Module 7 (Part II)
5.0(2)Studied by 1 person
Card Sorting
1/20
Last updated 1:53 AM on 3/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
1
New cards
VSEPR Model
\-Valence Shell Electron Pair Repulsion model
\-based on arrangement that MINIMIZES REPULSION of shared & unshared electron pairs around central atom
\-bond angles & unshared electron pairs help determine shape of molecule
-shared electron pairs are pushed slightly together by lone pairs b/c lone pairs contribute to repulsion
\-electron pairs are located in a molecule as far apart as they can be
\-based on arrangement that MINIMIZES REPULSION of shared & unshared electron pairs around central atom
\-bond angles & unshared electron pairs help determine shape of molecule
-shared electron pairs are pushed slightly together by lone pairs b/c lone pairs contribute to repulsion
\-electron pairs are located in a molecule as far apart as they can be
2
New cards
bond angle
\-electron pairs repel each other and cause molecules to be in fixed positions relative to each other
\-angle formed by 2 terminal atoms w/ central atom is called bond angle
\-angle formed by 2 terminal atoms w/ central atom is called bond angle
3
New cards
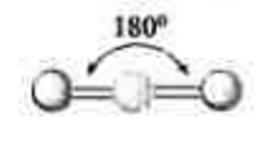
2 electron groups
0 lone pairs
0 lone pairs
\-linear
\-180 degrees
\-180 degrees
4
New cards
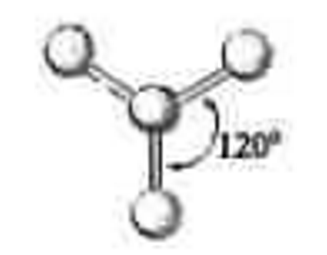
3 electron groups
0 lone pairs
0 lone pairs
\-trigonal planar
\-120 degrees
\-120 degrees
5
New cards
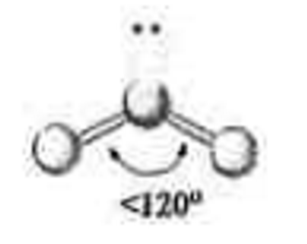
3 electron groups
1 lone pair
1 lone pair
\-bent
\-
\-
6
New cards
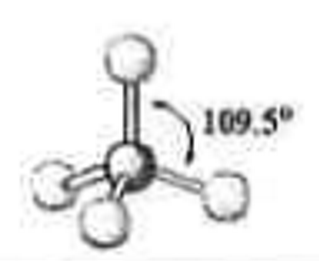
4 electron groups
0 lone pairs
0 lone pairs
\-tetrahedral
\-109.5 degrees
\-109.5 degrees
7
New cards
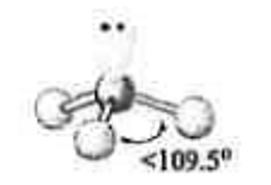
4 electron groups
1 lone pair
1 lone pair
\-trigonal pyramid
\-
\-
8
New cards
4 electron groups
2 lone pairs
2 lone pairs
\-bent
\-
\-
9
New cards
electronegativity & bond character
\-**equal** sharing of electrons results in **nonpolar** covalent bond
\-**unequal** sharing of electrons results in **polar** covalent bond
\-bonding is often not clearly ionic or covalent
\-the greater the electronegativity difference → the greater the ionic character
\-**unequal** sharing of electrons results in **polar** covalent bond
\-bonding is often not clearly ionic or covalent
\-the greater the electronegativity difference → the greater the ionic character
10
New cards
polar covalent bonds
\-electrons spend more time around more electronegative atom
\-results in partial charges at the ends of the bond
\-results in partial charges at the ends of the bond
11
New cards
nonpolar covalent bond
\-between 2 identical or very similar atoms
\-not great electronegativity difference
\-electrons shared equally & charge is balanced evenly
\-not great electronegativity difference
\-electrons shared equally & charge is balanced evenly
12
New cards
determining bond character according to EN difference
\- > 1.7 = mostly ionic
\- 0.4 - 1.7 = polar covalent
\- < 0.4 mostly covalent
\- 0 nonpolar covalent
\- 0.4 - 1.7 = polar covalent
\- < 0.4 mostly covalent
\- 0 nonpolar covalent
13
New cards
polar molecules
\-molecules are polar when electrons are shared unequally btwn atoms (contain polar bonds)
\-this causes molecule to have partial neg charge on part of atom w/ more electrons (more electroneg atom)
\-non-polar molecules aren’t attracted by an electric field
\-polar molecules align w/ an electric field & are called **dipoles**
\-this causes molecule to have partial neg charge on part of atom w/ more electrons (more electroneg atom)
\-non-polar molecules aren’t attracted by an electric field
\-polar molecules align w/ an electric field & are called **dipoles**
14
New cards
organic compound exceptions
\-all carbon-containing compounds
\-EXCEPTIONS:
-carbon oxides (ex. CO2)
-carbonides (carbon + a metal)
-carbonates (CaCO3)
\-EXCEPTIONS:
-carbon oxides (ex. CO2)
-carbonides (carbon + a metal)
-carbonates (CaCO3)
15
New cards
organic compound structure
\-carbon nearly always shares its electrons & forms 4 covalent bonds
\-in organic compounds, carbon usually bonded to H or elements near carbon on periodic table (N, O, S, P, & halogens)
\-bc C forms 4 bonds → forms complex, branched-chain structures, ring structures, & even cage-like structures
\-in organic compounds, carbon usually bonded to H or elements near carbon on periodic table (N, O, S, P, & halogens)
\-bc C forms 4 bonds → forms complex, branched-chain structures, ring structures, & even cage-like structures
16
New cards
hydrocarbons
\-simplet organic compounds
\-contain ONLY elements C & H
\-contain ONLY elements C & H
17
New cards
saturated hydrocarbon
\-contains only single bonds (ALKANES)
18
New cards
unsaturated hydrocarbon
\-contains at least one double or triple bond (ALKENES & ALKYNES)
\-watch names of alkenes & alkynes
-ex. (alkene example) 1-Butene → double bond is btwn 1st & 2nd carbon, but 2-Butene → double bond is btwn 2nd & 3rd carbon
\-watch names of alkenes & alkynes
-ex. (alkene example) 1-Butene → double bond is btwn 1st & 2nd carbon, but 2-Butene → double bond is btwn 2nd & 3rd carbon
19
New cards
alkanes
\-one single bond btwn atoms
\-simplest hydrocarbons
\-name ends in -*ane*
\-General formula: **C(n)H(2n+2)** where n=# of C
\-simplest hydrocarbons
\-name ends in -*ane*
\-General formula: **C(n)H(2n+2)** where n=# of C
20
New cards
alkenes
\-double covalent bonds btwn carbon atoms
\-name ends in -*ene*
\-for alkenes w/ only one double bond & 4 or more C, general formula: **C(n)H(2n)** where n=# of C
\-name ends in -*ene*
\-for alkenes w/ only one double bond & 4 or more C, general formula: **C(n)H(2n)** where n=# of C
21
New cards
alkynes
\-triple covalent bonds btwn carbon atoms
\-name ends in -*yne*
\-General formula: **C(n)H(2n-2)** where n=# of C
\-name ends in -*yne*
\-General formula: **C(n)H(2n-2)** where n=# of C