Linear Transformations and Matrices - Matrix Algebra
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
What is a transformation?
Essentially another word for function (takes in a vector and spits on another vector)
We call it transformation so we can describe movement.
The input vector moves over to the output vector
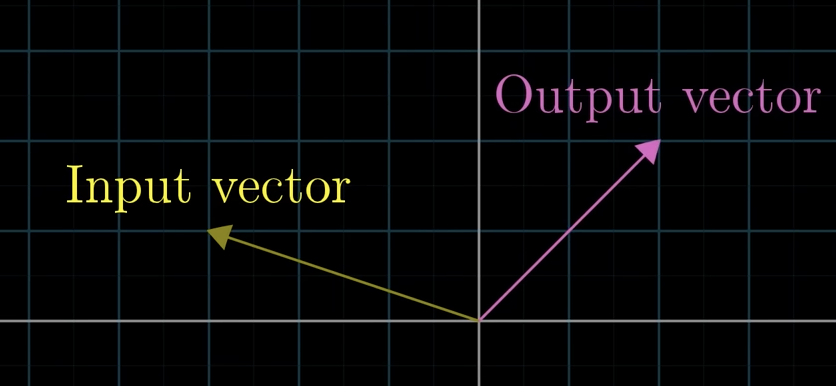
Whats the trick to visualize all the vectors transformation?
Imagine the vectors head as points, then move the points to the output point.
What does linear mean in this case?
They have to be lines, straight lines. (no curves)
The origin has to be fixed in place.
diagonal lines should also not get curvy.
The lines should be parallel and evenly spaced.
So, what does linear transformations do to space?
It redraws the grid
Lines stay lines, origin stays still - the grid gets stretched, rotated, or squished.
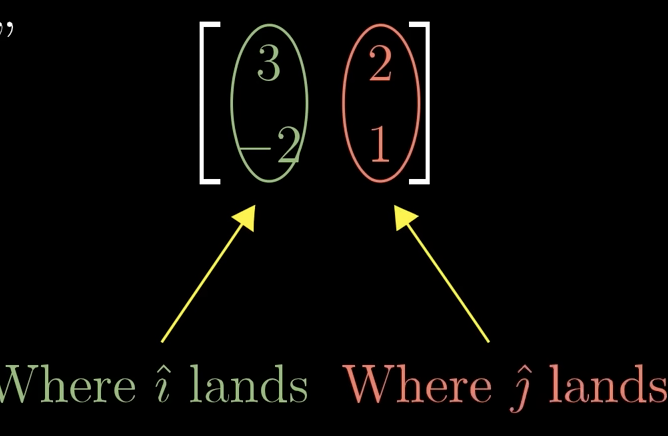
How id a matrix tied to a transformation?
each column shows where the basis vectors (i, j) go.
The whole grid follows from those two moves.
Matrix form meaning?
let the matrix xy just be some random matrix input. You can scale your original i and j to anywhere on a 2D plane
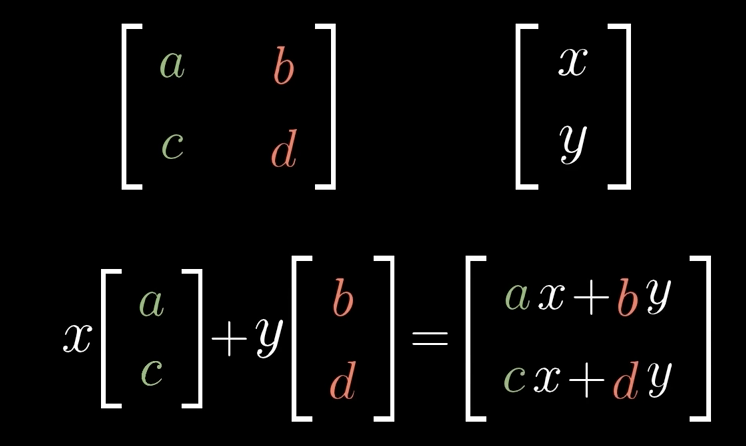
How do we find what a point a vector lands on if we rotate the vector 90 degrees counterclockwise?
rotate the i and j hat 90 degrees counterclockwise and then multiply that new matrix to your original vector
i and j hat would be [0,1 : -1,0] in this case
![<p>rotate the i and j hat 90 degrees counterclockwise and then multiply that new matrix to your original vector</p><ul><li><p>i and j hat would be [0,1 : -1,0] in this case</p></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/1b1e9db4-d83d-4af6-ad9b-3f7eb6a9a15a.png)
Whats the process to view matrix multiplication?
