Chapter 7: Rays and Waves
Light Rays and Waves
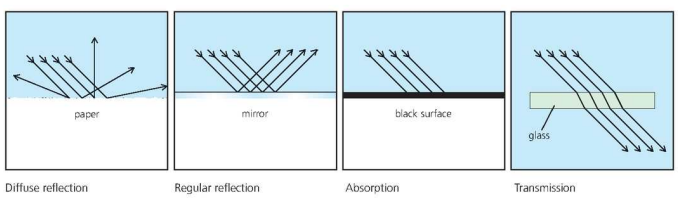
Features of Light
- Is a form of radiation.
- ==They travel in straight line and in form of transverse wave.==
- Transfers energy when materials absorb light.
- They can travel in empty spaces/vacuum.
- Nothing can travel faster then light.
Reflection in plane mirrors
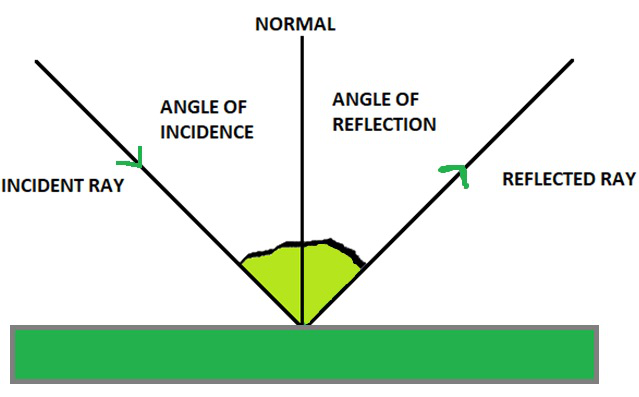
Laws of Reflection
==The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.==
==The incident ray, the reflected and the normal all lie in the same plane.==
Images formed in a plane mirror
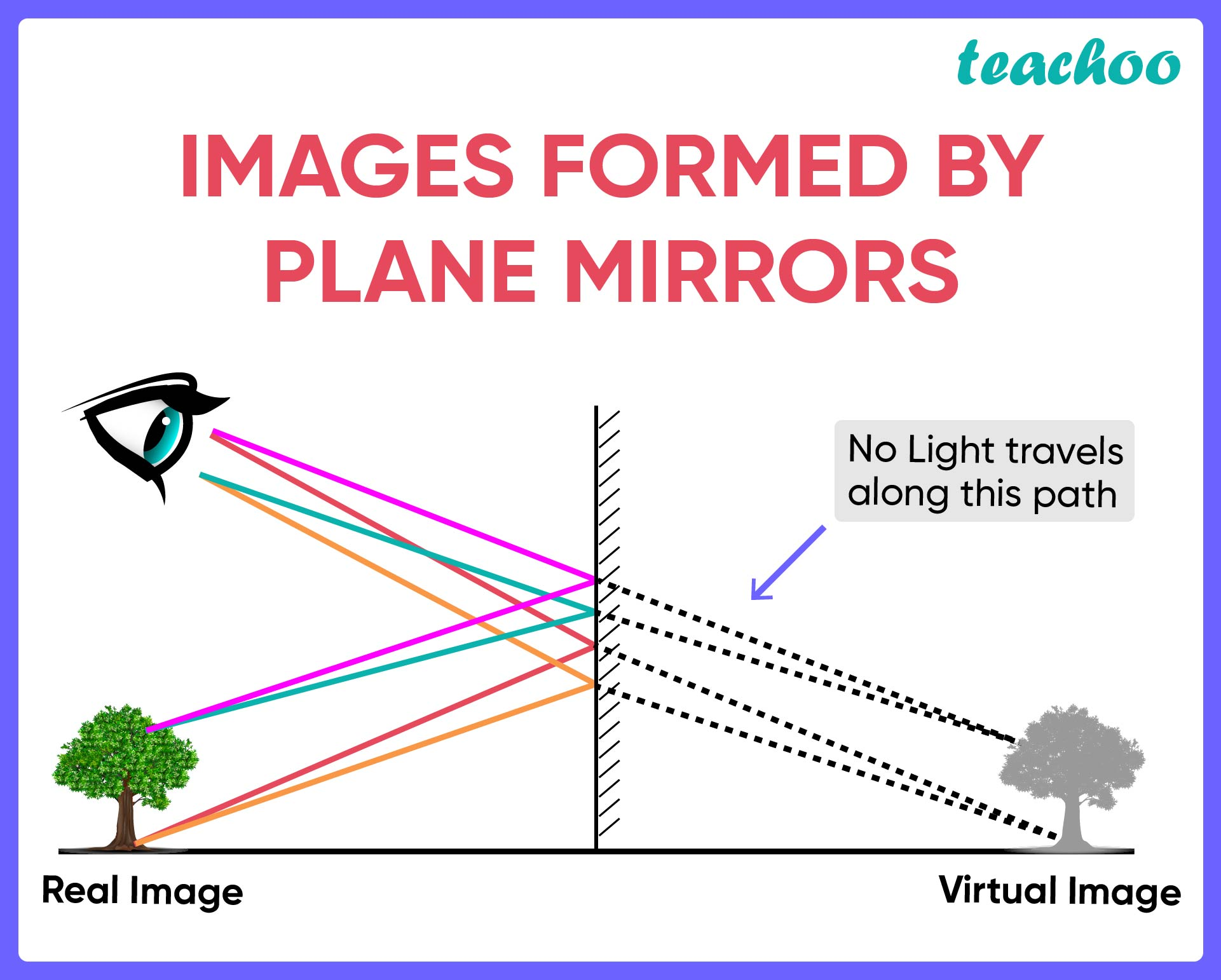
- This image is ^^laterally inverted.^^
Finding the position of an image in a mirror
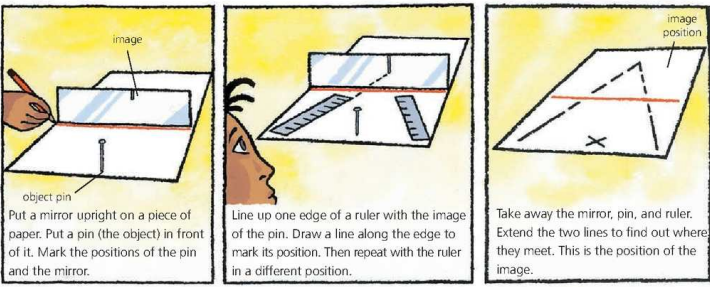
Points to keep in mind for image size and position
- ==When a plane mirror forms an image:==
- image is the same size as the object
- image is as far behind the mirror as the object is in front.
- a line joining equivalent points on the object and image passes through the mirror at right angles.
Refraction of Light
==Refraction is the change in speed of a wave crossing a boundary between two media, resulting in a change in direction.==
As shown below:
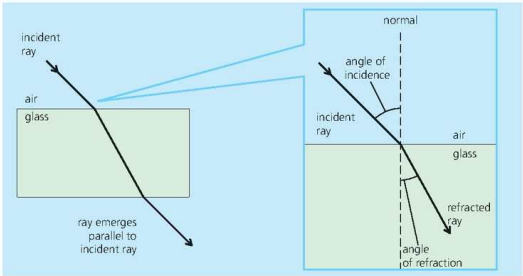
Also explained as:
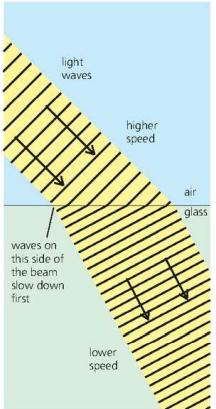
When light enters a ^^more optically dense medium^^, the angle of incidence is greater than the angle of refraction.
- The opposite is true when light enters a less optically dense medium.
