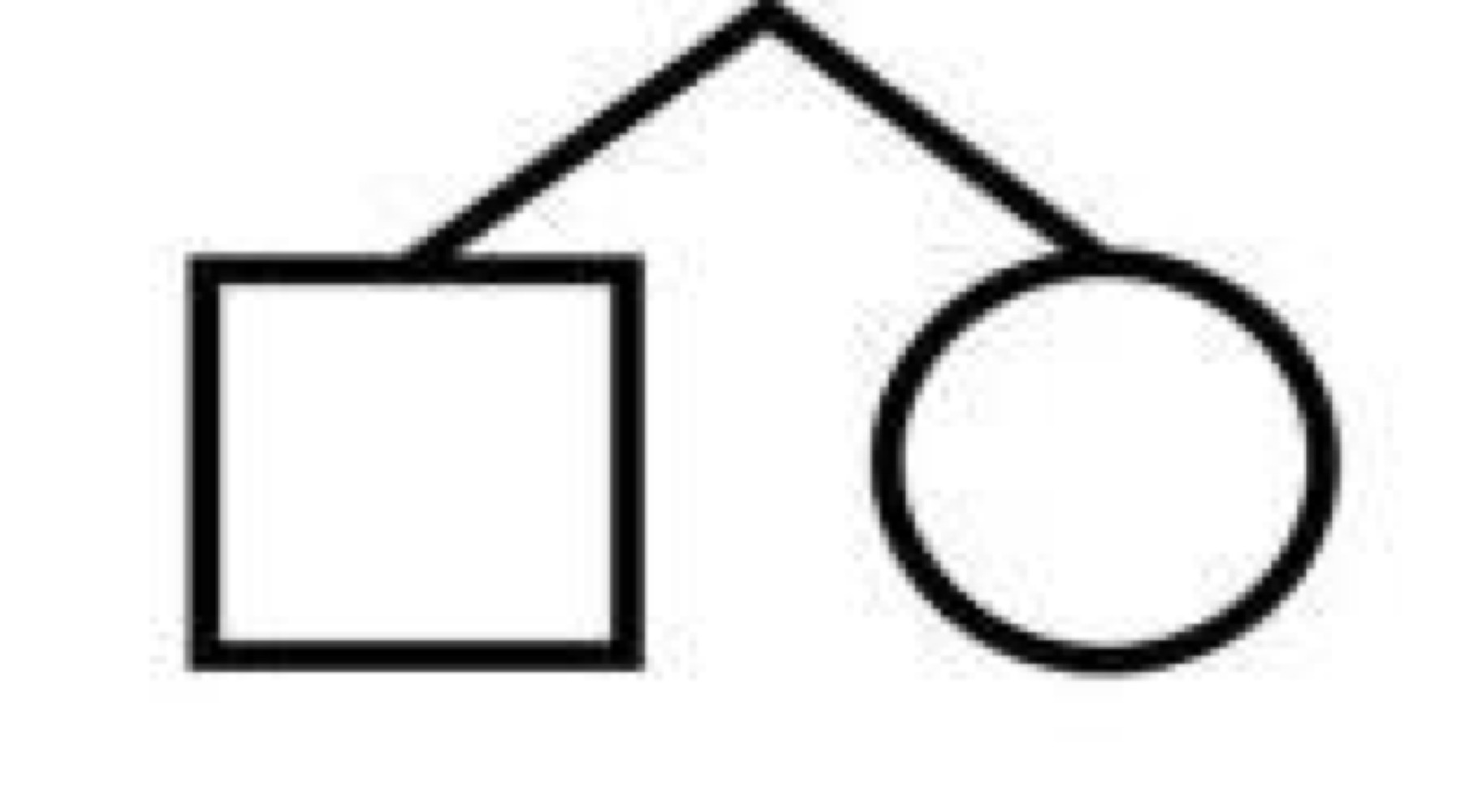
Consanguinity
Dizygotic twins
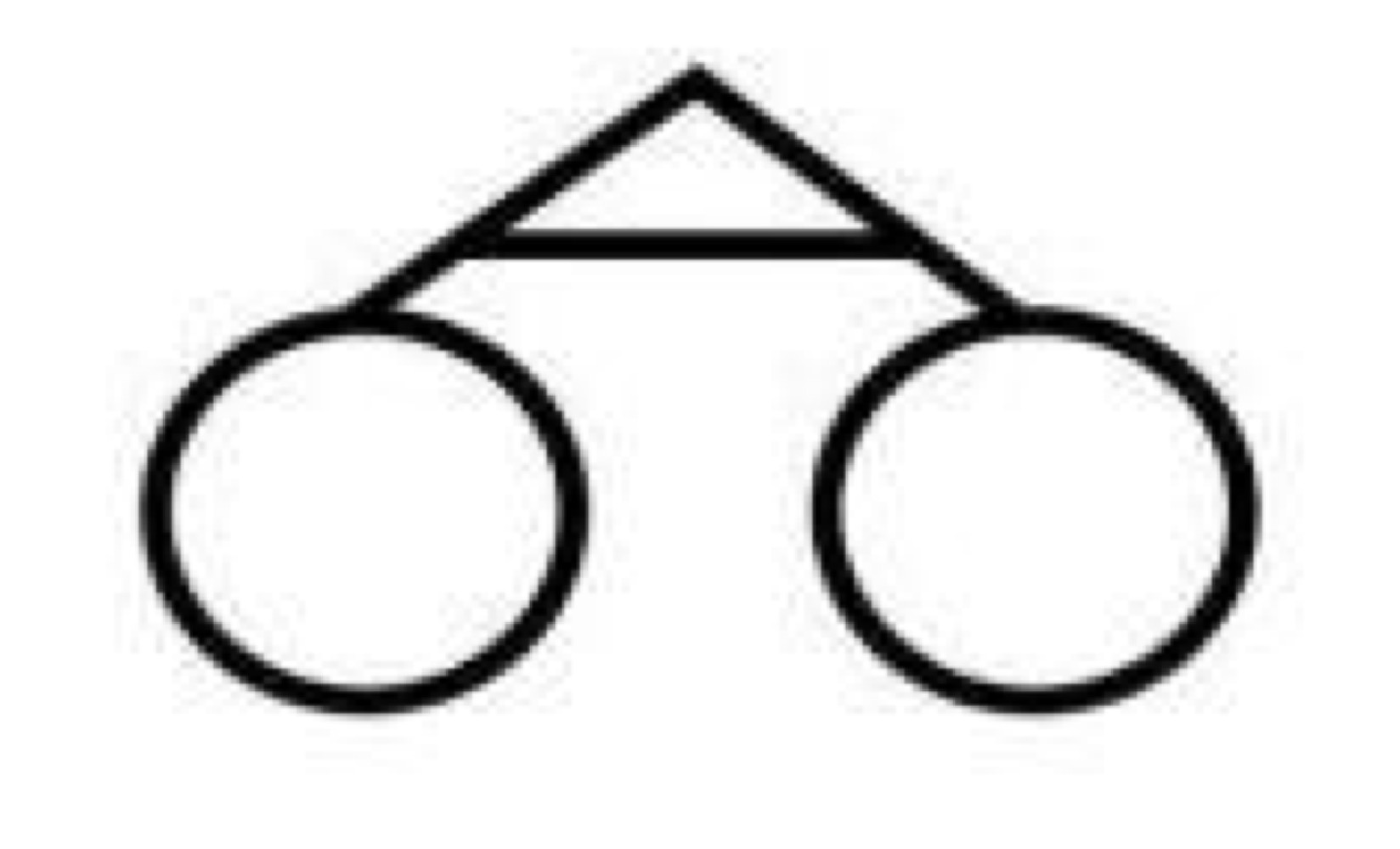
Monozygotic twins
First degree relatives
Second degree relatives
Third degree relatives
Autosomal Dominant Inheritance
Unaffected parent + Affected Heterozygote parent
No skip generations
If neither parent has the trait, none of the children will have it
50/50
Recurrence risk for
Affected heterozygote and unnafected
50% will be affected
Recurrence risk for
Affected heterozygote + affected heterozygote
75% affected
Recurrence risk for
Affected homozygote+ unnaffected
100% affected
Recurrence risk for
Affected homozygote + affected homozygote
100% 50 het 50 homo
Familial hypercholesterolemia
LDLR gene
19p13.1
APOB and PCSK9 genes
High cholesterol
Artherosclerosis
Xanthomas
Achondroplasia
Dwarfism
Autosomal dominant
Mutation in FGFR3 gene (4)
Gain of function for the protein
Homozygous is usually lethal
Hereditary Multiple Exostoses (M. Osteochondromas)
Multiple benign cartilage-capped bone tumors
Autosomal dominant
EXT1 or EXT2
Risk of chondrosarcoma
Marfan Syndrome
Connective tissue disorder
Autosomal dominant
FBN1 gene (fibrillin-1)
Tall stature/extremities
Aortic root dilation
Beta blockers reduce risk of aorta complication
Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (NF1, von Reckling)
Neurocutaneous
Autosomal dominant
NF1 gene (neurofibromin)
Freckling
Optic gilomas
Malignant tumors
