Genetics DQs, updated to dq 13
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
115 Terms
How many kinds of gametes can be produced by an individual of genotype Aa Bb CC dd Ee FF GG Hh?
16
What proportion of the offspring of the mating Aa Bb Cc by Aa Bb Cc are expected to be homozygous for all three genes?
1/8
1
1/2
1/4
1/16
1/8
What proportion of the offspring of the mating Aa Bb Cc DD Ee by aa Bb Cc dd Ee are expected to be aa bb cc dd ee?
0
1/258
1/6
1/2
1
0
What was the importance of Mendel performing reciprocal crosses?
To be able to breed plants all year round
To obtain enough plants to perform the experiments that Mendel wanted, which would not have been sufficient without performing reciprocal crosses
To demonstrate that the inheritance of a trait was not dependent on which parent carried the trait
To disprove a hypothesis at the time the experiments were performed that stated the ovum carried all the information for progeny
To demonstrate that the inheritance of a trait was not dependent on which parent carried the trait
A genome can be best described as
an A-T or G-C nucleotide pair.
DNA associated with proteins
a segment of DNA that codes for a protein.
entire collection of chromosomes for an organism
entire collection of chromosomes for an organism
Calculate the probability of homozygous recessive offspring from the cross Aa Bb cc dd Ee Ff × Aa Bb Cc dd Ee Ff.
The alleles of all six genes assort independently.
1/256
1/6
1/512
1/64
1/128
1/512
If an individual has 10 gene pairs, how many different gametes can be formed if four of the gene pairs are homozygous and the remaining six gene pairs are heterozygous?
1054
128
36
64
16
64
T/F: Clear dominant/recessive of traits in F1 disproves the blending theory in Mendel's monohybrid crosses.
False
Assume that in guinea pigs, dark brown fur (B) is dominant to black fur (b). If you mate a homozygous black guinea pig with a heterozygous brown guinea pig, what proportion of the progeny will be black?
None
All
1/2
1/4
3/4
½
What proportion of the offspring of the mating Aa Bb cc by Aa Bb cc are expected to be homozygous for all three genes?
1/32
1
1/8
1/16
1/4
¼
What proportion of the offspring of the mating Aa BB Cc DD Ee by aa Bb Cc dd Ee are expected to be aa bb cc Dd ee?
0
1/64
1
1/128
1/16
0
What proportion of the offspring of the mating Aa Bb Cc Dd Ee by aa Bb Cc dd Ee are expected to be aa bb cc dd ee?
0
1/256
1/64
1/128
1
1 / 256
Consider a family with three children in which both parents are carriers for cystic fibrosis. What is the probability that they will have no affected children?
0
1/64
27/64
9/64
16/64 = 1/4
27/64
Consider a family with three children in which both parents are carriers for cystic fibrosis. What is the probability that they will have exactly one affected child?
1/64
16/64=1/4
27/64
1
9/64
27/64
Consider a family with three children in which both parents are carriers for cystic fibrosis. What is the probability that they will have exactly two affected children?
16/64=1/4
1
3/64
27/64
9/64
9/64
Consider a family with three children in which both parents are carriers for cystic fibrosis. What is the probability that all three children will be affected?
1/64
9/64
1
16/64 = 1/4
27/64
1/64
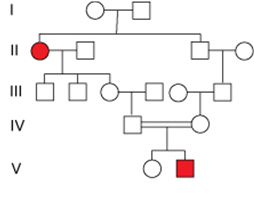
What does the pattern of inheritance in this pedigree indicate about the disease allele?
The disease allele is recessive
The disease allele is not inherited but only arises by a new mutation in those individuals that are affected.
There is no indication that the disease allele is either dominant or recessive
The disease allele is dominant
The disease allele is recessive
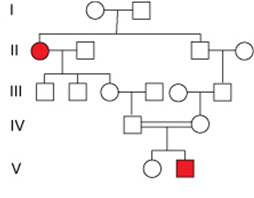
What is the probability of the male of IV generation to be the carrier?
0%
25%
100%
75%
50%
25%
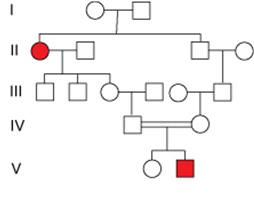
What is the probability for the female of V generation to be the carrier?
2/5
2/4
2/3
0
1
2/3
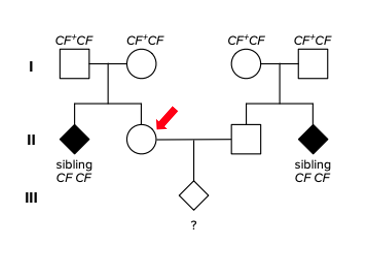
What is the probability of the female in II generation (red arrow) to be the carrier?
1/2
2/3
3/4
1/4
2/3
Dihybrid cross AAbb X aaBB
Starting with the parental cross AAbb X aaBB, what proportion of the F2 offspring is expected to be homozygous at least one of two genes?
