BIO130: Week 7 - Membrane Proteins
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
What are integral membrane proteins?
proteins DIRECTLY attached to bilayer:
inserted OR attached
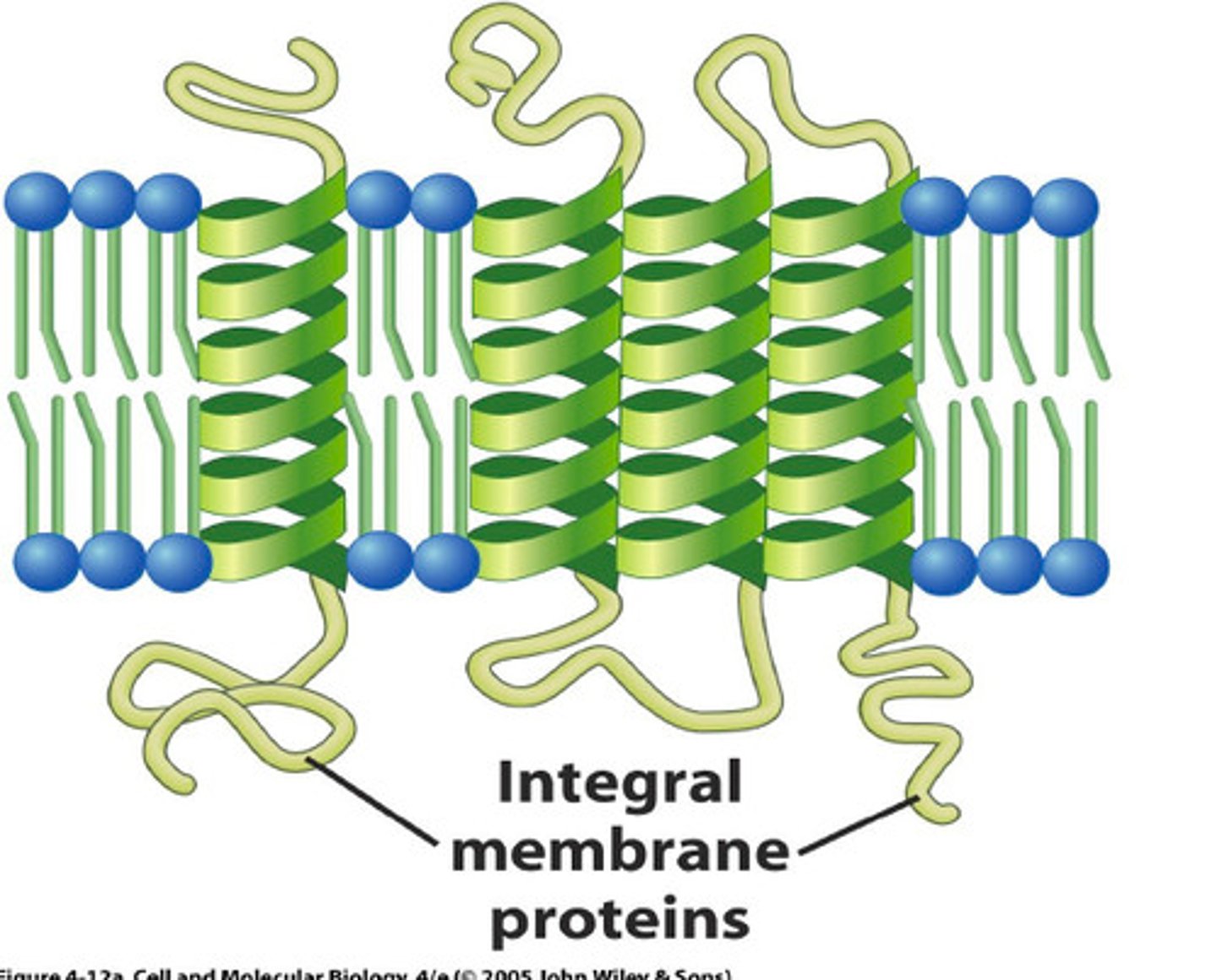
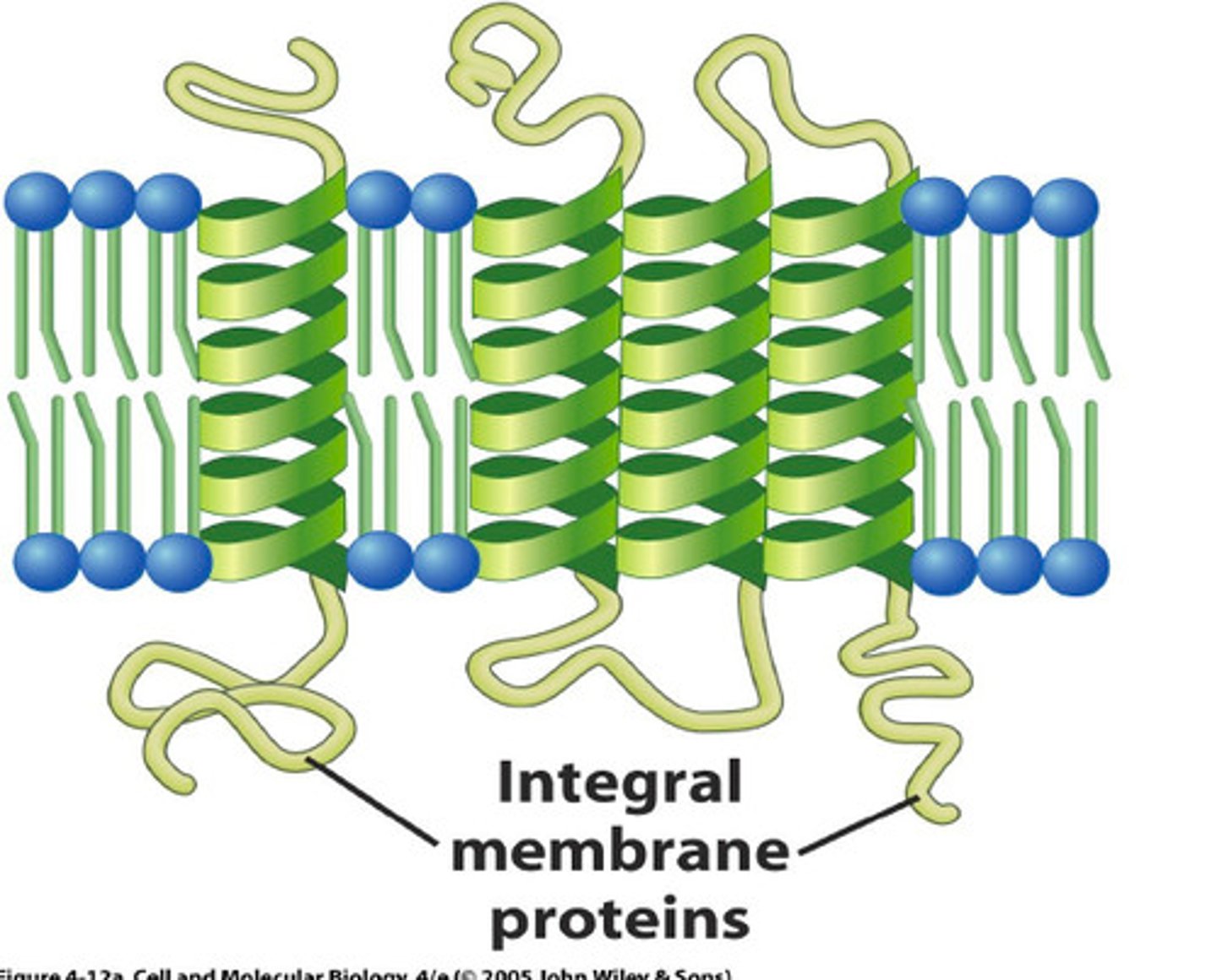
What are the 3 types of integral membrane proteins?
1. Transmembrane (amphipathic): fully through
2. Mono-layer associated (amphipathic): semi-through
3. Lipid-linked: not through
What are the 3 types of transmembrane proteins?
