ATP water and inorganic molecules
1/11
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
12 Terms
examples of inorganic ions
iron in haemoglobin
sodium
hydrogen
potassium
explain the polarity of water
water is polar as oxygen is neg and hydrogen is positive
the polarity of water makes it an excellent solvent in the cytoplasm
chemical reaction occur faster in the cell when in a solution
hydrogen bonding in water
adjacent molecules are attracted between the positive H and the negative O the hydrogen bonding between water molecules causes cohesion which causes surface tension. cohesion is required for water transport in a plant causing water to be pulled up the xylem in a continuous column
high specific heat capacity in water
a lot of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds and raise the temperature
ie body temperature remains stable
makes water a good habitat as the temperature does not change much
high latent heat of vaporisation of water
a lot of energy is needed to break the hydrogen bonds to form water
ie a lot of heat energy can be removed through evaporation of water during sweating to cool the body without loosing too much water
water as a metabolite
water is required for hydrolysis and water is produced during condensation reactions
how does ATP provide energy to the cell during respiration
during respiration the energy stored in glucose is not released directly
instead the energy released is used to form adenosine triphosphate
when ATP is hydrolysed it releases energy for processes
what is the structure of ATP
it is a nucleotide derivative and contains adenine and ribose sugar and 3 phosphate groups
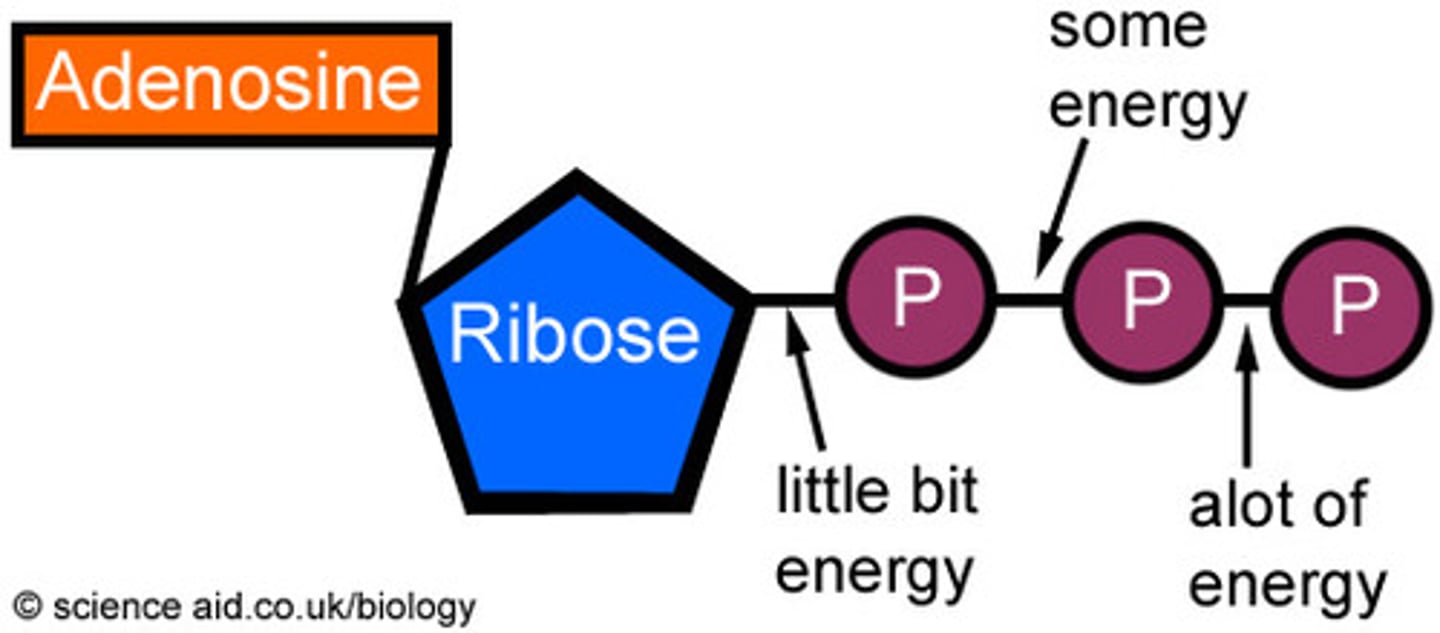
contrast the structures of ATP and a nucleotide found in DNA
atp has a ribose and dna nucleotide has deoxyribose
atp has 3 phosphate groups and dna nucleotides has 1 phosphate
atp base always has adenine dna the base varies
ATP hydrolysis
the release of energy from ATP is released through the hydrolysis to form ADP and Pi requiring ATP hydrolase
making atp
made in a condensation reaction requiring ATP synthase
why is ATP useful
energy is released in small and useable amounts
it adds phosphate to molecules to make them more reactive
it can be reformed
it is soluble
a single step reaction