CH 4 CNS DRUGS PART 1
1/70
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Overview CNS Drugs and Antipsychotics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
CNS
it includes everything in the brain and areas which are outside the autonomic nervous system
DRUGS AFFECTING THE CNS
antipsychotics, sedative, anxiolytics, antidepressants, anti-seizures, anesthetic agents, and central dopaminergic signaling agents
2 TYPES OF ANTIPSYCHOTICS
typical and atypical
TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
classical, traditional, 1st generation (has side effects)
ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
2nd generation, lesser side effects
ANTI-SEIZURES
may also include anti-Parkinsons
2 TYPES OF ANESTHETIC AGENTS
local and general
LOCAL ANESTHETIC AGENT
used for wounds, minor surgery (eg. dental), stitches
GENERAL ANESTHETIC AGENT
used in surgical operations
CENTRAL DOPAMINERGIC SIGNALING AGENTS
either block or nagiinduce (eg. GABA, 5HT [serotonin])
PSYCHOSES
one of the most severe mental illnesses, symptoms: delusions and hallucinations, with anxiety disorders; inability to comprehend reality with mood, thought, and behavioral dysfunction
PSYCHOSES COMMON DISORDERS
delirium and dementia; schizophrenia & other psychotic illnesses, and manic phase of manic-depressive disorder
DELUSIONS
extreme sense of false belief (eg. paranoia)
SENSORY HALLUCINATIONS
most common is auditory hallucinations
DELIRIUM
hallucination but more on visionary things (not FDA approved indication)
SCHIZOPHRENIA
described as having a clear sensorium but with marked thinking disorder
2 SETS OF SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
positive and negative
POSITIVE SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized speech
NEGATIVE SYMPTOMS OF SCHIZOPHRENIA
flat affect (very low emotional response), apathy
[ less common, mas mahirap itreat ]
SCHIZOPHRENIA PRIMARY HYPOTHESIS FOR ETIOLOGY
very high levels of dopaminergic transmission
[ drugs usually target/block D2-type dopamine receptors ]