1. Single-pass: one a-helix
2. Multipass: 2+ a-helices
3. B-barrel: rolled sheet
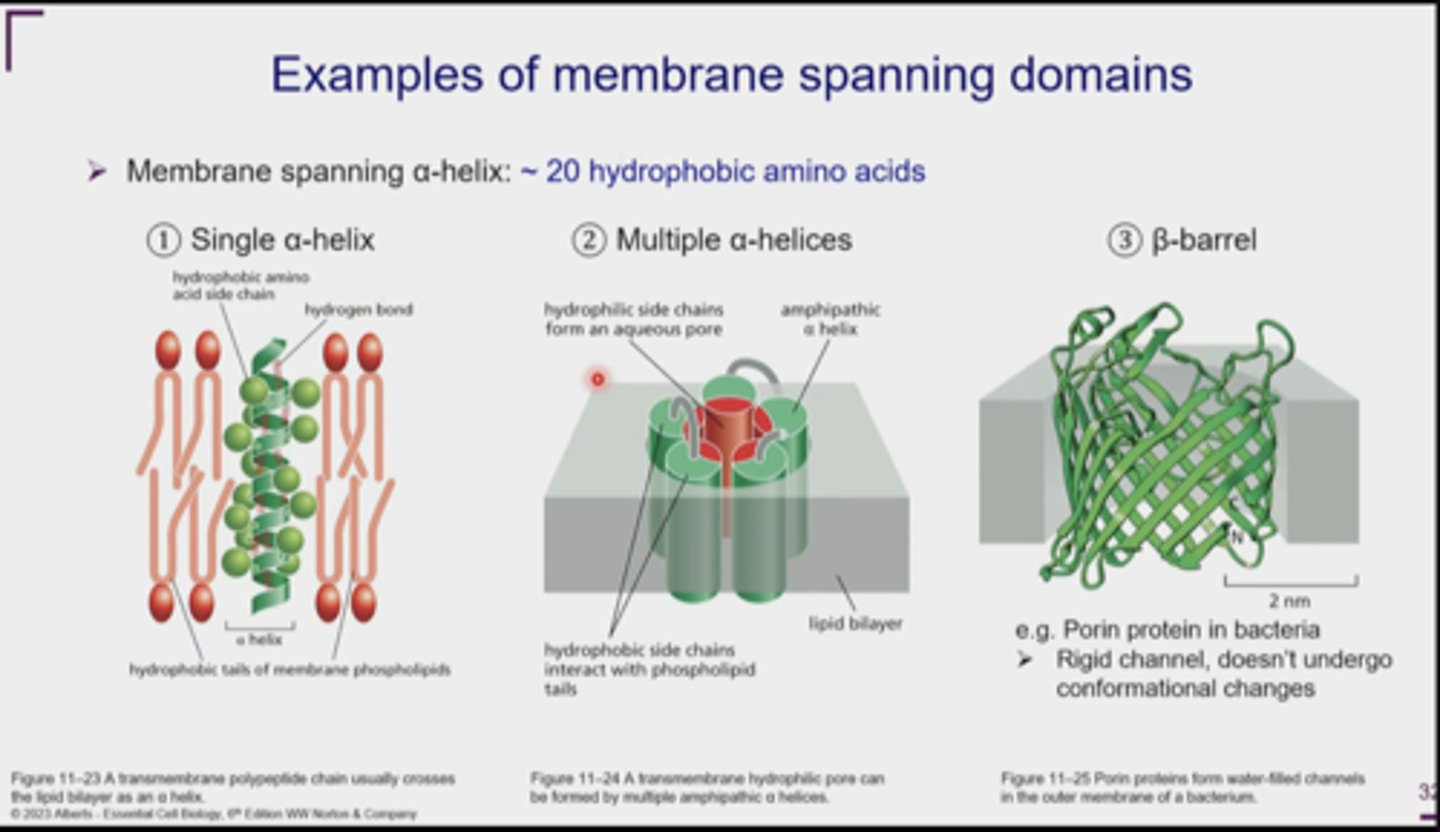
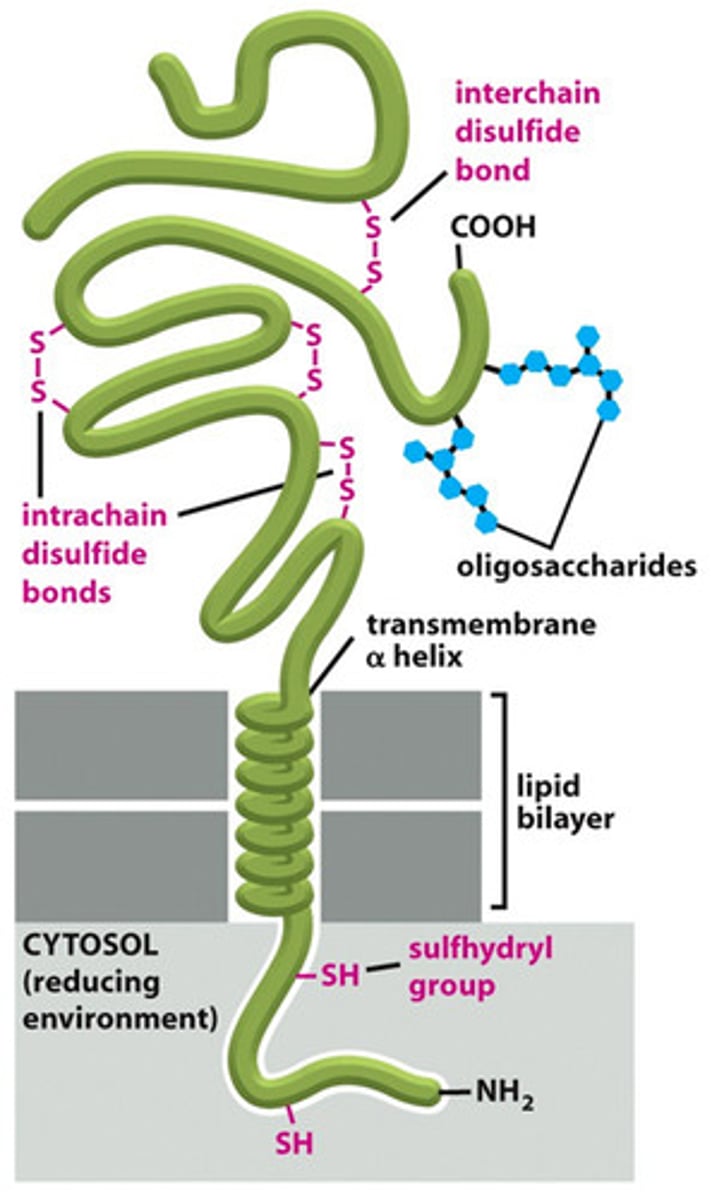
What are membrane-spanning alpha helices?
a-helix shape used to pass through the membrane
How long are membrane-spanning alpha helices?
about 20 hydrophobic amino acids
How do single-pass proteins work?
