Water Abstractions (Week2) (copy)
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
31 Terms
Interception
rainfall trapped on leaves and other vegetative surfaces
trapped water doesn’t reach ground surface, subsequently lost in atmosphere
Throughfall or Stemflow
rainfall that drops through vegetation or rainfall that got intercepted but eventually will drop to ground
Coniferous Trees
group of seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. They are mainly evergreen trees with a regular branching pattern, reproducing with male and female cones, usually on the same tree. They are wind-pollinated and the seeds are usually dispersed by the wind.
Intercepts water more
Deciduous Trees
plants that seasonally shed their leaves, typically in autumn (fall) in temperate climates, or during dry seasons in tropical areas, as a survival mechanism to conserve water and energy.
Intercepts water less
Complex Stratified Forests
refers to ecosystems that exhibit a high degree of vertical layering of vegetation(stratification)
Intercepts water more
Single Tree Plantation
refers to the concept or initiative of individuals planting trees, often promoted by organizations
Single tree intercepts water less
Interception Loss
Cycle:
Precipitation is caught by vegetation
Water evaporates from leaf surface(interception storage) to atmosphere
Water lost from surface system
How human activity affect interception
Deforestation
Farming
Deforestation
Less interception, more runoff. Therefore flashier response in rivers, increased river discharge and risk of flooding. Less evapotranspiration
Farming
leads to increased exposure to sunlight and less surface storage. Less evapotranspiration
Surface or Depression Storage
volume of precipitation temporarily held in small, low-lying areas(depressions) on land surface
will either infiltrate into the soil, evaporate, or become a runoff
Evaporation
liquid changes into a gaseous state
Factors Affecting Evaporation
Vapor Pressure
Temperature
Wind
Atmospheric Pressure
Soluble Salts
Heat Storage in Water Bodies
Vapor Pressure Formula
Dalton’s Law
EL = C(es - ea)
EL - rate of evaporation
C - coefficient of evaporation
es - saturation vapor pressure at water temperature
ea - actual vapor pressure in air
Temperature
rate of evaporation increases as water temperature increases
air temperature don’t have high correlation between evaporation rate with increasing temperature
Wind
aids in removing evaporated water vapor from the zone of evaporation, creating greater scope for evaporation
if wind velocity is large enough to remove all evaporated water, any increase to wind velocity doesn’t influence evaporation
rate of evaporation increases with wind speed up to a critical speed beyond which any further increase of wind speed has no influence in evaporation rate
Atmospheric Pressure
decrease in barometric pressure (such as in high altitude) increases evaporation
Soluble Salts