PHENOTHIAZINES & BUTYROPHENONES
typical antipsychotics
MOA OF TYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
direct interaction with D2-type receptors;
combines inverse agonist, antagonist, partial agonist acitvity to provide spectrum of effects
EPS
extrapyramidal syndrome
EPS of PHENOTHIAZINES & BUTYROPHENONES
dystonia (spasms), akathisia (motor restlessness), parkinsonian effect, and tardive dyskinesia (irregular jerking movement)
PHENOTHIAZINES: trans alpha-rotamer conformation
D2-type receptor binding
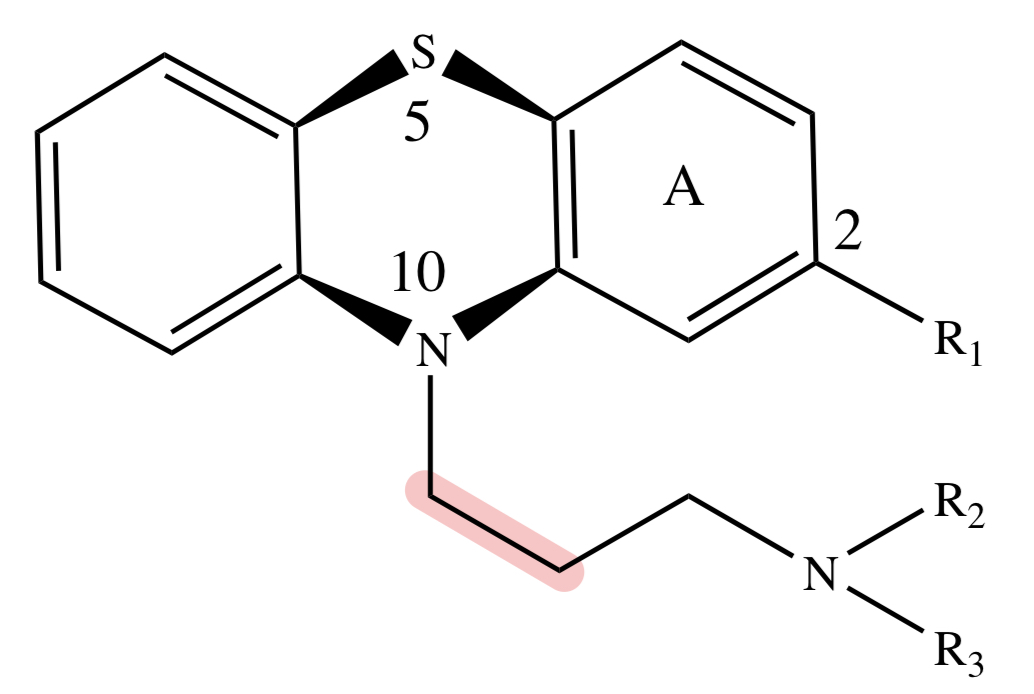
PHENOTHIAZINES: N-atoms on the ring and side chain
essential for antipsychotic action; must be separated by 3 carbons
PHENOTHIAZINE W 2 CARBONS
used as an antihistamine/sedative action [ Promethazine (Phenergan) ]
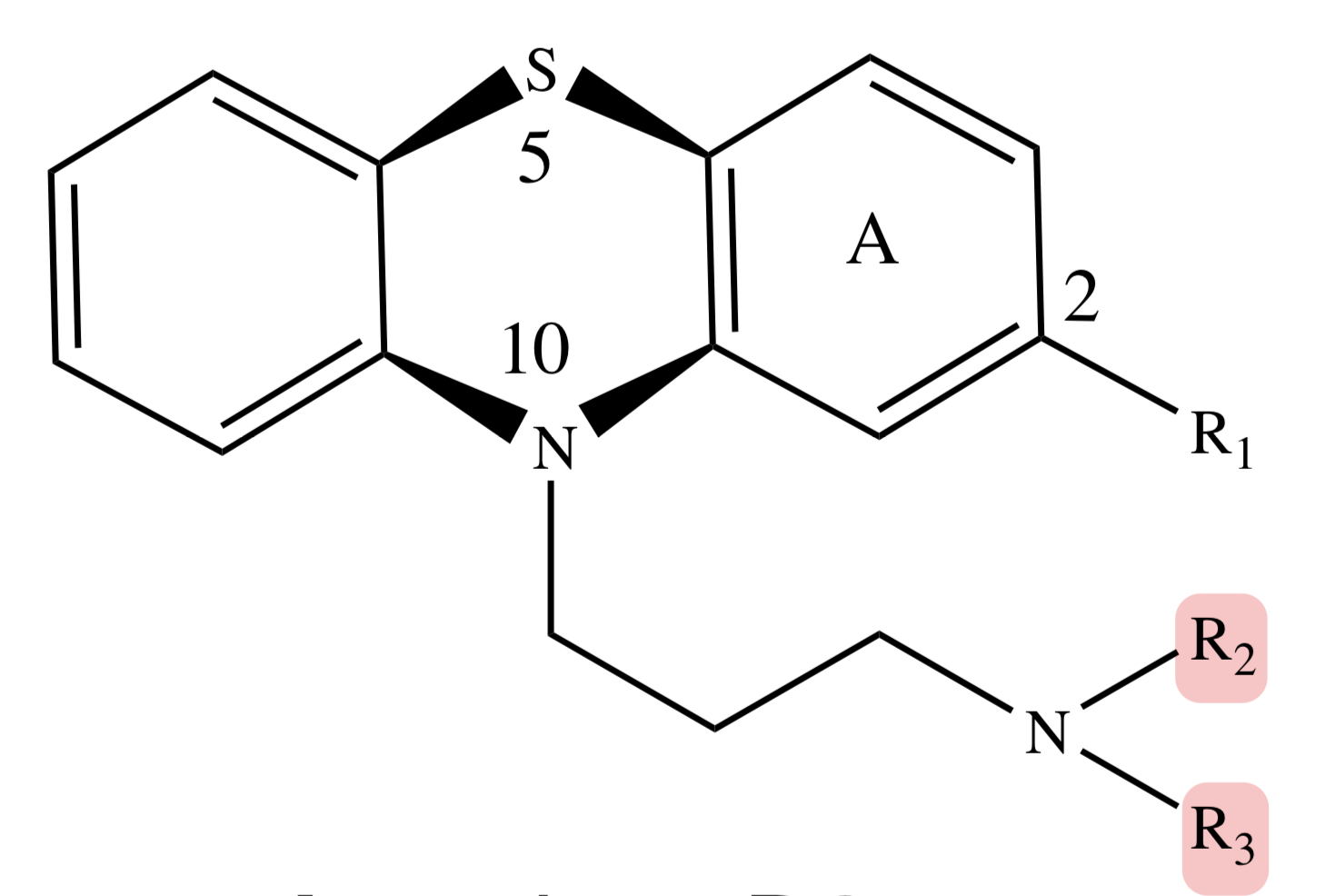
PHENOTHIAZINE: side chains (R2 and R3)
can be aliphatic aminopropyl, piperidine ring, or piperazine ring (highest potency and activity)
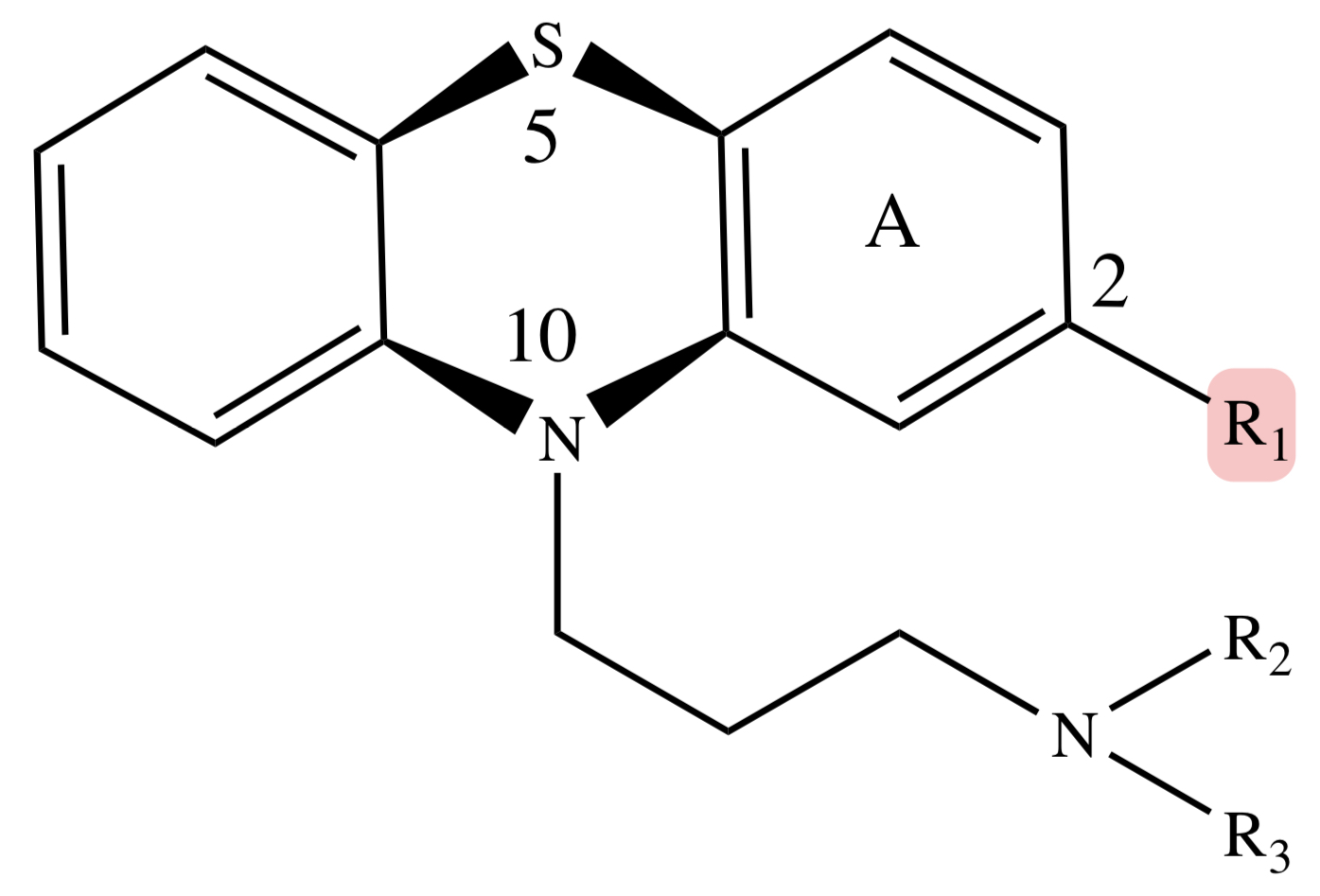