Variable expressivity
Tuberous Sclerosis Complex
Hamartomas
Autosomal dominant
TSC1 (hamartin)
TSC2 (tuberin)
mTOR pathway dysregulation
Ash leaf spots
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma (SEPA)
Everolimus (mTOR inhibitor)
Autosomal recessive inheritance
We must have carriers to present disease
Horizontal transmission
Consanguinity is present
Cystic Fibrosis
CFTR gene
7q31.2
Chloride ion transport defect
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Inborn error of amino acid metabolism
Autosomal recessive
Mutation in phenylalanine hydroxylase
Accumulation of phenylalanine
Low phenylalanine diet, avoid aspartame
Tay Sachs
Lysosomal storage disorder
Autosomal recessive
Deficiency of hexosaminidase A
GM2 ganglioside accumulation
Cherry red spot macula
NO hepatosplenomegaly
Early death
Wilson disease
Copper metabolism
Autosomal recessive
ATP7B
Copper accumulation
Kayser-Fleischer rings
Chelation and Zinc
Xeroderma pigmentosum
DNA repair disorder
Autosomal recessive
Nucleotide excision repair
UV induced damage
Incomplete penetrance
person who has a disease-causing genotype might not exhibit the disease phenotype at all
Variable expression
degree of severity of disease phenotype
Allelic heterogeneity
different types of mutations at the same disease locus
Locus heterogeneity
mutations at different loci in different families
Pleiotropy
genes that have more than one discernible effect on body