the circulatory system 🫀
4.7(12)Studied by 74 people
Card Sorting
1/92
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:57 PM on 6/15/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
93 Terms
1
New cards
what does the circulatory system consist of? (3)
heart, blood vessels and blood
2
New cards
what is the total length of the blood vessels in the body?
100, 000 kilometers
3
New cards
what is the function of the circulatory system?
to transport various substances around the body
4
New cards
what 5 substances does the circulatory system transport and where are they transported to?
1) oxygen: lungs to all cells
2) nutrients: SI to all cells
3) carbon dioxide: all cells to lungs
4) urea: liver to kidney to urine
5) hormones: endocrine glands to all cells
2) nutrients: SI to all cells
3) carbon dioxide: all cells to lungs
4) urea: liver to kidney to urine
5) hormones: endocrine glands to all cells
5
New cards
what are the three main types of blood vessels and what do they do?
1) arteries- carry blood away from the heart
2) veins- carry blood towards the heart
3) capillaries- carry blood from arteries to veins
2) veins- carry blood towards the heart
3) capillaries- carry blood from arteries to veins
6
New cards
what is the smallest blood vessel?
capillaries
7
New cards
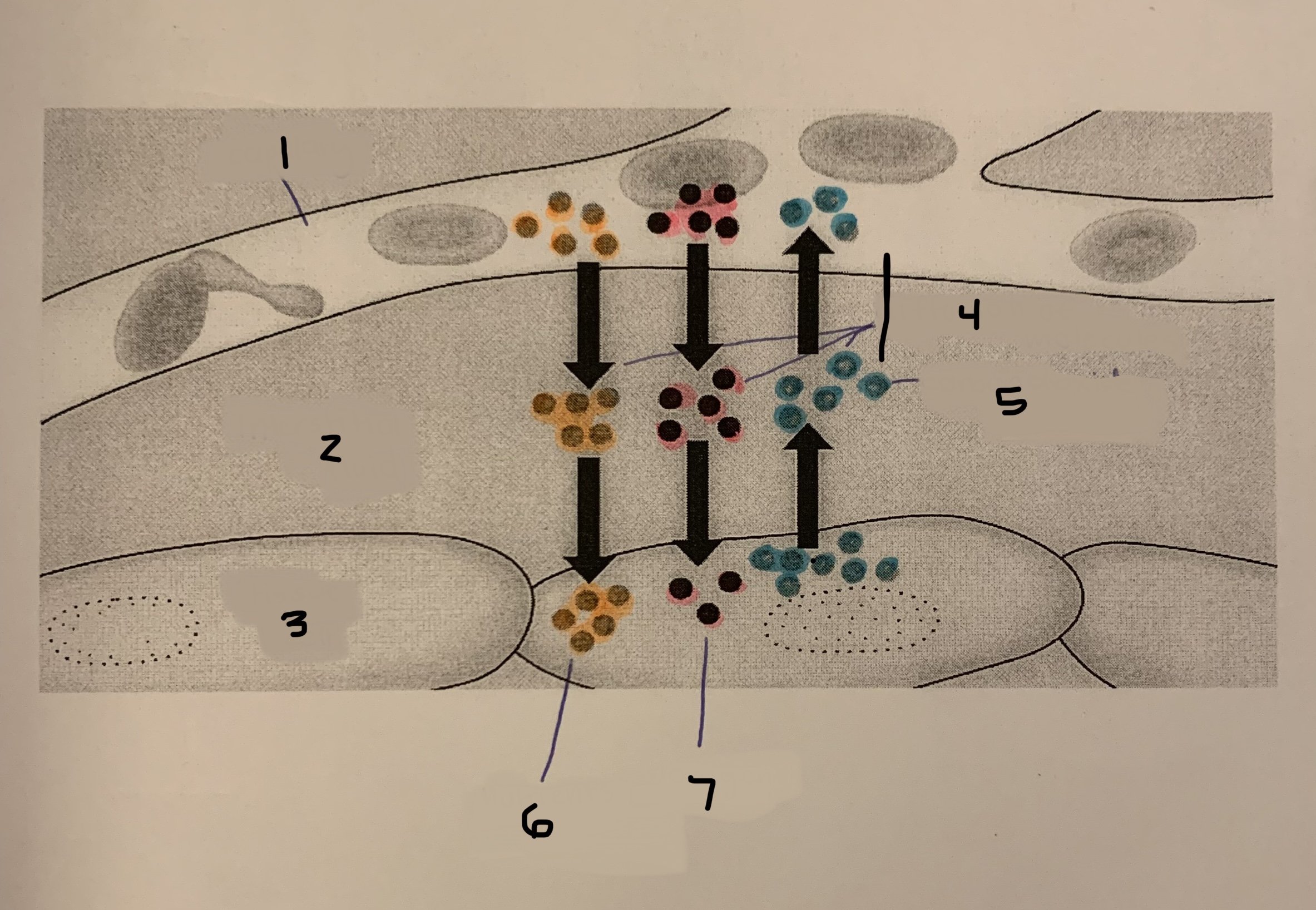
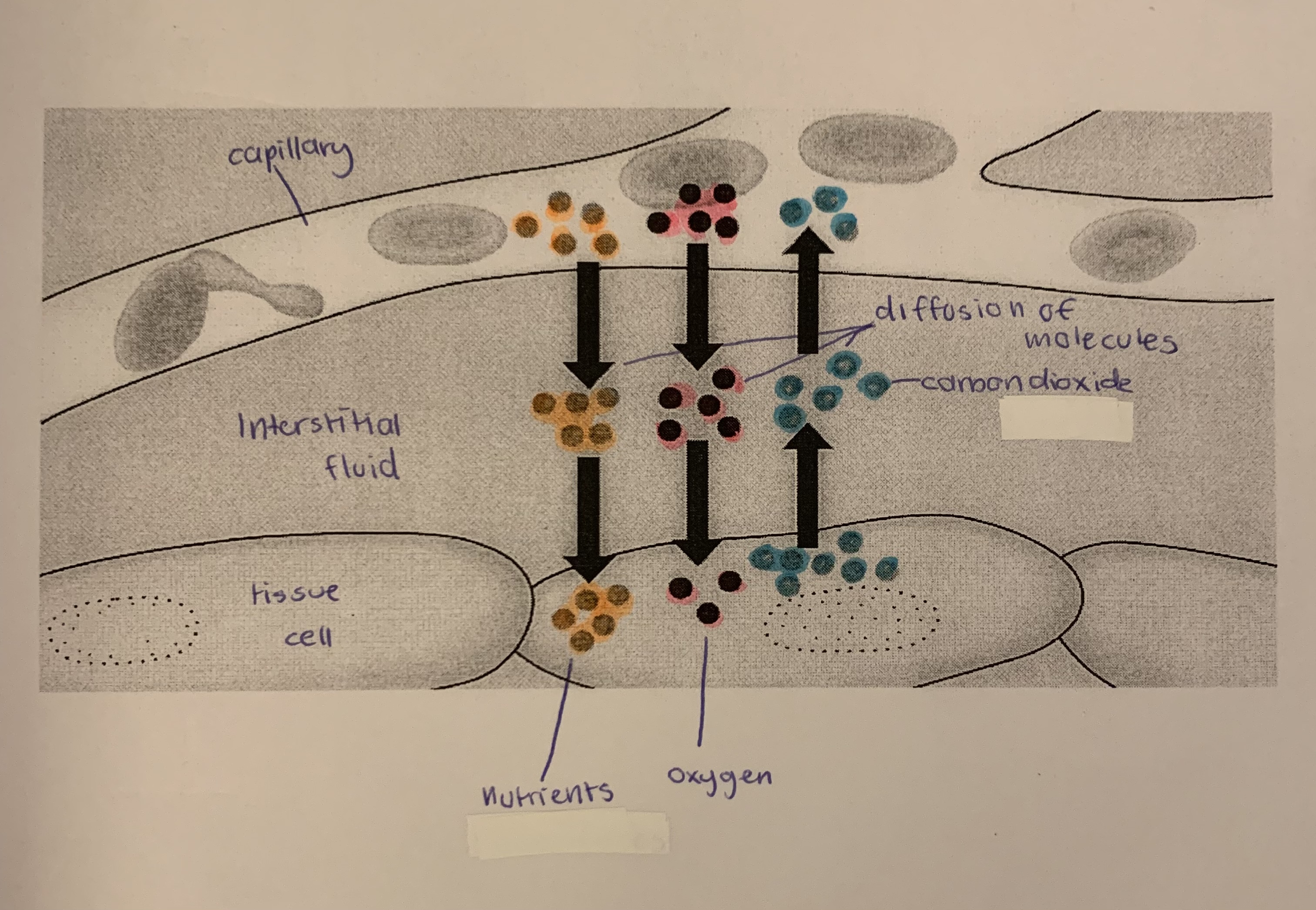
what is interstitial fluid? (3)
\-fluid that all the cells of the body “bathe” in
\-helps materials pass between body cells and blood
\-consists of water, salts, proteins and nutrients
\-helps materials pass between body cells and blood
\-consists of water, salts, proteins and nutrients
8
New cards
what is a closed circulatory system? do humans have an open or closed circulatory system?