PHENOTHIAZINE: C2 (R1)
must have an electronegative atom or electron-withdrawing group — essential to activity
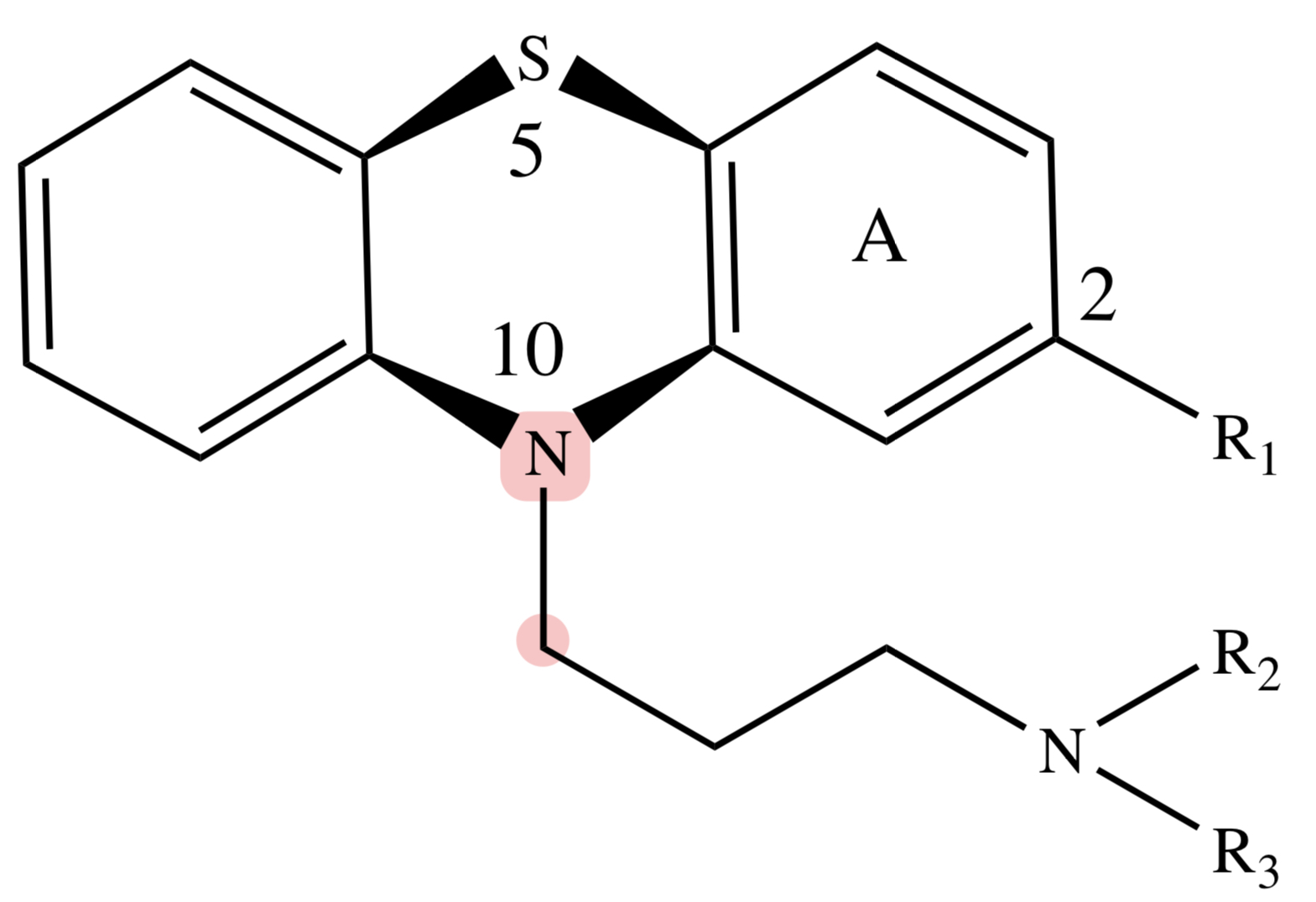
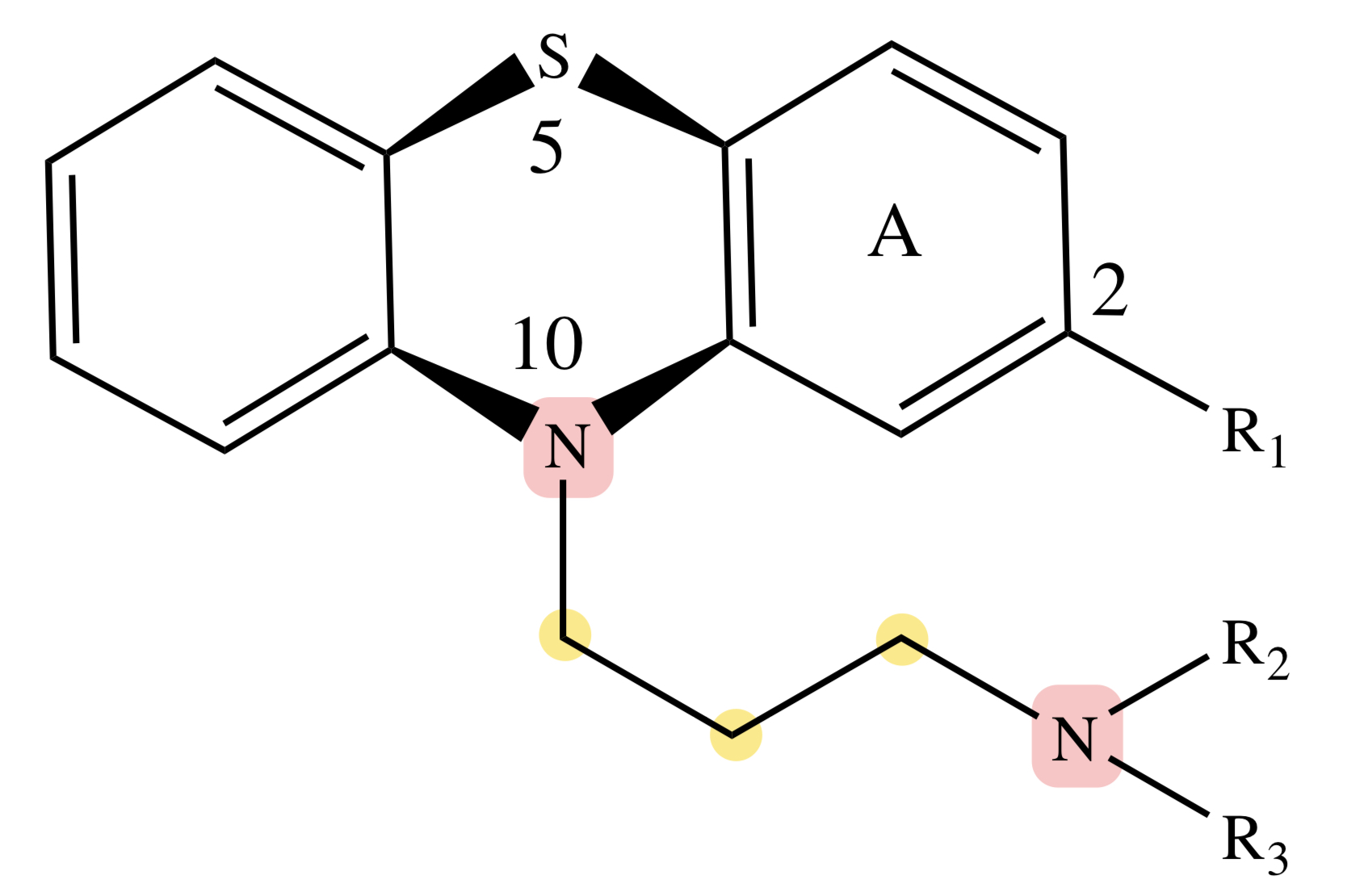
PHENOTHIAZINE: N10-C11
can be replaced with C=C (in cis form) for greater activity (eg. thiothixene)
PHENOTHIAZINE: free -OH in the side chain moiety
(eg. fluphenazine) can yield stable, lipophilic ester with longer DOA
-AZINE; -PERIDOL
what typical phenothiazine antipsychotics usually end with
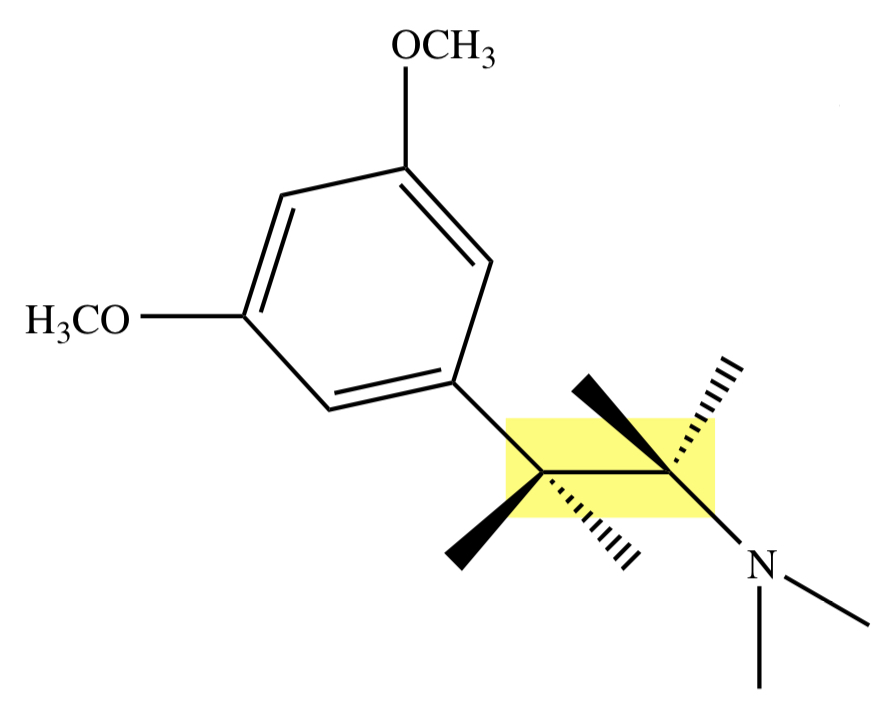
PHENOTHIAZINE: DOPAMINE
trans alpha-rotamer
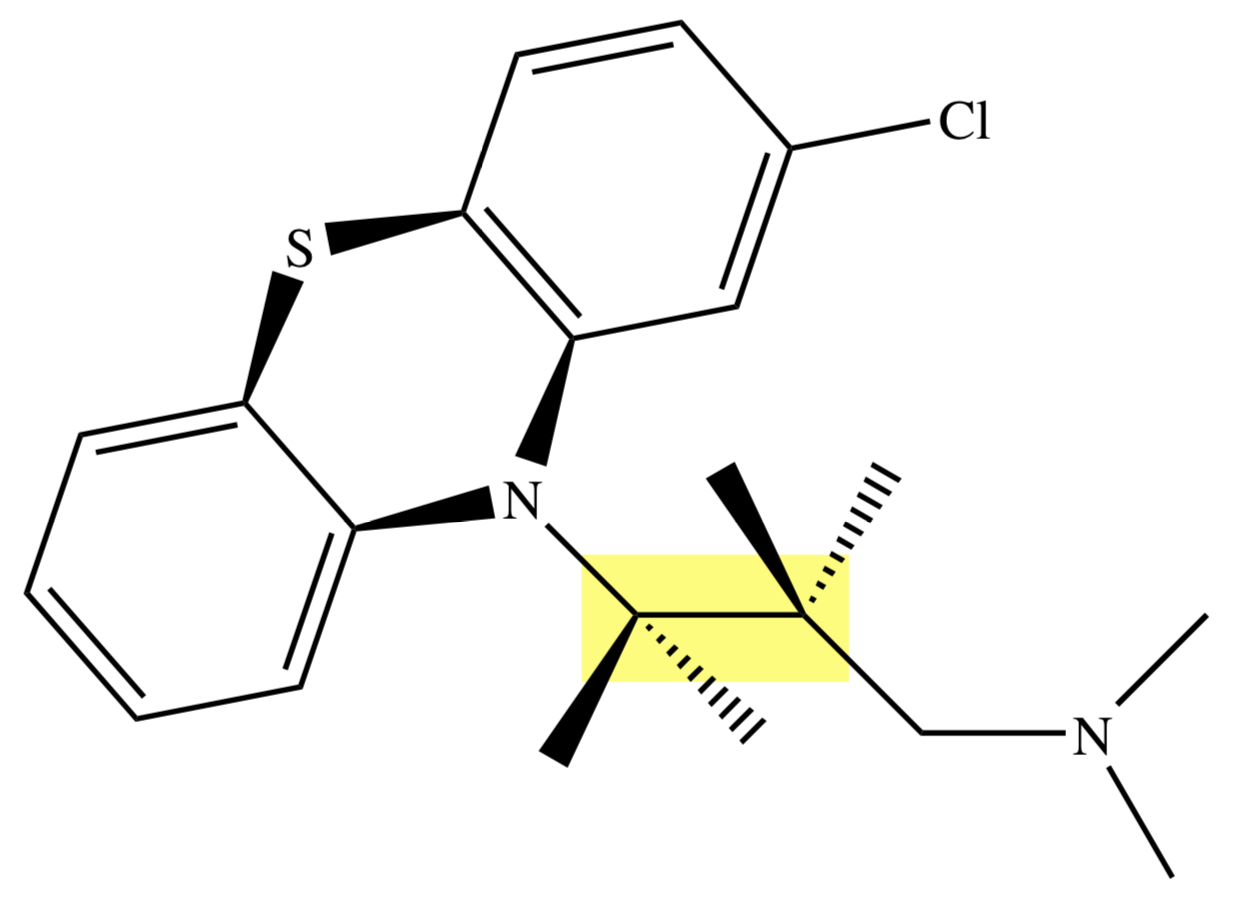
PHENOTHIAZINE: CHLORPROMAZINE
protoype phenothiazine;
aliphatic aminopropyl side chain
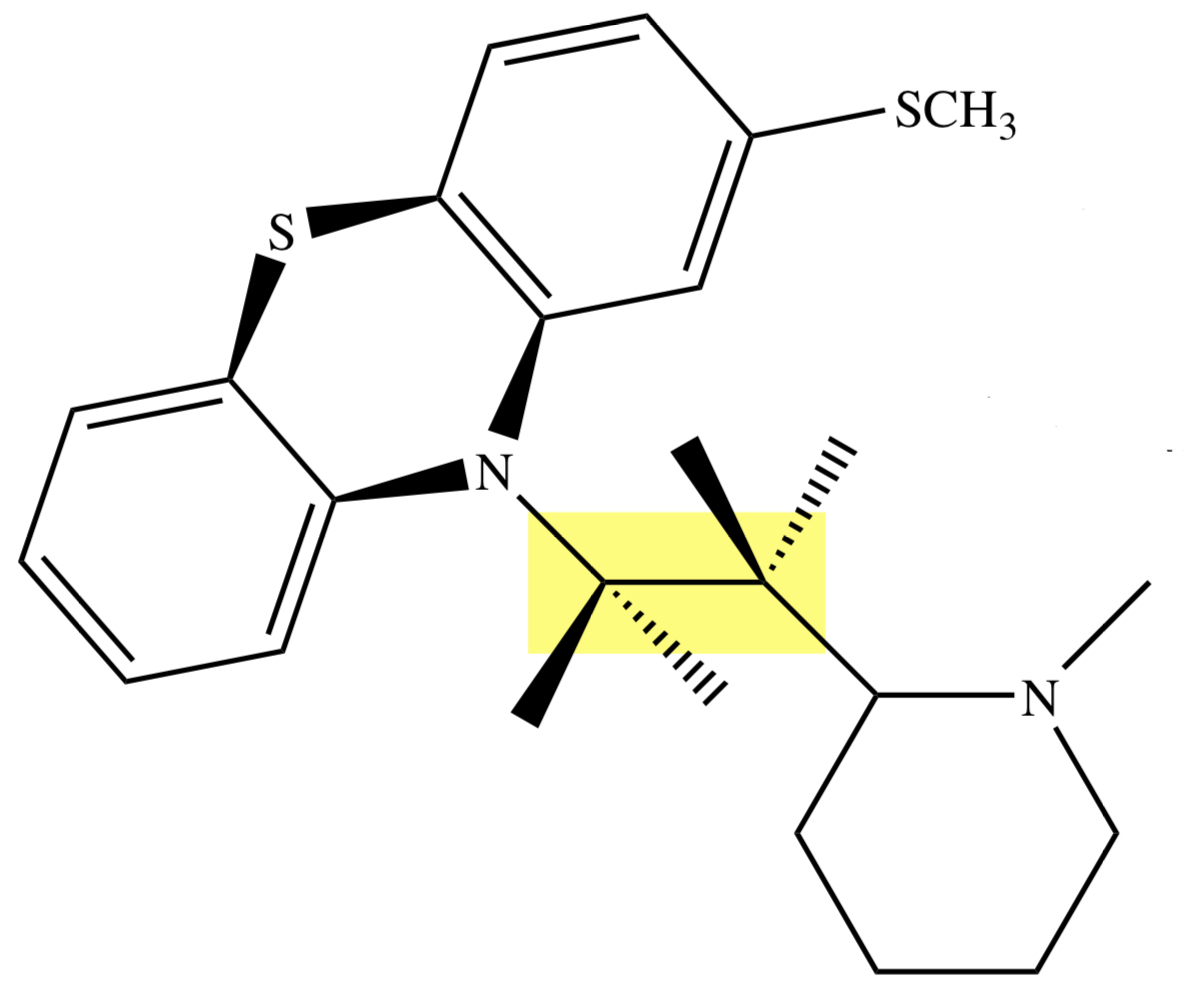
PHENOTHIAZINE: THIORIDAZINE
methylthio (R1);
piperidine phenothiazine
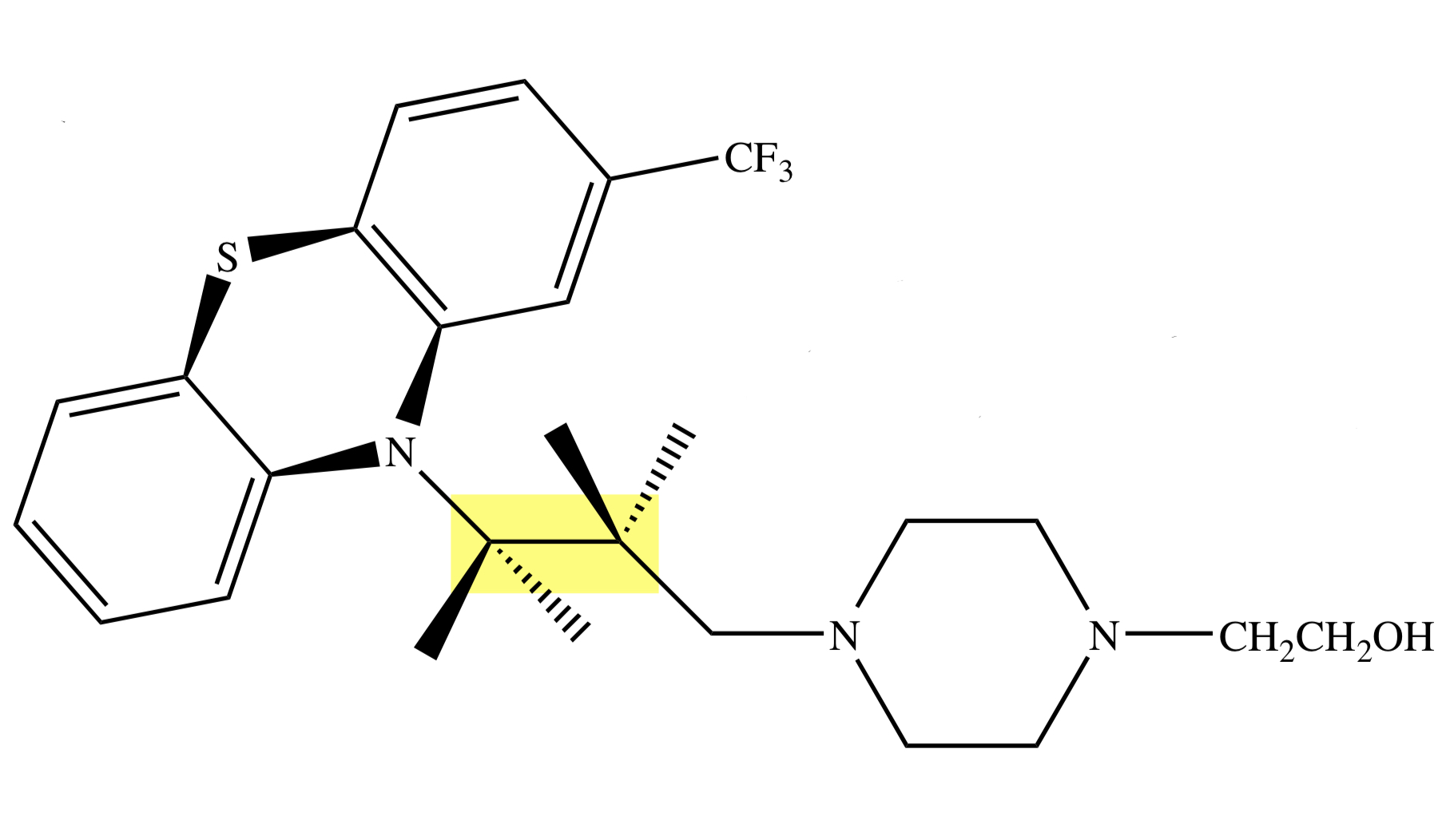
PHENOTHIAZINE: FLUPHENAZINE
-OH side chain moiety;
piperazine phenothiazine
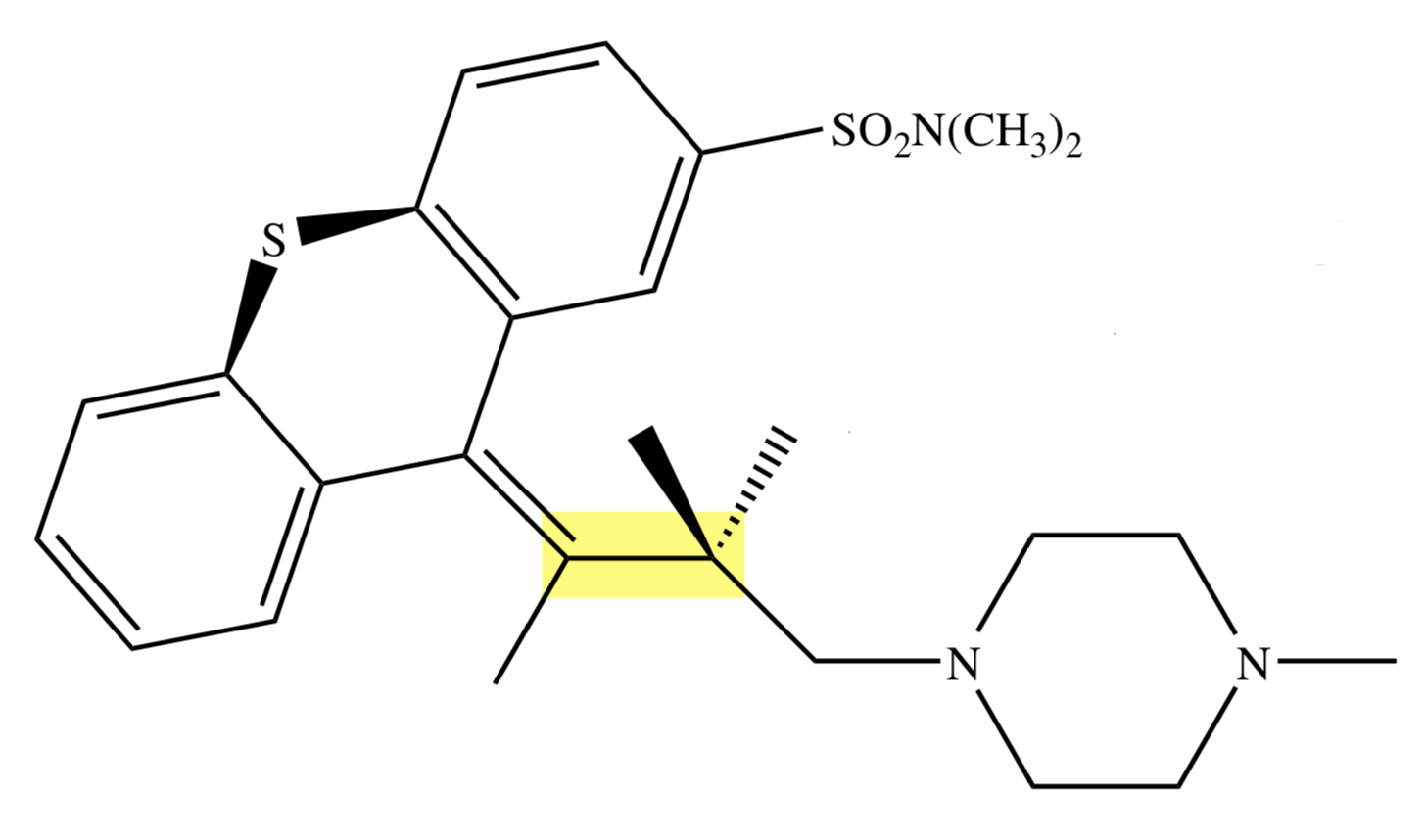
PHENOTHIAZINE: THIOTHIXENE
C10-11 double bond;