Change the grid first, then the vector
Matrix columns = new grid directions.

Whats a shear?
A transformation that slides one axis while keeping the other fixed - turning squares into parallelograms.
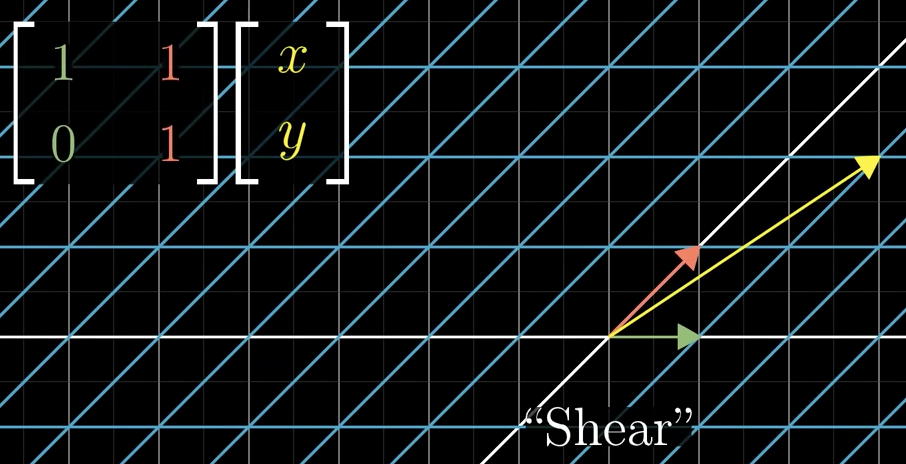
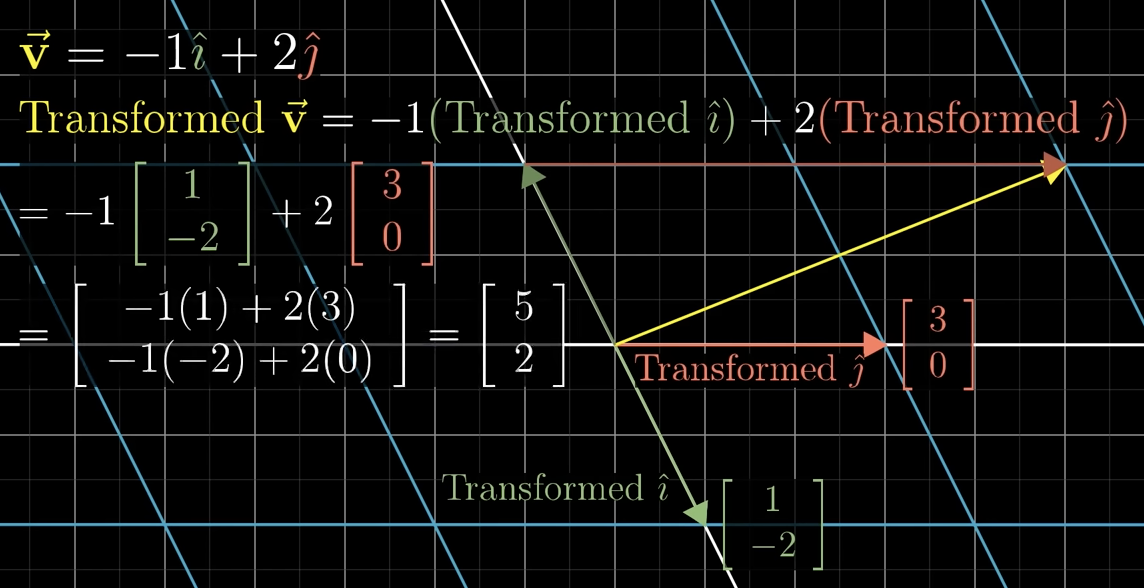
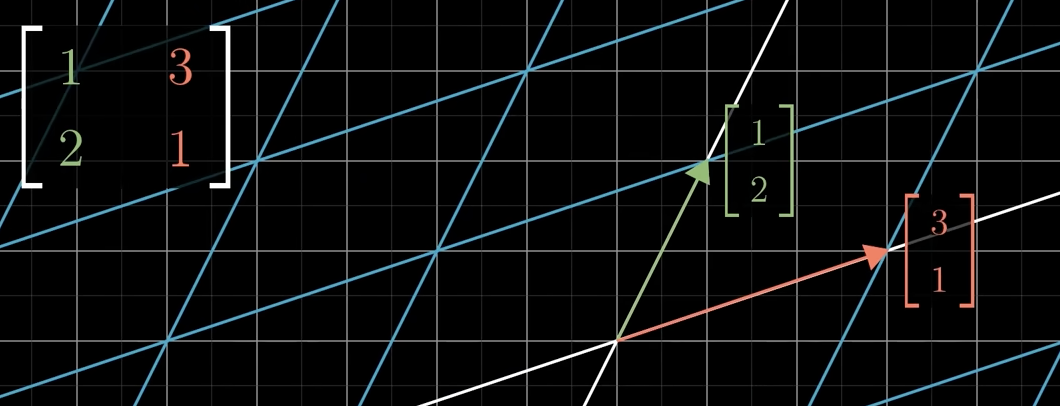
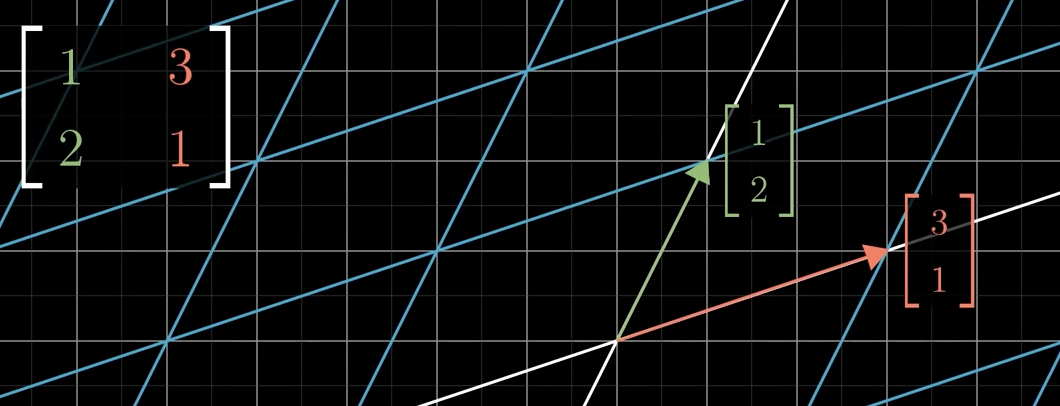