hydrophobic side chains of a-helix interact w/ lipid tails
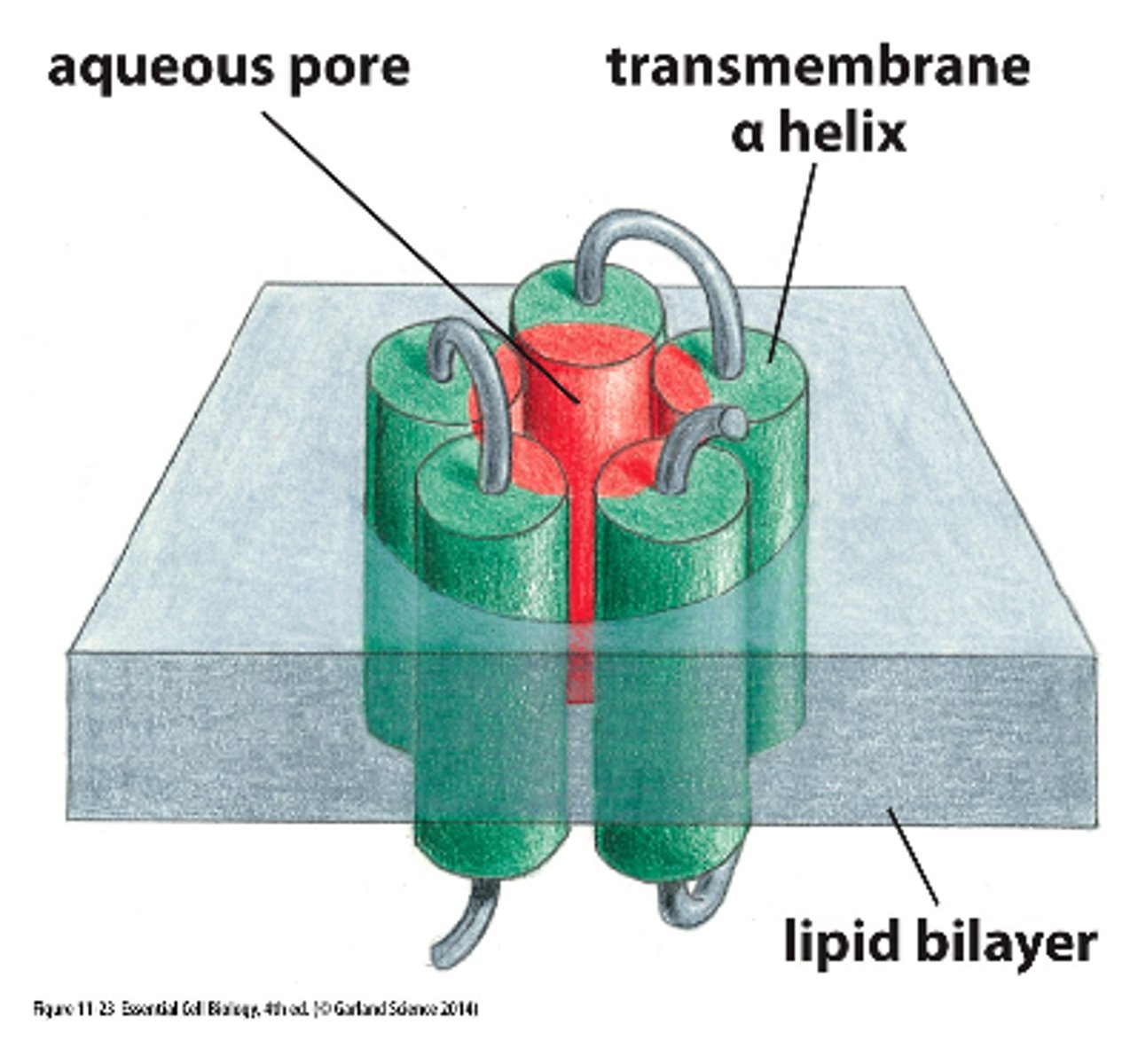
How do multipass proteins work?
protein channel w/ aqueous core surrounded by amphipathic a-helices
- aq. transfer!
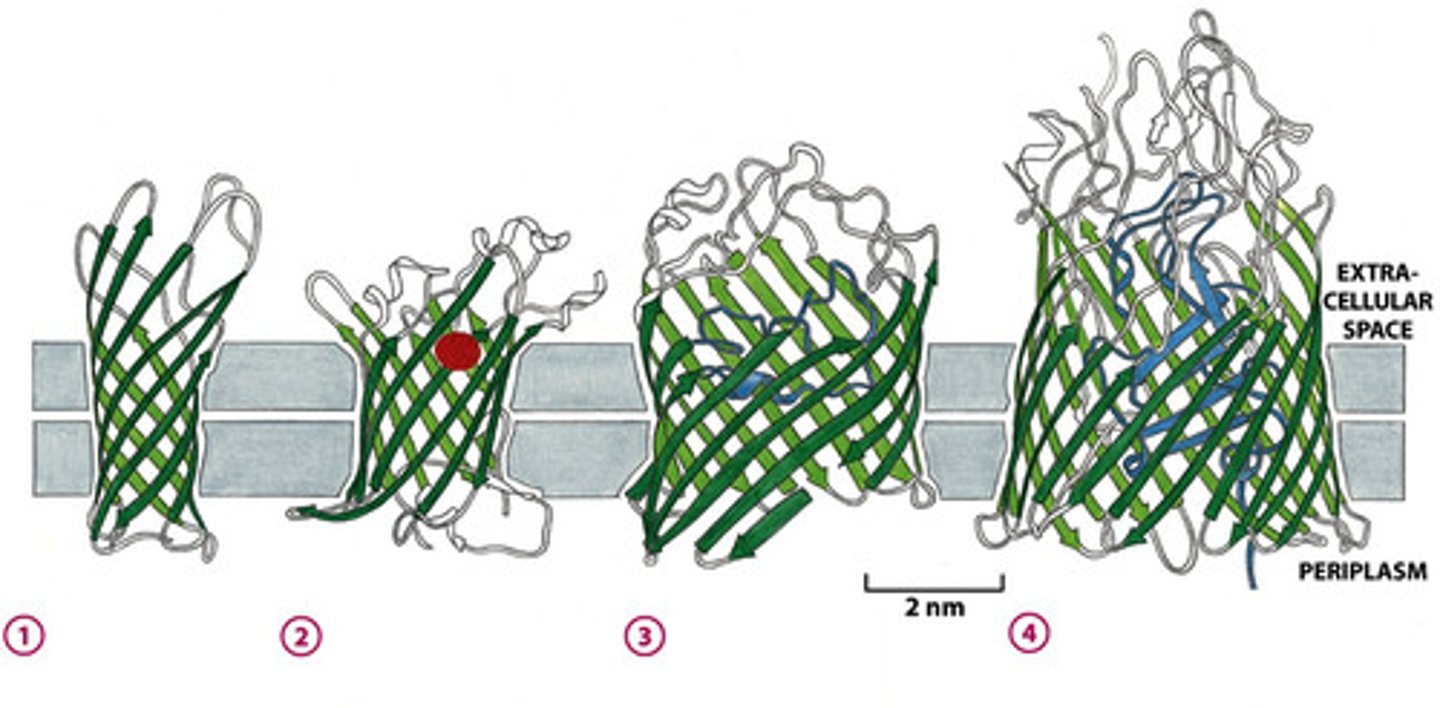
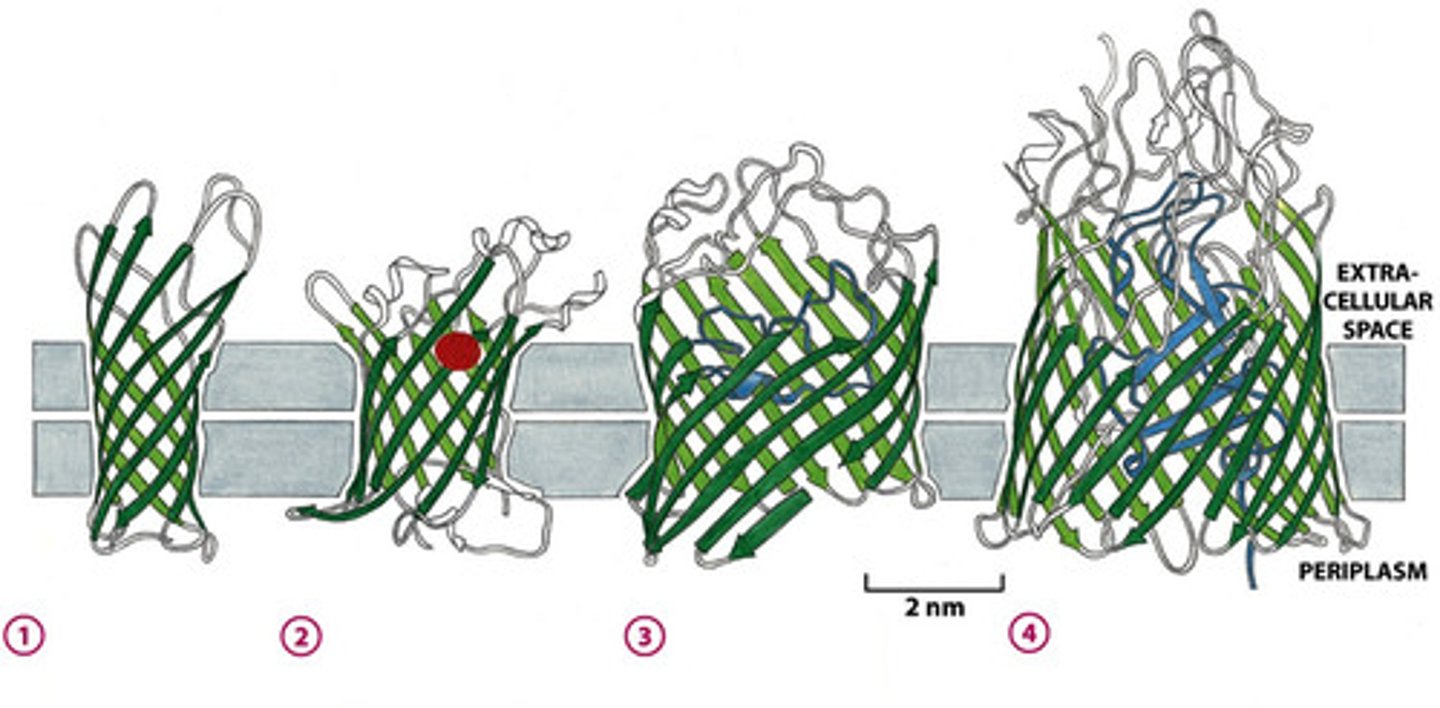
How do B-barrel proteins work?
protein channel w/ hydrophilic core surrounded by hydrophobic beta sheets
- aq. transfer!
