Chapter 7: blots, hemoglobin, myoglobin
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Western blotting
method for detection of specific proteins. aka immunoblotting. Identifies immunoreactive proteins in a complex mixture. Proteins are resolved by electrophoresis then transferred to a membrane filter where they are treated with an antibody raised against specific targets. Presence of bound antibody is detected in the western blot.
Southern bloating
method used for detection of a specific DNA sequence in DNA samples by a radioactive DNA probe. The DNA probe has a sequence that will base-pair with the DNA sequence you want to analyze
Northern blot
a method used for detection of a specific RNA sequence in a RNA sample by a radioactive DNA probe. The DNA probe has a sequence that will base-pair (hybridize) with the RNA you want to analyze. ‘
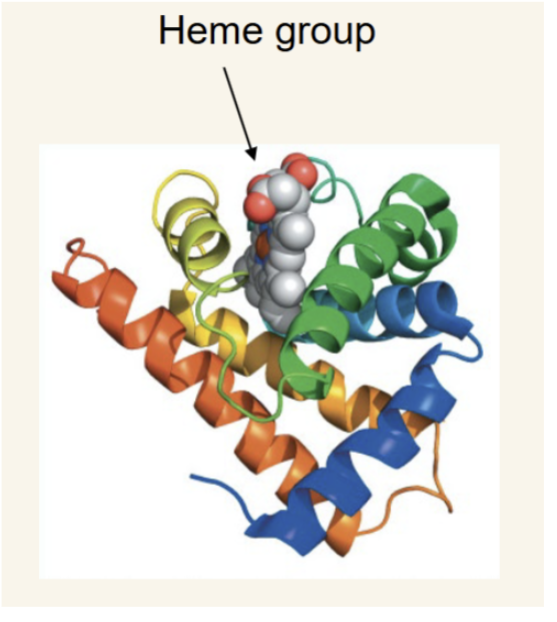
Myoglobin(Mb)
monomeric heme protein that binds and releases O2 in tissues (misconception that it is only found in skeletal muscle, it is found in all tissues.)
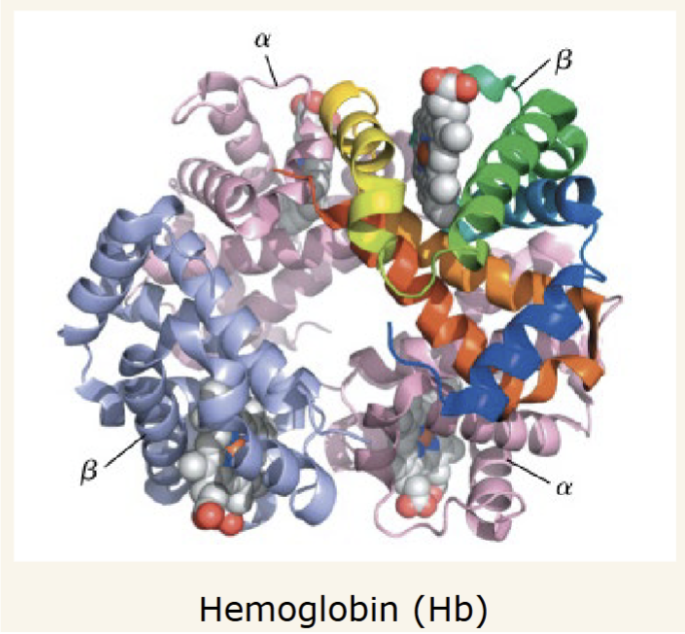
Hemoglobin(Hb)
tetrameric heme protein that transports O2 from lungs or gills to peripheral tissues and returns CO2 to gills or lungs for exhalation.
About —- mg/g of human muscle tissue is —- for efficient delivery of O2 to the mitochondria
2; myoglobin
Deep diving animals have —-- fold more myoglobin. Why?
