Mod 3 Applied Lec - Lipid Rafts
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What are lipid rafts in simple terms?
Lipid rafts are small, dynamic clusters of proteins and lipids in the cell membrane that regulate cell function.
What are lipid rafts in proper terms?
Lipid rafts are plasma membrane microdomains rich in cholesterol and sphingolipids, which provide a particularly ordered lipid environment.
Lipid rafts are hard to…
...are hard to extract, locate in imaging, etc.
WHY are lipid rafts hard to locate and extract?
cuz of their transient fluid nature!
they’re not always there or they’ll keep restlessly moving spots.
Recall that the cell membrane is considered a _______ ___________ model. What does that mean?
Recall that the cell membrane is considered a fluid mosaic model.
so the macromolecules within the bilayer can move laterally. they’re not confined to one spot.
Let’s name some components of the cell membrane. And explain their purpose.
-adhesion proteins
-adhesion proteins facilitate things to adhere to the cell or the ECM and crawl along it. (e.g. heart cells need to be close tg
they also interact with the cytoskeleton, etc.
Membrane activities differ based on …
… based on protein composition!
Recall majority of the cell membrane bilayer is composed of…
… phospholipids!
There are several subsets of phospholipids. It could be a…
Phospholipid subsets:
1. Phosphoglycerides AKA glycerophospholipids (GPLs)
or
2. Sphingolipids.
What are phosphoglycerides?
What does their chemical composition allow them to do?
they are short and largely unsaturated acyl chains —> tend to kink —> pack more loosely —> allows lateral movement / fluidity
What are sphingolipids?
What does their chemical composition allow them to do?
long and largely saturated acyl chains —> tight packing (gel-like)
So regions that have more phosphoglycerides are going to pack more [tightly/loosely].
loosely!
So regions that have more sphingolipids are going to pack more [tightly/loosely].
tightly!
What special molecules are found in between those phospholipids?
cholesterol molecules! a type of steroid.
What does cholesterol do?
they help DECREASE the fluidity of the membrane to maintain rigidity in extreme conditions
(to prevent membrane from melting / being too fluid/loose).
∴ Cholesterol favors phase ___________.
∴ Cholesterol favors phase separation.
Cholesterol interacts preferentially (but not exclusively) with sphingolipids, and favours phase separation between sphingolipids and glycerophospholipids.
What do you mean by phase separation?
well we really just mean physical separation between sphingolipids and GPLs.
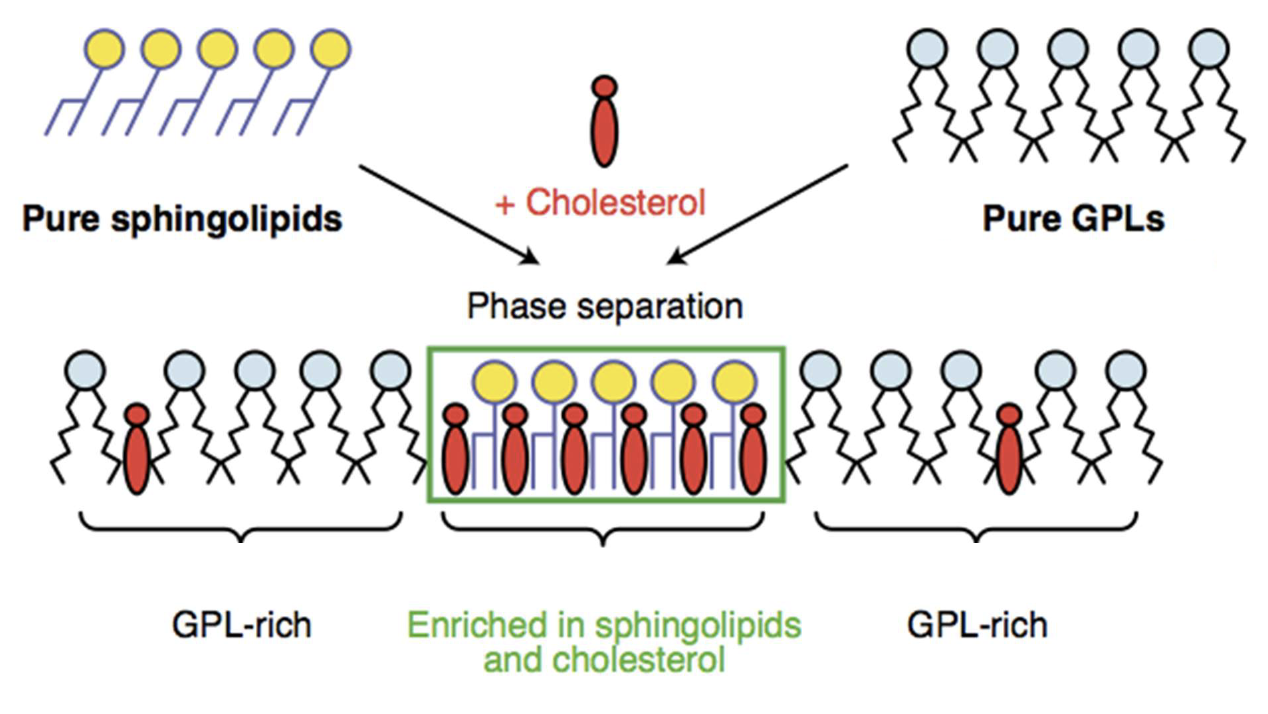
Think!!! Why does cholesterol selectively prefer binding to sphingolipids?