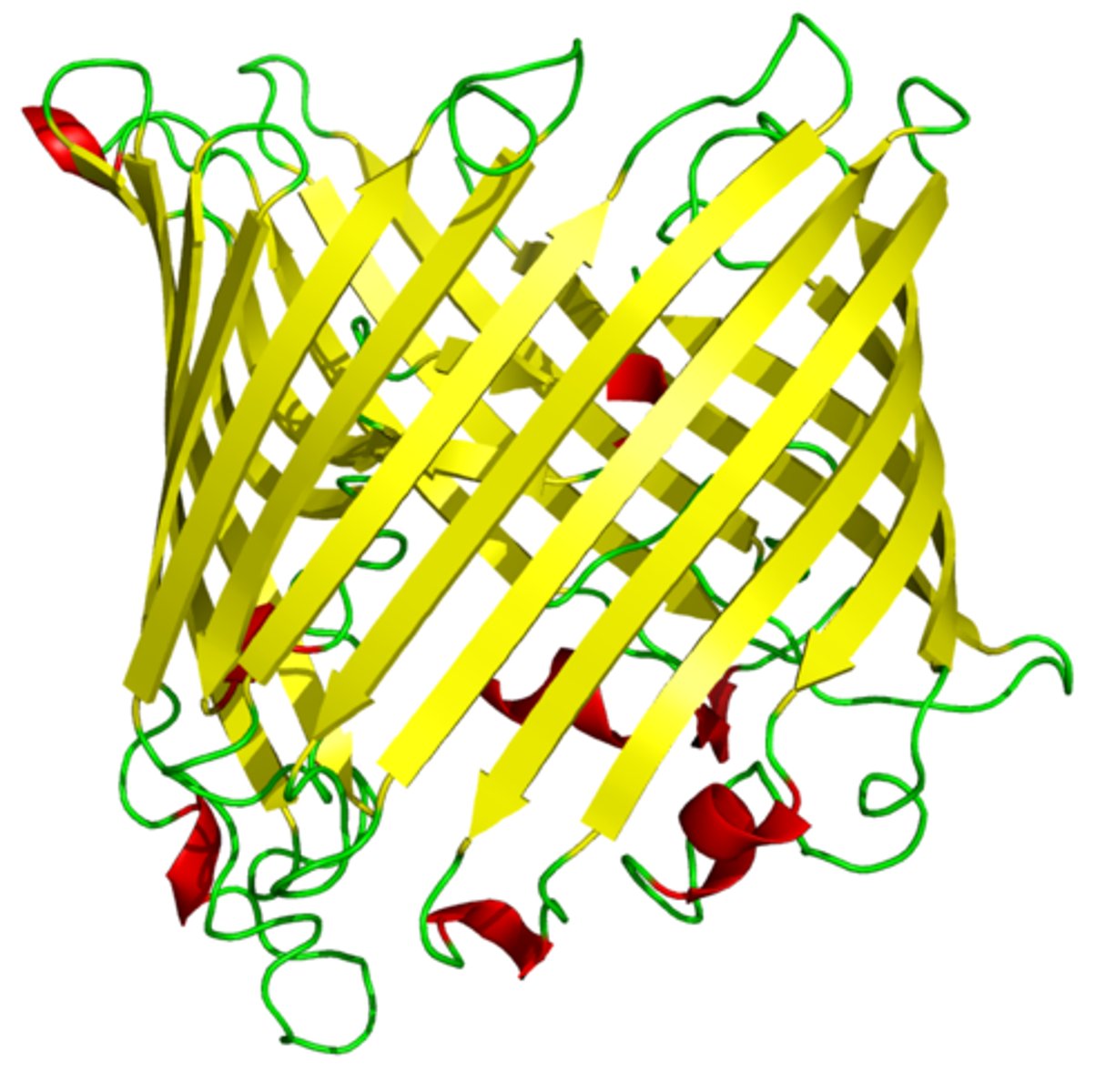
What are the 2 ways transmembrane structures can be identified?
1. X-ray crystallography: 3D structure
2. Hydrophobicity plots
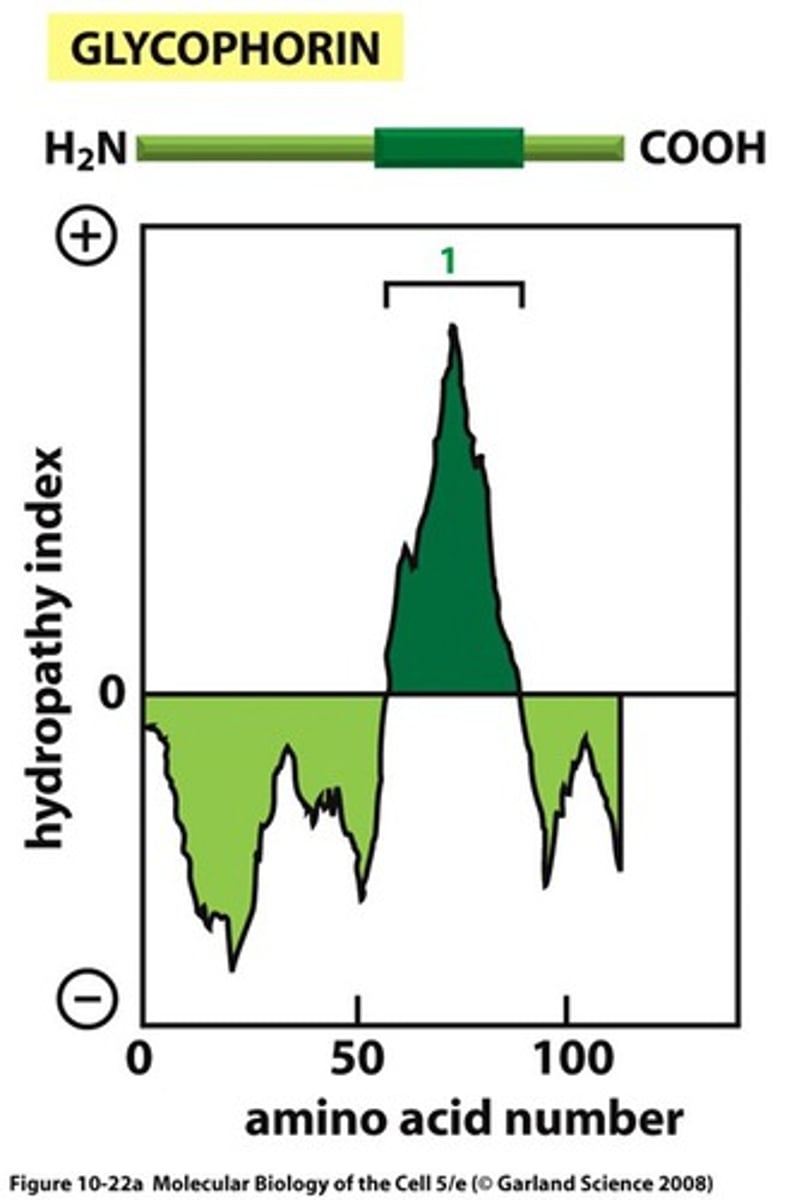
What are hydrophobicity plots?