10-30 fold more; capacity for oxygen storage permits for long periods underwater without breathing
Show a basic representation of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin

Show how RBCs deliver oxygen from lungs to tissues and then return to lungs
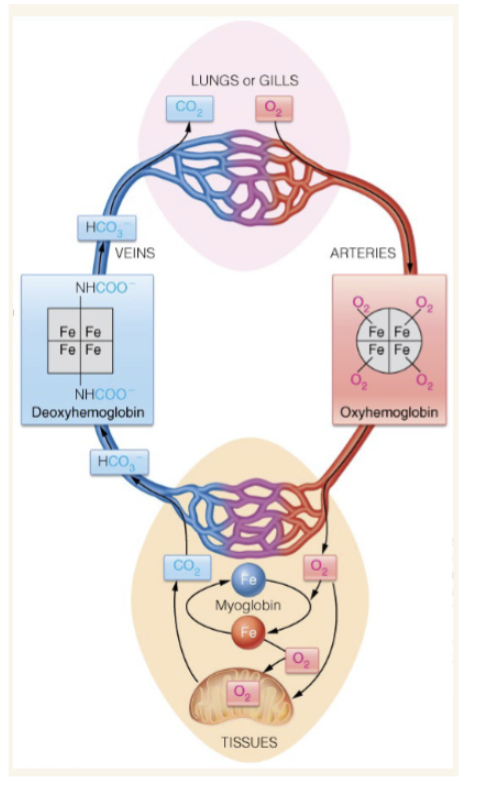
Red blood cells provide what for hemoglobin
safety and structure
Characteristics of RBC(erythrocytes) shape
biconcave disk, flexible, large SA to V ratio.
RBCs are the carrying vehicle of —--
hemoglobin
The subunits of hemoglobin and the structure of myoglobin are very —-.
similar
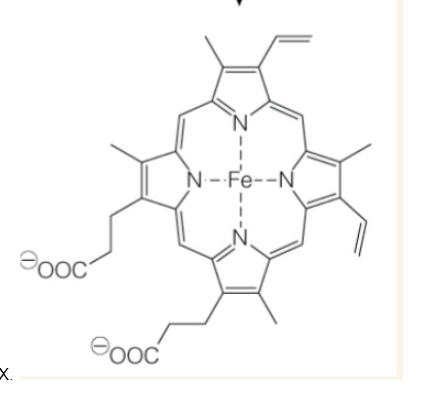
heme
iron porphyrin (conjugated tarapyrrole ring system). Fe2+ is bound to protoporphyrin IX.
Myoglobin or hemoglobin without heme is called an —--; with heme they are called a —-
apoprotein; holoprotein
Hb and Mb with O2 bound are called what respectively? Hb and Mb without O2 bound are called what respectively?
oxyhemoglobin and oxymyoglobin; deoxyhemoglobin and deoxymyoglobin
The Fe2+ of heme has — coordinating positions. What are bonded at each position
6 ; 4 positions are nitrogens of the heme, one is O2 and the last is the proximal histidine
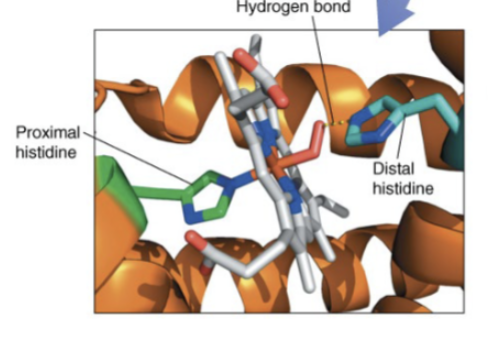
Proximal histidine
in hb or mb, histidine which binds directly to the Fe2+ of the heme group
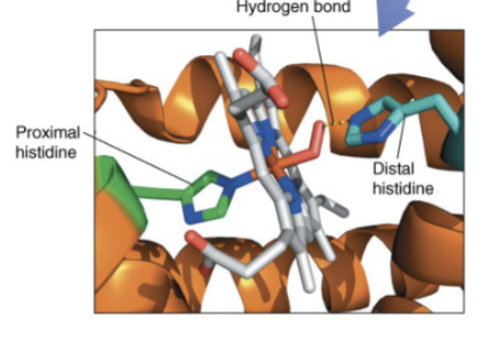
Distal histidine
in hb or mb, the histidine which stabilizes the O2 bound to the Fe2+ of the heme group via H-bonding
Why can carbon monoxide kill you?
it binds to myoglobin better than O2
As more O2 binds to Hb, the visible spectrum shifts from the —- spectrum to the — spectrum. Due to this arterial blood is (more or less) of a brighter red than veinous blood
blue to the red; more
PO2
partial pressure of oxygen (proportional to conc. Of O2)
YO2
fraction of site occupied. =sites occupied/total sites available. =Po2/(P50+PO2)
Kd=?
[Mb][O2]/[MbO2]
P50
PO2 (partial pressure of O2) at half saturation (YO2=0.5). Constant that reflects the binding affinity of myoglobin to O2.
Given an oxygen binding curve for myoglobin with YO2 as the y axis and Po2 as the x-axis, how would you find P50?