piperazine phenothiazine
PHARMACOLOGIC PROFILES: Antipsychotic Potency & EPS Frequency
Piperazines > Piperidines > Aliphatics
PHARMACOLOGIC PROFILES: Sedation
Aliphatics = Piperidines > Piperazines
PHARMACOLOGIC PROFILES: Hypotension
Aliphatics > Piperidines > Piperazines
PHENOTHIAZINES: Metabolism
N-dealkylation, Aromatic hydroxylation at C7, S-oxidation, Ester hydrolysis (only for Fluphenazine), CYP 3A4 (for Pimozide)
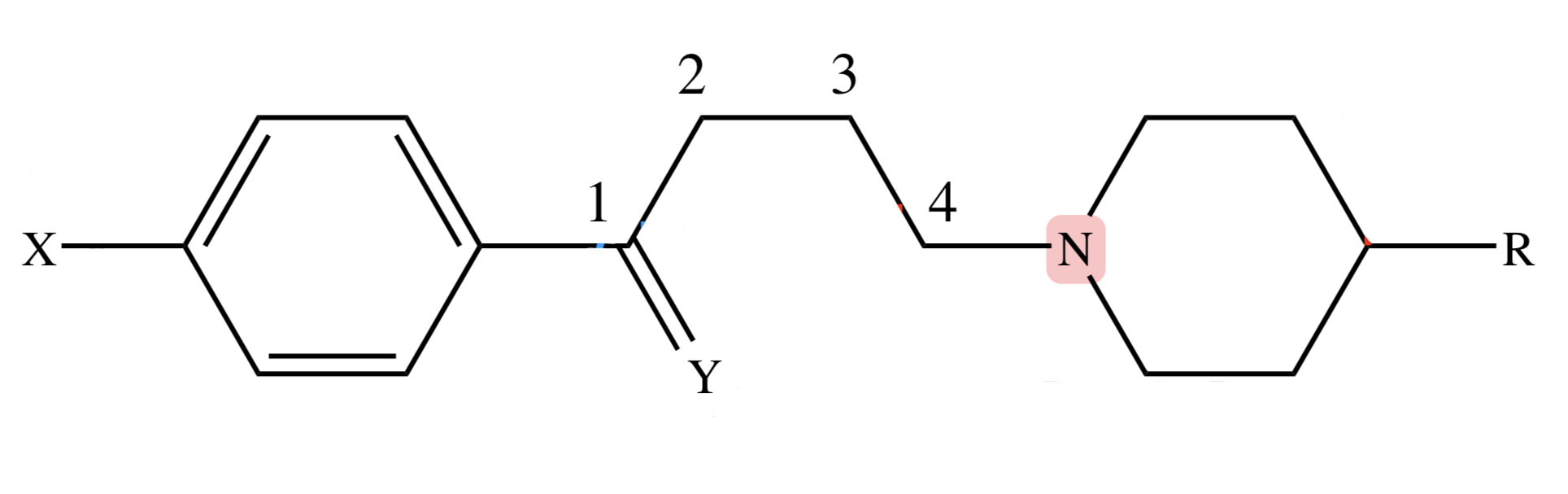
BUTYROPHENONES: C4 Tertiary Amino (C4 3* N) of the skeleton
essential for activity
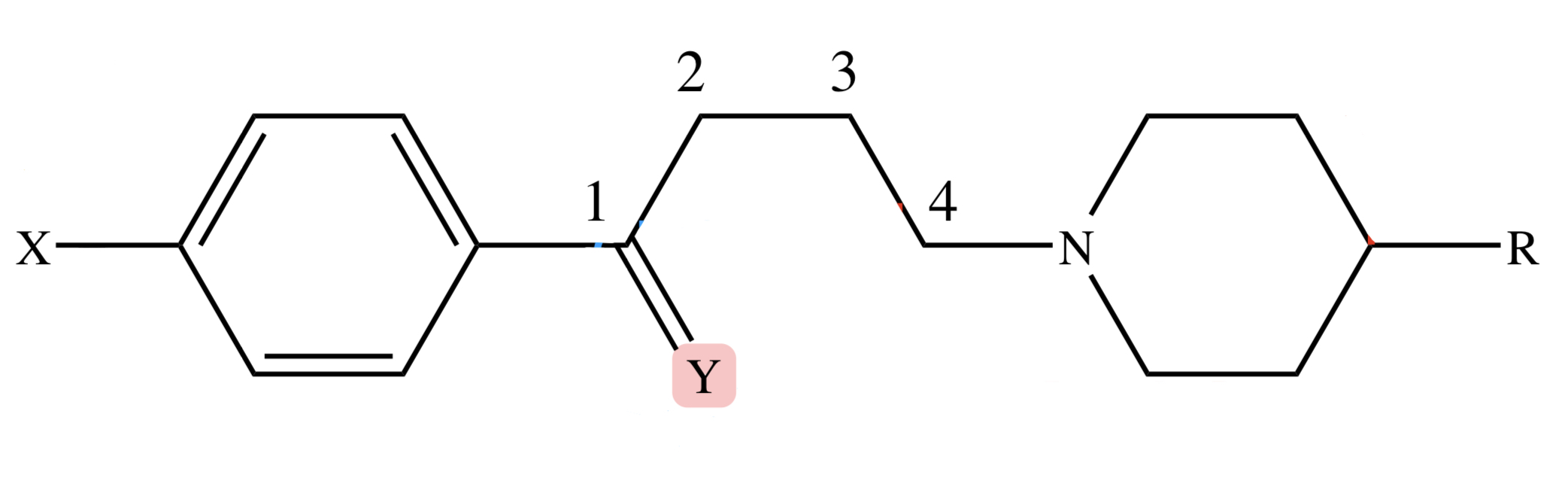
BUTYROPHENONES: Y (Carbonyl) position replaced with: thioketone, olefinic, phenoxy or reduction
decrease potency
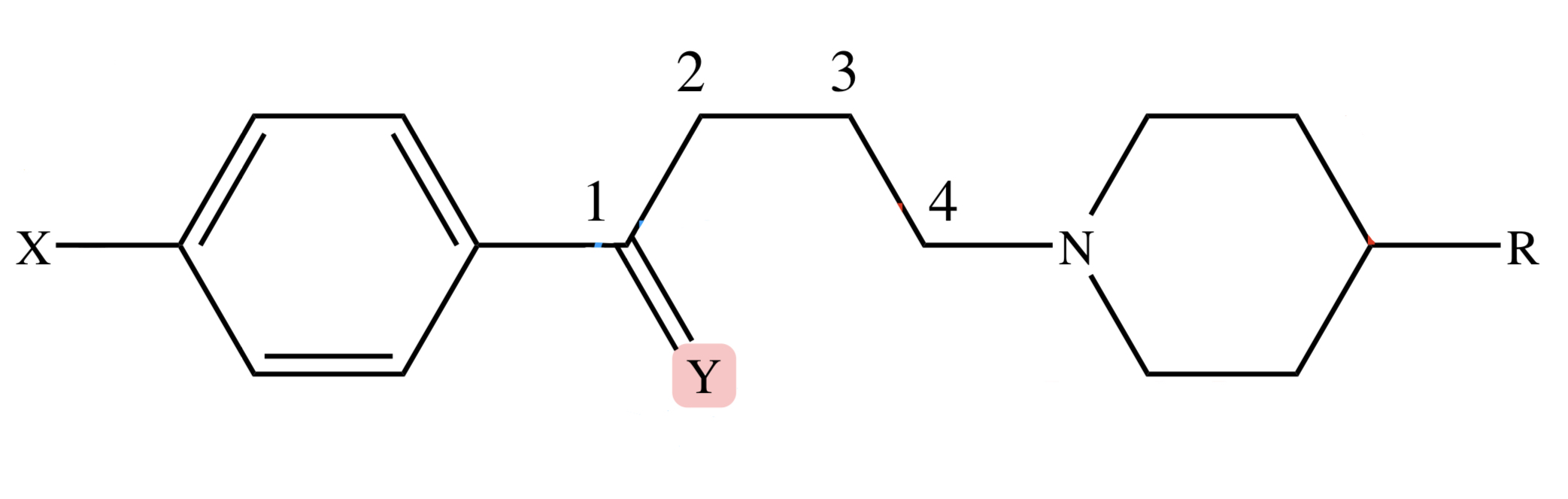
BUTYROPHENONES: Y (Carbonyl) position replaced with: 4-fluorophenyl
increase potency
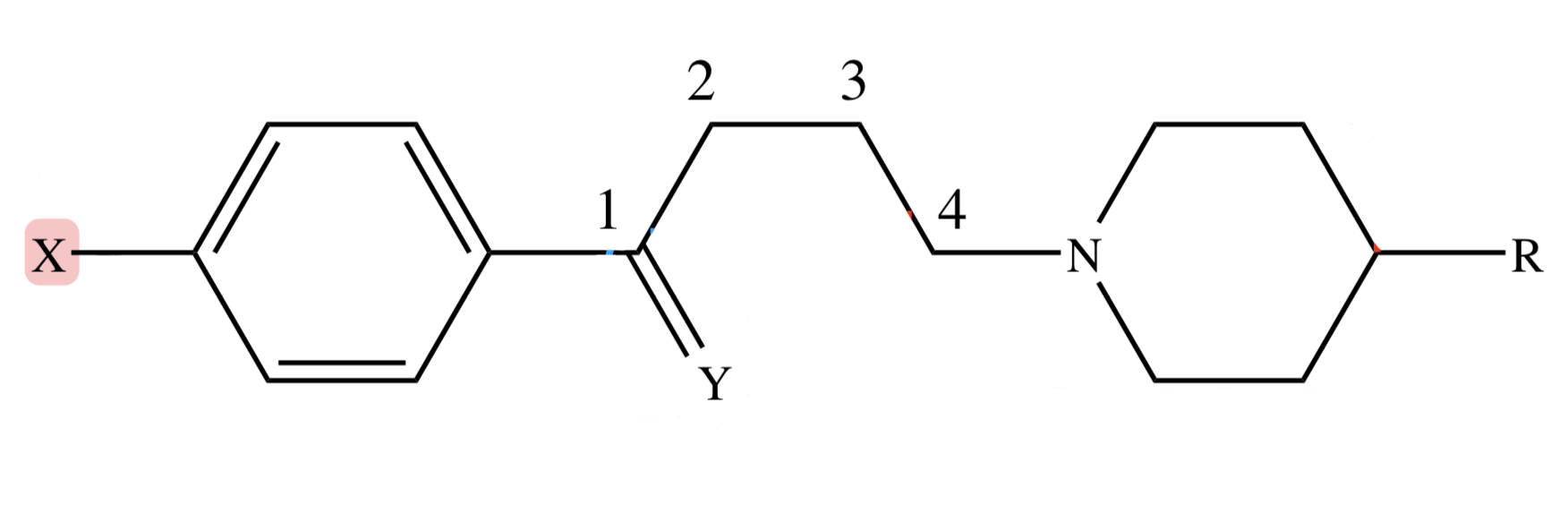
BUTYROPHENONES: X position replaced with -F at -para position of benzene
maximum potency
-PERIDOL; -PERIDONE