\-all blood is found in blood vessels/the heart
\-humans have closed systems
\-humans have closed systems
9
New cards
what do heart valves do?
prevent blood from flowing backwards
10
New cards
what does the heart do?
pumps blood throughout the circulatory system
11
New cards
where is the heart found?
the chest cavity
12
New cards
what is another name for the chest cavity?
thoracic cavity
13
New cards
what is the heart also known as?
a double pump
14
New cards
what is the pericardium?
a sac surrounding the heart that protects it
15
New cards
define:
a) peri
b) cardium
a) peri
b) cardium
a) around
b) relating to the heart
b) relating to the heart
16
New cards
what are the four chambers of the heart?
right and left atria, right and left ventricles
17
New cards
which of the two types of heart chambers has thicker walls?
the ventricles
18
New cards
what is the wall that separates the right and left sides of the heart?
the septum
19
New cards
what are the 2 main periods of the heart’s pumping?
systole and diastole
20
New cards
what happens during diastole?
the heart muscle relaxes
21
New cards
what happens during systole?
the heart muscles contract
22
New cards
which heart chambers contract first?
the atria
23
New cards
what causes the lub-dup noise?
heart valves closing
24
New cards
which valves make the ___ sound?
a) lub
b) dup
a) lub
b) dup
a) bicuspid and tricuspid
b) semilunar valves
b) semilunar valves
25
New cards
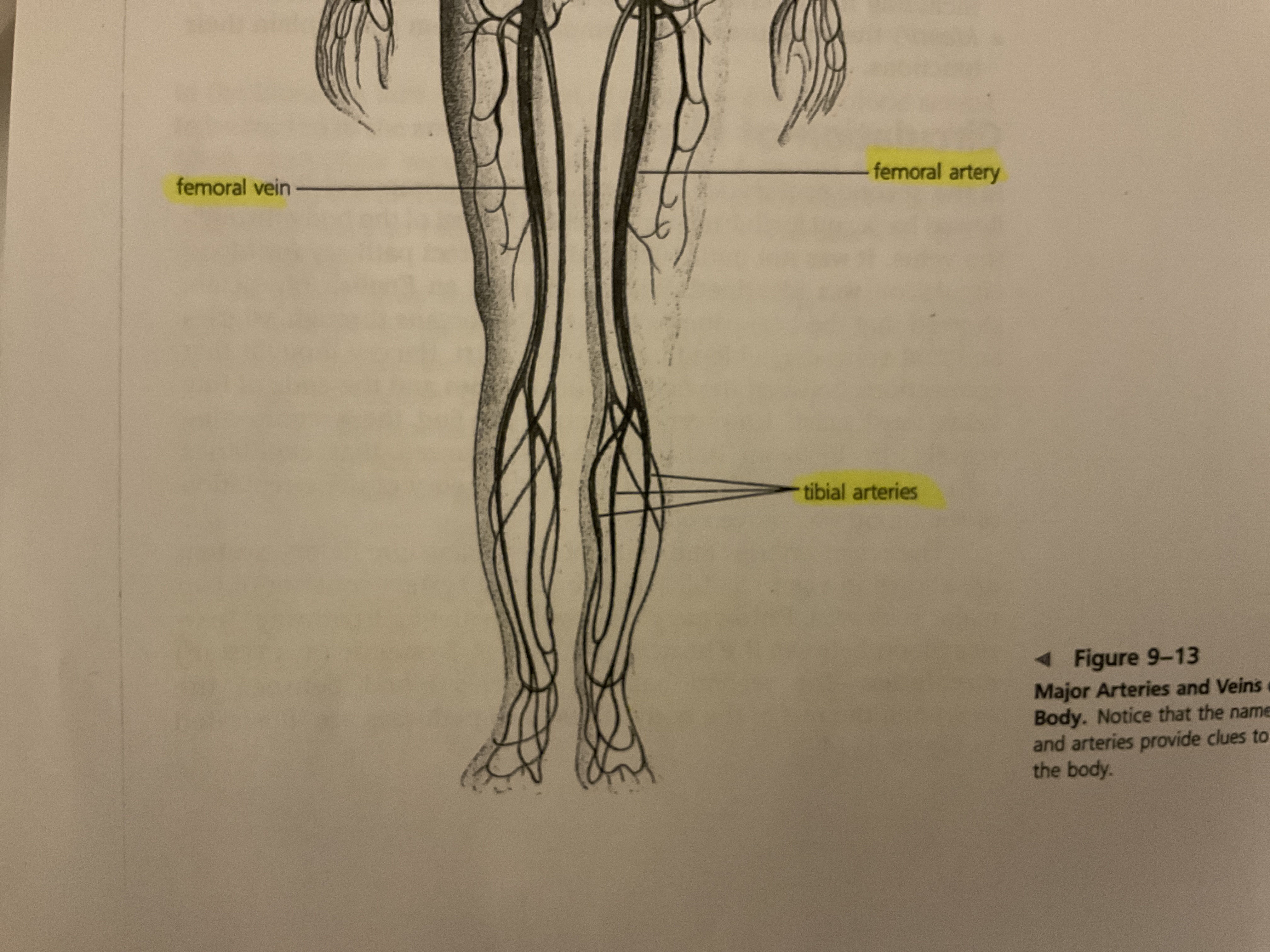
label
26
New cards
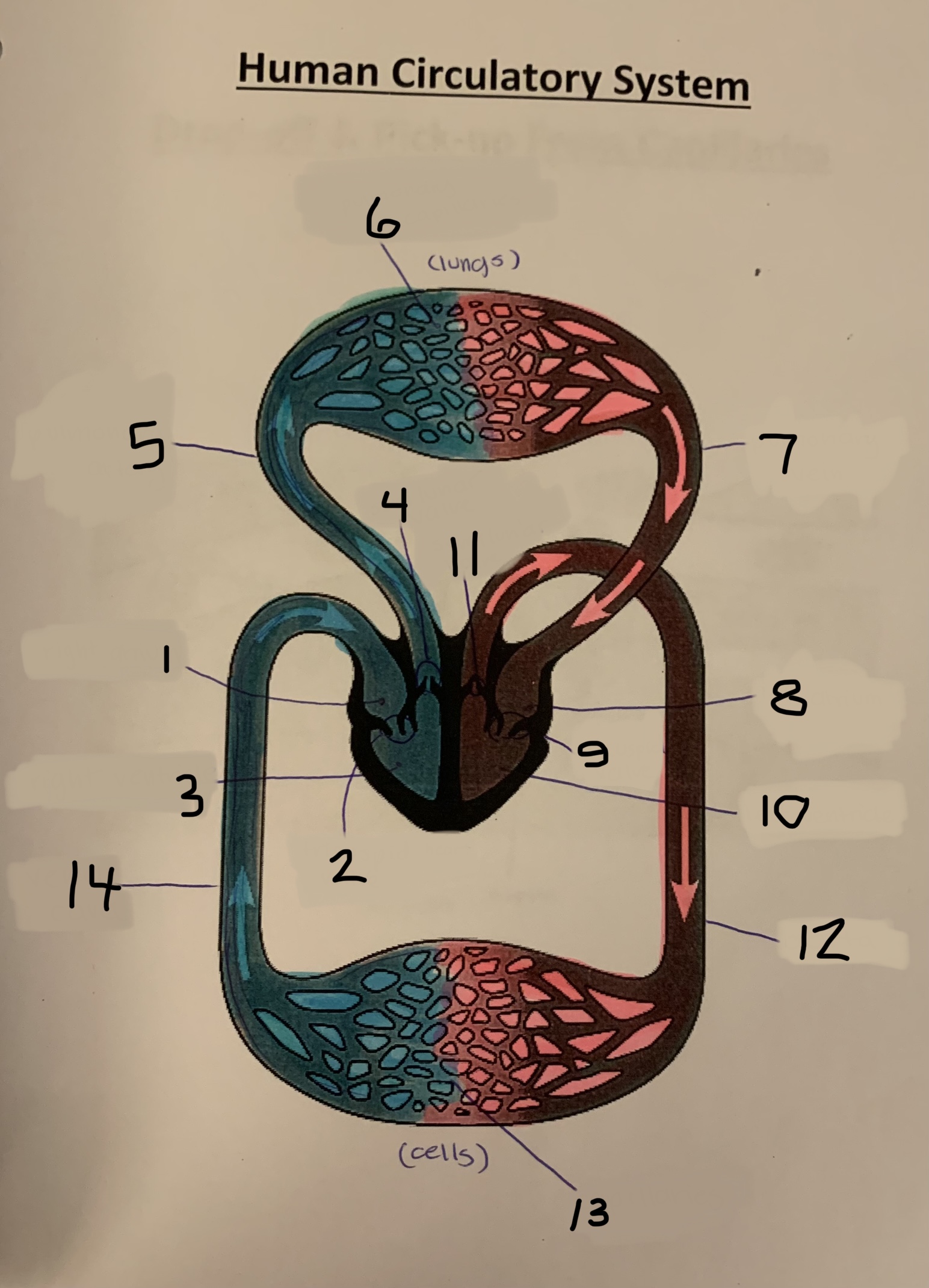
label
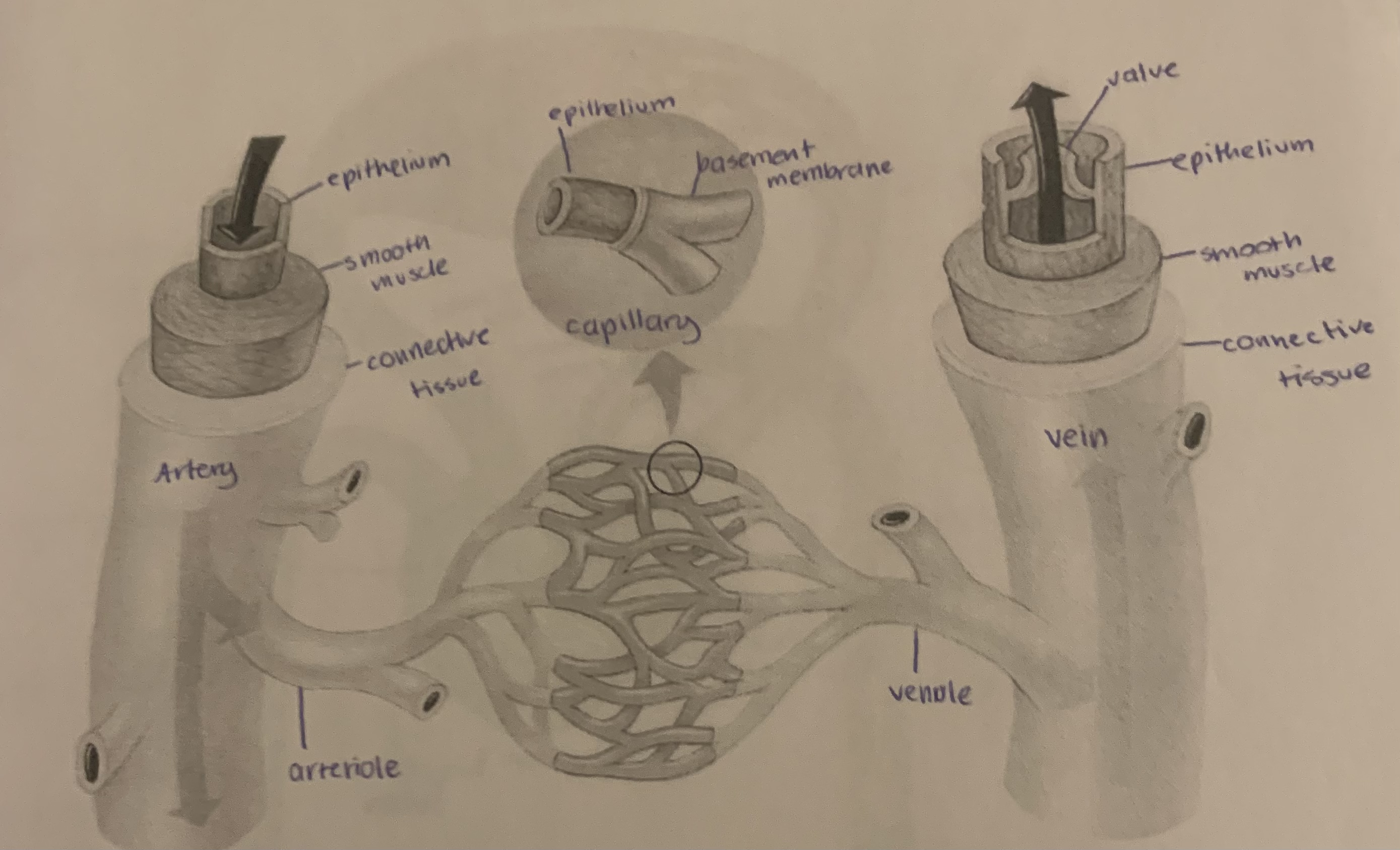
27
New cards
label
28
New cards
what is a special ability of the heart/cardiac muscle?
it can keep beating after being removed if it is in a certain substance
29
New cards
what are the two special muscle regions in the heart?
the AV-atrioventricular node and the SA-sinoatrial node
30
New cards
what is the sinoatrial node also known as?
the pacemaker
31
New cards
where is each node found and what do they do?
SA-upper right wall of the r atrium, sets the rate at which the heart contracts
AV- base of the r atrium, has long projections passing down into the ventricle walls
AV- base of the r atrium, has long projections passing down into the ventricle walls
32
New cards
how do the nodes help the heart beat?
1) the SA node sends out an electrical signal, causing the atria to contract
2) when the signal reaches the AV, it causes the ventricles to contract
2) when the signal reaches the AV, it causes the ventricles to contract
33
New cards
what does blood pressure refer to?
the fact that blood pushes against blood vessels
34
New cards
what happens to blood pressure as blood moves away from the
🫀?
🫀?
it decreases
35
New cards
what causes a pulse?
arteries bulging during systole
36
New cards
how does blood move through the veins?
skeletal muscles beside the vein contract
37
New cards
why are there valves in veins?
to prevent blood from flowing backwards
38
New cards
what is the purpose of coronary circulation?
to supply the heart muscle with blood
39
New cards
which ventricle has the thickest walls?
left
40
New cards
which veins drain directly to the heart’s chambers?
coronary veins
41
New cards
what is atherosclerosis and what does it increase the risk of?
the arteries narrow due to buildup of plaque which increases the risk of heart attacks and strokes
42
New cards
what is coronary artery disease also known as?
atherosclerosis
43
New cards
what causes heart attacks?
buildup of plaque in a coronary artery prevents blood flow to a section of the heart and it dies
44
New cards
what are heart attacks also known as?
myocardial infarction
45
New cards
define:
a) myo
b) infarction
a) myo
b) infarction
a) muscle
b) death
b) death
46
New cards
what are the 3 methods of treatment for coronary artery disease?