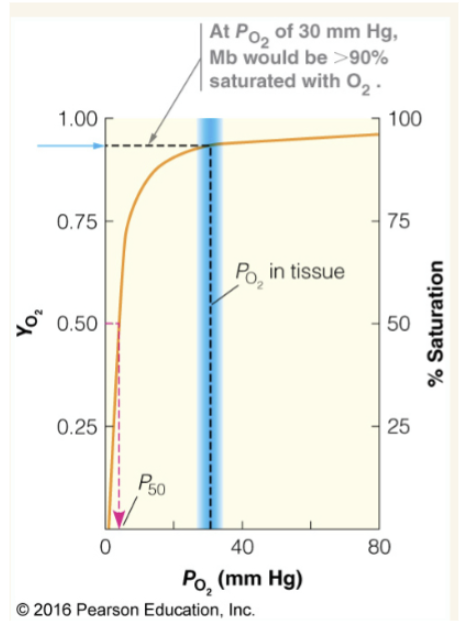
Smaller P50 means what? Higher P50 means what?
smaller P50= higher affinity to O2 and larger P50= lower affinity to O2
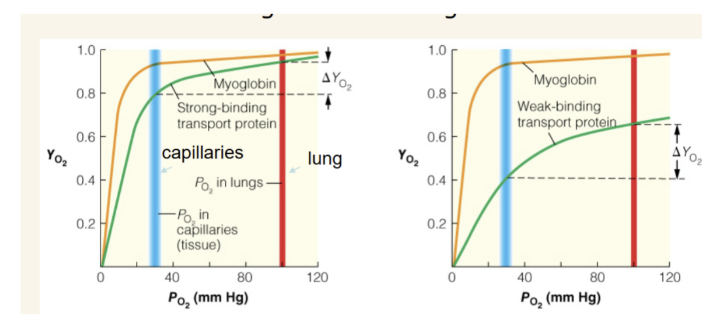
explain why both of these representations of blood oxygen-transport proteins are not ideal
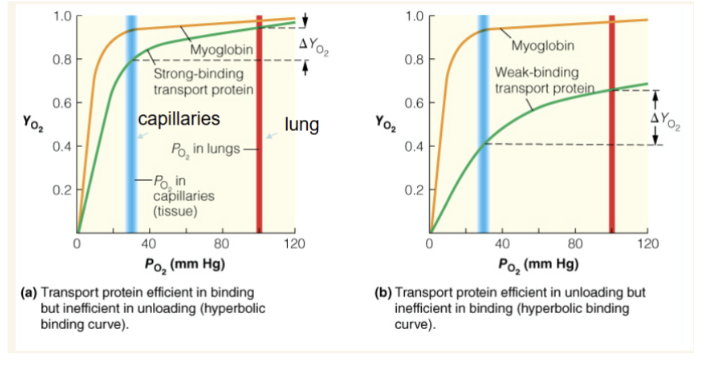
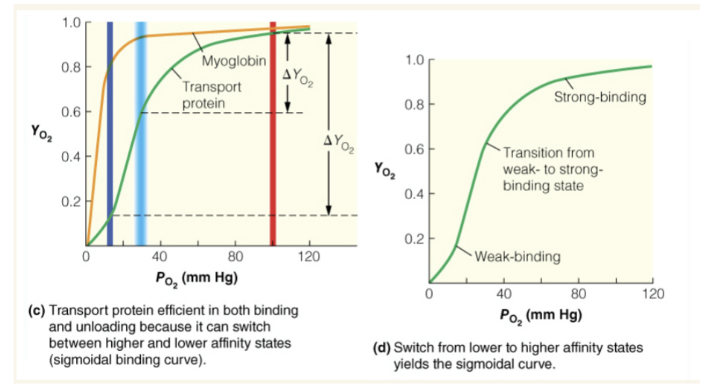
What type of binding curve is the most efficient for an oxygen delivery system and why?
blue line is PO2 in capillaries and red line is PO2 in lung
Hill-equation
n=Hill coefficient
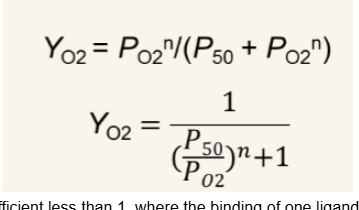
Negative cooperativity
hill coefficient less than 1. where the binding of one ligand decreases the affinity of other binding sites on the protein
Non-cooperative binding
hill coefficient is 1. Binding of ligand does not affect other binding sites on a protein
Positive cooperativity
Hill coefficient is greater than 1. binding of one ligand increases the affinity of subsequent ligands at other sites on a protein
allostery/allosteric regulation
Binding event on one site of a protein or protein complex affects the binding event in a distal and distinct site.
