Tufts DPT Anatomy: Week 2 - Questions, Origins, Insertions, Innervations, Functions
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Genu valgum
genu verum
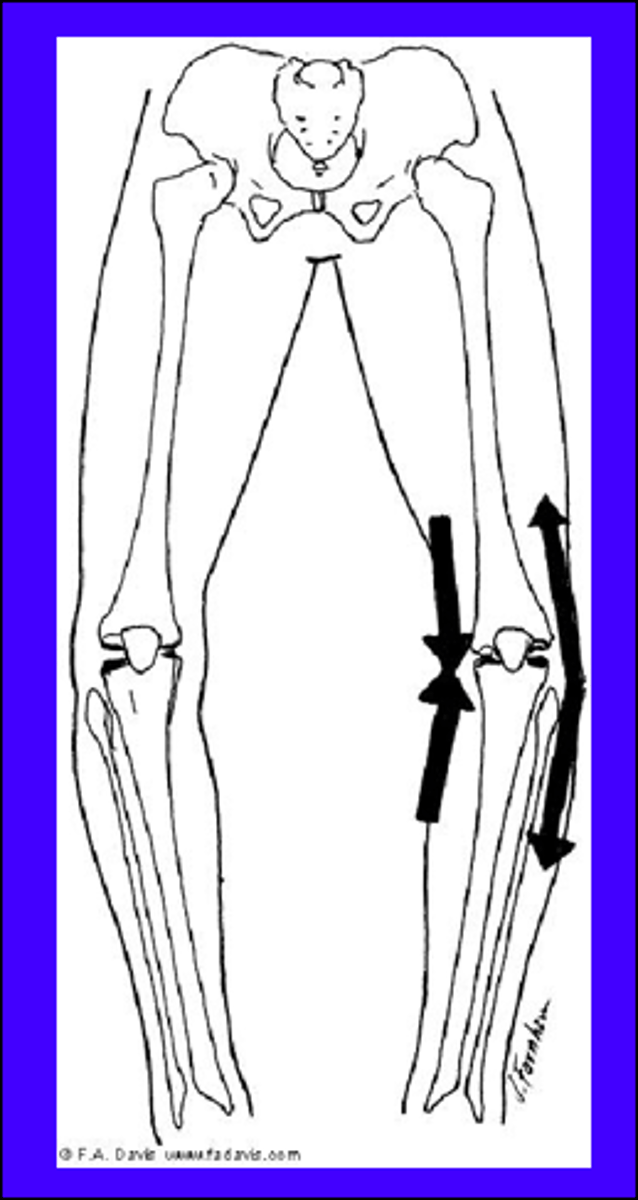
How ACL and PCL are injured
ACL: Posterior translation of the femur
PCL: Posterior translation of the tibia
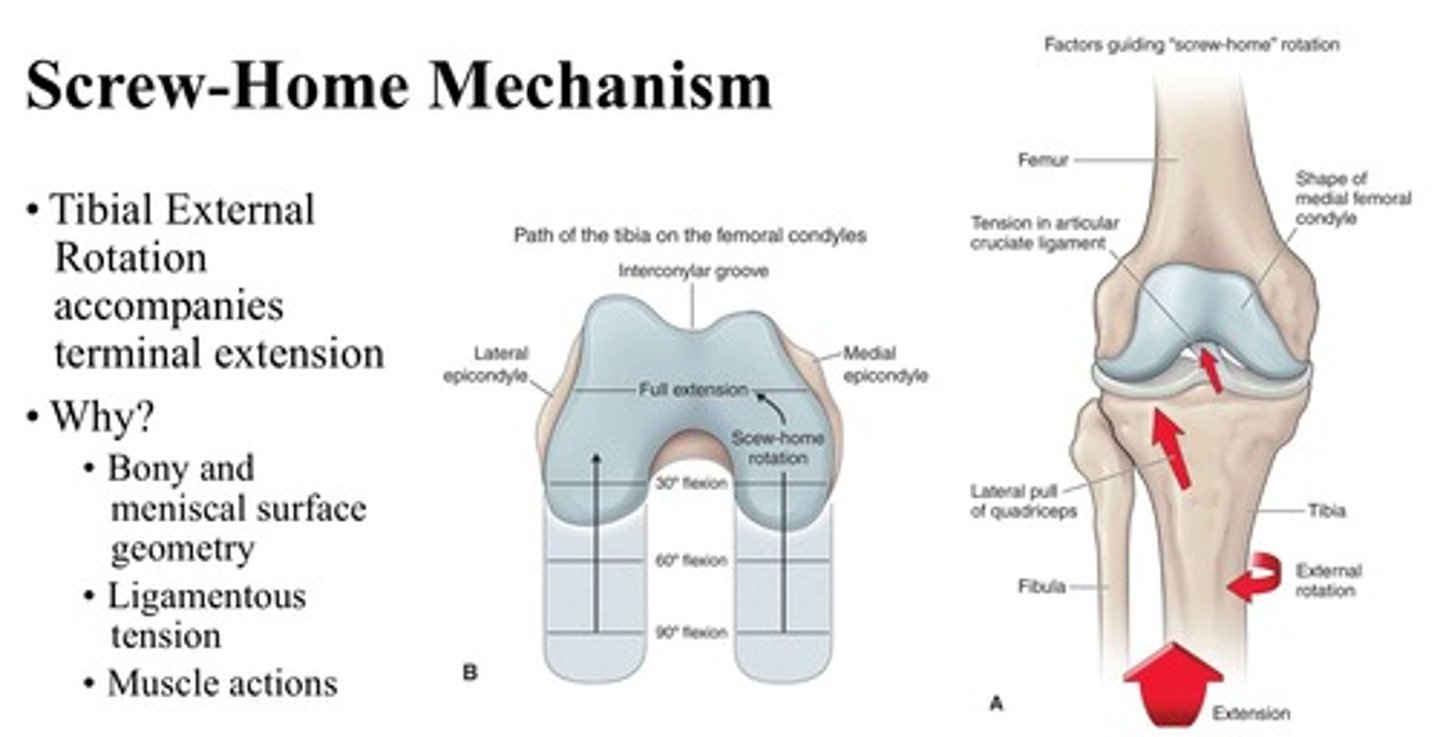
screw home mechanism
-increases knee-joint stability by locking the femur on the tibia when the knee is fully extended.
-Allows for quad and hamstring relaxation while standing.
active insufficiency
when a 2 joint muscle contracts (shortens) across both joints simultaneously it can limit sufficiency across one of the joints.
passive insufficiency
when a 2 joint muscle is lengthened over both joints simultaneously it can limit sufficiency across one of the joints.
Order of structures in the retro inguinal space
"NAVL"
Nerve
Artery
Vein
Lymphatic (not important for this class)
all femoral
2 part of adductor magnus
adductor portion
hamstring portion
boundaries of femoral triangle
superior: inguinal ligament
medial: adductor longus
lateral: sartorius
floor: iliopsoas, pectineus
roof: fascia latae, subcut. tissue and skin
what goes through the adductor hiatus
Femoral artery and vein which turns into the popliteal artery
criteria of hamstrings
1) prox origin at ischial tuberosity
2) distal attachment to leg bones over the hip and knee joint
3) innervated by the tibial division of the sciatic nerve
what are the hamstring muscles?
semitendinosus, semimembranosus, biceps femoris long head
not a hamstring
bicep femoris short head
pes anserine group
semitendinosus, gracilis, sartorius
what goes through the popliteal fossa?
tibial nerve
common fibular nerve
popliteal artery
Pectineus
Origin: Pubic Ramus
Insertion: Pectilineal line of femur inferior to lesser troch.
