Fundamentals of Management Exam 3 - Module 7+8 (Imported)
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
Contingency theories of leadership (Fiedler)
Leader effectiveness is determined both by characteristics of leaders and by the level of situational control
-Relationship oriented and task oriented
-3 facors: leader member relations, task structure, position power
Task structure
the degree to which the requirements of a subordinate's tasks are clearly specified
Position power
the degree to which leaders are able to hire, fire, reward, and punish workers
Leader-member relations
the degree of confidence, trust, and respect subordinates have in their leader
Least preferred co-employee scale
A questionnaire that measures leader style by scoring leaders' responses to questions about the co-employee with whom they have the most difficulty working
Relationship oriented leader
Leaders that value interpersonal relationships
-Wants to be liked by and to get along well with subordinates
-Getting job done is second priority
Task Oriented Leader
Leaders that value efficient completion of tasks
-Wants high performance and accomplishment of all tasks
-Getting job done is first priority
Consideration
Behavior indicating that a leader trusts, respects, and values good relationships with their leaders
-Employee-centered behavior
Initiating structure
Behavior that ensures work gets done, and that subordinates perform their jobs acceptably
-Job-oriented behavior
Leader-member exchange theory
Leaders form different relations with various subordinates and these relationships influence subordinates' performance and satisfaction
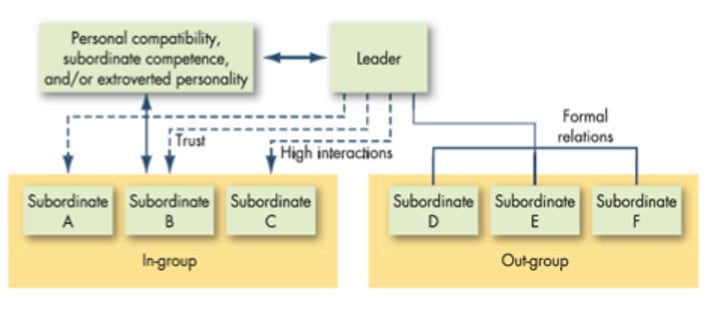
Leaders
A person who influences other people toward the direction of a goal
Leadership
The process whereby one individual influences other group member toward the attainment of defined goals
-Requires non-coercive influence (respect, like, or admiration)
Transactional leadership
"If you do this, I'll give you this"
-Contingent reward
-Management by exception (active and passive)
Transformational leadership
"Trying to really motivate and inspire people to do the job"
-Idealized influence
-Inspirational motivation
-Intellectual stimulation
-Individualized consideration
Vroom and Yetton model (participative leadership)
Guides leaders in determining the extent to which subordinates should participate in decision-making
-balancing authority with empowerment
-Maximize perceptions of justice
-Maximize acceptance of change
Autocracy vs delegation
Problems with trait theories of leadership
Traits do a better job of predicting the emergence of leaders than they do at distinguishing between effective and ineffective leaders
Communication
The transfer and understanding of meaning
Channel richness
The amount of information that can be transmitted during a communication episode
Decoding
Transforming a sender's message back into the ideas
-What you understand when you hear the message
Encoding
Transforming an idea into symbols or language so that it can be transmitted
Grapevine
an informal channel of communication, separate from management's formal, official communication channels
Information distortion
The change in the meaning a message undergoes when travelling between people (accidental or on purpose)
Information overload
A condition in which information inflow exceeds and individual's processing capacity
-Receiving too much information at once
Communication channel
The pathways over which messages are transmitted
ex: over the phone, mail, email, etc
Noise
Factors capable of distorting the clarity of messages at any point during the communication process
ex: multi-tasking, distractions, daydreaming
Feedback
Knowledge about the impact of messages on receivers
Nonverbal communication
communication using body movements, gestures, and facial expressions rather than speech
Receiver
The recipient of a message
Rumor
unfounded information spread among people
Sender
the originator of the message in the communication process
Verbal communication
expressing ideas to others by using spoken words
Formal channels
communication channels established by an organization to transmit messages related to the professional activities of members
Informal channels
communication channels that are created spontaneously and that emerge as responses to individual choices
High context cultures
Cultures that rely heavily on nonverbal and subtle cues in communication
ex: Japan, Kenya, Saudi Arabia, India
Low context cultures
Cultures that rely heavily on verbal cues in communication - straightforward
ex: USA, Australia, Germany, Denmark, Poland
Challenges to effective cross cultural communication
Linguistic styles vary across cultures:
-Tone, volume, speed, use of pauses, (in)directness, choice of words, questions, jokes, willingness to take credit for ideas, nonverbals
How to effectively communicate across cultures
Intercultural communication should be based on sensitivity and pursuit of common goals
-From an ad hoc "third culture"
Autocratic decision making style
The leader makes the decision without input from subordinates
Consultive decision making style
subordinates have some input but the leader makes the decision
Group decision making style
the group makes the decision, and the leader is just another group member
Delegated decision making style
the leader gives exclusive responsibility to subordinates
Choose to delegate when...