KNF hemoglobin allostery model
Binding O 2 at one Hb subunit changes conformation at that subunit, facilitating transition at adjacent subunits in the same molecule; mixed tetramers with low- and high-O 2 binding affinity subunits are allowed
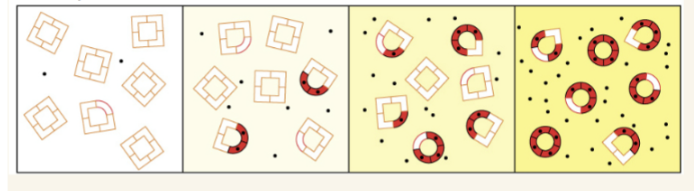
MWC hemoglobin allostery model
Hb exists in two states: T (tense; lower O 2 binding affinity) and R (relaxed); O 2 binding perturbs the T ⇌ R equilibrium toward the R state, and O 2 release favors the T state; mixed tetramers are not allowed in this model.
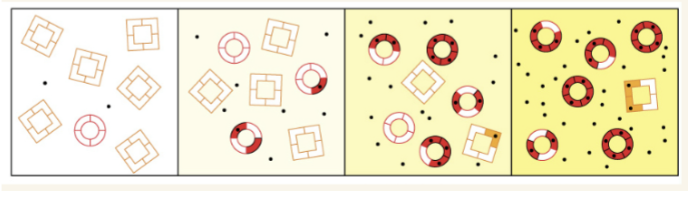
Which model is correct, MWC or KNF?
neither is completely right.
Hb exists mostly in — state at low O2 affinity and —- state at high O2 affinity
T state; R state
Silly slogan to memorize T and R state
R is for oxygen
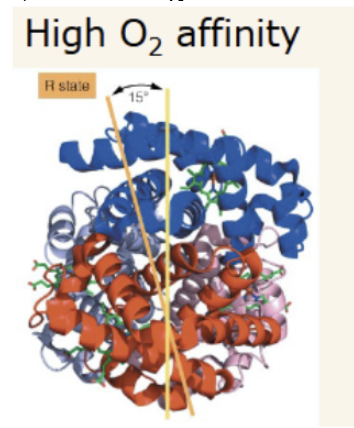
R state
relaxed state. 15 degree rotation of alpha-beta1 dimer with respect to alpha-beta2 dimer. Oxygenated state. More narrow central channel.
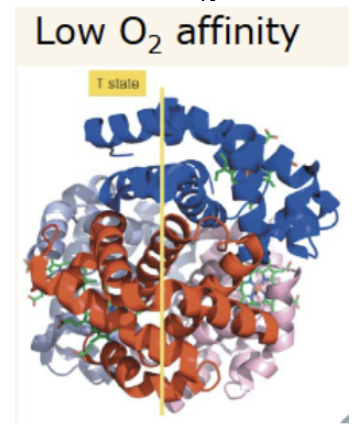
T state
tense state. Deoxygenated state. Has a less narrow central channel.
What happens in the T to R transition of hemoglobin?
There is a 15 ̊ rotation of α1β1 with respect to α2β2 upon switching from the T to R state
In the T to R transition the central channel through the hemoglobin does what?
narrows
At high O2 pressure, what Hb state is more favorable?
R state
At low O2 pressure, what Hb state is more favorable
T state
Why is oxygen binding not favorable in the T state of hemoglobin? Why is it favorable in R state? There is an unfavorable enthalpy loss in the switch from T to R state, how is this compensated for?
In the T state, more noncovalent interactions (salt bridges or H-bonds) are present between αβ and ββ interfaces. All these interactions are broken in the R state or Oxygen bound state. This unfavorable enthalpy loss is compensated by favorable O 2 -heme binding interactions.
What stabilizes R-state? What stabilizes T state?
R-state is stabilized by strong Fe-O2 bonds while T state is stabilized by intersubunit interactions (H-bonds and salt bridges)
In hemoglobin, – state is more stable when no ligands are bound as it is at a (lower/higher energy). — state is more stable when 4 ligands are bound as its at a (lower/higher) energy
T; lower; R ; lower
Perutz mechanism for T to R transition
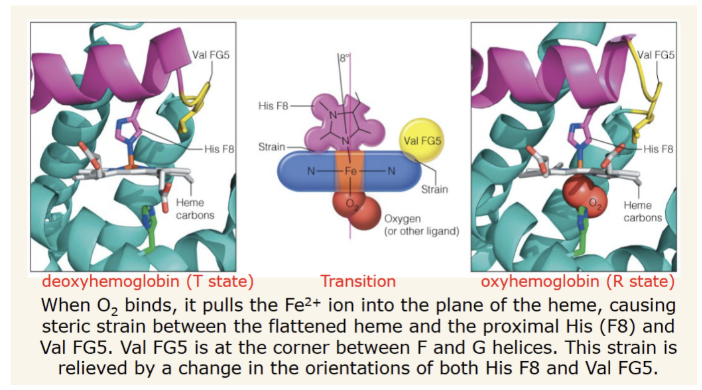
How does the H93G mutation affect hemoglobin?