what typical butyrophenone antipsychotics usually end with
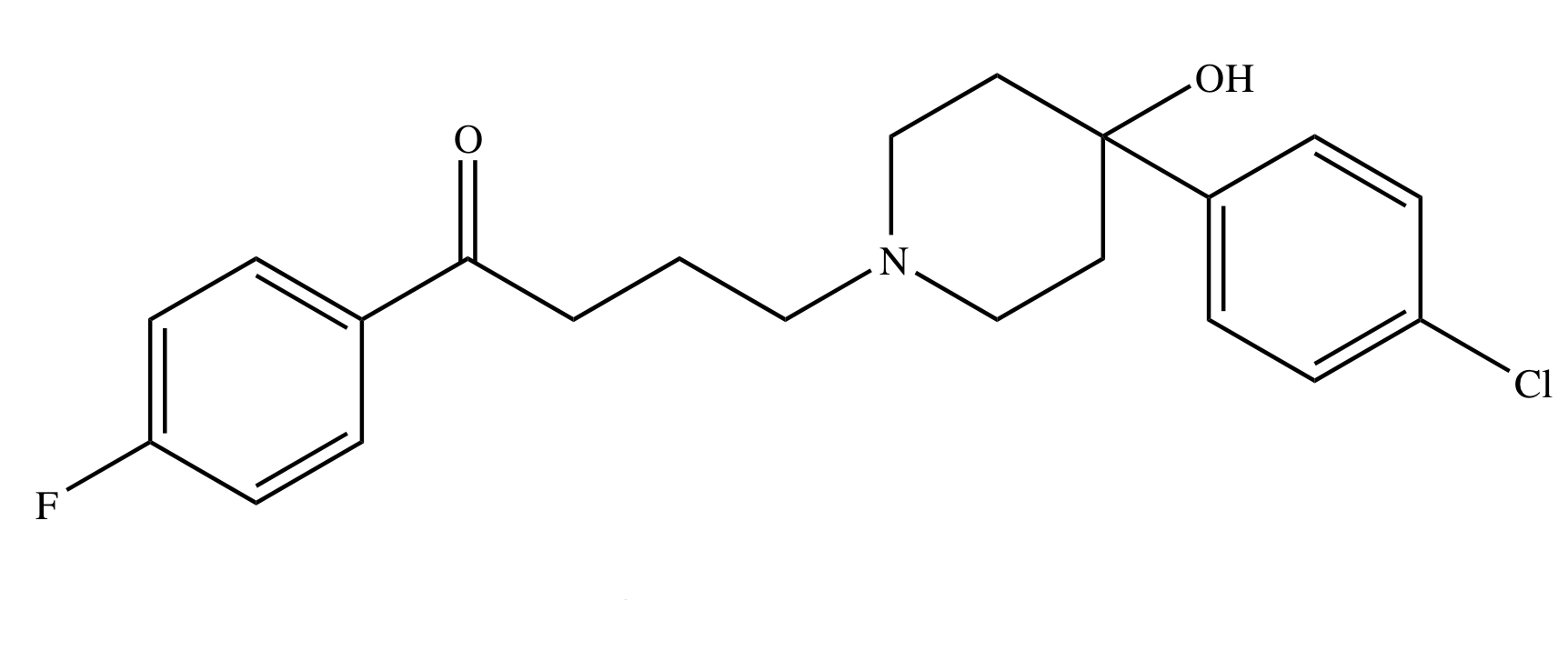
BUTYROPHENONE: HALOPERIDOL
prototype butyrophenone
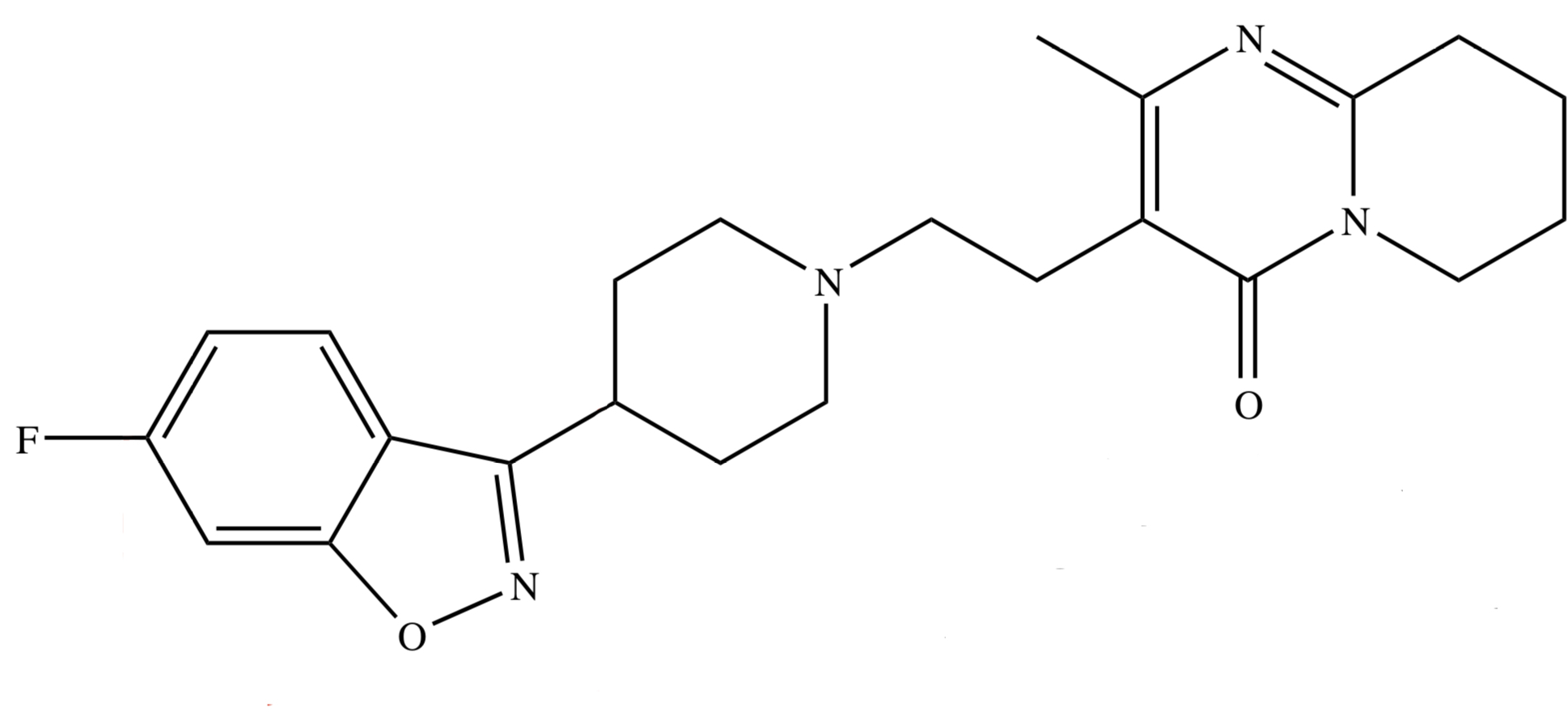
BUTYROPHENONE: RISPERIDONE
has benzisoxazole ring; di directly attached yung F
[ treats positive & negative symptoms of Schizophrenia ]
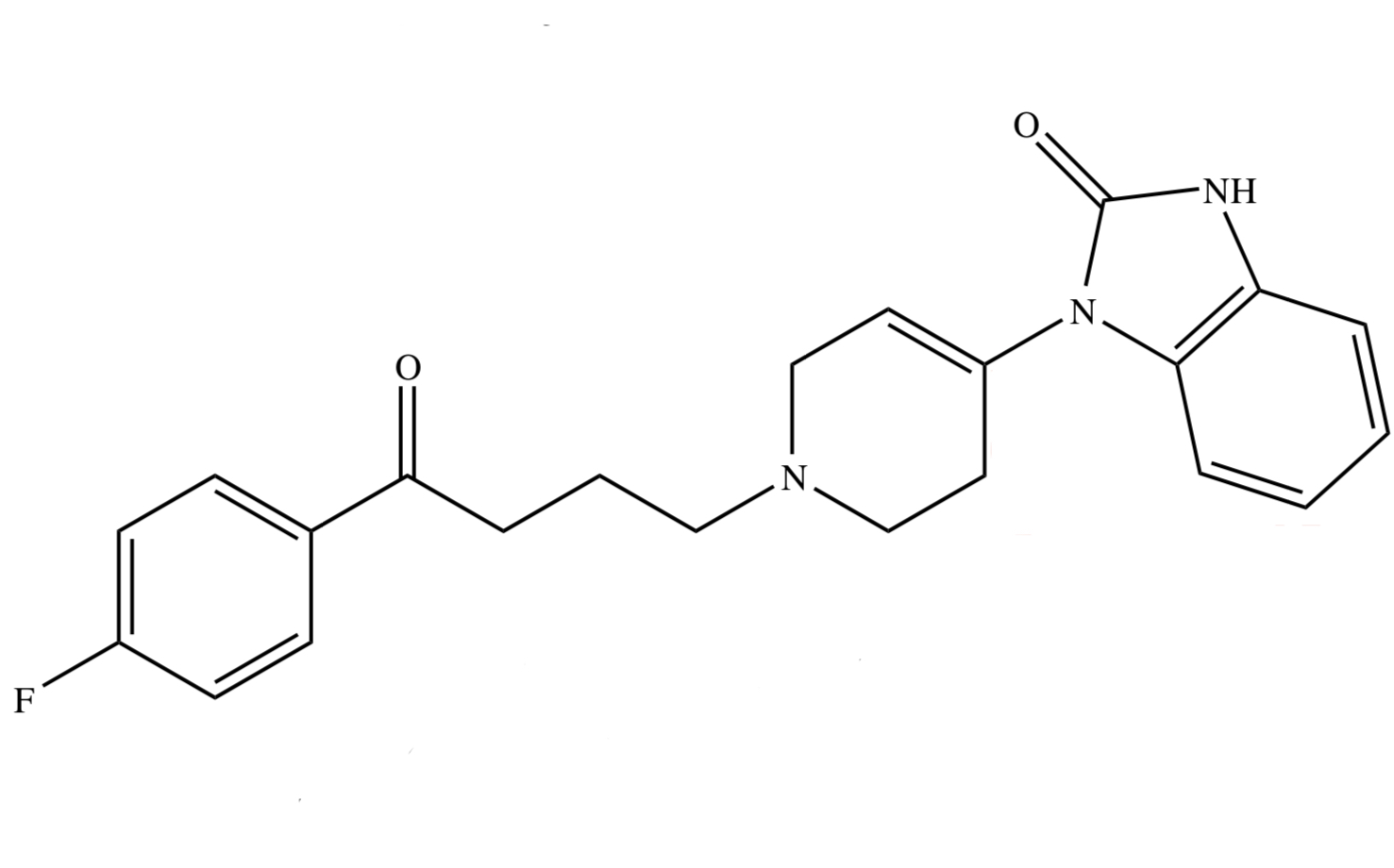
BUTYROPHENONE: DROPERIDOL
has benzimidazoline ring;
[ used as preanesthetic neuroleptic ]
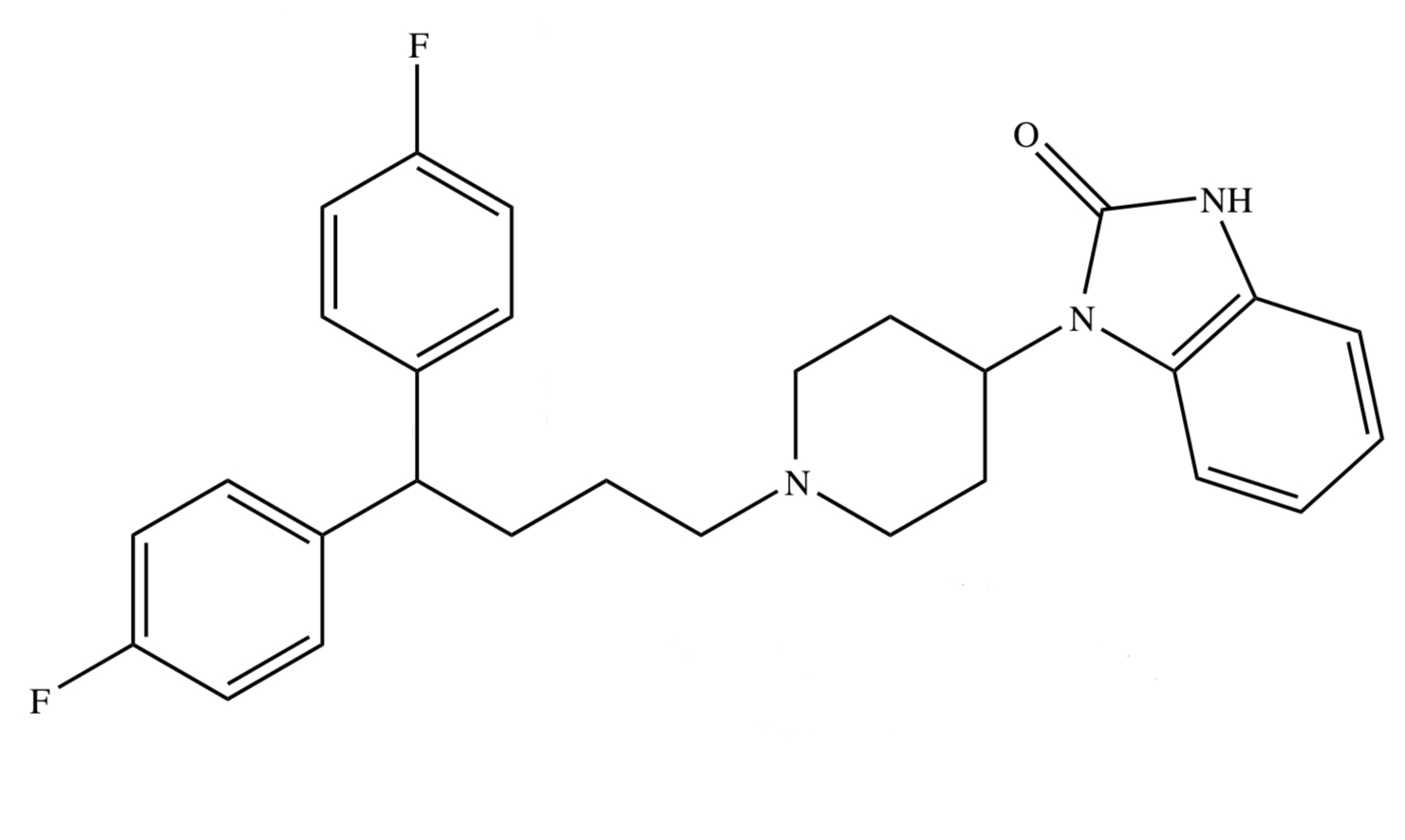
BUTYROPHENONE: PIMOZIDE
has 4-fluorophenyl ring
[ used as preanesthetic neuroleptic ]
3 ATYPICAL ANTIPSYCHOTICS
diarylazepine derivatives, benzisoxazole / benzisothiazoles, & arylpiperazine quinolinone
-XAPINE; -ZAPINE
what atypical diarylazepine derivatives antipsychotics end with
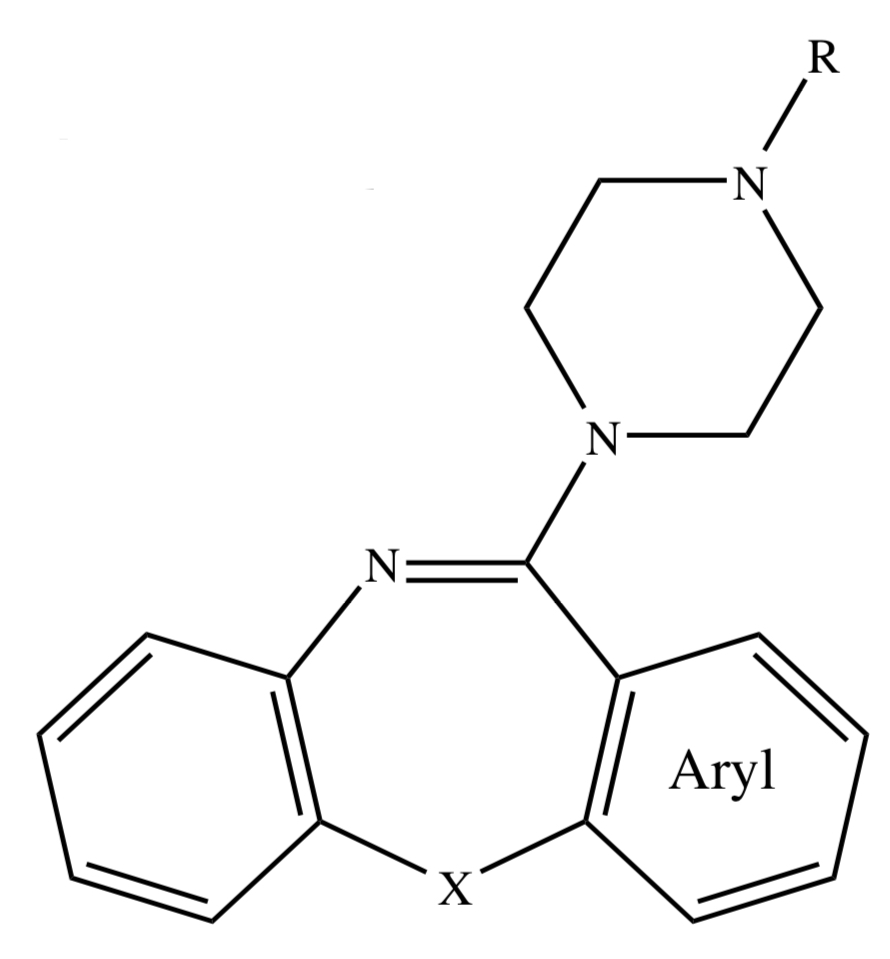
DIARYLDIAZEPINE PHARMACOPHORE
reduces positive & negative symptoms;
improves cognitive function
MOA OF DIARYLAZEPINE DERIVATIVES
direct D2-type antagonism + partial D2-type agonism;
5-HT2 receptor antagonism (reduced EPS)