Refractive Index
==The refractive index== ==n== ==of a medium is defined as the ratio between the speed of light in two different mediums.==
It is calculated with the use of following equation:

Refraction by Prism
==When light enters a glass prism it splits into seven colours (when light exists).==
- This range of colors is known as spectrum.
==This effect is called== ==dispersion.==
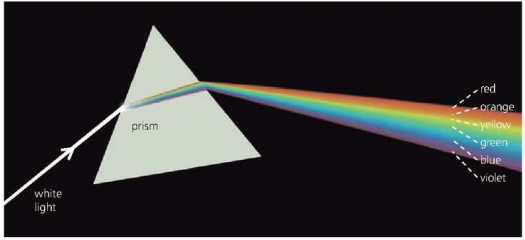
- Easy way to remember these colors is using the mnemonic Roy G Biv.
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
Total Internal Reflection
- At a certain angle of incidence called the critical angle, the ^^light will travel along the boundary between the two media.^^
- Total internal reflection occurs when the ^^angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle and the light reflects back into the medium.^^
- For total internal reflection to occur, the ^^light must also be travelling from a more optically dense medium into a less optically dense medium (most common example is glass to air).^^
- The critical angle can be related to the refractive index by the equation:
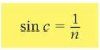 Common Uses of Reflecting Prisms
Common Uses of Reflecting Prisms
- Periscope
- Rear Reflectors
- Binoculars
- Optical FIbres
Lenses
Two main kinds:
- {{Convex/Converging Lens{{
- thickest in the middle and thin round the middle.
- when rays are parallel they pass through the lens and are bent inwards.