coronary bypass surgery, balloon angioplasty and stenting
47
New cards
what happens during coronary bypass surgery?
a vein is removed from somewhere else in the body and grafted behind and in front of the blockage so blood can flow
48
New cards
what happens during a balloon angioplasty?
a small balloon is threaded through the aorta to the blockage and inflates for 60 seconds, flattening the plaque
49
New cards
what happens during a stenting?
a stent is guided to the blockage and remains there, keeping the blood vessel open
50
New cards
what is a stent?
a tiny mesh cylinder
51
New cards
which two treatments for coronary artery disease are often done together?
balloon angioplasty and stenting
52
New cards
what happens during an angiography? (3)
\-a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel in the arm or leg and moved to the desired artery
\-dye is injected through the catheter which allows X-rays to be taken
\-blocked regions are visible
\-dye is injected through the catheter which allows X-rays to be taken
\-blocked regions are visible
53
New cards
what is an angiogram?
the image/ results from an angiography
54
New cards
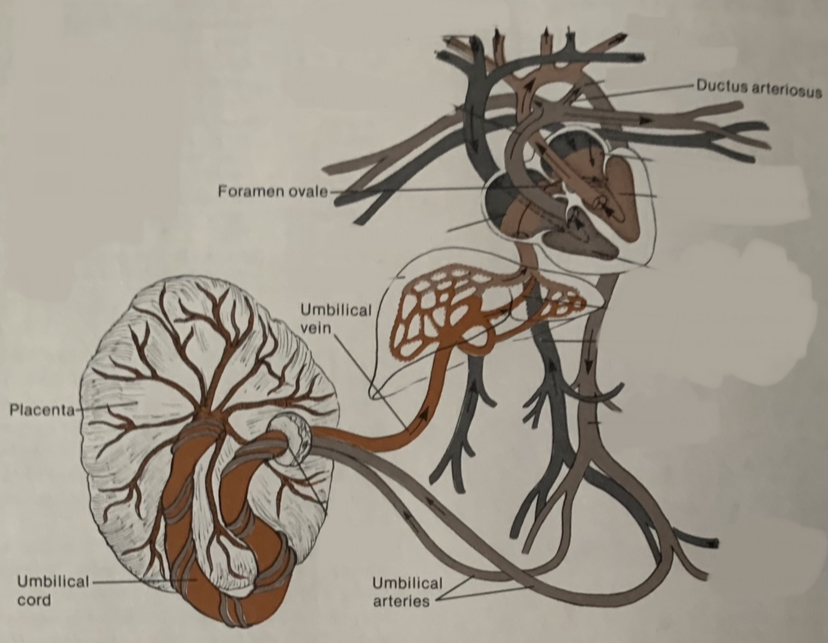
what is the placenta and when does it form?
an organ that forms only in pregnant women
55
New cards
what happens to the placenta after birth?
it detaches from the uterus and exits the body
56
New cards
what is afterbirth?
when the placenta exits a woman’s body after a baby is born
57
New cards
what is the point of fetal adaptations?
to divert blood flow away from the lungs
58
New cards
what are the 2 fetal adaptations and what do they do
1. foramen ovale-a hole in the septum between the right and left atria
2. ductus arteriosus-artery that connects the pulmonary artery to the aorta
59
New cards
what happens to blood that passes through the foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus?
it bypasses the fetal lungs
60
New cards
what are varicose veins?
veins that have lost their elasticity because valves do not work properly
61
New cards
how do red blood cells pass through capillaries?
in single file
62
New cards
what are the atrioventricular valves? (2)
tricuspid and bicuspid valves
63
New cards
what percent of the ventricle is full after diastole?
70%
64
New cards
what causes a heart murmur?
damaged heart valves
65
New cards
what is an electrocardiogram?
a recording of the hearts electrical currents that is used to determine if the heart is healthy
66
New cards
which nerves regulate the pacemaker? what does each one do? (2)
\-vagus nerve: slows the pacemaker
\-cardioaccelerator nerve: speeds up the pacemaker
\-cardioaccelerator nerve: speeds up the pacemaker
67
New cards
what happens if the natural pacemaker fails?
an artificial pacemaker is surgically placed
68
New cards
what is the average…
a) systolic pressure
b) diastolic pressure
a) systolic pressure
b) diastolic pressure
a) 120mmHg
b) 80mmHg
b) 80mmHg
69
New cards
how is blood pressure measured?
using an instrument called a sphygmomanometer
70
New cards
how is blood pressure usually stated?
systolic pressure/ diastolic pressure
71
New cards
what is hypertension?
high blood pressure
72
New cards
what increases the risk of atherosclerosis?
high cholesterol intake
73
New cards
what would happen if all capillaries opened at the same time?
there wouldn’t be enough blood to fill them
74
New cards
what is located at the end of every arteriole?
a ring of muscle
75
New cards
what are the two major pathways of circulation?
pulmonary and systemic circulation
76
New cards
what happens to blood flow when we eat?
it is diverted to the digestive tract
77
New cards
what are the three branches of systemic circulation? what does each branch do?