scans 20-30 hydrophobic amino acids & checks their hydrophobicity
- to find single/multipass proteins
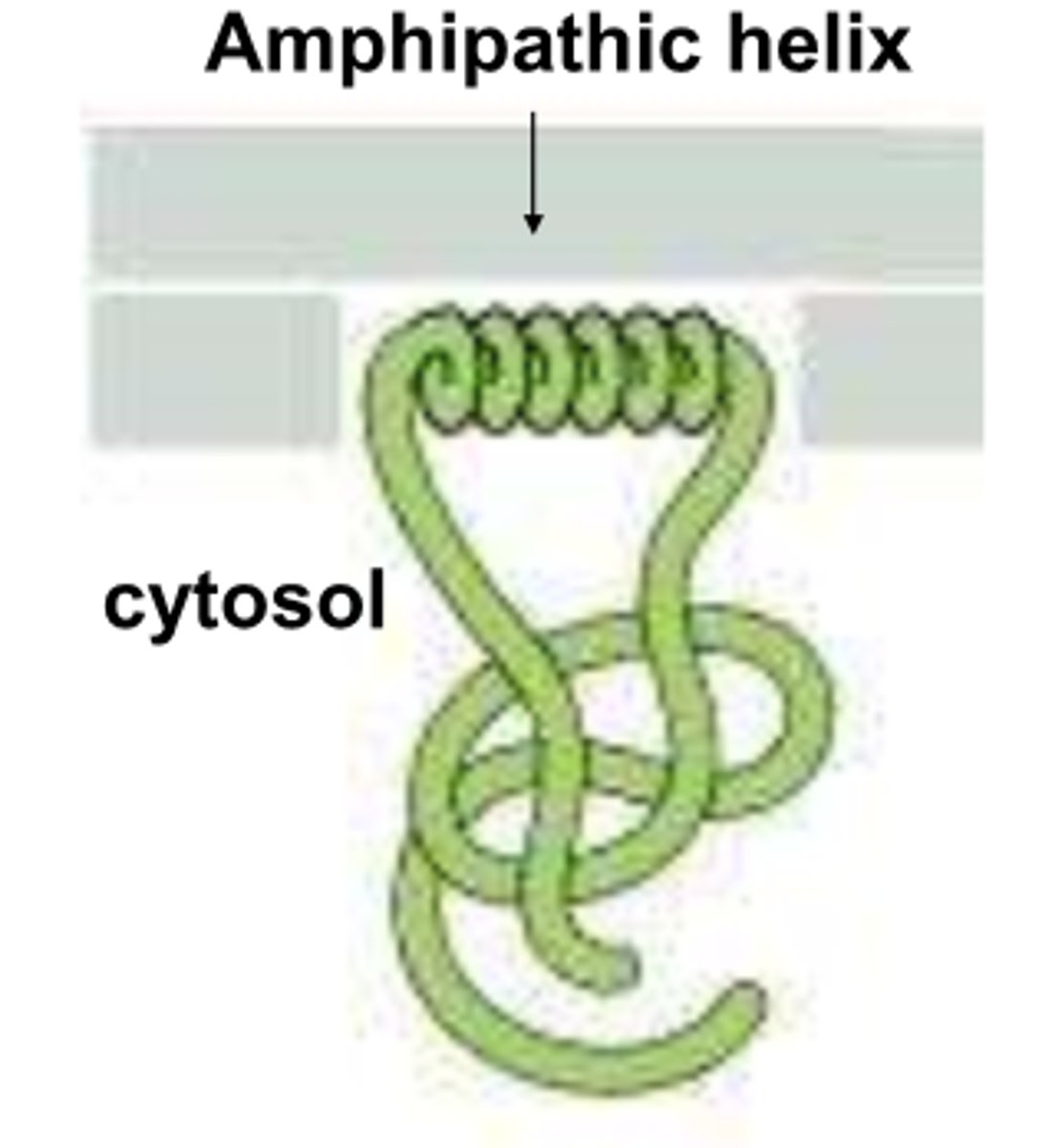
How do monolayer-associated proteins work?
amphipathic a-helix = some part inside bilayer
- only in CYTOSOL leaflet
- curves membrane = vesicle budding
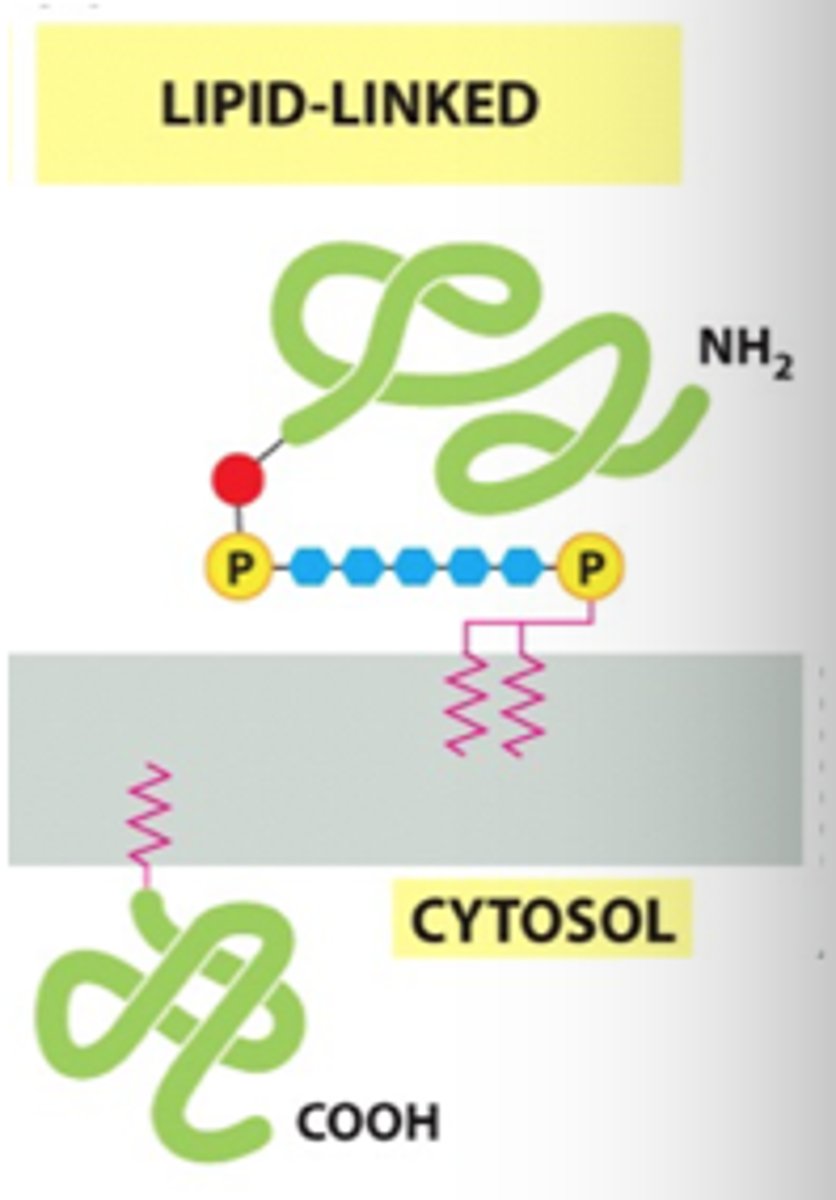
What are the 3 components of lipid-linked membrane proteins?
1. Protein
2. GPI anchor/Lipid anchor
3. Lipid
How do lipid-linked membrane proteins work?
lipid is inside bilayer while lipid/GPI anchors are outside
- GPI: in ER lumen
- Lipid anchor: in cytosol
How are integral membrane proteins extracted?
detergents = bilayer destruction

What are peripheral membrane proteins?