- {{Concave/Diverging Lens{{
- thin in the middle and thickest round the edge.
- when rays parallel to the principal axis pass through the lens, they are bent outwards/they are spread out.
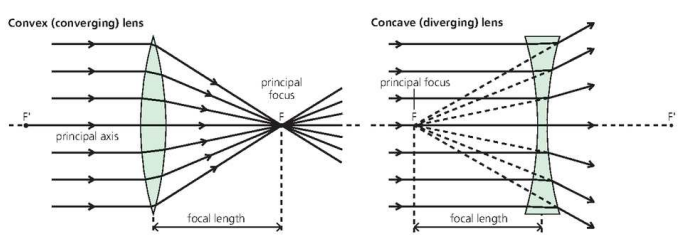 Terms
Terms
- ==The point where rays meet the lens is called== ==principal focus.==
- Its distance from the center of the lens is called focal length.
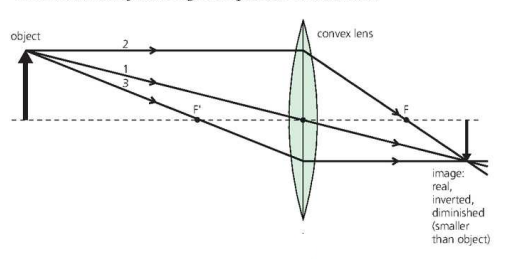
Images formed by convex lenses
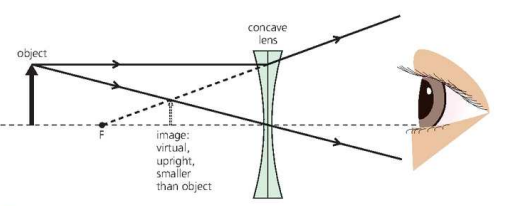
 Images formed by concave lenses
Images formed by concave lenses
 Common Uses of Lens in daily life
Common Uses of Lens in daily life
- Camera
- Human eye
- Projector
Electromagnetic Waves
Light waves is one of the example.
Common features:
- they can travel through vacuum, at a speed of 300 000 kilometers per second.
- they are transverse waves.
- they transfer energy. A material gains energy when they it absorbs it.
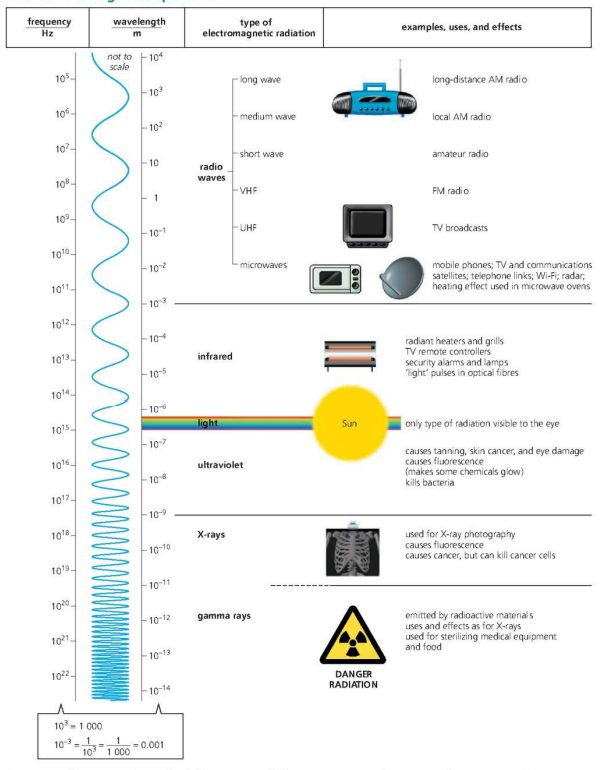
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Radio Waves
- ==Can be produced artificially by making a current oscillate in a transmitting aerial.==
- Commonly used to transmit TV pictures.
Infrared Radiation and Light
- All objects radiate infra red due to the motion of their atoms or molecules.
- As an object heats up, it radiates more and more infrared, and shorter wavelengths.
- ==Short wavelength infrared is often== ==called== =='infrared light', even though it is invisible.==
Ultraviolet Radiation
- Sun’s ultraviolet radiation is harmful to living cells - can cause skin cancer.
- Ultraviolet rays are harmful to living cells - commonly used to sterilize medical equipment.
X-rays
- Are given off when fast moving electrons lose energy quickly.
- In engineering or in medical - they are used to detect flaws inside the material or a damaged bone.
- They can be dangerous because they damage living cells deep in the body and can cause cancer or mutations.
Gamma Rays
- Come from radioactive materials.
- Are produced when an unstable nuclei of unstable atoms break up or lose energy.