1) coronary- supplies the heart muscle with blood
2) hepatic portal- carries blood from the digestive tract to the liver
3) renal circulation-carries blood to and from the kidneys where waste is removed
2) hepatic portal- carries blood from the digestive tract to the liver
3) renal circulation-carries blood to and from the kidneys where waste is removed
78
New cards
what is interstitial fluid also known as?
intercellular fluid
79
New cards
how is extra fluid and protein in the intercellular space returned to the blood?
the lymphatic system
80
New cards
what is the portal vein?
a vein that brings nutrient rich blood from the digestive tract to the liver
81
New cards
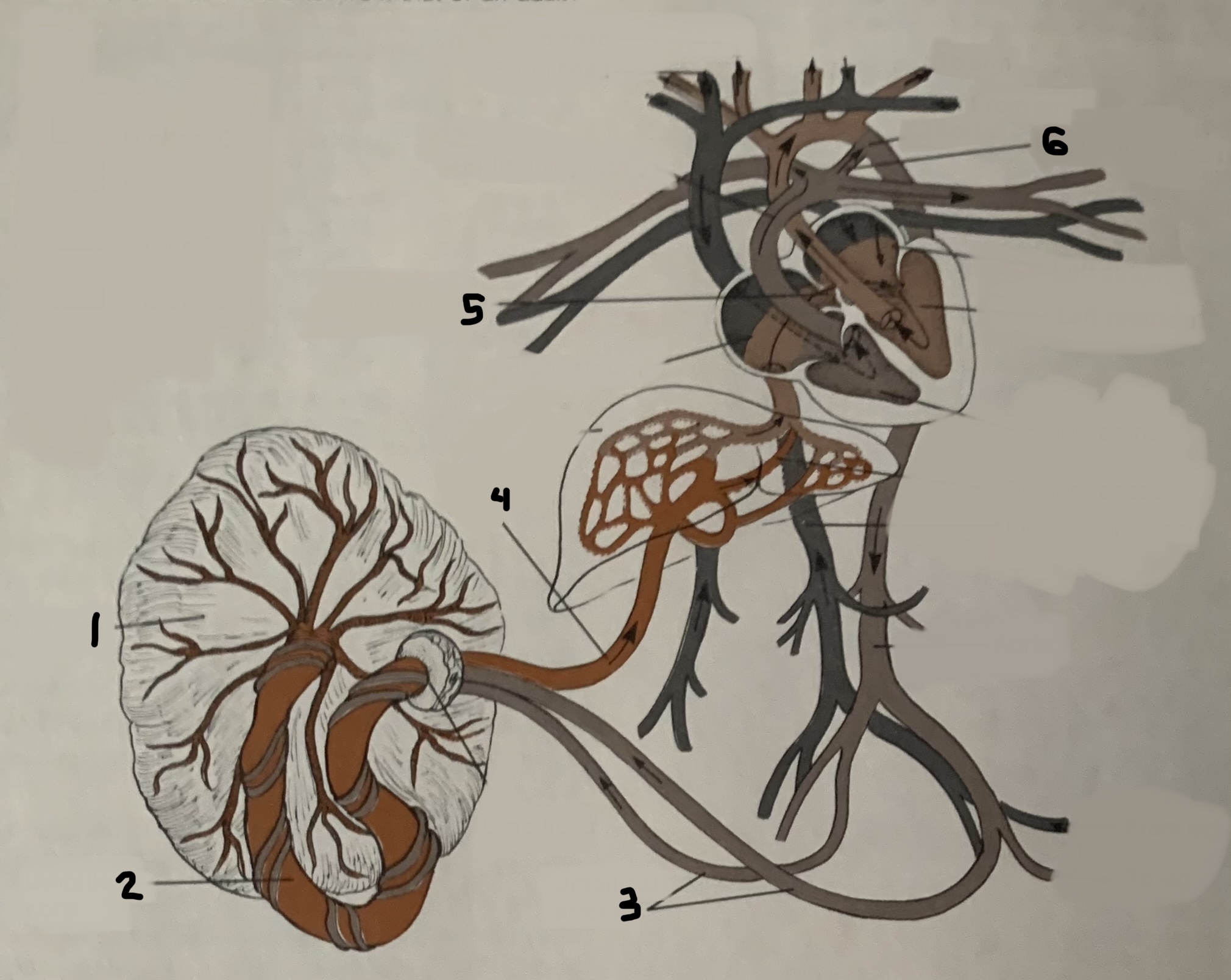
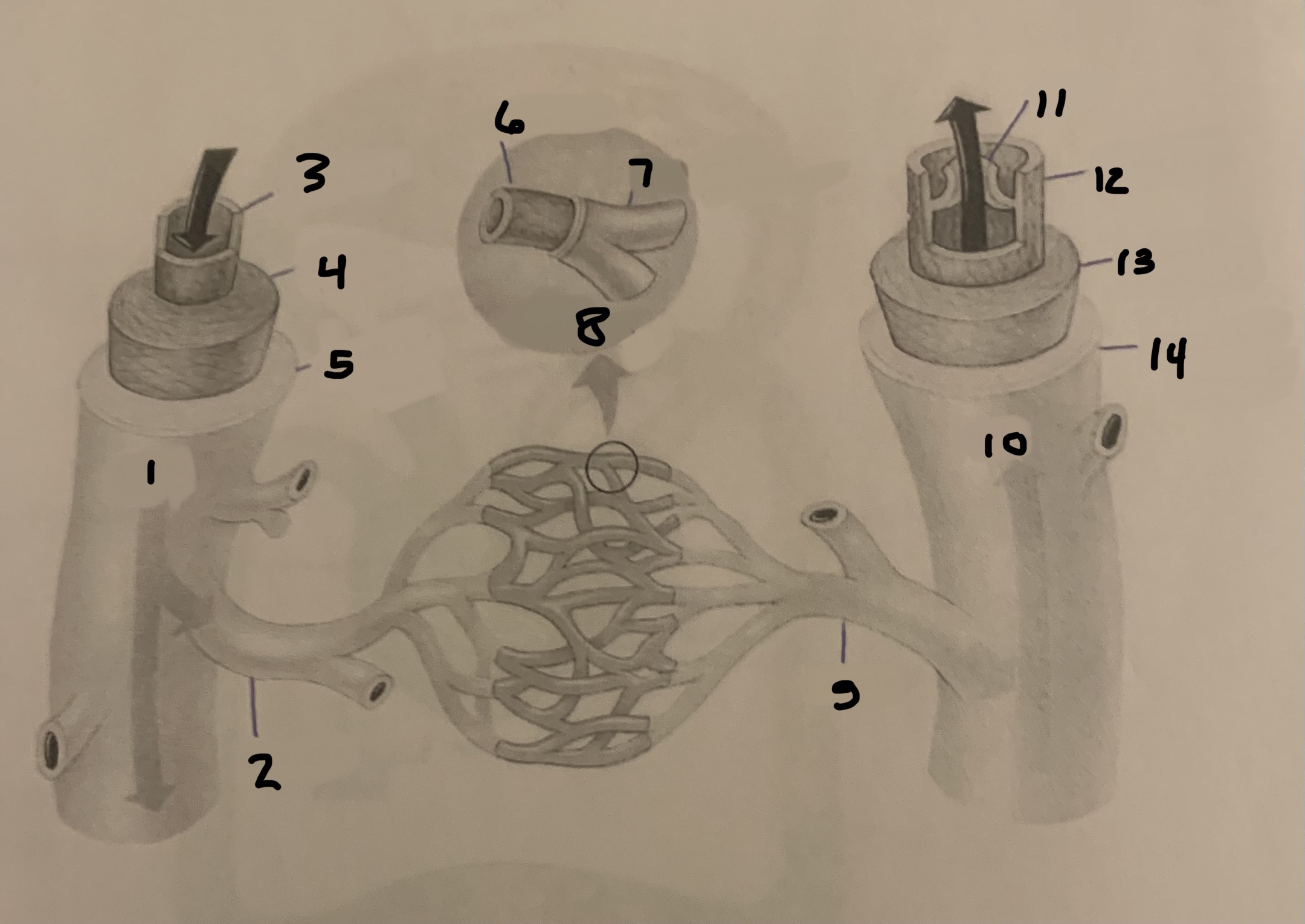
label
82
New cards
what happens to blood in the portal vein once it reaches the liver?
nutrients are collected by hepatic sinuses and blood continues to the vena cava
83
New cards
what is a function of the liver?
to absorb and store excess glucose as glycogen
84
New cards
what does the lymphatic system do?
returns excess fluid and protein to the blood
85
New cards
what would happen without the lymphatic system? (2)
\-the circulatory system would drain because of the loss of fluid
\-body tissue would become flooded and swell up
\-body tissue would become flooded and swell up
86
New cards
what is fluid called once it enters the lymphatic system?
lymph
87
New cards
what are lymph capillaries?
microscopic tubes that join together to form larger vessels
88
New cards
what do lymphatic vessels have in common with veins?
they have valves
89
New cards
what is the thoracic duct?
the largest lymphatic vessel in the body
90
New cards
where do the thoracic and right lymph ducts empty into?
a large vein in the neck
91
New cards
what do lymph nodes do? (3)
\-filter foreign matter from lymph
\-produce some white blood cells
\-become swollen around infected areas
\-produce some white blood cells
\-become swollen around infected areas
92
New cards
what do lymphoid tissues do in the spleen?
filter bacteria and worn out red blood cells from the blood
93
New cards
label