it decouples the F helix and heme group connections ( i.e. there is no proximal his bound to the Fe). This means the F helix is not disturbed by O2 binding as it is in the perutz model.
Allosteric effectors
bind target proteins and promote a conformational change that modulates the functional properties of the protein
Homotropic allosteric effectors vs heterotropic allosteric effectors
homotropic bind at active site while heterotropic bind at other sites on the protein
Positive effector
binding of this effector increases binding affinity of other ligands to a protein
In the case of hemoglobin, O2 is a (positive or negative) (heterotropic or homotropic) effector. What does this mean
positive homotropic effector; its binding to heme increases the binding affinity of O2 to other hermes in the tetramer
Negative effectors
binding of one or more of these effector decreases the binding affinity of O2 to hemoglobin
At the oxygen resource area of an organism, what resources are high and which are low? Why?
High in O2 Low in BPG, CO2 , and H+ Need to load O2 Therefore, higher affinity to O2 or decreased P50
At the oxygen destination area of an organism, what resources are high and which are low? Why?
Low in O2 High in BPG, CO2 , and H+ Need to unload O2 Therefore, lower affinity to O2 or increased P50
Examples of negative heterotropic effectors for hemoglobin
H+, CO2, 2,3-BPG (2,3-bisphosphoglycerate)
Bohr effect
as pH drops, H+ binding to Hb favors the T state; thus P50 and O2 release in tissue increases
Most CO2 is transported dissolved in — to the lungs but —% is bound to Hb amino groups as —-
plasma; 5-13%; carbamate
How does hyperventilation prevent O2 release in tissues?
O2 levels decrease, this favors the R state and reduces O2 release in tissues; treat by breathing into a paper bag to reintroduce exhaled CO2 and increase its concentration in plasma
How does CO2 contribute to bohr effect?
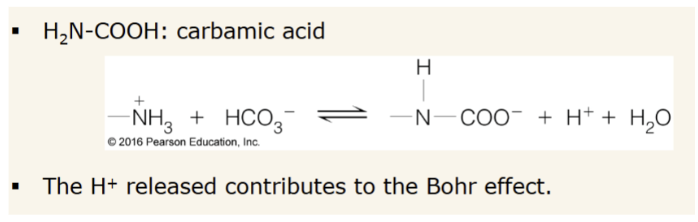
How does 2,3-BPG act as an allosteric effector
negative heterotropic effector. binds in the cleft that opens in the T state and perturbs the T ⇌ R equilibrium in favor of the T state (resulting in greater O2 delivery)
Why is there higher O2 binding affinity for fetal Hb
His 143 Ser 143 in fetal Hb reduces BPG binding affinity, which favors the R state and results in a higher O 2 binding affinity
Negative effectors stabilize — state of hemoglobin. This promotes what?
they stabilize the T state, and thereby promote greater O2 delivery/release to tissues by lowering O2 binding affinity
How does binding of allosteric effectors affect hemoglobin in lungs? Show the chemical rxn

How does binding of allosteric effectors affect hemoglobin in capillaries? Show the chemical rxn
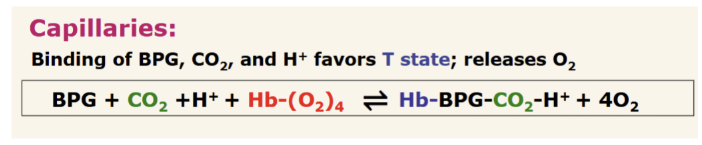
Show the chemical rxn for oxygen exchange with respiring cells

silence/synonymous mutations
mutation results in no amino acid change
missense/nonsynonymous mutations
mutation results in single amino acid change
Nonsense mutation
mutation results in production of a stop codon
Frameshift mutation
addition or deletion which shifts the reading frame
Sickle cell disease
Abnormal erythrocytes block circulation in capillaries and lyse due to their fragility, causing anemia. Heterozygotes with half mutant and half normal Hb are asymptomatic except when oxygen-stressed. This helps to increase malaria resistance.