proteins NOT directly attached to bilayer:
bound to other proteins OR lipids
- through non-covalent interactions
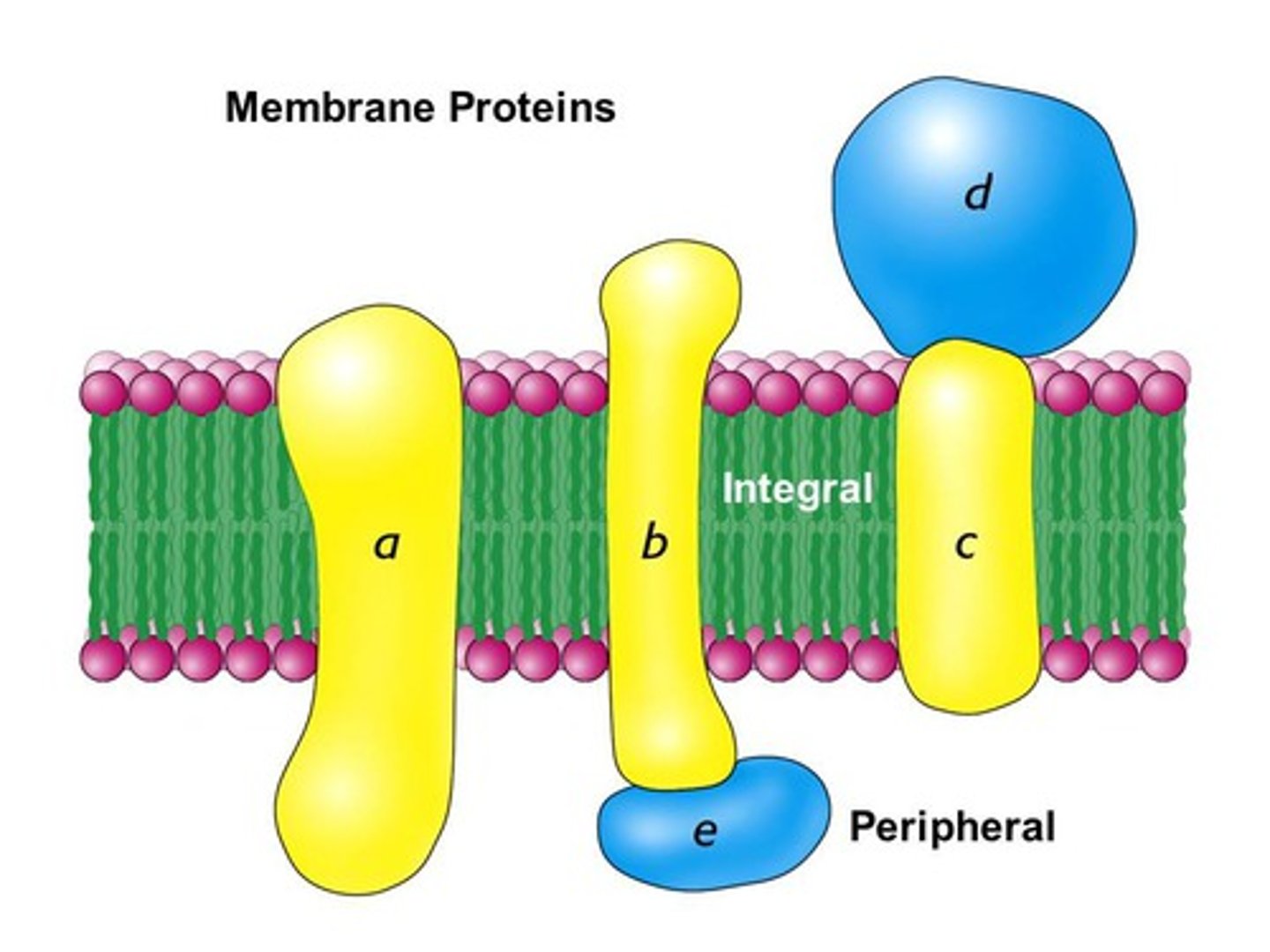
What is the 1 types of peripheral membrane proteins?
1. Protein-attached
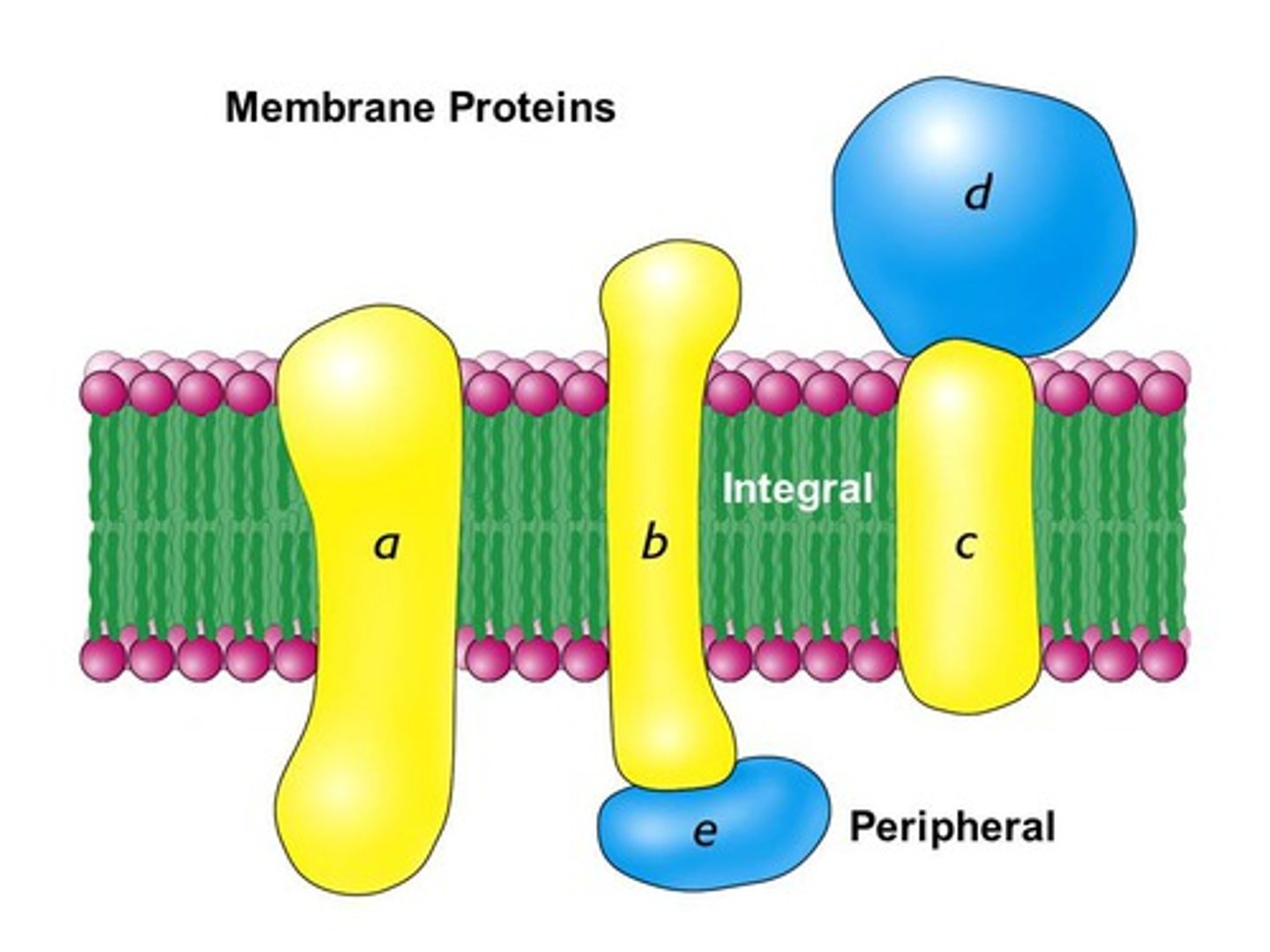
How are peripheral membrane proteins extracted?
gentle buffer = bilayer safe!