3/4
None are homozygous
All are homozygous
1/2
1/4
¾
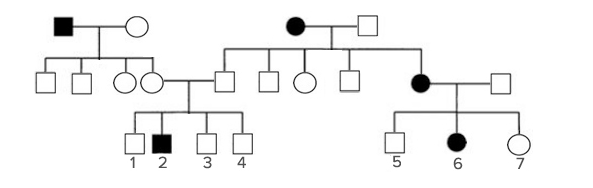
A pedigree for a common human characteristic (not a disease) controlled by a single gene is shown.
Shaded symbols indicate individuals exhibiting the characteristics.
If individuals 4 and 7 have a child, what is the probability that the child will exhibit the characteristic?
0
1/2
1/6
2/3
1/4
1/6
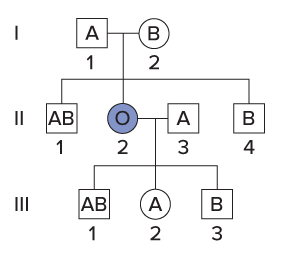
In addition to the three common alleles of gene I, the ABO blood type is controlled by a second gene, gene H. Individuals with at least one copy of the wild-type H allele produce substance H, a sugar polymer, on the surface of their red blood cells. Substance H is the precursor molecule to which the A and B polysaccharides are attached by the products of gene I. Individuals with the genotype hh do not have Substance H on their red blood cells, and so even if they have an IA or IB allele, the A and B polysaccharides cannot be attached to the red blood cell surface. Therefore, hh individuals have blood type O regardless of their gene I alleles. This phenomenon, called the Bombay phenotype, can result in surprising pedigrees. Examine this pedigree, then classify each statement as true or false.
If you did not know about the H gene, this pedigree would appear inconsistent because person II-2 has children with B and AB blood types
True
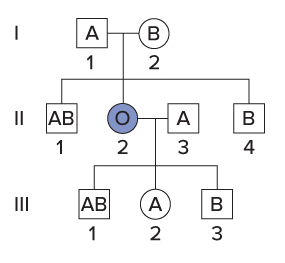
In addition to the three common alleles of gene I, the ABO blood type is controlled by a second gene, gene H. Individuals with at least one copy of the wild-type H allele produce substance H, a sugar polymer, on the surface of their red blood cells. Substance H is the precursor molecule to which the A and B polysaccharides are attached by the products of gene I. Individuals with the genotype hh do not have Substance H on their red blood cells, and so even if they have an IA or IB allele, the A and B polysaccharides cannot be attached to the red blood cell surface. Therefore, hh individuals have blood type O regardless of their gene I alleles. This phenomenon, called the Bombay phenotype, can result in surprising pedigrees. Examine this pedigree, then classify each statement as true or false.
II-2's genotype could be hh ii or hh IAi.
False
Huntington disease is a rare condition in humans, caused by a dominant allele of a single gene, and that results in a slow but inexorable deterioration of the nervous system. The probability that a person with the Huntington genotype will express the phenotype varies with age. Assume that 50% of those inheriting the HD allele will express the symptoms by age 40. Janelle is a 35-year-old woman whose father has Huntington disease. She currently shows no symptoms. What is the probability that Janelle will show symptoms in five years?
1/3
1/8
2/9
1/2
1/9
1/4
2/3
¼
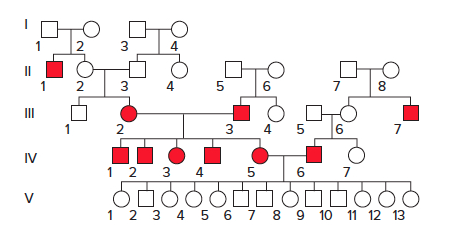
The pedigree that follows is showing the inheritance pattern of deafness, a heterogeneous trait, in a family. What is the genotype of the individuals in generation V? What phenomenon occurs in generation V?
Aa Bb ; complementation
aa bb ; epistasis
AA Bb ; complementation
Aa BB ; complementation
Aa Bb ; epistasis
aa bb ; complementation
AA BB ; complementation
Aa Bb ; complementation
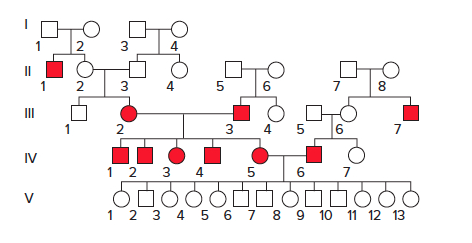
The pedigree that follows is showing the inheritance pattern of deafness, a heterogeneous trait, in a family. What are the genotypes of individuals IV-5 and IV-6?
aa bb and AA BB
AA BB and aa bb
Aa Bb and Aa Bb
Aa bb and aa Bb
AA bb and aa BB
AA bb and AA bb
AA bb and aa BB
Recall that in Mendel's peas, yellow is dominant to green, and round is dominant to wrinkled. Parent plants where one is homozygous for yellow and wrinkled peas and the other is homozygous for green and round peas produce an F1 generation. The F1 plants self-fertilize. One of the F2 pods contains 6 peas. What is the chance that all 6 peas are yellow and round?
