Respiratory Fxn- Kline
1/23
Earn XP
Description and Tags
5Q- based off pp
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
24 Terms
FEV1 stands for…
Forced expiratory volume in 1 sec
FVC stands for…
forced vital capacity or the max amount of air that can be exhaled during a forced expiration
By looking at the ratio of FEV1/FVC we can measure/ see what?
Basically, we can tell whether there is an OBSTRUCTION or not!
Technical definition: measure of airway obstruction with or without restriction
What is a normal adult (>20) FEV1/FVC %?
80%
What FEV1/FVC % in adults SUGGESTS an obstruction?
<70-75%
In people <20 years old what FEV1/FVC percent suggests an obstruction?
≤85%
Practice:
If I had a 50-year-old patient with asthma (an obstructive disease), what would I expect their FEV1/FVC ratio to be?
a. 80%
b. 85%
c. 70%
d. 100%
c
What is a Pulmonary Function Test (PFT)?
FYI
used to evaluate physiological processes and measure abnormalities like obstructions, changes, decreases in gas exchange
What is the most commonly used PFT?
spirometry

What does a peak flow meter measure?
measures how fast you can push air out of your lungs on forced exhale
measures how open are the airways in the lungs
Obstructive lung disease is inability to get air ____ the lungs.
(into /out of)
OUT
Restrictive Lung disease is inability to get air ____ the lungs.
(into /out of)
INTO
What are some common obstructive lung disease?
asthma
COPD
emphysema
chronic bronchitis
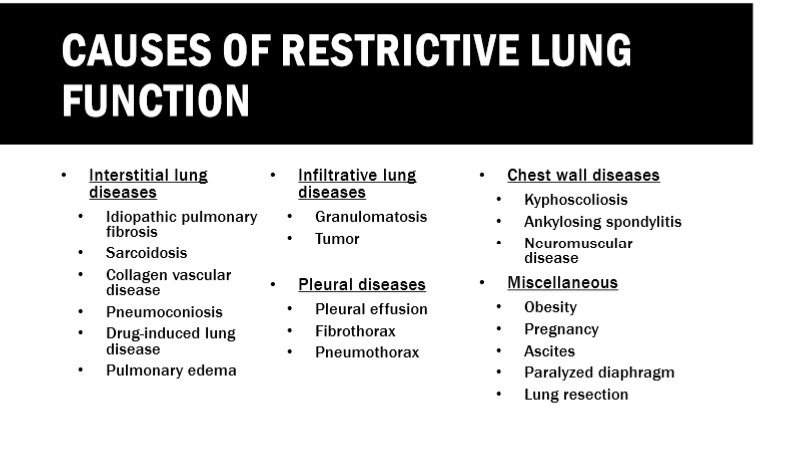
What are some causes of restrictive lung diseases?
basically anything that makes it so the lung can’t expand
Tip: I’m going to remember the obstructive diseases, so if I see a disease that’s doesn’t belong to obstructive, I’m gonna assume it’s restrictive
For Obstructive Lung Disease, what happens to the FEV1, FVC, and FEV1/FVC ratio?
FEV1= DECREASED
FVC= normal
FEV1/FVC ratio= decreased
For Restrictive Lung Disease, what happens to the FEV1/FVC ratio?
NORMAL/ Stays the same (75-80%)
What value is used to classify restrictive lung diseases instead of the FEV1/FVC ratio?
TLC (total lung capacity)
How is the TLC effected in restrictive lung diseases?
DECREASED
Mild restrictive lung disease is a TLC <____-____%
Mild restrictive lung disease is a TLC <70-80%
Moderate restrictive lung disease is a TLC <____-____%
Moderate restrictive lung disease is a TLC <61-69%
Severe restrictive lung disease is a TLC <___%
Severe restrictive lung disease is a TLC <60%
For DIAGNOSIS of obstructive lung disease the FEV1/FVC ratio must be less than ____%.
70%
Practice:
Which of the following would indicate a diagnosis of an “obstructive” patter in pulmonary function testing?
a. positive bronchodilator response
b. increased FEV1/FVC ratio
c. Decreased FEV1/FVC ratio
d. increased total lung capacity
c
Practice:
All of the following are causes of restrictive lung pattern in pulmonary function tests except which:
a. COPD
b. pulmonary fibrosis
c. pleural effusion
d. pulmonary edema
a- COPD is obstructive