- hydrophobic and hydrophilic sides match with bilayer to denature them
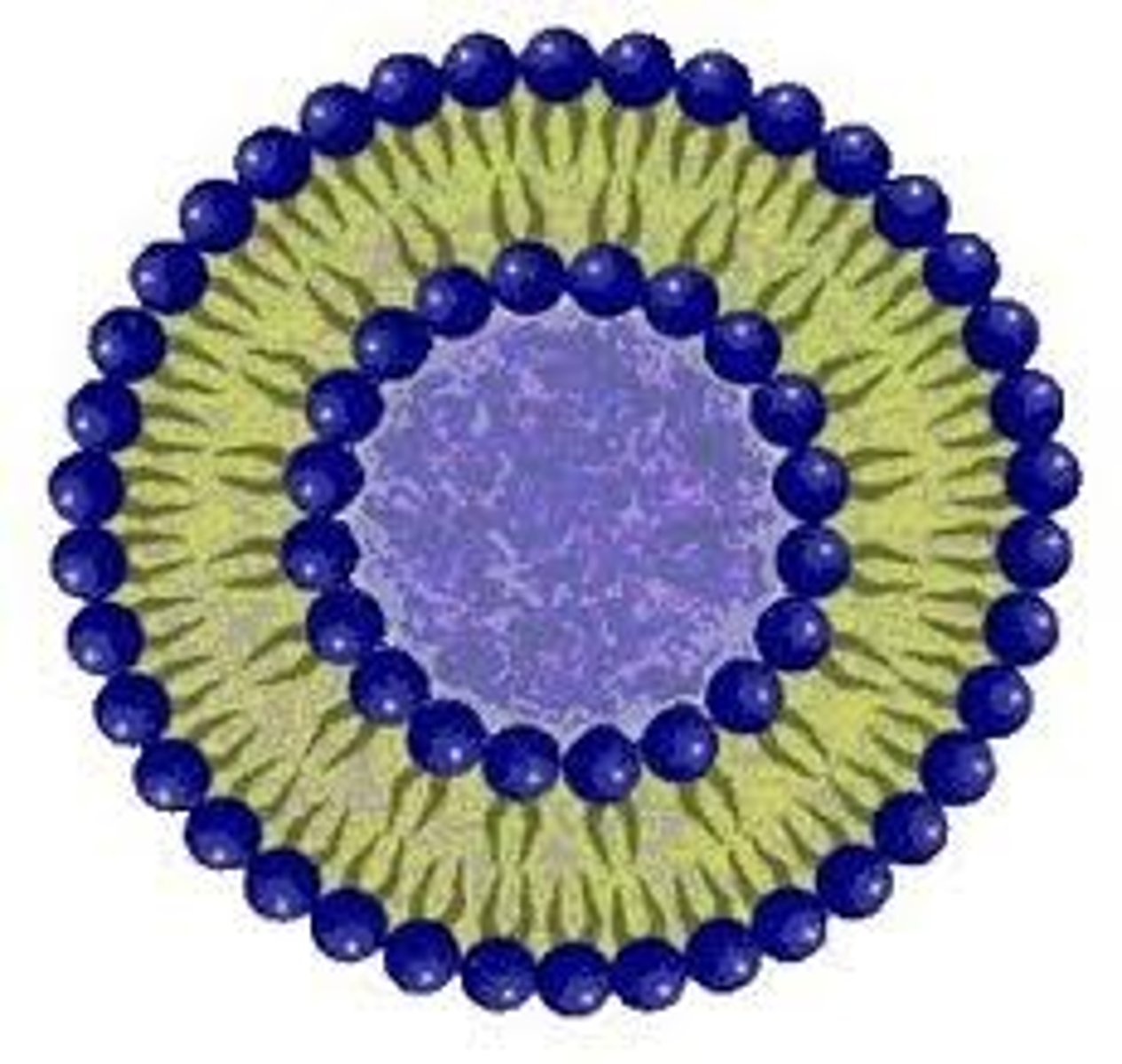
What are the 3 steps to create a liposome?
1. Purification: addition of detergent
2. Addition of phospholipids (mixed w detergent)
3. Removal of detergent
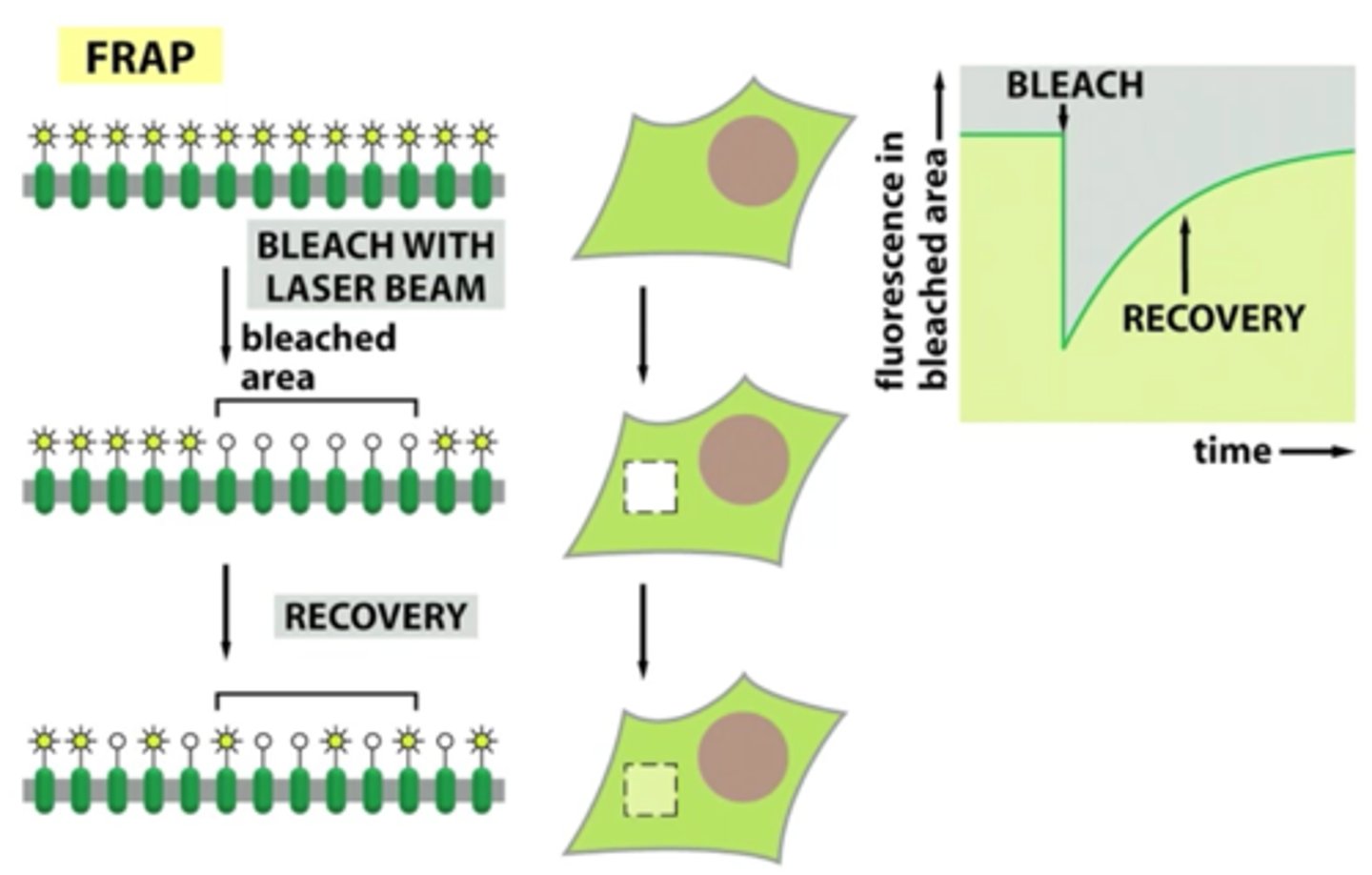
What process is used to study protein movement?
FRAP: Fluorescence Recovery After Photobleaching
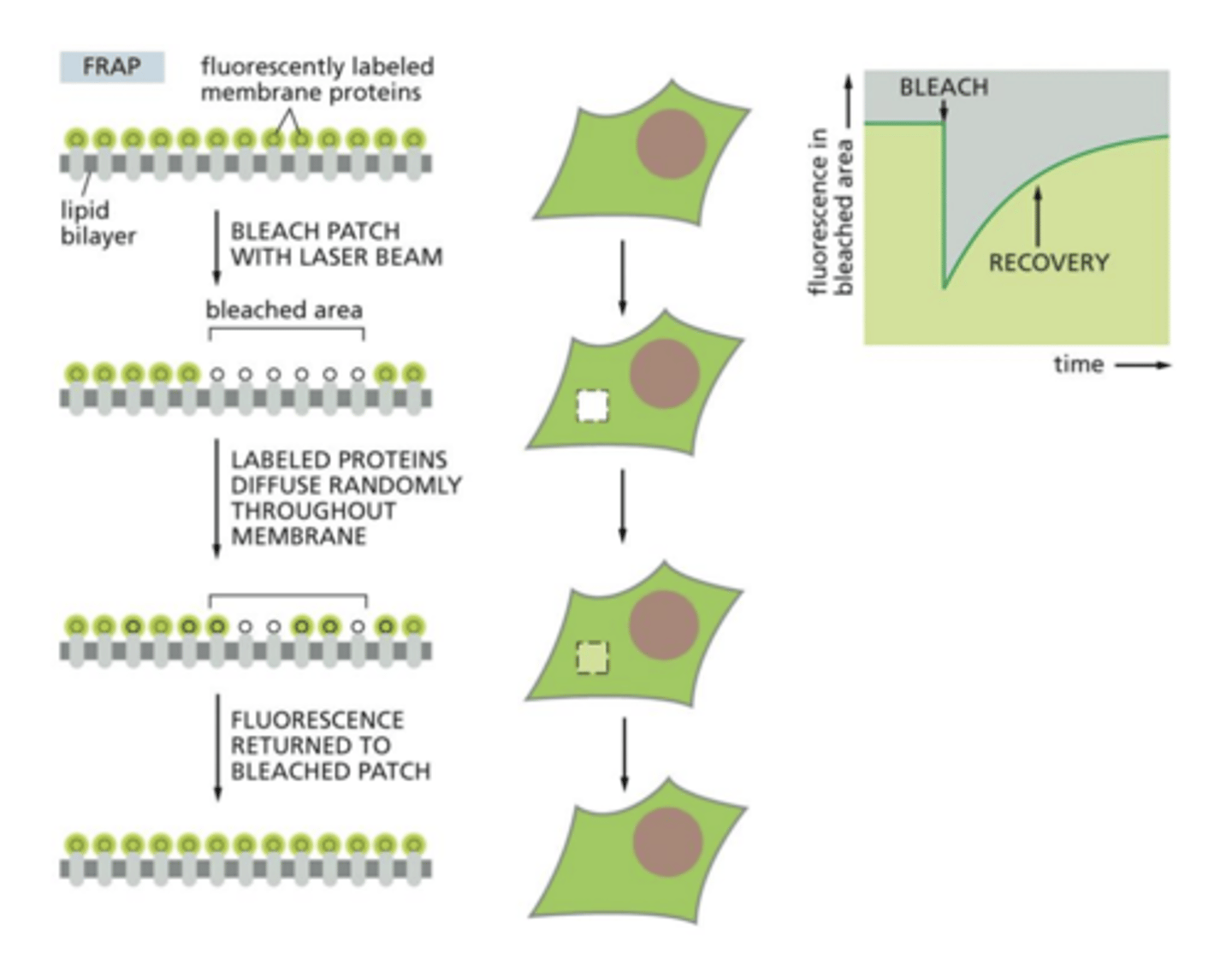
How does FRAP work?