6/16^6
1/6
18/16
(9/16)^6
1/6^6
6/16
1
(3/16)^6
3/16
(9/16)^6
In a family of 7 children, what's the chance that 3 are one sex and 4 are the opposite sex?
(1/2)^7 X 7!/*3! X 4!)
(1/2)^7 X 2 X 7!/(3! X 4!)
(1/2)^7
2 X (1/2)^7
2 X (1/7)^2
(1/2)^7 X 2 X 7!/(3! X 4!)
A man with Huntington disease (he is heterozygous HD/HD+) and a normal woman have two children. What is the probability that only one of the children has the disease?
1/4
1/8
1
1/2
½
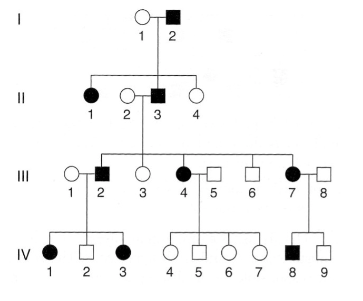
The following pedigree is for a rare, but relatively mild, hereditary disorder of the skin.
Consider parents, III-4 and III-5. This couple has four children but no one is affected. What is the probability of this given the genotype of this parents?
1/8
1/16
1
1/2
1/4
1/16
In the common daisy, genes A and B control flower color. Both gene have a dominant allele (A or B) and a recessive allele (a or b). At least one copy of each dominant allele is required for flowers to be colorful instead of white.
Predict the genotype and phenotype of the F1 progeny of a cross between two white-flowered plants, one homozygous AA and the other homozygous BB.
aabb, colorful
AsBb, white
AaBb, colorful
AAbb, white
aaBB, white
AaBb, colorful
In primroses, the dominant allele of gene K is necessary to synthesize blue flower pigment. Blue pigment synthesis is inhibited by a dominant allele of gene D. In other words, plants with the genotype K_D_ will not produce pigment (and their flowers will be white) because of the presence of the D allele.
If two dihybrid plants (KkDd) are crossed, what is the ratio of blue to white offspring in the progeny?
1 blue: 15 white
3 blue: 13 white
4 blue: 12 white
3 blue: 1 white
7 blue: 9 white
3 blue: 13 white
In Mendel's dihybrid cross, you expect to have 9:3:3:1 ration in F2 progeny. You repeated Mendel's dihybrid crosses (yellow/green; round/wrinkled), and obtained 1600 seeds. Therefore, the probability of obtaining 900 yellow round, 300 yellow wrinkled, 300 green round, and 100 green wrinkled seeds is 100%.
True
False
False
If an individual has 10 gene pairs, 210 different gametes can be formed after meiosis.
T/F
True
Below is a schematic model during mitosis
T/F
False
Hemophilia is caused by an X-linked recessive mutation in humans. If a woman whose maternal uncle (mother's brother) was a hemophiliac marries a man whose brother is also a hemophiliac, what is the probability that their son will have hemophilia? (no other cases of hemophilia)
0
1
1/2
1/8
1/4
1/8
Color blindness is caused by an X-linked recessive allele that is rare in humans. Suppose a man and a woman, both of whom have normal color vision and color-blind fathers, have a child. What is the chance that their first son will be color blind?
1/2
1/4
1/3
2/3
0
½
Daughter cells produced in meiosis are identical.
True
False
False
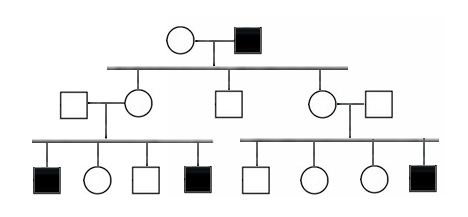
In the following pedigree, the indicated trait most likely is caused by which type of allele?
Y-linked
X-linked dominant
X-linked recessive
autosomal dominant
autosomal disease
X-linked recessive
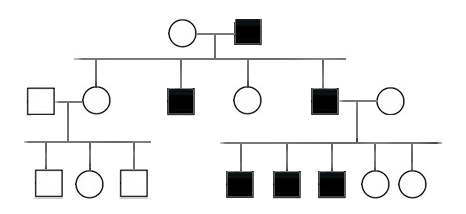
In the following pedigree, the indicated trait is most likely caused by which type of allele?