DIARYLAZEPINE DERIVATIVES: Metabolism
Oxidation, N-dealkylation, Conjugation, CYP 1A2, CYP 3A4
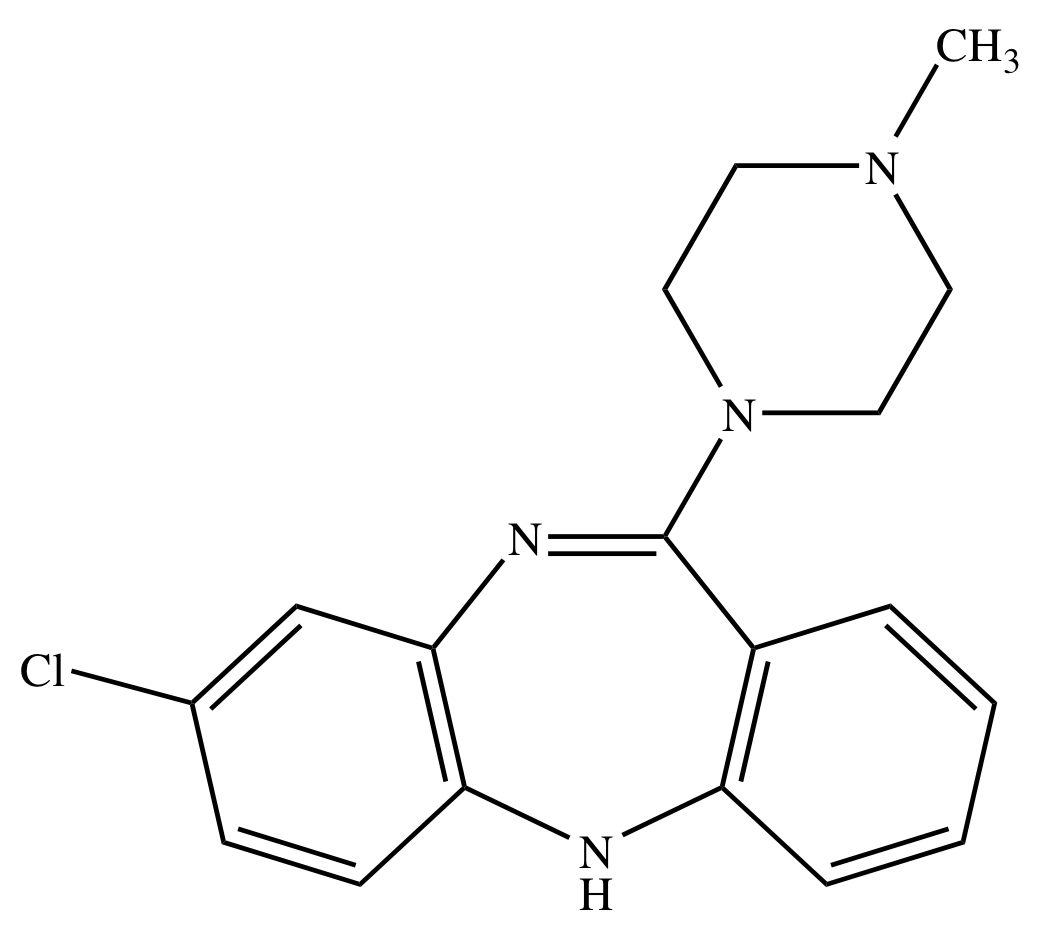
DIARYLAZEPINE DERIVATIVES: CLOZAPINE
dibenzodiazepine derivative
[ used to decrease hallucinations and helps in preventing suicide attempts ]
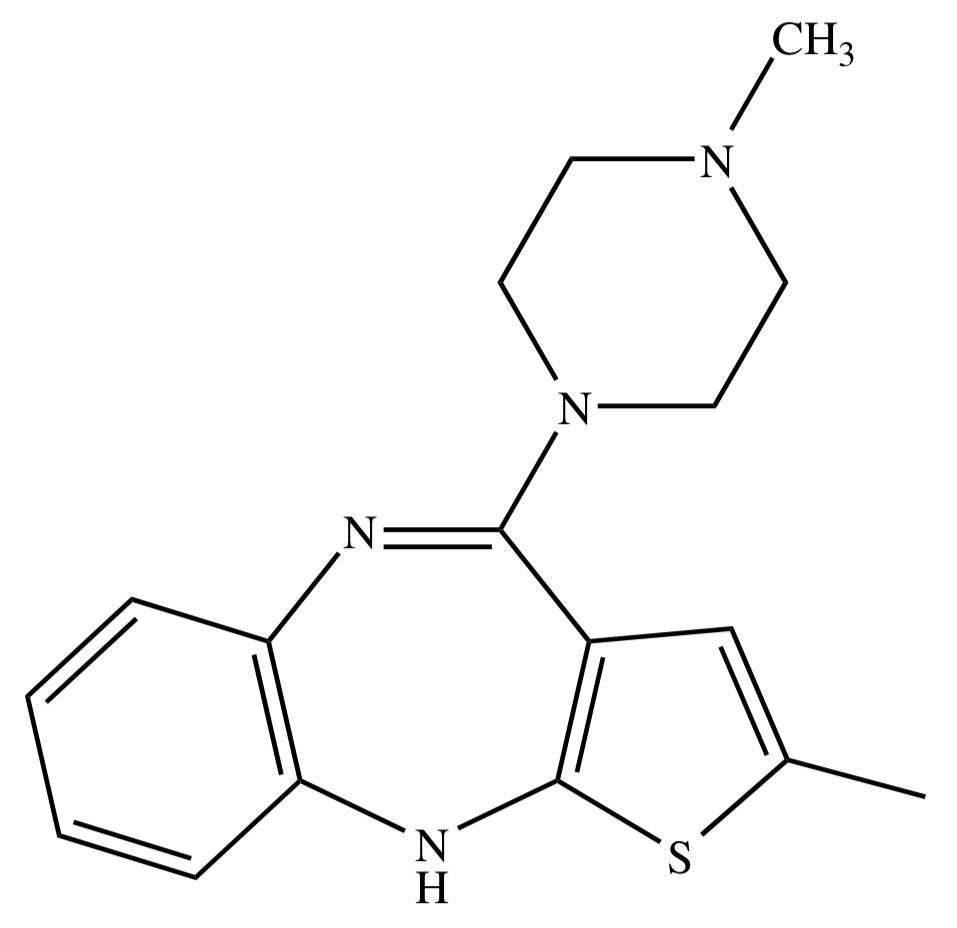
DIARYLAZEPINE DERIVATIVES: OLANZAPINE
clozapine analog; more potent D2 antagonism
[ used also for bipolar disorder and depression ]
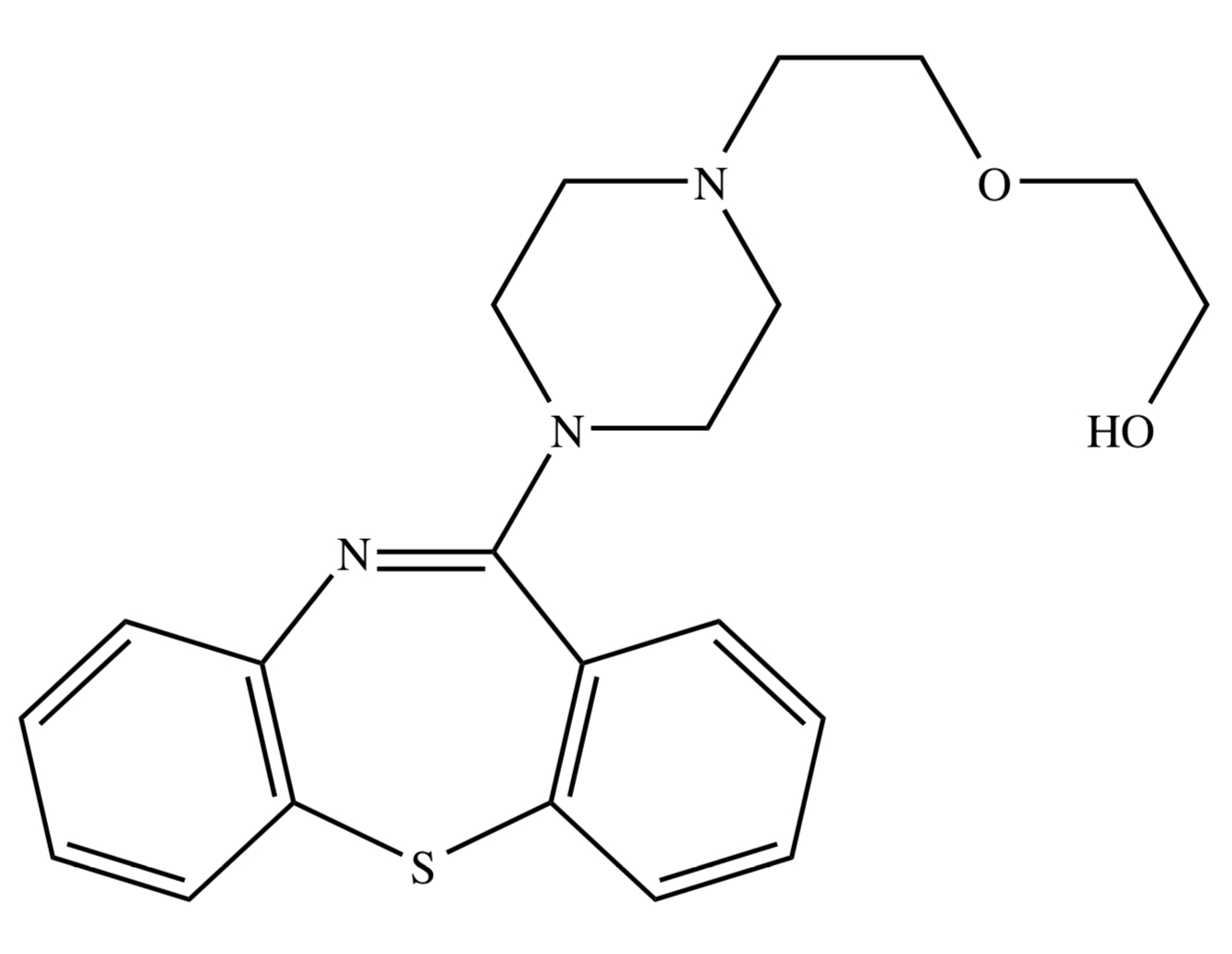
DIARYLAZEPINE DERIVATIVES: QUETIAPINE
clozapine analog
[ used for bipolar disorders; has mood-improving effects ]
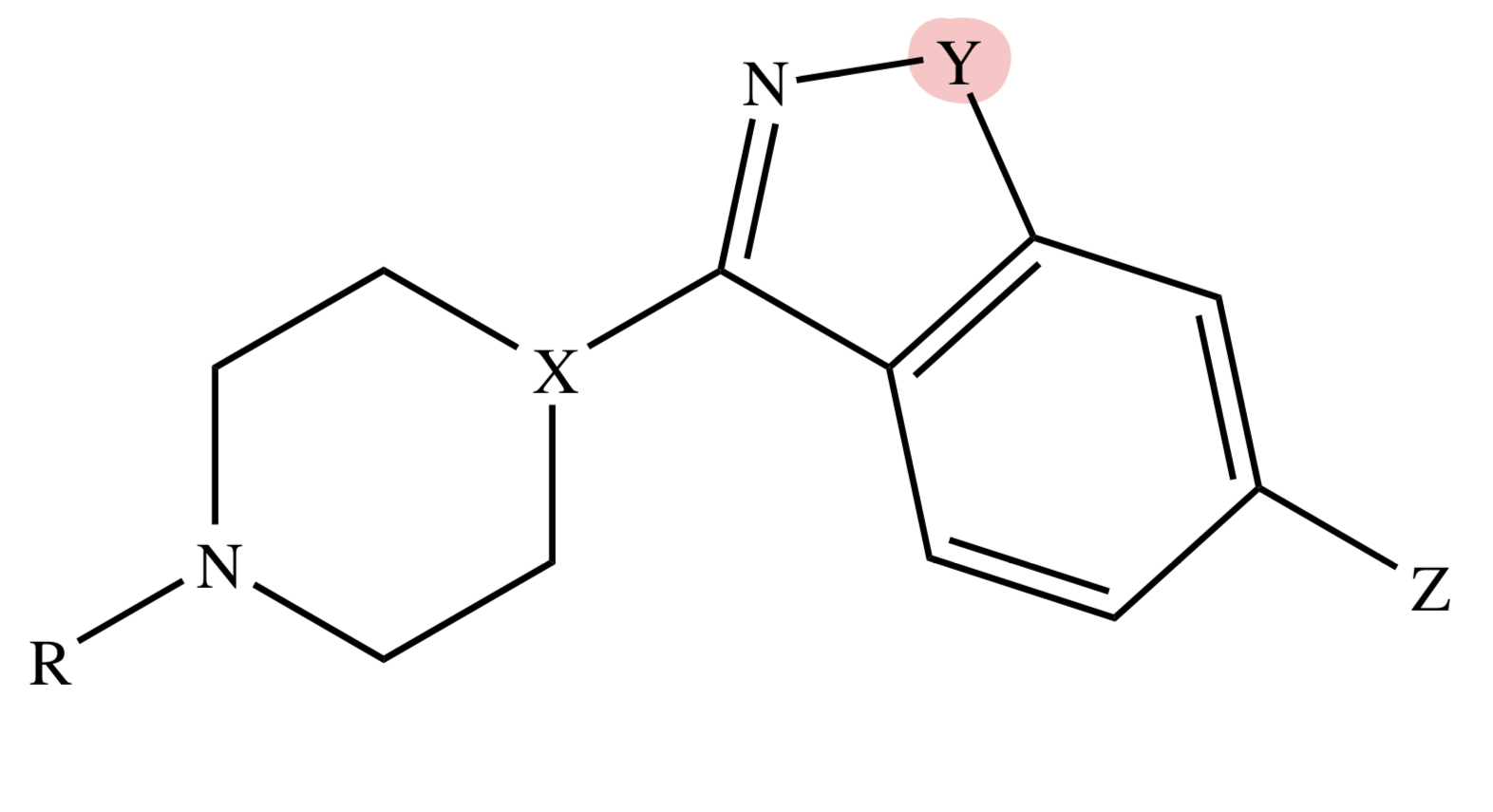
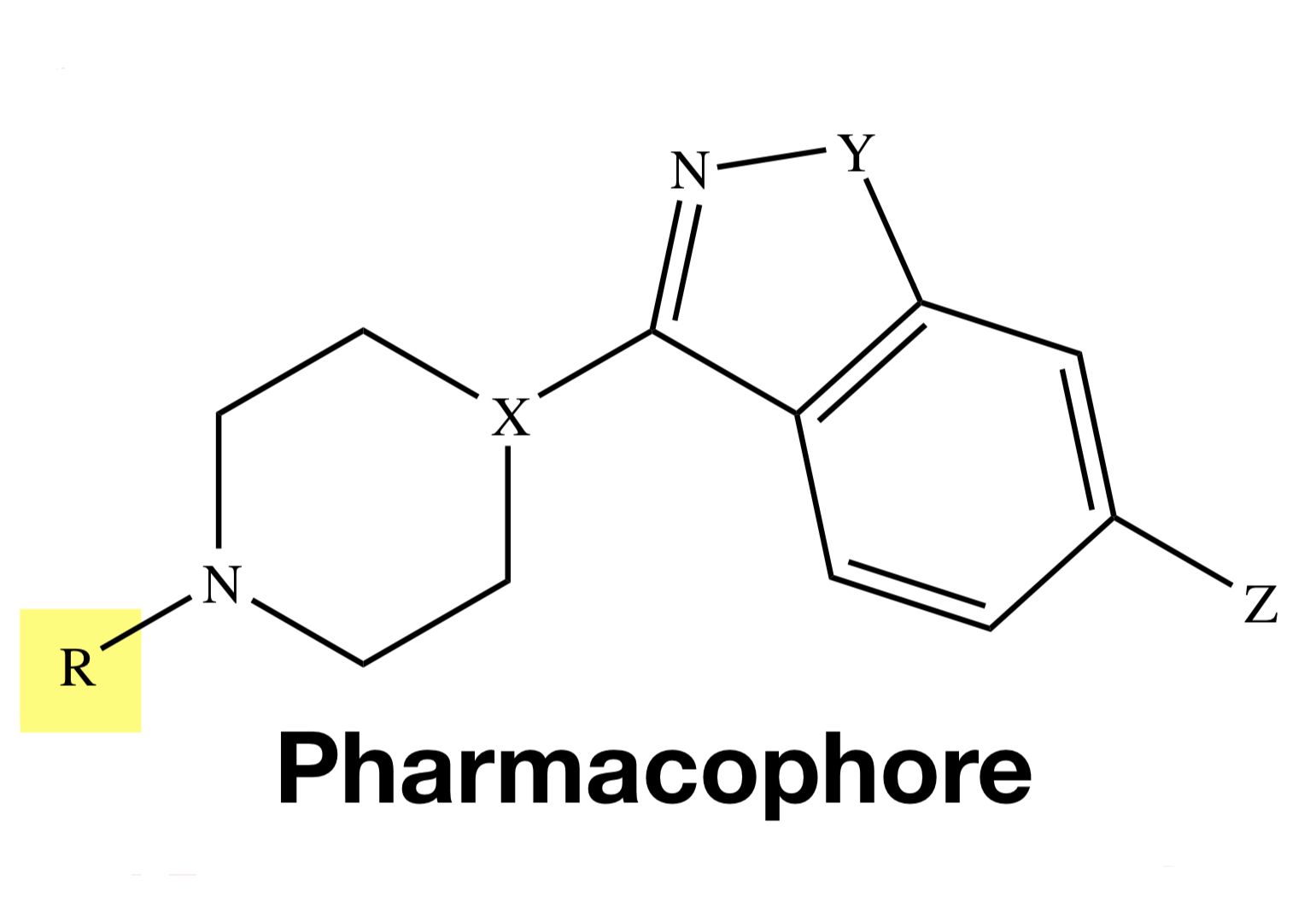
BENZISOXAZOLE
Y = O
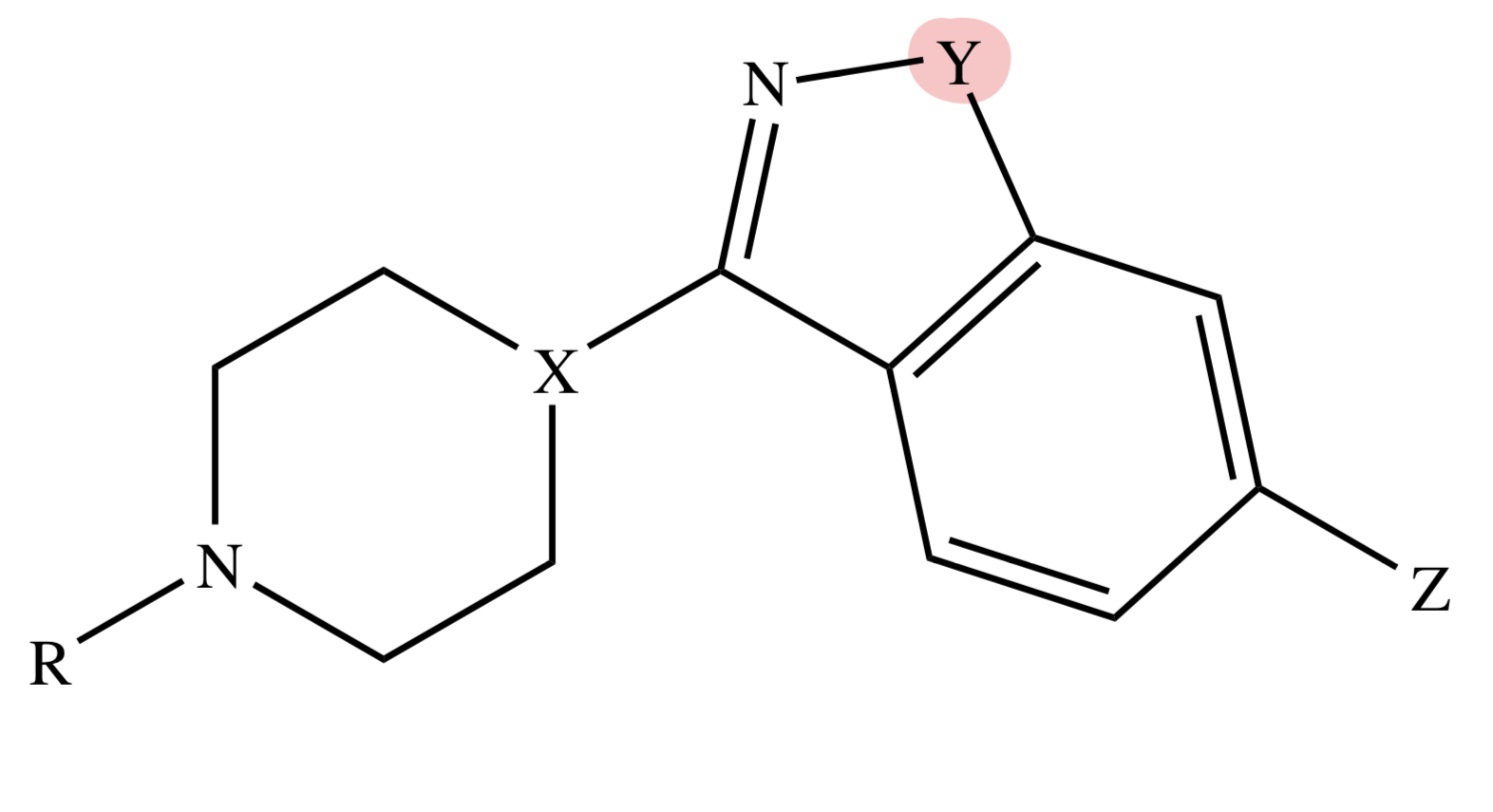
BENZISOTHIAZOLE
Y = S
MOA OF BENZISOXAZOLE / BENZISOTHIAZOLE
similar with diarylazepines but with higher affinity and antagonism at 5-HT2 receptors
BENZISOXAZOLE / BENZISOTHIAZOLE: Metabolism
CYP 2D6 and 3A4: Risperidone & Iloperidone, Ziprasidone (3A4 only)