-Decision significance is high
-Importance of commitment is high
-Leader expertise is low
-Goal alignment is high
-Likelihood of disagreement is high
-Group expertise is high
-Team Competence is high
Organizational Justice
An overall perception of what is fair in the workplace, composed of distributive, procedural, informational, and interpersonal justice
Procedural Justice
The perceived fairness of the process used to determine the distribution of rewards
Informational Justice
The degree to which employees are provided truthful explanations for decisions
Interpersonal Justice
The degree to which employees are treated with dignity and respect
Equity Theory
A theory stating that individuals compare their job inputs and outcomes with those of others and then respond to eliminate any inequities
Distributive Justice
Perceived fairness of the amount and allocation of rewards among individuals
Overpayment Inequity
The inequity that exists when a person perceives that his or her own outcome-input ratio is greater than the ratio of a referent
-You are getting overpaid and you don't deserve it
Underpayment Inequity
The inequity that exists when a person perceives that his or her own outcome-input ratio is less than the ratio of a referent
-You are getting underpaid and you don't deserve it
Expectancy Theory
A theory that the strength of a tendency to act in a certain way depends on the strength of an expectation that the act will be followed by a given outcome and on the attractiveness of that outcome to an individual
Instrumentality
the perceived relationship between performance and rewards
-"Will I really get the reward if I achieve this goal?"
Valence
the attractiveness or desirability of a reward or outcome
- "Do I value this reward?"
Expectancy
the perceived relationship between effort and performance
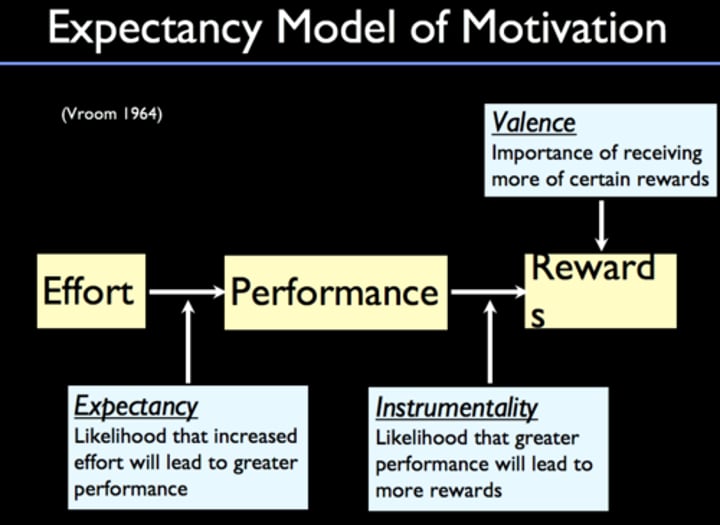
Extrinsically motivated work behavior
Behavior performed to acquire rewards or avoid punishment
-motivation is coming from outside of the individual
Intrinsically Motivated work behavior
Behavior performed for personal satisfaction
-motivation is coming from within the individual
Work Motivation
Psychological forces that determine the direction of a person's behavior in an organization, a person's level of effort, and a person's level of persistence.