Y-linked
autosomal dominant
X-linked recessive
autosomal recessive
X-linked dominant
Y-linked
In human, XO individuals are females with Turner syndrome and XXY individuals are males with Klinefelter syndrome. Which of the following events cannot give rise to Klinefelter male?
nondisjunction at meiosis II in the father
nondisjunction at meiosis I in the father
nondisjunction at meiosis II in the mother
nondisjunction at meiosis I in the mother
All of the choices could give rise to a Klinefelter male
nondisjunction at meiosis II in the father
In human, XO individuals are females with Turner syndrome and XXY individuals are males with Klinefelter syndrome. Red-green color blindness is caused by an X-linked recessive allele. Suppose a color-blind man and a woman with normal vision and no family history of color blindness had a daughter who was color blind and had Turner syndrome. Which event could have given rise to this offspring?
nondisjunction at meiosis I in the mother
nondisjunction at meiosis II in the father
nondisjunction at meiosis I in the father
nondisjunction at either meiosis I or meiosis II in the mother
nondisjunction at meiosis II in the mother
nondisjunction at either meiosis I or meiosis II in the mother
Individuals with an XXY karyotype are ( ) in humans and ( ) in fruitflies.
female; male
female; female
male; female
male; intersexual
male; male
male; female
Normal fruit flies have red eyes. Flies with mutations that block the function of the X-linked white gene have white eyes. The wild-type allele is completely dominant to mutant alleles. White-eyed female fruit flies are mated to red-eyed males. One of the hundreds of female progeny is white-eyed. What is the likely karyotypes of this white-eyed daughter?
XXX
XO
XYY
XY
XXY
XXY
In which of the following cases will a Barr body be seen?
only XX
only XXY
XY
both XX and XXY
XO
both XX and XXY
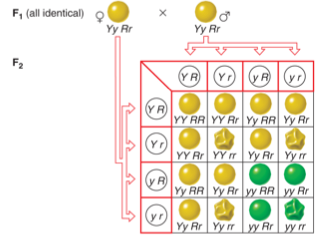
The figure that follows shows one of Mendel's dihybrid cross experiments where the alleles of the Y and R assorted independently. In the F2, what would be the frequency of yy rr if the Y and R genes were linked and 10 m.u. apart?
40%
20.25%
16%
12.25%
32%
20.25%
The P and Q genes of a plant are 20 m.u. apart. A PP QQ and a pp qq individual cross, and the F1 cross with each other to produce the F2. The P and p, and Q and q alleles are completely dominant and recessive, and there are no interactions between genes P and Q. What phenotypic ratio would you expect in the F2?
9 P- Q- : 3 P- qq : 3 pp Q- : 1 pp qq
16 P- Q- : 66 P- qq : 9 pp Q- : 9 pp qq
74 P- Q- : 5 P- qq : 5 pp Q- : 16 pp qq
1 P- Q- : 1 P- qq : 1 pp Q- : 1 pp qq
66 P- Q- : 9 P- qq : 9 pp Q- : 16 pp qq
66 P- Q- : 9 P- qq : 9 pp Q- : 16 pp qq
The measured distance between genes D and E in a two-point testcross is 50 map units. Where are genes D and E in relation to each other ? (Check all that apply.)
D and E are on the same chromosome, at least 50 map units apart.
D and E are on different homologous chromosomes.
D and E are on the same chromosome, less than 50 map units apart
t's impossible to measure an RF of 50% in a testcross.
D and E are on the same chromosome, exactly 50 map units apart.
D and E are on the same chromosome, at least 50 map units apart.
D and E are on different homologous chromosomes.
Two autosomal genes, G and H, are 80 map units apart. You perform the following testcross: G h / g H x g h / g h. At what frequency would you find G H / g h progeny?
20%
30%
50%
25%
40%
25%
In Drosophila, yellow bodies (y ) and white eyes (w ) are both caused by recessive X-linked alleles. The normal alleles (y+ amd w+ ) cause tan bodies and red eyes, respectively. A y w female is mated to a y+ w+ male and the F1 progeny are allowed to mate with each other. Two hundred F2 were observed and they are: 55 y w; 45 y w+; 45 y+ w; 55 y+ w+. What is the chi-square value for the test for goodness of fit of the null hypothesis of no linkage? (Recall that the chi-square statistic is the sum, for all classes, of (O-E)2/E.)
20
10
1.0
0.4
0.5
2.0
2.0
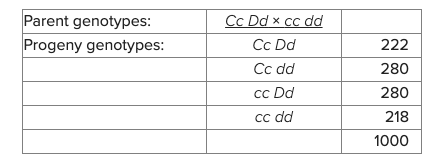
A dihybrid testcross is made to determine if genes C and D are linked. The results are shown in the table.
Calculate Chi-square value and determine whether genes C and D are linked. Which of the following statements is correct?
***X² for df=3 is 7.81
Chi-square value is 14.4; C & D are linked
Chi-square value is 10.8; C & D are linked
Chi-square value is 10.8; C & D are not linked
Chi-square value is 14.4; cannot determine the linkage
Chi-square value is 14.4; C & D are not linked
Chi-square value is 10.8; cannot determine the linkage
Chi-square value is 14.4; C & D are linked
The map of a chromosome interval is:
A --- 10 m.u. ---- B --- 40 m.u. --- C
From the cross Abc/aBC X abc/abc, how many double crossover chromosomes would be expected among 1000 progeny?
