Statistics- 1: Description and Inferences
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
variable=
any characteristic, number or quantity that can be measured and can differ across entities or across time
variables examples
hair colour, level of trust in the government, age, number of consecutive stairs climbed…
Types of variables:
different levels of measurement: nature of information of the values assigned to variables
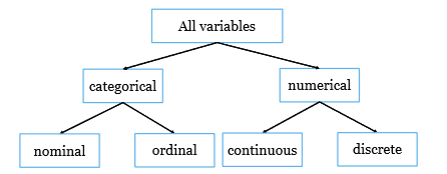
Categorical (level of measurement): nominal
2 or more exclusive categories
no natural order
no arithmetic operations possible
eye colour, marital status, hair colour, political party affiliation…
Categorical (level of measurement): ordinal
clear ordering of the values (high to low)
distance between values not the same across levels
education level, political interest, performance ratings, agreement to a statement…
Numerical (level of measurement): continuous
can be measured to any level of precision
height, weight…
Numerical (level of measurement): Discrete
only countable variables are possible
whole and positive numbers
Can be measured in discrete terms= whole numbers
pets owned, point in an exam, number of car accidents…
Explanatory variables
= cause
often x
Independent variable
Response variable
Outcome
often y
Dependent variable
Organizing data in a dataset:
column= variable
row= a given record of the data set
cell= one observation
Frequency distribution:
= how the values are distributed in relation to other values.
display of the pattern of frequencies of a variable
how often they occur in a data set.
Skewness:
negative (left) skew: mass concentrated on the right, left tail is longer.
positive (right) skew: mass concentrated on the left, tail longer on the right
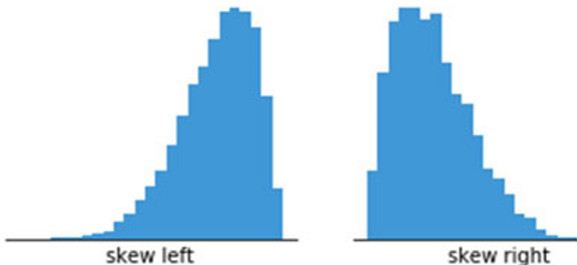
how can we summarize/ describe distributions of variables?
visualize data
Calculate measures
measure of dispersion: how stretched or squeezed the distribution is.
Measures of central tendency/ level of measurement: nominal
mode
Measures of central tendency/ level of measurement: ordinal
median +mode
Measures of central tendency/ level of measurement: numeric
Mean + median+ mode
Mode=
most frequent score in a data set
data with 1 mode= uni modal
can be several
Median=
middle score of a set of data that has been arranges in order of magnitude:
when even numbers: divide by 2
Mean=
arithmetic
average of numbers.
sensitive to extreme values (outliers)
= robust statistic.
Measures of central dispersion/ level of measurement: nominal
not possible
Measures of central dispersion/ level of measurement: ordinal
range, inter-quartile range
Measures of central dispersion/ level of measurement: numeric
Range, inter-quartile range, variance/ standard deviation
Range=
difference between the lowest and highest values
Percentiles=
split data into chunks
percentile= 100
deciles= 10
quintiles=5
quartiles=4
Inter-quartile range=
= range of the middle 50% if the data:
calculate by subtracting 1st quartile from the 3rd quartile.
robust statistic → not affected by outliers as covers middle 50% of the values
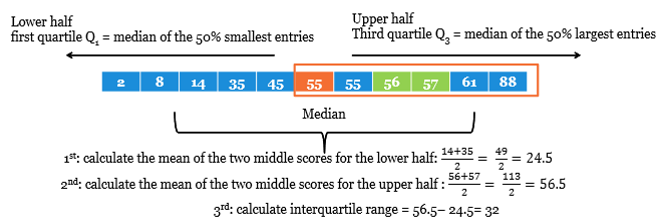
Problem with IQR?
‘robust’ → sensitive to outliers
only uses a selection of data
Measures using all data:
deviance= how much does each value deviate from the mean.
Deviance=
calculate all deviances= value- mean
and then the sum of them = total deviance
Problem with total deviance + solution=
when added up=0 → not useful measure of spread
instead → calculate sum of squared errors (SS)
square the deviances
sum of the squared deviances.
Problem with squared errors + Solution=
increase n -→ increase in SS= NOT useful to compare.
Solution= divide sum of squared errors by number of observations (N) minus 1.
=VARIANCE
calculate variance=
divide sum of squared errors by number of observations (N) minus 1.
Standard deviation:
calculated once we have the variance.
Letter sigma (σ)
= square root of the variance
dependent on the scale.
Larger standard deviation=
bigger dispersion around the mean
Can you identify mode? (in levels of measurement)
nominal= YES
ordinal= YES
numeric= YES
Can you identify median and percentiles? (Level of measurement)
nominal= NO
ordinal= YES
numeric= YES
Can you add/ subtract? (Level of measurement)
nominal = NO
ordinal= NO
numeric= YES
Can you identify the mean & standard deviation? (level of measurement)
nominal = NO
ordinal= NO
numeric= YES