keto reduction: Iloperidone; N-dealkylation - Lurasidone
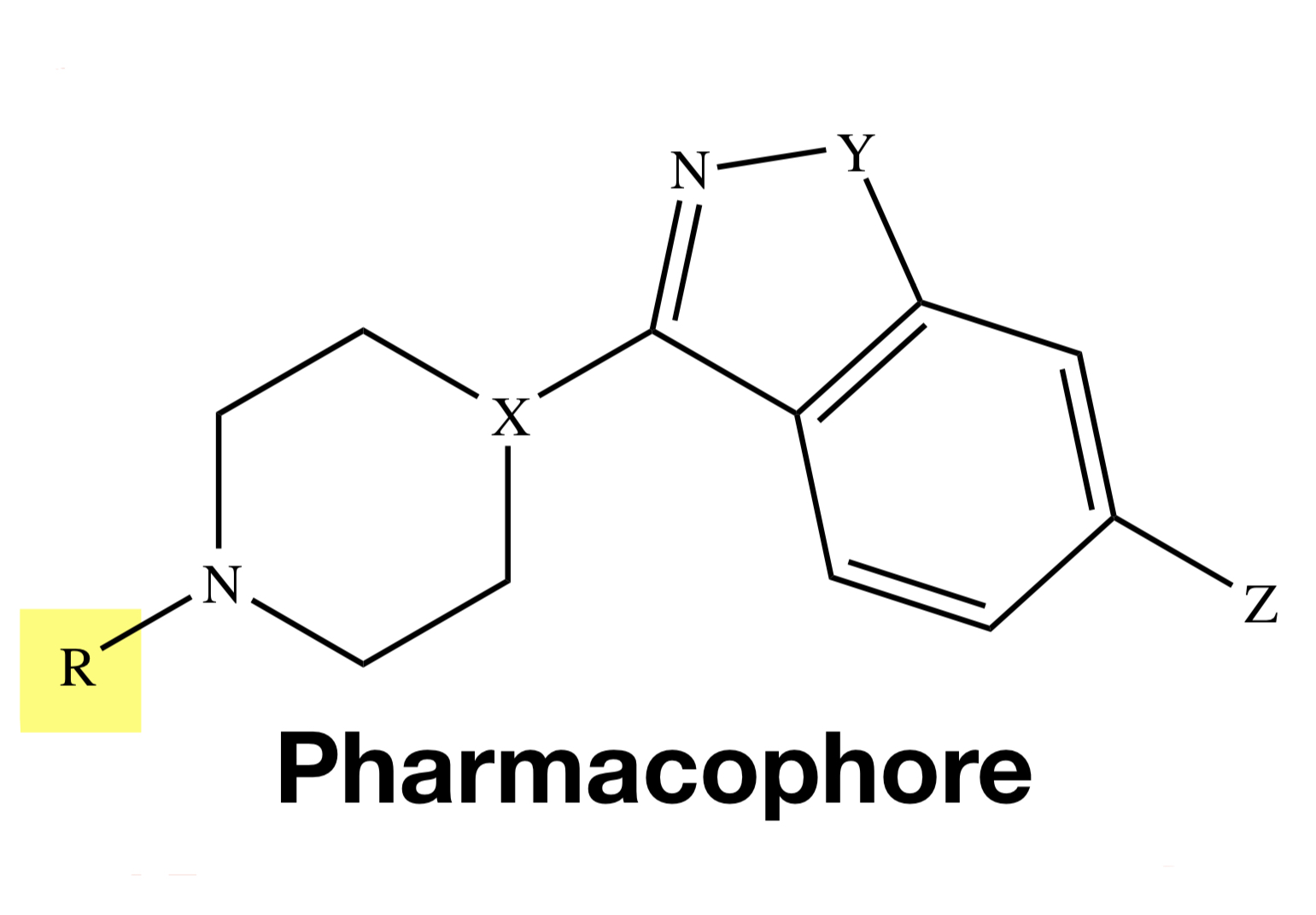
ZIPRASIDONE
Y = S;
X = N;
Z = H
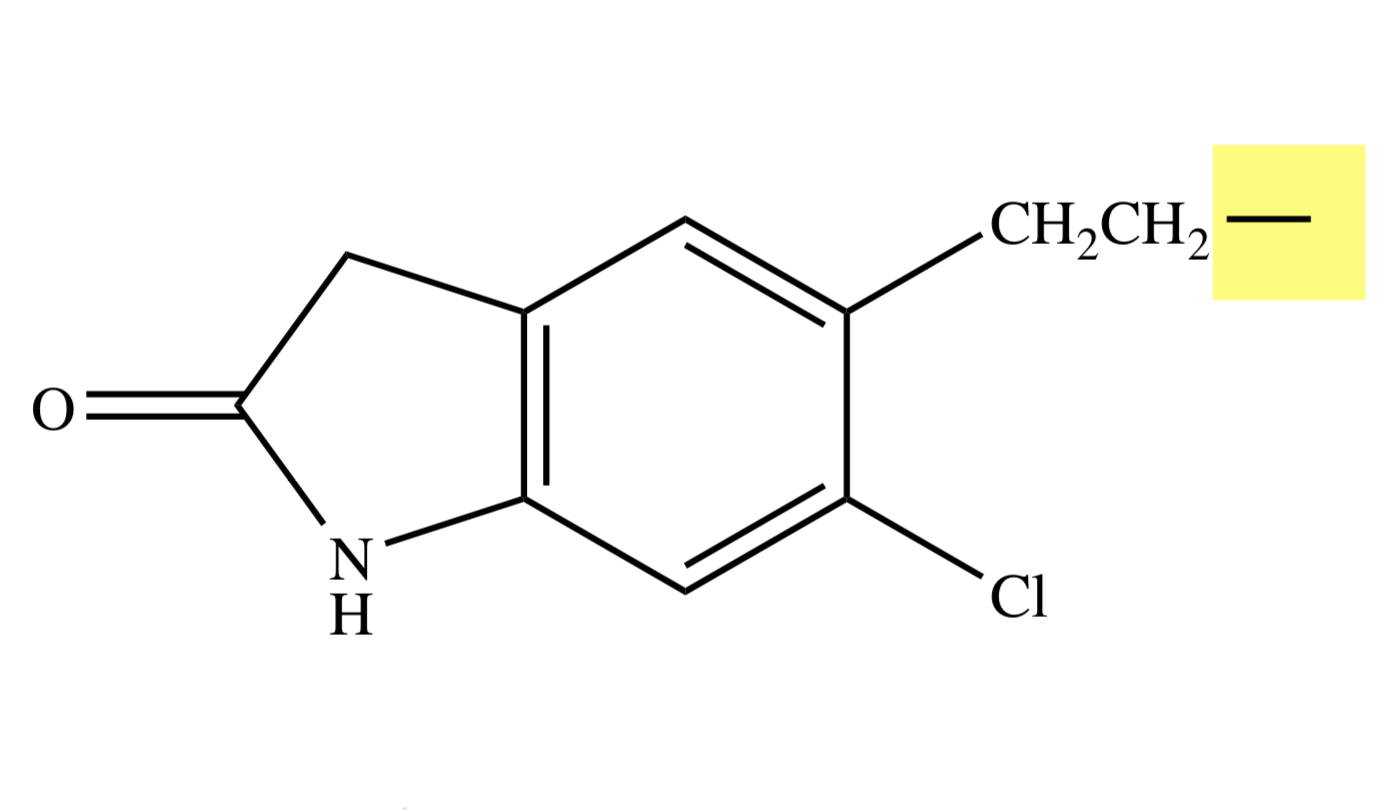
TIOSPIRONE
Y = S;
X = N;
Z = H
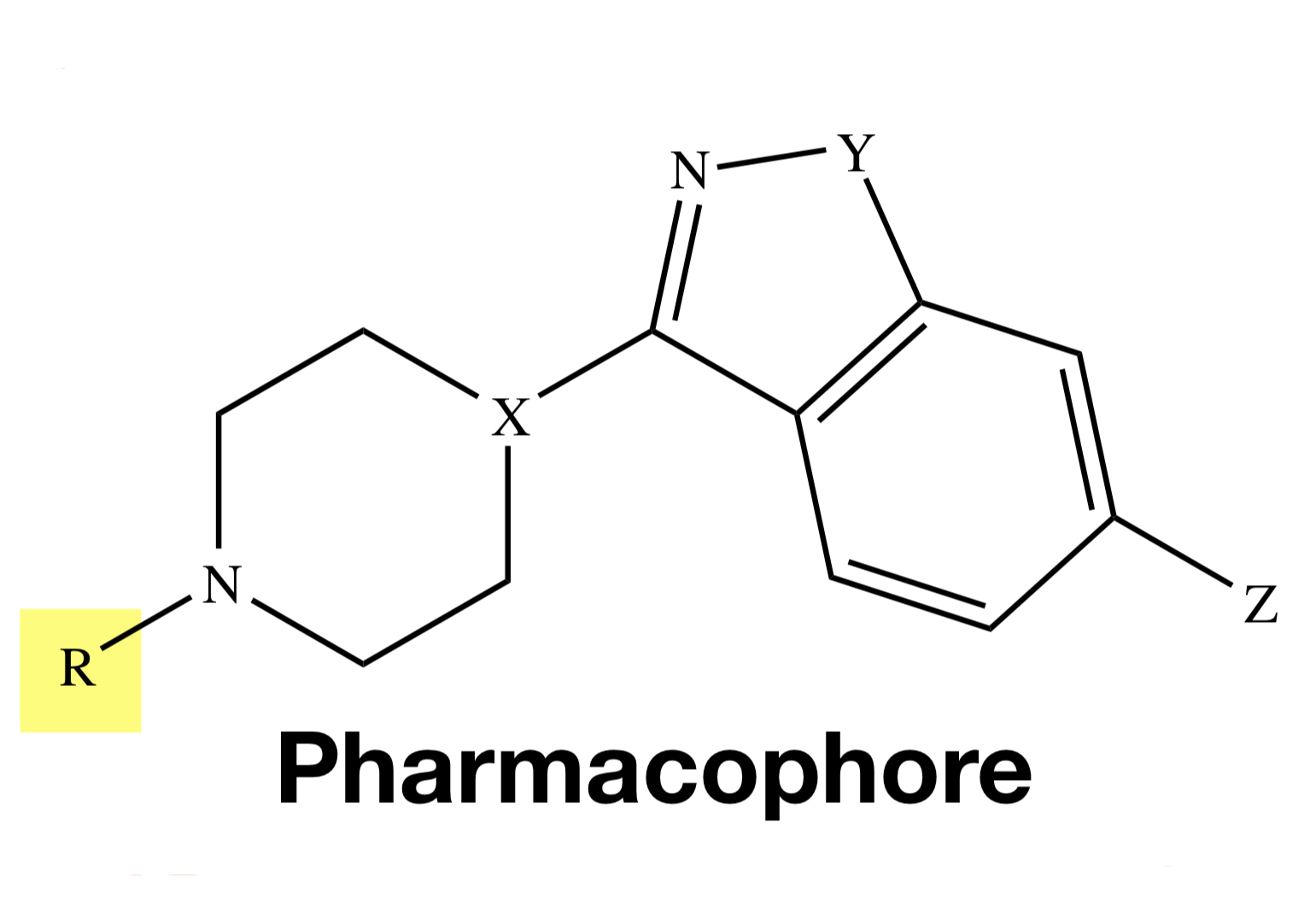
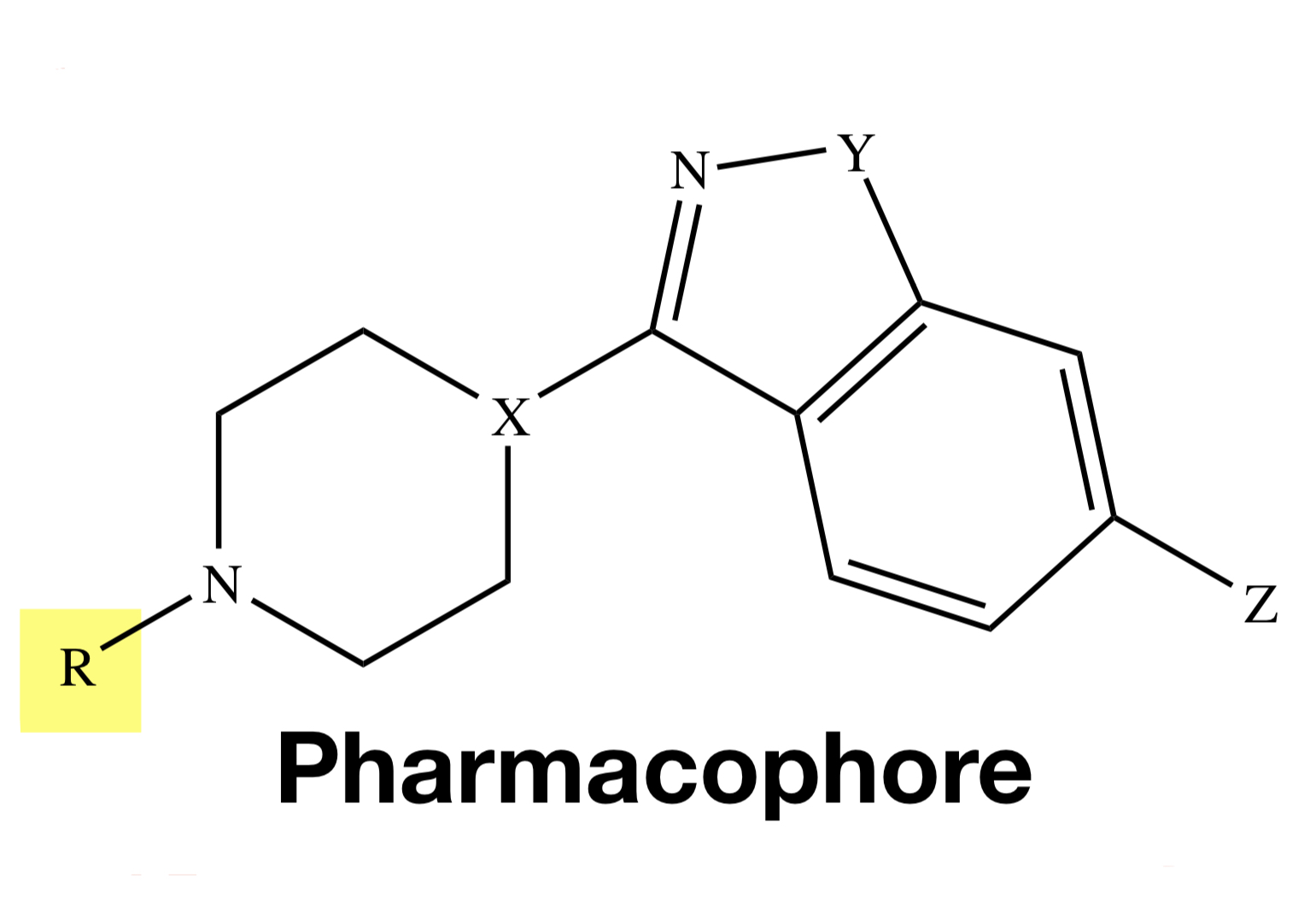
RISPERIDONE
Y = O;
X = CH;
Z = F;
W = H
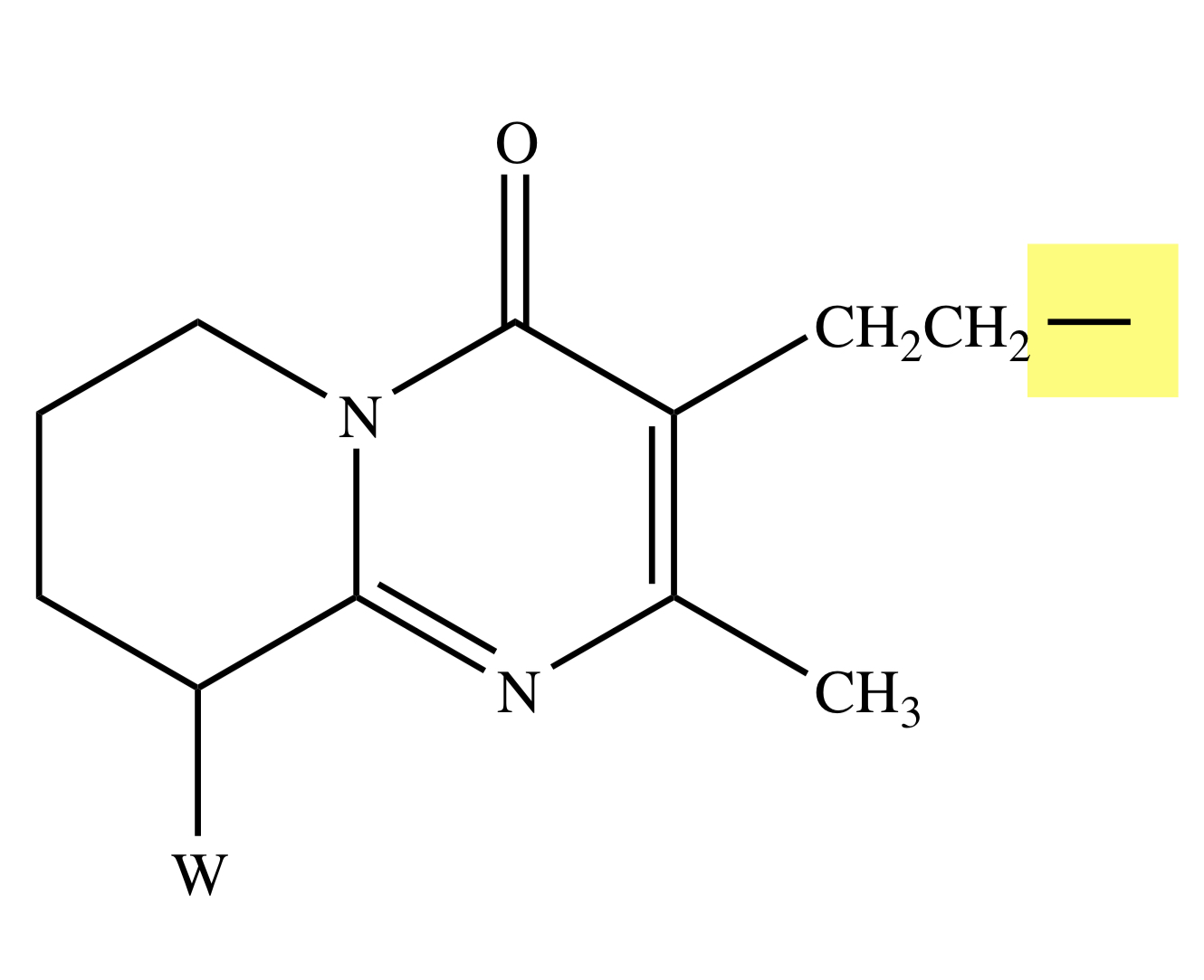
PALIPERIDONE
Y = O;
X = CH;
Z = F;
W = OH
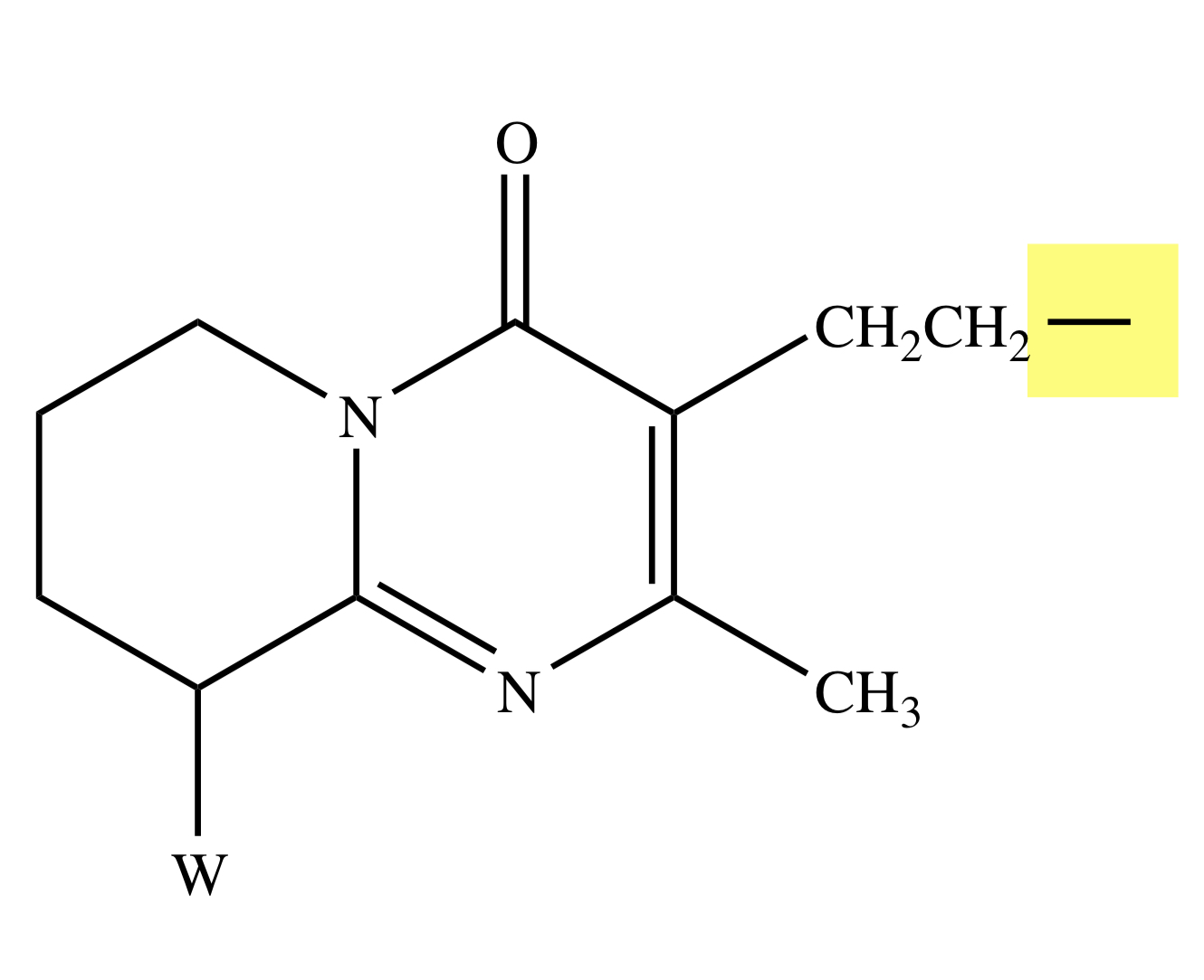
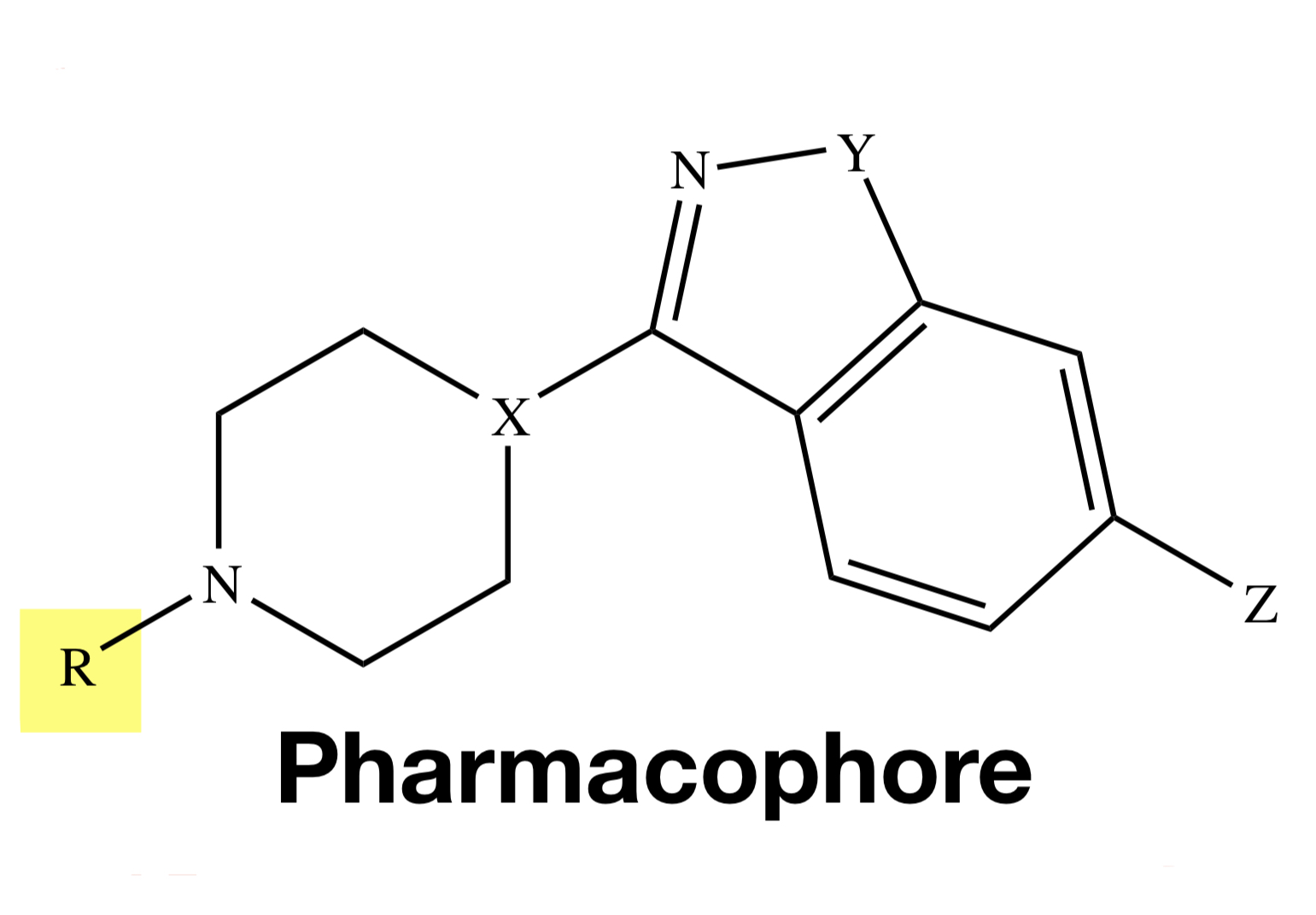
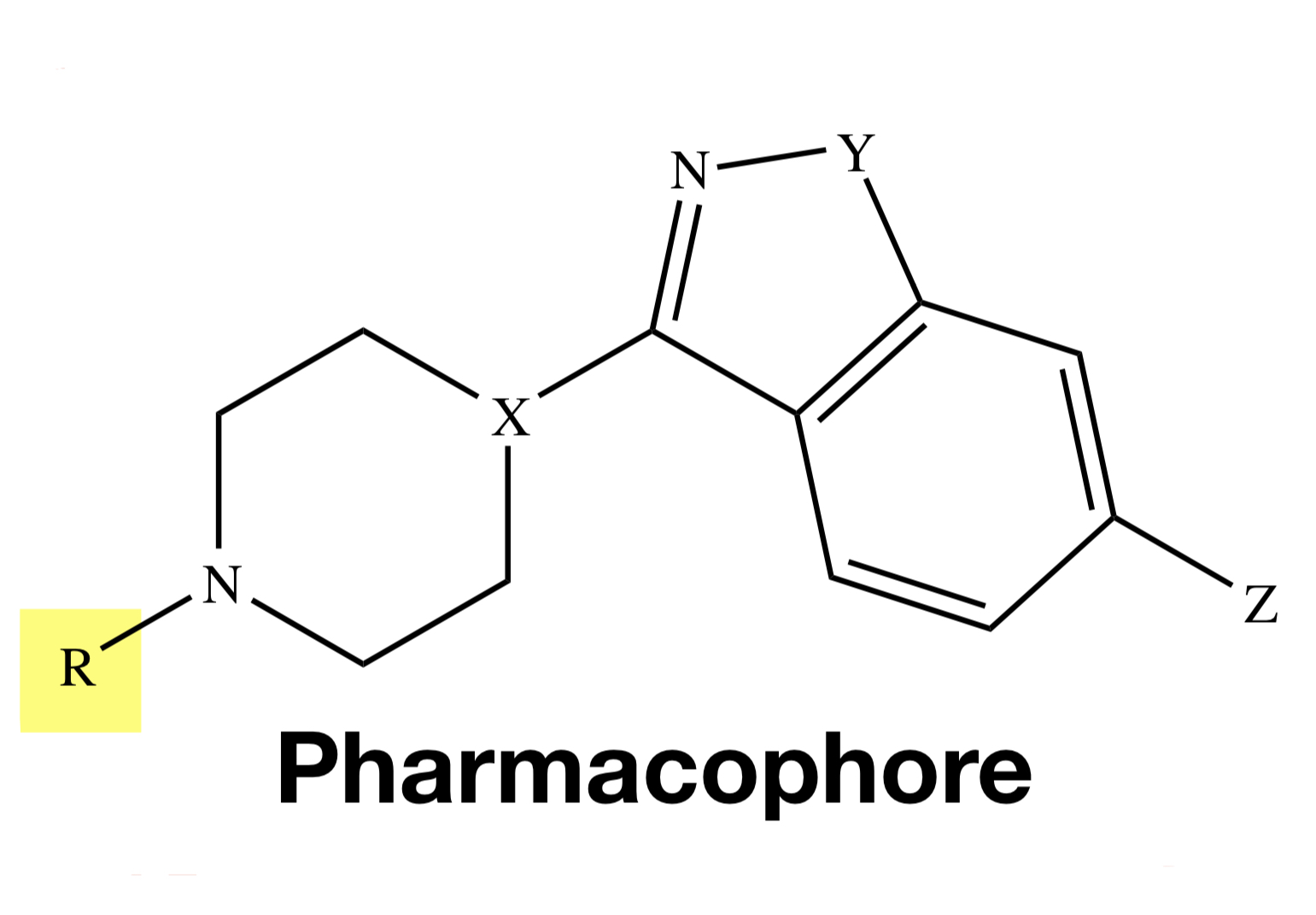
ILOPERIDONE
Y = O;
X = CH;
Z = F
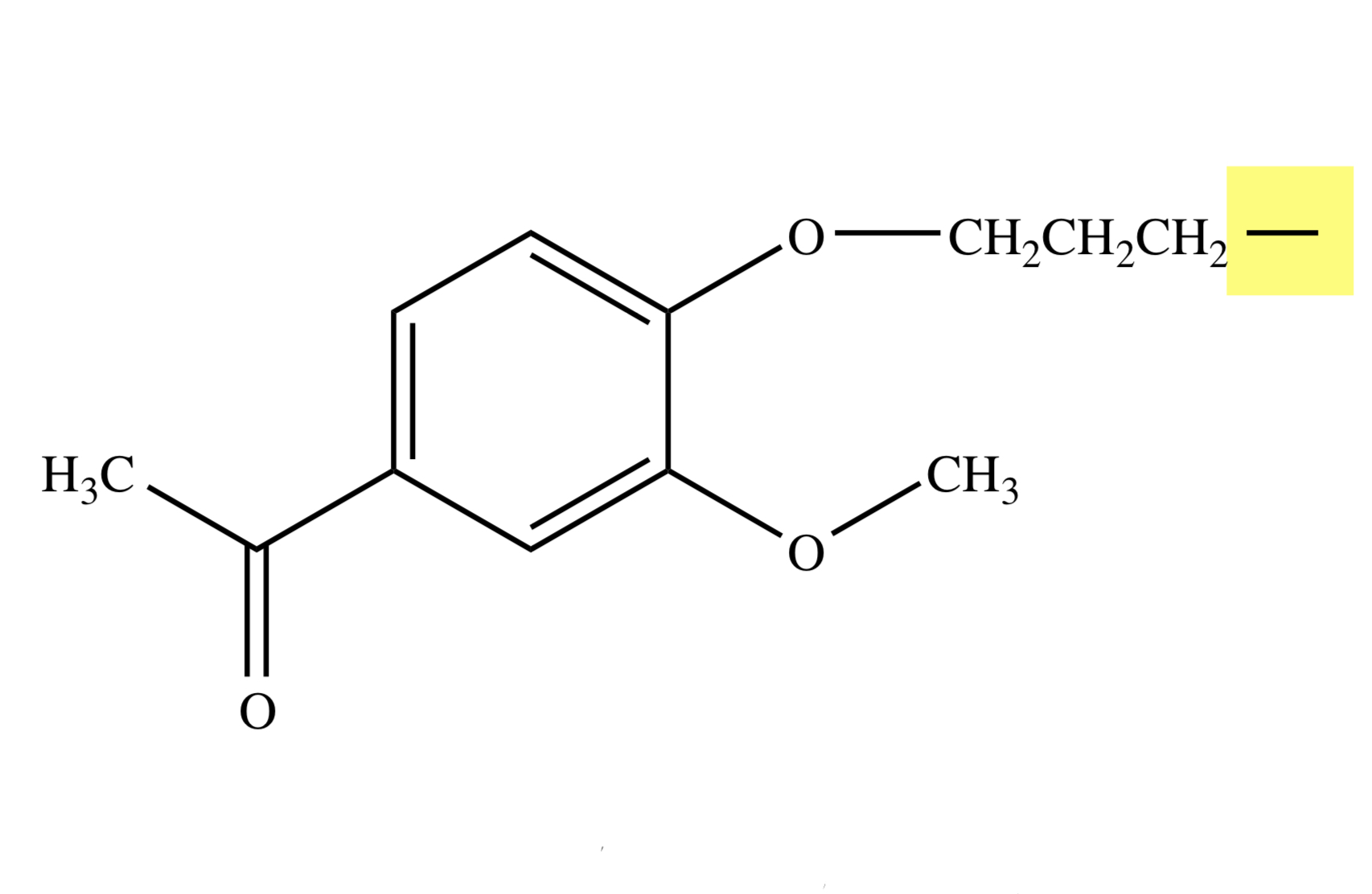
LURASIDONE
Y = S;
X = N;
Z = H
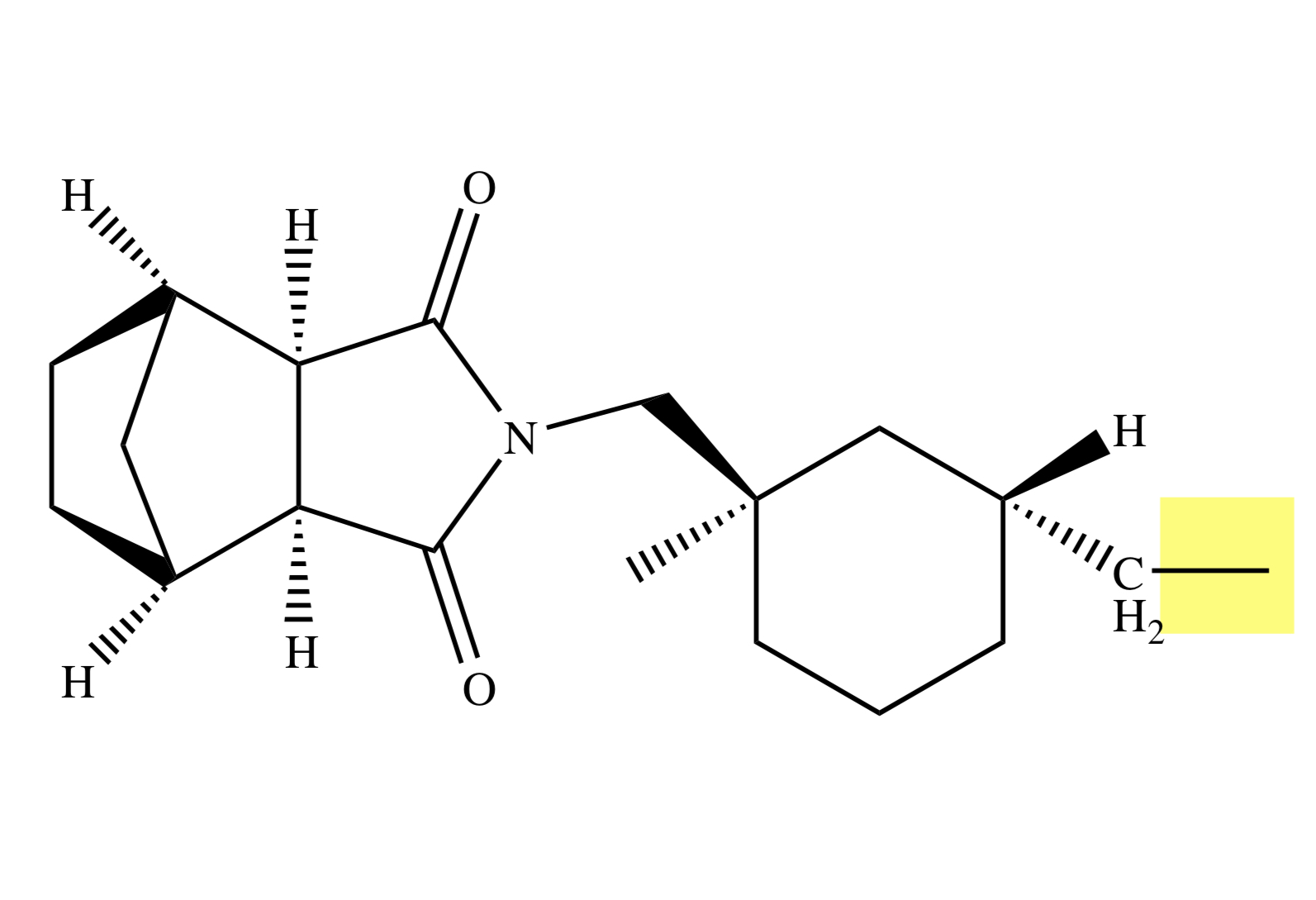
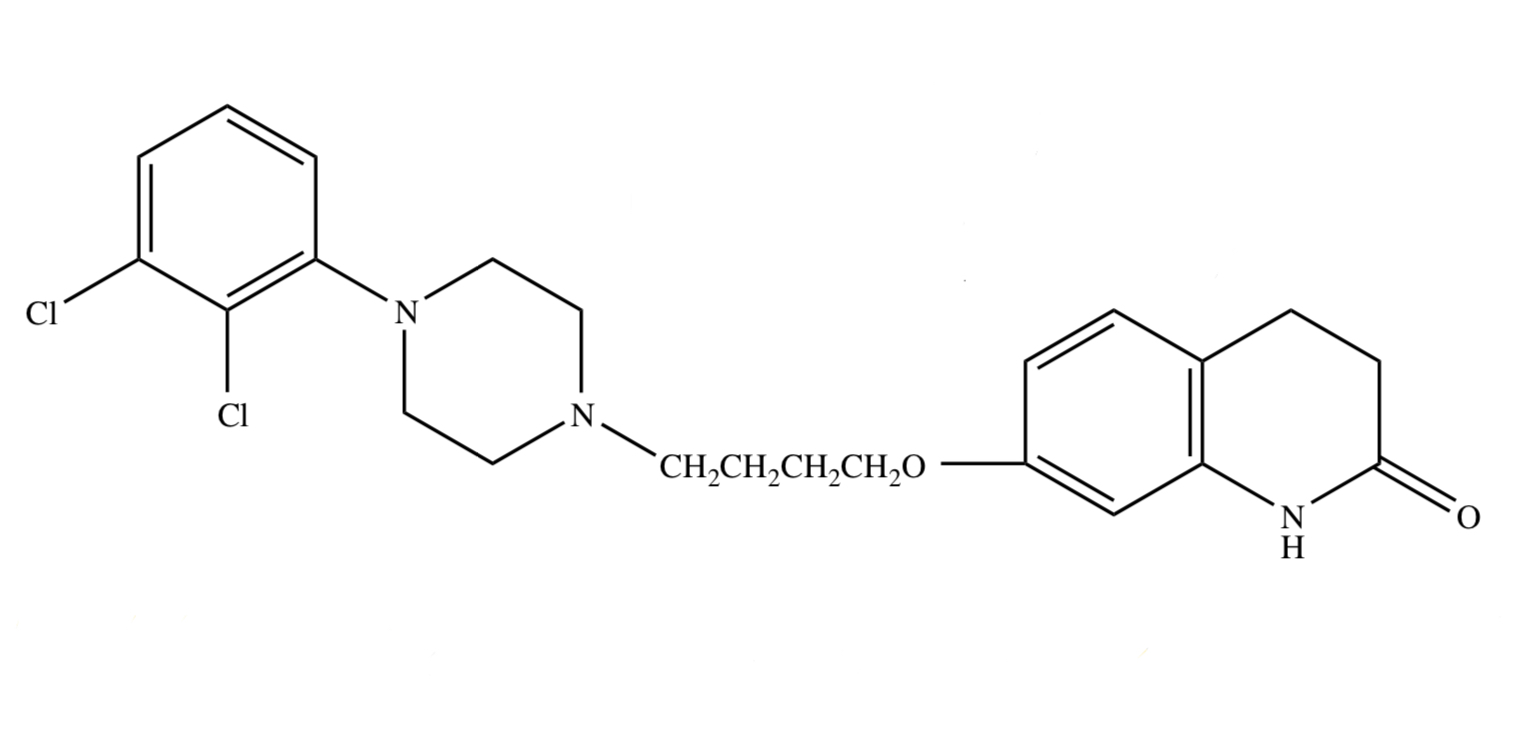
ARIPIPRAZOLE
only drug in the arylpiperazine quinolinone group;
has high oral bioavailability;
highly protein bound, longer DOA
MOA OF ARYLPIPERAZINE QUINOLINONE
high affinity for D2-type receptors (partial agonist) & serotonin (5-HT) GPCRs
ARYLPIPERAZINE QUINOLINONE: Metabolism
CYP 2D6 & 3A4