80
20
10
5
40
40
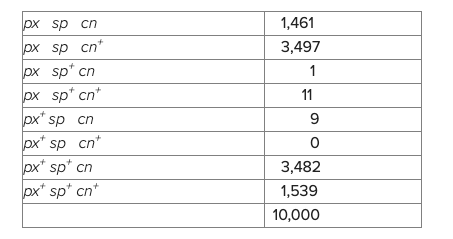
Females heterozygous for the recessive mutations px, sp, and cn on the second chromosome and normal alleles are mated to a male homozygous for all three mutations. The offspring are as follows:
What is the interference?
.5
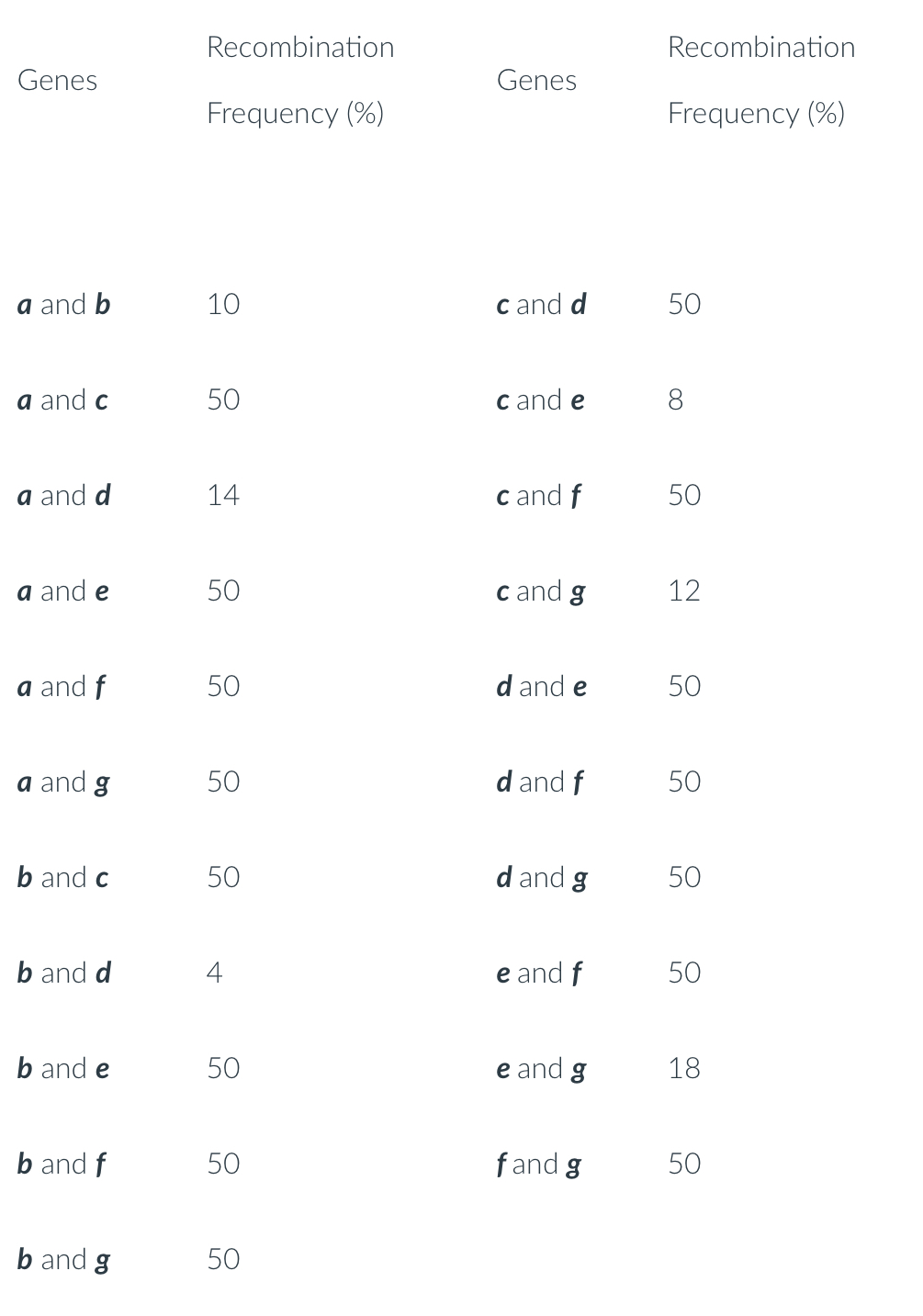
A series of two-point crosses were carried out among seven genes (a, b, c, d, e, f, and g) producing the following recombination frequencies. Using these recombination frequencies, you map the seven genes, showing their linkage groups. How many linkage groups did you find? - Take your time this is 4 point questions
Hint - you need to draw the genetic map for all seven genes first.
3
4
6
2
1
5
7
3
Neurospora with the genotype a+ a form tetrads in the following frequencies:
a+ a a a a+ a+
a+ a a+ a+ a a
a a+ a a+ a+ a
a a+ a+ a a a+
192 208 23 27 29 21
What is the genetic distance between the gene A and centromere?
5 m.u.
0 m.u.
20 m.u.
Not linked
10 m.u.