vapor pressure of solution is less than that pure water which causes reduction of rate in evaporation
evaporation from seawater is about 2-3% less than freshwater
Heat Storage in Water Bodies
deep water bodies have more storage than the shallow ones
deep bodies of water may store more radiation energy in summer and release it in winter causing less evaporation in summer but more in winter
Estimation of Evaporation
Evaporimeters
Analytical Methods
Empirical Equation
Evaporimeter
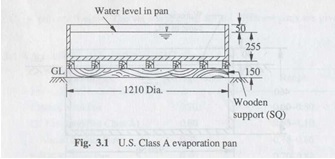
Class A Evaporation Pan
used by US Weather Bureau
aka Class A Land Pan
made of unpainted galvanized iron sheet
measurements are made by measuring the depth of water with a hook gauge in a stilling well
Evaporimeter
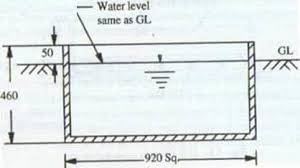
Colorado Sunken Pan
square pan made of unpainted GL sheet, buried on ground
its aerodynamic and radiation characteristics are similar to a lake
difficult to detect leaks, expensive to install, extra care is needed to keep surrounding areas free from tall grass, dust, etc
Evaporimeter
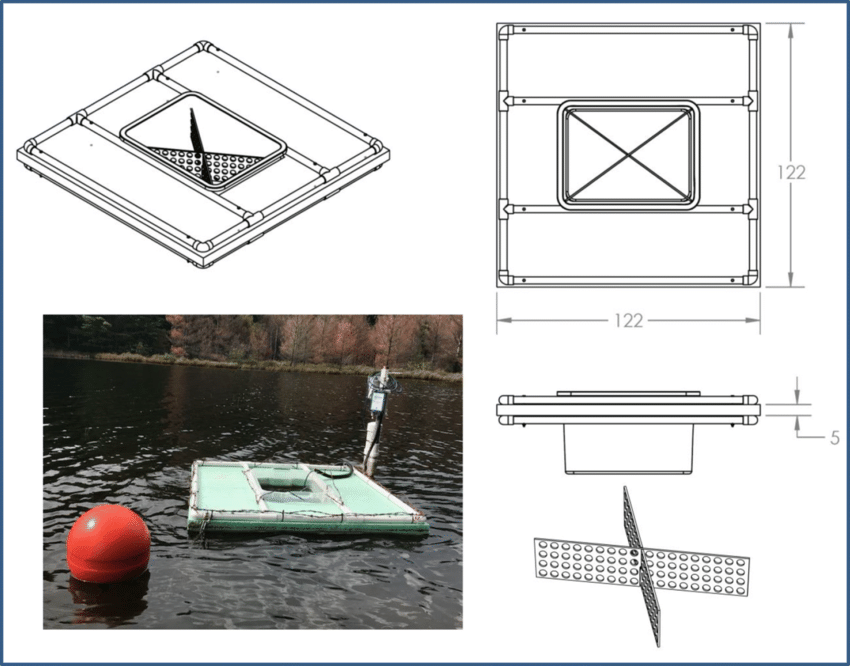
USGS Floating Pan
square pan of 900mm sides, 450mm deep
supported by drum floats in the middle of raft with size 4.25m x 4.87m
set afloat in a lake with a view to simulate the characteristics of large body of water
water level in the pan is maintained at same level as in the lake
diagonal baffles are provided in the pan to reduce surging in the pan due to wave action
high cost of installation and maintenance, difficulty in measurements
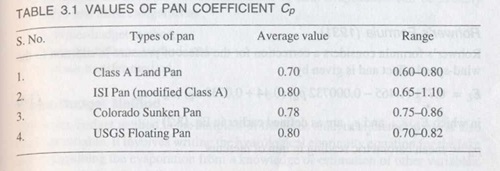
Pan Coefficient
Lake evaporation = Cp x pan evaporation
Cp = pan coefficient
Water Budget Method
simplest but least reliable
involves writing the hydrological continuity equation for the lake and determining the evaporation from a knowledge or estimation of other variables
P + Vis + Vig + Vos + Vog + EL + S + TL
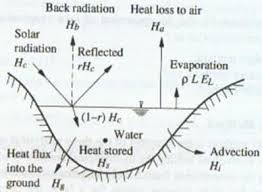
Energy-Budget Method
law of conservation of energy
energy for evaporation is determined by considering the incoming, outcoming, and stored energy in a water body over a known time interval
energy in terms of calories per square mm per day
Mass-transfer Method
based on theories of turbulent mass transfer in boundary layer to calculate mass water vapor transfer from surface to surrounding atmosphere
Transpiration
plants release water vapor through small pores(stomata) on their leaves and stems
important part of hydrologic cycle, typical mechanism on how precipitated water in land brings back to atmosphere
Evapotranspiration (ET)
combined evaporation and transpiration
maximum if water supply to plant and soil is unlimited
max amount of water that can be evaporated and transpired if there was unlimited supply of water is potential evotranspiration
Field Capacity
moisture content above which water will be drained by gravity
Wilting Point
moisture content below which plants cannot extract further water