Negative Reinforcement
Trying to increase good behavior by "pushing" the individual until they do the good behavior. The reward for this good behavior is that they are no longer being pushed
ex: micromanaging, nagging, threatening; leads to learned helplessness/giving up
Operant conditioning - Reinforcement
A method of learning that involves rewards and punishments to reward good behavior and discourage bad behavior
Using reinforcement well:
-emphasize positive reinforcement
-tell employees explicitly what's rewarded
-specify what behavior will entail a reward
-make consequences equivalent to behavior
-be consistent
-Do not reward all people equally, reward relative to effort
Positive Reinforcement
Trying to increase good behavior by offering rewards for good behavior
ex: recognition, praise, monetary rewards
Punishment
Making bad behavior less likely to reoccur by issuing penalties
Using punishment effectively:
-Catch the negative behavior early
-Punishment should follow negative behavior immediately
-Punishment should focus on negative behavior, not on the individual
-Provide specific information about the right way of doing things and how this positive behavior will be rewarded
-Praise in public, punish in private
Self-efficacy
An individual's belief of being capable of performing a task
Social cognitive theory
The belief that an individual has control over and is able to execute a behavior
-One's beliefs that one has the resources available to accomplish tasks
How to increase self-efficacy
-Past performance
-Vicarious modeling (if others have been successful)
-Verbal persuasion (encouragement)
-Arousal (physical manifestations of anxiety)
Vicarious learning
How individuals learn from the experiences of others
Need for achievement
The need to excel or achieve to a set of standards
Need for affiliation
The need to establish friendly and close interpersonal relationships
Need for power
The need to make others behave in a way in which they would not have behaved otherwise
Self-determination theory
A theory of motivation at work concerning autonomy, intrinsic motivation, extrinsic motivation, and the satisfaction of psychological work needs
Goal setting theory
A theory that intentions to work toward a goal are considered a major source of work motivation and lead to higher performance
What characteristics of goals lead to more success?
Goals lead to more success when they are specific, measurable, reasonably achievable (more difficult tasks generate higher task performance), and time-bound
SMART goals
Specific
Measureable
Achievable
Reasonable
Timetable
Counterproductive Work Behavior
actions that actively damage the organization, including stealing, behaving aggressively toward coworkers, or being late or absent
Job Engagement
The investment of an employee's physical, cognitive, and emotional energies into job performance
Management by Objectives (MBO)
A program that encompasses specific goals, participatively set, for an explicit time period, with feedback on goal progress
Job Crafting (Job design)
Changing the characteristics of a job in order to get more favorable personal and work outcomes
Job Characteristics Model
A model proposing that any job can be described in terms of five core job dimensions: skill variety, task identity, task significance, autonomy, and feedback
Autonomy
The degree to which a job provides substantial freedom and discretion to the individual in scheduling the work and in determining the procedures to be used in carrying it out
Skill Variety
The degree to which a job requires a variety of activities using different skills or talents
Task Significance
The degree to which a job has a substantial impact on the lives or work of other people
Task Identity
The extent to which a job involves performing a whole piece of work from its beginning to its end
Feedback
The degree to which carrying out the work activities required by a job results in the individual obtaining direct and clear information about the effectiveness of their performance
Experienced meaningfulness of work
the degree to which employees feel their jobs are important, worthwhile, and meaningful
Experienced responsibility for work outcomes
The extent to which employees feel personally responsible or accountable for their job performance
Knowledge of results
A psychological state indicating the extent to which employees are aware of how well or how poorly they are doing.
Job Design / Job Redesign
The way the elements in a job are organized
Relational job design
Constructing jobs so employees see the positive difference they can make in the lives of others directly through their work
Job enlargement
Horizontal job loading - increasing the number of tasks an employee performs, while keeping all the tasks at the same level of difficulty and responsibility
Job enrichment
Vertical job loading - Providing opportunities for employee growth by giving employees more responsibility and control, increasing autonomy
Job rotation
The periodic shifting of an employee from one task to another
Motivating potential score (MPS)
a predictive index that suggests the motivating potential in a job
Flextime
Flexible work hours
Job Sharing
An arrangement that allows two or more individuals to split a traditional full-time job
Telecommuting
Working from home, or anywhere else the employee chooses that is outside of the physical workplace
Participative Management
a process in which subordinates share a significant degree of decision-making power with their immediate superiors
Variable Pay Program
A pay plan that bases a portion or all of an employee's pay on some individual and/or organizational measure of performance
Merit based pay
A pay plan based on performance appraisal ratings
Profit Sharing Plan
An organization-wide program that distributes compensation based on some established formula designed around a company's profitability
Employee Recognition Program
A plan to encourage specific employee behaviors by formally appreciating specific employee contributions