10 m.u.
The following tetrad data were obtained from the cross AB x ab in Neurosopora:
AB AB AB ab
AB AB AB ab
AB aB Ab aB
AB aB Ab aB
ab Ab aB AB
ab Ab aB AB
ab ab ab Ab
ab ab ab Ab
1560 220 20 200
On the basis of these data, what is the genetic distance between gene A and gene B in m.u.?
Only write the number !
11
Within the same linkage group, two genes cannot be more than 50 m.u. apart because they are linked.
True
False
False
The diploid pea plant has 28 chromosomes. The haploid fungus Neurospora crassa has 7 chromosomes. Neither organism has separate male and female individuals. Therefore, the number of linkage groups in these two organisms is:
A. Garden pea has 14 linkage groups, and Neurospora has 7.
B. Garden pea has 7 linkage groups, and Neurospora has 7.
C. Garden pea has 28 linkage groups, and Neurospora has 8.
D. Garden pea has 29 linkage groups, and Neurospora has 8.
A
The ratio of _____ is 1:1.
A. guanine to adenine
B. adenine to thymine
C. cytosine to adenine
D. uracil to cytosine
B
Which one of the following is an element found in DNA
A. helium
B. sulfur
C. nitrogen
D. magnesium
E. silicon
C
Which of the following statements are NOT true about double-stranded DNA? Check all that apply!
(C + A) / (G + T) = 1
A/G = C/T
A + C = T + G
A/G = T/C
A + T = G + C
A + G = C + T
A/G = C/T
A + T = G + C
Females heterozygous for the recessive second chromosome mutations pn, px, and sp are mated to a male homozygous for all three mutations. The offspring are as follows:
px sp cn 1,461
px sp cn+ 3,497
px sp+ cn 1
px sp+ cn+ 11
px+ sp cn 9
px+ sp cn+ 0
px+ sp+ cn 3,482
px+ sp+ cn+ 1,539
Total 10,000
Which of three genes is in the middle?
px
sp
insufficient data, cannot determine
cn
px
Which statement is true about the structure of DNA?
The two strands of a DNA molecule are held together by base pairing.
It contains nitrogenous bases known as A, C, G, and U.
Each different sequence folds into a different three-dimensional shape.
It is a polymer made up of a string of amino acids.
The two strands of a DNA molecule are held together by base pairing.
One strand of DNA has the sequence 5′ ATCTGG 3′. What is the sequence of the other strand?
5′ CCAGAT 3′
5′ TAGACC 3′
5′ ATCTGG 3′
3′ GGTCTA 5′
5′ CCAGAT 3′
If 30% of the bases in human DNA are G, what percentage are T?
60%
30%
50%
80%
20%
20%
If 30% of the bases in a region of the mouse genome are cytosine, what percentage in that region are adenine?
A. 15%
B. 20%
C. 30%
D. 35%
E. Cannot be determined
B
Which of the following DNA (double helix) is identical as "TGCATGGCATGCGTA"?
A. ATGCGATCGGTACGT
B. TACGCATGCCATGCA
C. ACGTACCGTACGCAT
D. None of the above
B
___________ bonds are responsible for the chemical affinity between A and T (or G and C).
Covalent
Hydrogen
Phosphodiester
Hydrophobic
Ionic
Hydrogen
Two alleles of gene C controls hair color in horses: C1 and C2. Horses homozygous for allele C1 are red, heterozygous are yellow, and C2 homozygous are cream. What type of allele interaction is described?
complete dominance
recessive lethality
incomplete dominance
codominance
pleiotrophy
incomplete dominance
Homologous recombination occurs in a heterozygote in which alleles D and d differ by a single base pair. The D allele has a G (a GC base pair) at one position, whereas the d allele has a C (a CG base pair) at the same position. If branch migration causes heteroduplex formation across this position, what is the expected outcome?
Both D and d alleles will remain unchanged because G can base pair with C.
Mismatch repair will identify an abnormal C-G base pair and will ensure that the cell has two copies of each allele.
Mismatch repair will identify abnormal G-G and C-C base pairs and may convert the D allele to a d allele or the d allele to a D all
Mismatches will cause the Holliday junction to be unstable and to resolve by the noncrossover pathway.
Mismatch repair will identify abnormal G-G and C-C base pairs and gene conversion will always occur in situations like this one when mismatched bases exist within the heteroduplex region.
Mismatch repair will identify abnormal G-G and C-C base pairs and may convert the D allele to a d allele or the d allele to a D all
The protein that repeatedly synthesizes RNA primer is called
A. primase.
B. helicase.
C. topoisomerase.
D. telomerase.
E. ligase.
A
In peas, tall (T) is dominant to short (t), red flowers (R) is dominant to white flowers (r), and wide leaves (W) is dominant to narrow leaves (w). A tall, red, wide-leaved plant is crossed to a short, white, narrow-leaved plant and the progeny are as follows:
tall, red, wide | 381 |
tall, white, wide | 122 |
short, red, wide | 118 |
short, white, wide | 379 |
| 1000 |
What is the genotype of the tall, red, wide-leaved parent?