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L3)
Action: Hip Adduction, Hip Flexion
Iliopsoas
Composed of: Psoas Major, Psoas Minor, Iliacus
Most powerful hip flexor with most range
Iliacus
Origin: Iliac Crest, Iliac fossa, Ala of sacrum, SIJ
Insertion: Tendon of psoas major, lesser trochanter
Innervation: femoral nerve (L2-L3)
Action: Hip flexion
Psoas major
Origin: Transverse Processes T12-L5 Vertebrae, Lat. aspects
Insertion: Lesser Trochanter
Innervation: Ventral Rami (L1-L3)
Action: Hip Flexion
Psoas Minor
Origin: T12-L5 Vertebrae
Insertion: Pectilineal Line, Iliopubic eminence via iliopectineal arch (Top of the pubis)
Innervation: Ventral Rami (L1-L2)
Action: Hip Flexion
Sartorius
Origin: ASIS and inferior notch
Insertion: Pes Anserine
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2,L3)
Action: Hip- Flexion, abduction, external rotation
Knee- flexion
What is pes anserine?
the tendons of the sartorius, gracilis, and semitendinosus muscles as they join and insert into the tibia at the medial side of the knee.
Quadriceps femoris common insertions, innervations, and actions
Insertion: Quadriceps tendon to base of patella -> patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Knee Extension
Rectus Femoris
Origin: AIIS
Insertion: Quadriceps tendon to base of patella -> patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Knee Extension, Flexes and Stabilizes Hip
Vastus Lateralis
Origin: Greater Trochanter, Linea Aspera
Insertion: Quadriceps tendon to base of patella -> patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity, tibia via aponeurosis
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Knee Extension
Vastus Medialis
Origin: Intertrochanteric Line, Linea Aspera, Tendons of adductor magnus
Insertion: Quadriceps tendon to base of patella -> patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity, tibia via aponeurosis
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Knee Extension
Vastus intermedius
Origin: Anterior and Lateral surface of the femur
Insertion: Quadriceps tendon to base of patella -> patellar ligament to tibial tuberosity
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Knee Extension
Articularis Genu
Origin: anterior femur
Insertion: synovial membrane of knee, suprapatellar bursa
Innervation: Femoral Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Pulls synovial membrane superiorly during extension
Adductor Longus
Origin: body of pubis inferior to pubic crest
Insertion: linea aspera
Innervation: Obturator Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Hip Adduction
Adductor Brevis
Origin: body of pubis and pubic ramus
Insertion: pectineal line, proximal linea aspera
Innervation: Obturator Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Hip Adduction, some flexion
Adductor Magnus (Adductor portion)
Origin: pubic ramus, ischial ramus
Insertion: linea aspera, gluteal tuberosity, medial supracondylar line
Innervation: Obturator Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Hip Adduction, Flexion
Adductor Magnus (Hamstring Portion)
Origin: Ischial tuberosity
Insertion: Pes anserine
Innervation: Obturator Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Hip Adduction, Knee Flexion, some internal rotation
Obturator Externus
Origin: surface of obturator foramen, Obturator membrane
Insertion: trochanteric fossa of femur
Innervation: Obturator Nerve (L2-L4)
Action: Hip external rotation, stabilize femoral head in acetab.
Contents of the Adductor canal
femoral artery, femoral vein, saphenous nerve
Semitendinosus
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: pes anserine
Innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S2)
Action: Hip extension, Knee Flexion, Knee Internal Rotation
Semimembranosus
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: medial condyle tibia
Innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S2)
Action: Hip extension, Knee Flexion, Knee Internal Rotation
Biceps Femoris Long head
Origin: Ischial Tuberosity
Insertion: head of fibula
Innervation: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S2)
Action: Hip extension, Knee Flexion
Biceps femoris short head
Origin: linea aspera, supracondylar line
Insertion: head of fibula
Innervation: Common Fibular nerve (L5, S2)
Action: Knee flexion
*does not cross hip joint*
contents of popliteal fossa
popliteal artery
popliteal vein
tibial nerve
common fibular nerve