transmembrane proteins are marked green by GFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) then a patch of the bilayer is bleached white
- movement = recovered green
- no movement = white spot remains
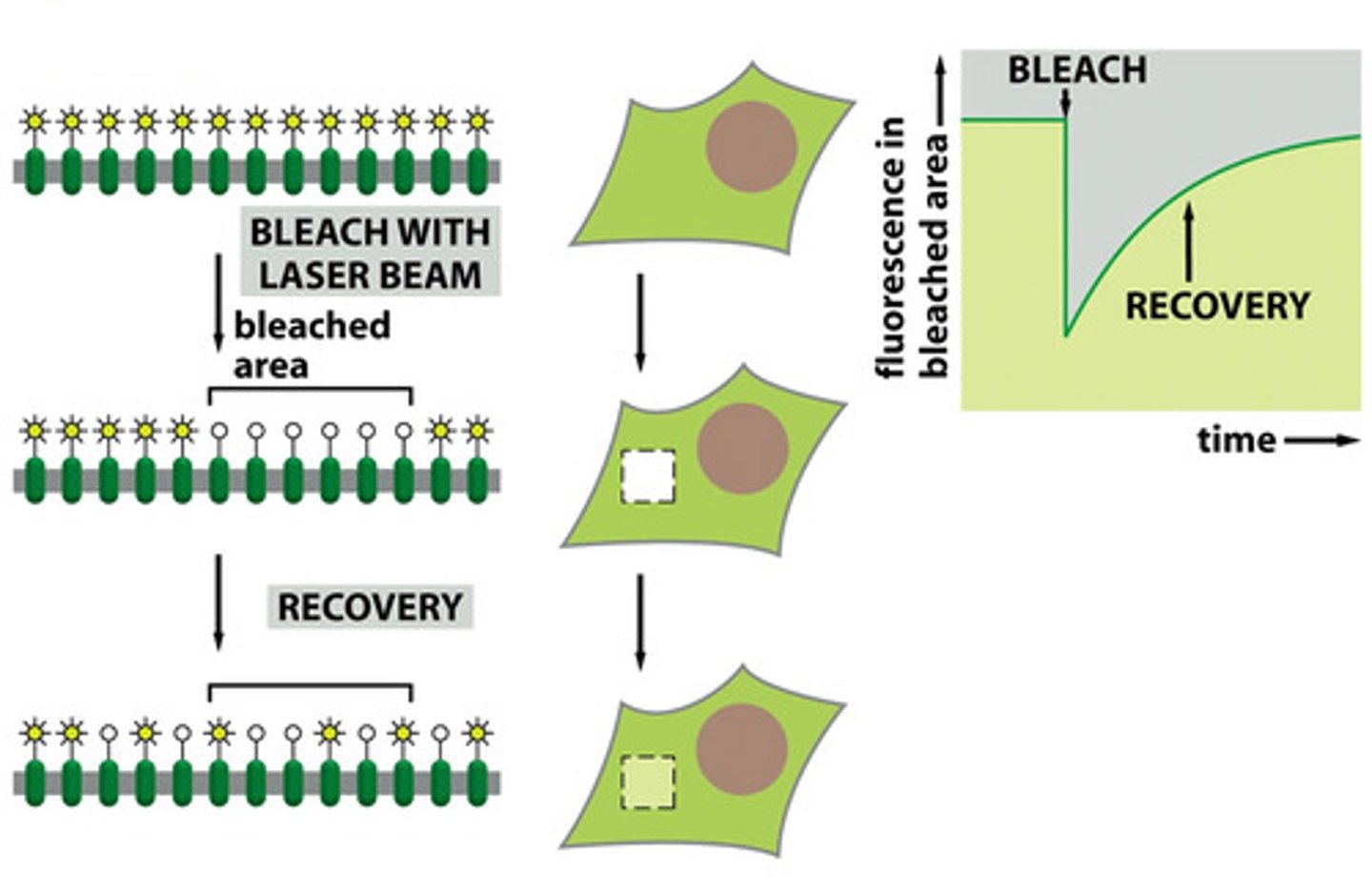
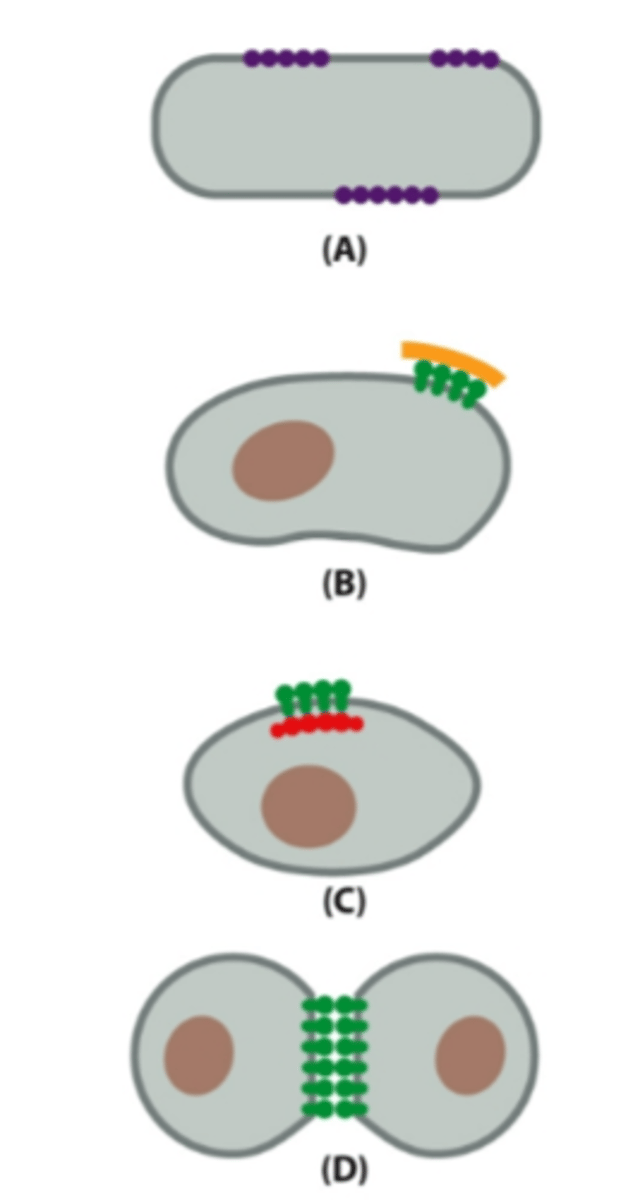
What 2 things can restrict lateral diffusion/movement?
1. Binding to other structures
2. Barriers
What is the rate of fluorescence recovery?
time it takes for green proteins to take over bleached area