Tt Rr Ww
TT RR WW
Tt Rr WW
TT Rr Ww
TT RR Ww
Tt Rr WW
The group of enzymes able to relax supercoils in DNA is called
A. primases.
B. helicases.
C. topoisomerases.
D. telomeres.
E. ligases.
C
Two strains of S. cerevisae (yeast) are crossed. One has the genotype ABC and the other abc. Five sets of the resultant tetrads are noted below. In which set did a gene conversion event occur?
abc, aBc, AbC, aBC
abc, abc, ABC, ABC
aBc, aBc, AbC, AbC
abC, abc, ABc, ABC
Abc, Abc, aBC, aBC
abc, aBc, AbC, aBC
A region of DNA 100 bp in length has the potential to be represented by 4100 unique sequences.
True
False
True
If there was a cross-over, there must be a heteroduplex formed.
True
False
True
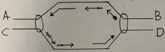
The picture is a schematic representation of a DNA replication fork. Where is the 5' end(s) of the template DNA?
A & D
B & C
A & C
A & B
C & D
A & D
In tetrad analysis, two genes are linked when
NPD = T
PD = T
PD = NPD
PD > NPD
PD > T
PD > NPD
After meiosis I, DNA content is 1C.
True
False
False
If a chemical inhibitor of DNA ligase was added to bacterial cells after DNA replication initiation, the outcome would be
elongation of both strands would not occur without ligase to join new nucleotides together
elongation would occur, but okazaki fragments would not be joined together
elongation of the lagging strand, but not the leading strand, would occur
normal DNA replication process would proceed as ligase is not required for DNA replication
too many supercoils would build up in the DNA, resulting in a halt of elongation
elongation would occur, but okazaki fragments would not be joined together
Fragile X syndrome is caused by
5-Bromouracil
Depurination
Microdeletions
Extension of trinucleotide repeats
Free radicals
Extension of trinucleotide repeats
During mutagenic treatment with nitrous acid, an adenine deaminates to form hypoxanthine, which bonds like guanine. The mutational event would be
AT to CG
AT to GC
AT to TA
GC to AT
GC to TA
AT to GC
You are studying a strain of bacteria that carries a temperature-sensitive mutation in one of the genes required for DNA replication. The bacteria grow normally at the lower temperature but when the temperature is raised they die. When you analyze the remains of the bacterial cells grown at the higher temperature you find evidence of partly replicated DNA. When this DNA is denatured by heating, numerous single-stranded DNA molecules around 1000 nucleotides long are found. Which one of the following proteins is most likely to be affected (malfunctioned) in these bacteria?
DNA polymerase
Helicase
Primase
DNA ligase
DNA ligase
If the genome of the bacterium E. coli requires about 20 minutes to replicate itself, how can the genome of the fruit fly Drosophila be replicated in only three minutes?
Drosophila DNA contains more origins of replication than E. coli DNA.
Eukaryotic DNA polymerase synthesizes DNA at a much faster rate than prokaryotic DNA polymerase.
Eukaryotes have more than one kind of DNA polymerase.
The Drosophila genome is smaller than the E. coli genome.
Drosophila DNA contains more origins of replication than E. coli DNA.
The enzyme DNA helicase relieves the superhelical strain that builds up in double-stranded DNA as it is unwound during DNA replication.
True
False
False
During DNA replication, the lagging strand is synthesized discontinuously because
DNA polymerase always falls off the template strand after every 10 nucleotides or so.
the lagging strand template is discontinuous.
DNA polymerase removes the last few nucleotides synthesized whenever it stops.
DNA polymerase can polymerize nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
DNA polymerase can polymerize nucleotides only in the 5’ to 3’ direction.
A chromosomally normal woman and a chromosomally normal man have a son whose sex-chromosome constitution is XXY.
In which parent did the nondisjunction take place?
Mom
Dad
either of them
either of them
If a plant with the genotype A/A · B/B is crossed to a plant with the genotype a/a · b/b, and the F1 is testcrossed, what percent of the testcross progeny will be a/a · b/b if the two genes are 10 map units apart.
10%
50%
20%
40%
45%
45%
In a segment of DNA, an A base is changed to a C and the error is copied during DNA replication. Under which circumstances is that change considered a mutation? Select all correct statement.
The change result in production of a novel protein.
The changes alter the phenotype of organisms's offspring.
The change is in a gene, but has no effect on a gene product or phenotype.
The change is in a somatic cell, such as skin cell.
All are correct
Assume that a wild-type sequence is 5'AGCCTATGCAC3'. which of the following sequences might be produced by an inversion of underlined sequence?
5'AGCCTATGCAC3'
5'AGCCTATGCCTATGCAC3'
5'AGGTATCCCAC3'
5'AGCAC3’
5'AGCATAGGCAC3
5'AGCATAGGCAC3
From Benzer’s experiment using T4 phage, he isolated two independent mutations at rIIA locus, rIIA-311 and rIIA-314. He coinfected two mutant phages into E. coli K strain and obtained 6X104pfu/mL. The same coinfection using rIIA-311 and rIIA-314 resulted in 2X109 pfu/mL when they are infected into E.coli B strain. What is the genetic distance between rIIA-311 and rIIA-314?