Whats the process to view a vector that is linearly transformed?
move i to the given coordinate in the matrix, then j like shown in the picture.

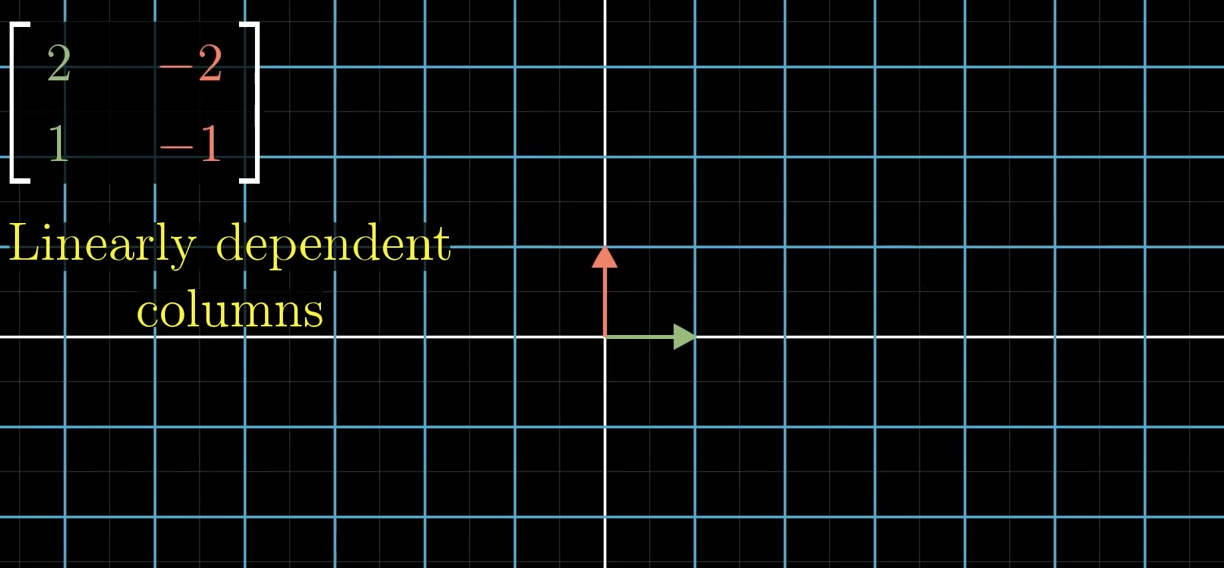
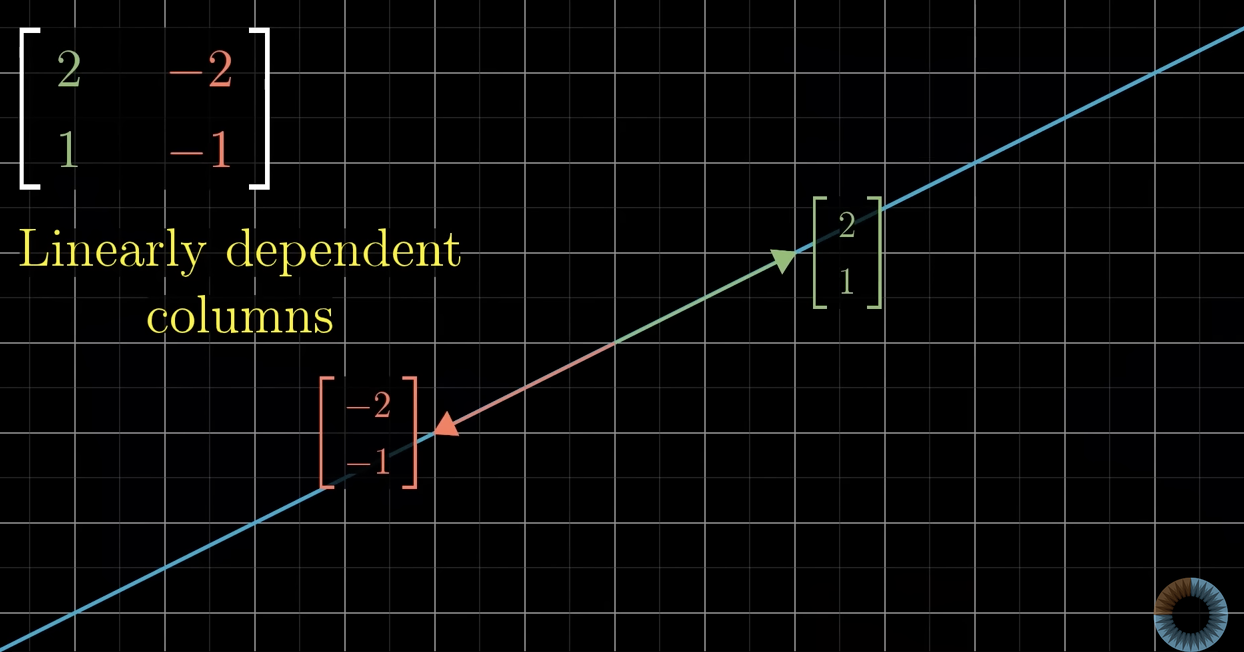
What happens when the i and j are linearly dependent of each other?
Then the transformation will squish all of 2D space onto the line where those two vectors sit.
also known as the one demensional span of those two linearly dependent vectors.
What do matrices do?
Give us a way to describe where these transformations, it gives us the coordinates where these basis vectors land.
What does matrix multiplication do?
Its just a way to compute what that transformation does to a given vector
How can we imagine matrices?
We can interpret it as a certain transformation of space