BIO220 (Genomes to Ecosystems) - Lecture 1, Week 2
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
What are the three agricultural species that comprise 60% of energy intake in Homo sapiens?
Rice, maize, and wheat
Where can you find the ancestral relatives of domesticated species?
The region where their ancestral species were first domesticated
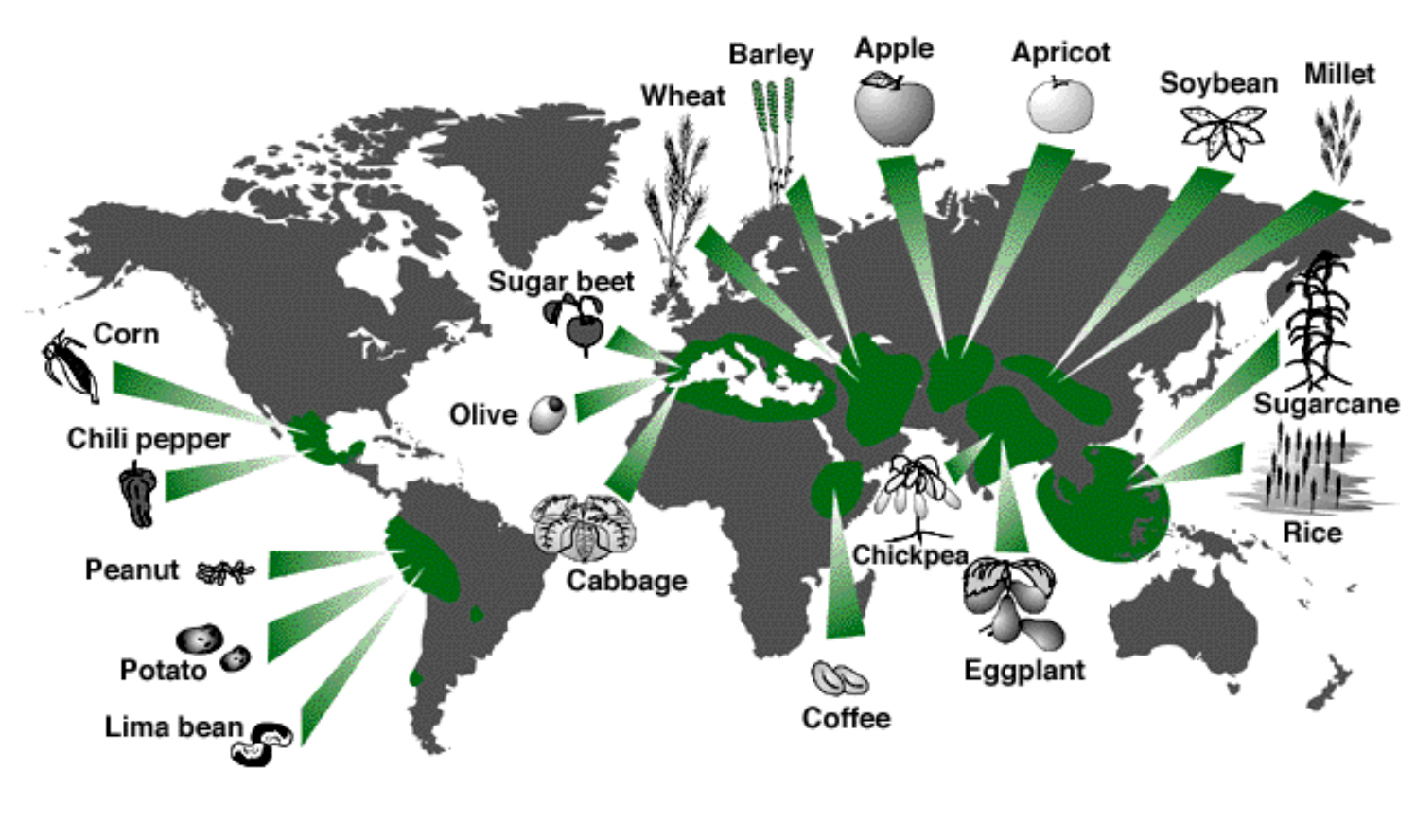
Ancestral relatives of domesticated species have greater [blank] [blank]
Genetic diversity
What are the two selective forces that occur during domestication?
Bottleneck, and artificial selection
Definition of bottleneck
When a limited number of individuals within a population contribute their genetic material to the subsequent generation
Definition of artificial selection
The process where humans intentionally select certain individuals (i.e., individual within desired phenotypes) within a population to contribute to their genetic material to the subsequent generation
Artificial selection and bottlenecks result in [blank] [blank] within a population
Genetic variation
Where is genetic variation absent in the genome of domesticated species?
The are of the genome that produces favourable phenotypes
What are the three ways to measure genetic variation?
1. Proportion of individual with heterozygosity per gene locus
2. Proportion of polymorphic gene loci
3. Average number of nucleoside differences per region of genome
Definition of effective population size (Ne)
Idealized population that loses genetic diversity with respect to the observed population (i.e., the number of reproductively active individuals within a population)
Definition of idealized
All individuals within a population have equal opportunity to contribute their genetic material to the subsequent generation
Definition of census size (N)
Total number of matured individuals within a population
The effective size of a population is [great than/less than] census size
Less than
What are the four factors the contribute to effective population size being lesser than census size?
1. Variation in number of progeny one reproductively active individuals within the population produces
2. Unequal sex ratio (i.e., number of reproductively active males outnumber the number of reproductively active females within the population)
3. Progeny mating with parents
4. General fluctuations in the number of individuals within a population (e.g., population bottleneck)
Reduced effective population size happens in the [blank] and [blank] of selection
Presence and absence
How do the presence of selective forces (e.g., natural selection or artificial selection) influence effective population size?
Reduces the effective population size
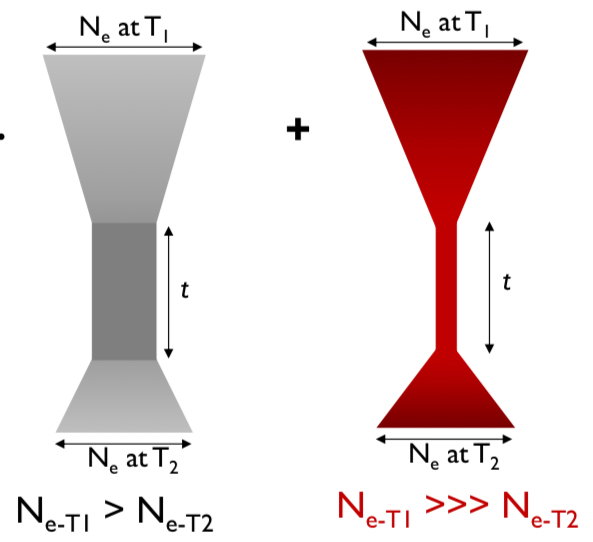
Describe what information is communicated in the figure below.
Left figure: Population bottleneck produces a reduction in the effective population size across all loci within the genome
Right: Artificial selection produce a greater reduction in the effective population size in locus-specific regions within the genome
What percentage of the teosinte genome experienced artificial selection?
2-4%