0.003 m.u.
0.6 m.u.
0.0015 m.u.
0.006 m.u.
0.15 m.u.
0.3 m.u.
0.006 m.u.
Assume a researcher is studying the rII locus of phage T4. Four rII- strains are obtained: A, B, C, and D. When coinfections are performed in E. coli strain K(λ) the following results are obtained:
A × B = lysis
A × C = lysis
B × C = no lysis
B × D = no lysis
C × D = no lysis
In a second experiment, coinfections are performed in E. coli strain B. When progeny phage are examined for their ability to form plaques in E. coli strain K(λ), the following results are obtained:
A × B = plaques
B × C = plaques
C × D = plaques
B × D = no plaques
A and B carry mutations in the same gene, C and D are on a different gene.
A, B, C, and D carry mutations in the same gene.
A carries a mutation in one gene, B, C, and D are on a different gene, B and C both carry the same mutation.
A carries a mutation in one gene, B, C, and D are on a different gene, C and D both carry the same mutation.
A carries a mutation in one gene, B, C, and D are on a different gene, B and D both carry the same mutation.
A carries a mutation in one gene, B, C, and D are on a different gene, B and D both carry the same mutation.
Wild-type allele refers to any allele that occurs naturally.
True
False
False
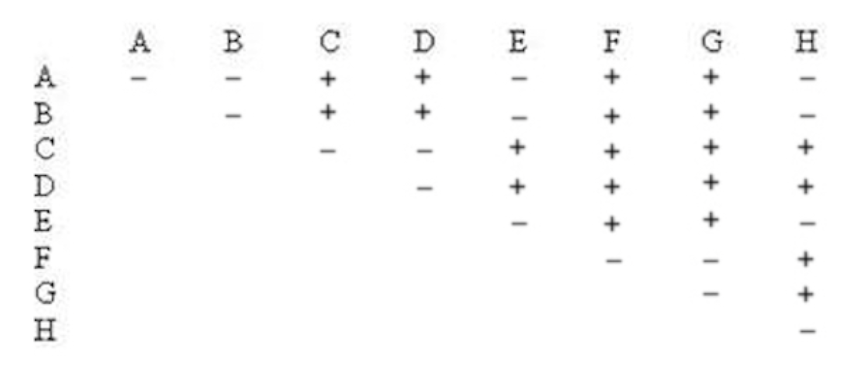
Eight different fruit fly strains (A-H) have recessive mutations that cause curly wings; flies normally have straight wings. A scientist performed every pairwise cross between homozygous curly-winged flies of the different strains and the results are shown in the complementation matrix below. A + means that complementation occurred in the offspring, and a − means that no complementation occurred.
What strains have a mutation in the same gene as does strain G?
A
G
A, E. G
C, D
B, E, H
G
If heteroduplex is formed, there is always crossing-over.
True
False
False
A collection of mutations that complement each other is known as a complementation group.
True
False
False
A cross is made between a haploid strain of Neurospora. From this cross, a total of 1,000 linear asci (ordered asci) are isolated and categorized as in the table below. nic and ad are linked. Draw the genetic map including nic, ad and centromere (including genetic distance).
1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad+ |
nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad+ |
nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad |
nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad |
nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad |
nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad | nic+ ad+ | nic+ ad |
nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad+ |
nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad | nic ad+ | nic ad+ | nic ad | nic ad+ |
808 | 1 | 90 | 5 | 90 | 1 | 5 |
After double cross-over correction, what is the genetic distance between centromere and gene ad?
10.25 m.u.
5.2 m.u.
9.3 m.u.
5.05 m.u.
10.25 m.u.
What is true about the mutations within a complementation group?
They complement each other and in different genes.
They always produce the same mutant phenotype.
They complement each other and are in the same gene.
They do not complement each other and are in different genes.
They do not complement each other and are in the same gene.
They do not complement each other and are in the same gene.
A researcher is studying coat color in mice. Wild-type fur in mice is brown. Three pure-breeding strains of mice with white fur have been isolated. The strains ae called "milky", "blanc", and "weiss". White fur is a recessive characteristic in each strain. These mice are crossed to each other in pairs and the progeny phenotypes are recorded.
milky X blanc = all white progeny
milky X weiss = all brown progeny
blanc X weiss = all brown progeny
What conclusion is consistent with these results?
All three strains have mutations in different genes.
The milky and blanc strains have mutations in the same gene; weiss has a mutation in a different gene.
All three strains have mutations in the same gene.
The weiss and blanc strains have mutations in the same gene; milky has a mutation in a different gene.
The milky and weiss strains have mutations in the same gene; blanc has a mutation in a different gene.
The milky and blanc strains have mutations in the same gene; weiss has a mutation in a different gene.