lecture 15 (ch 20: eukaryotic microbial diversity)
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
importance of eukaryotic microbes (3)?
Medicine: make antibiotics and cause infections
Food & industrial production: help with fermentation (bread, cheese) and enzyme production
Key part of food webs: do photosynthesis and serve as consumers in aquatic food webs
What nutritional modes do eukaryotic microbes use?
photoautotrophs and organoheterotrophs (lithotrophy extremely rare)
How does eukaryotic diversity compare in terms of size and complexity?
Greater variation in size & complexity
Range from unicellular, colonial, to multicellular
All have DNA inside a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
What does it mean that fungi are absorptive heterotrophs?
They secrete degradative enzymes to break down complex materials and absorb small molecules for nutrition.
Saprophytes
organisms that decompose dead organic matter; most fungi are saprophytes.
What is the key component of fungal cell walls?
chitin: a polymer of N-acetylglucosamine (NAG), a building block of peptidoglycan
yeast
unicellular fungus
How does yeast reproduce ?
Reproduces asexually by budding or by fission
Can also reproduce sexually by mating
components of mold
Made of thread-like filaments called hyphae
Can have septa or not (division between “cells”)
Hyphae form networks called mycelium
mushroom
spore-bearing structure (fruiting body) produced by some kinds of fungi
Arises from mycelium, so not really a separate morphology
Spread spores to new environments
ecological roles of fungi
saprophytes (decomposers)
beneficial symbionts
harmful symbionts
parasites/pathogens
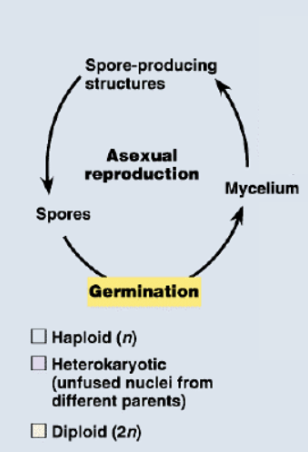
draw and describe asexual fungal life cycle
Spore germinates into mycelium
Mitosis in mycelium produces (mito)spores
Spores are disseminated to new location
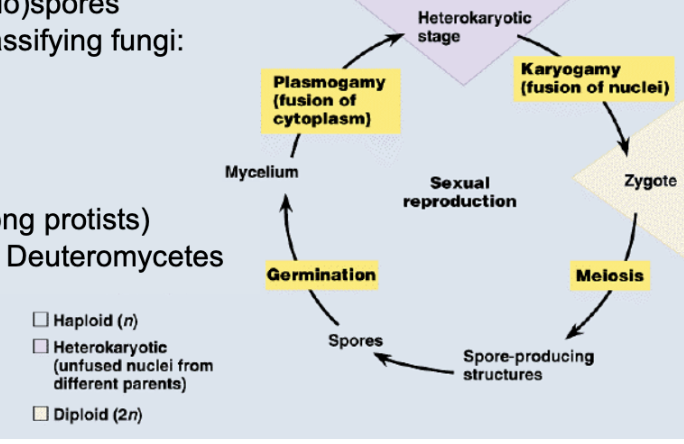
draw sexual fungal life cycle
chytridiomycota
aquatic environment, moist soil
Have motile spores (zoospores)
Saprophytic, occasionally parasitic
Zygotmycetes
mainly saprophytes that grow on decaying organic matter. Their habitats include soil, rotting fruits and vegetables, bread, and other decomposing plant material.
basidiomycetes
Terrestrial — forests, grasslands, soil, plants
Mainly decomposers
Their fruiting bodies (such as mushrooms) are often visible above ground in these habitats. Some species are also plant pathogens and can be found on crops
protist
unicellular or colonial eukaryotes that aren’t fungi (ex. protozoa, algae, slime molds)
Protozoa
heterotrophic single-celled protists
algae
Algae: uni or multicellular, phototrophic protists.
Found in soil, water, and symbiotic with other organisms
slime molds
heterotrophic spore-formers
primary algae
derived from a eukaryote that engulfed a cyanobacterium
secondary algae
derived from a protozoan that engulfed a primary algae
Are Blue-Green Algae actually algae?
No, they are Cyanobacteria, the only photosynthetic prokaryotes (i.e., with PS I & PS II)
plasmogamy
cells fuse w/o nuclei merging
karyogamy
nuclear fusion
mycorrhizae
a symbiotic relationship between fungi and plant roots
zoospore
motile spores
sporangium
bulbous membrane on top of aerial hypha
australia’s great barrier reef
(home to 10% of all Earth’s corals) has a problem
Since 1995, half the corals have died off by “bleaching”
Loss of algal symbionts that conduct photosynthesis and feed their coral hosts
Causes are complex, but important factor is increase in ocean temperature
harmful algal blooms
Bloom = large concentration of algal cells
Usually caused by increased nutrient availability (mostly N & P)
Can produce harmful toxins → fish, bird & mammal die-off