*prefer does not mean exclusively bind to sphingolipids. it just prefers it.
cuz sphingolipids are more saturated so they are straight (no kinks). so there is more available area for cholesterol to interact with it.
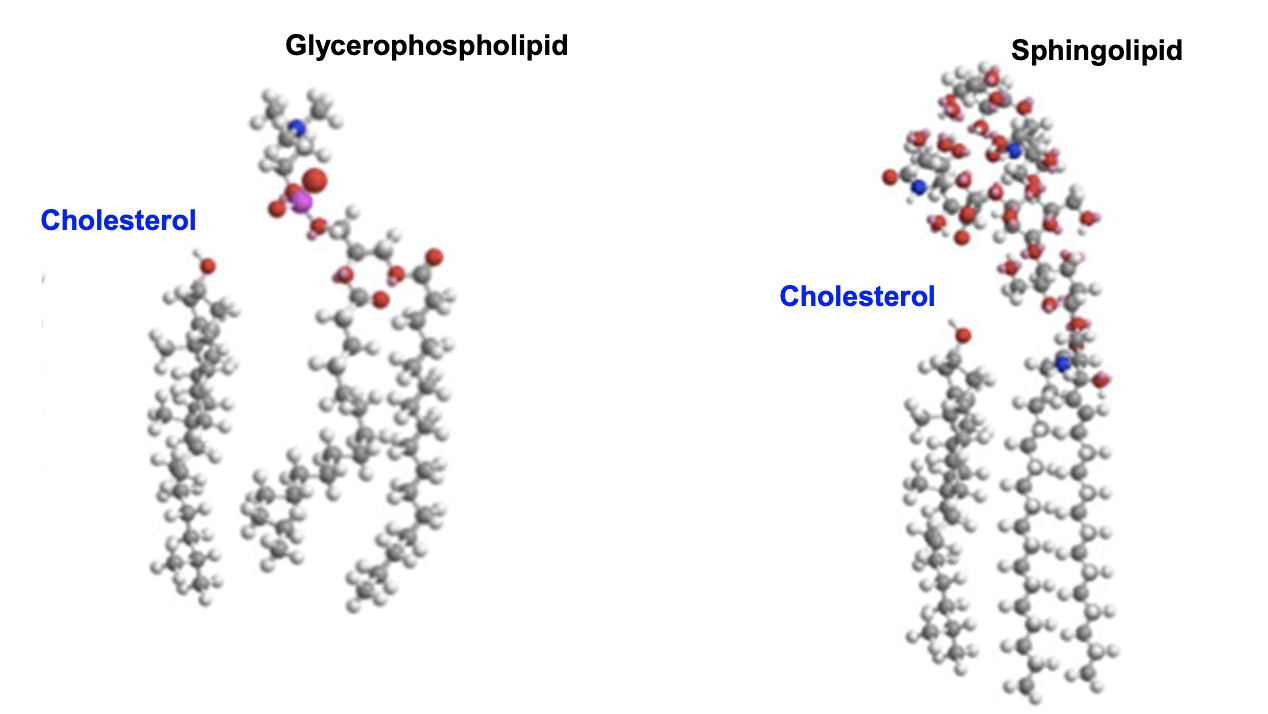
Think!!! Why does cholesterol selectively prefer binding to sphingolipids from a shape perspective?
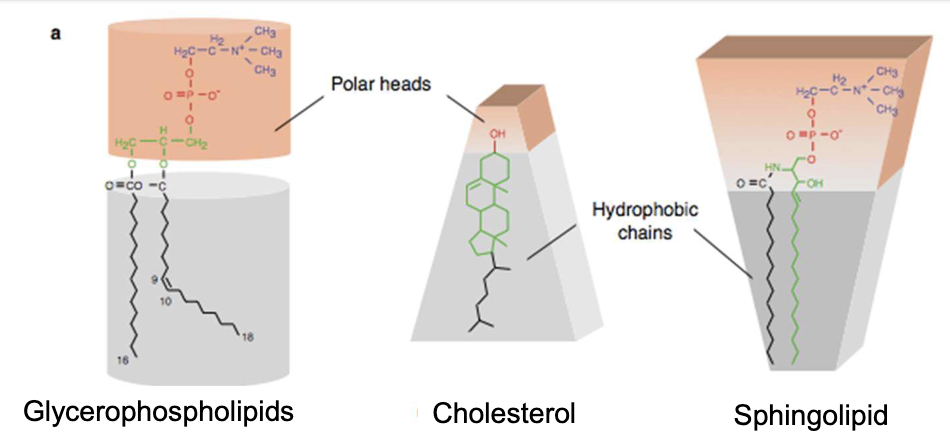
Glycerophospholipids are basically cylindrical
Sphingolipids are cone-shaped
Cholesterol is cone-shaped too. So they fit tg like pieces of a puzzle.
So given we now know the puzzle-fitting shapes of cholesterol-sphingolipids, what might a RAFT look like?
like this:
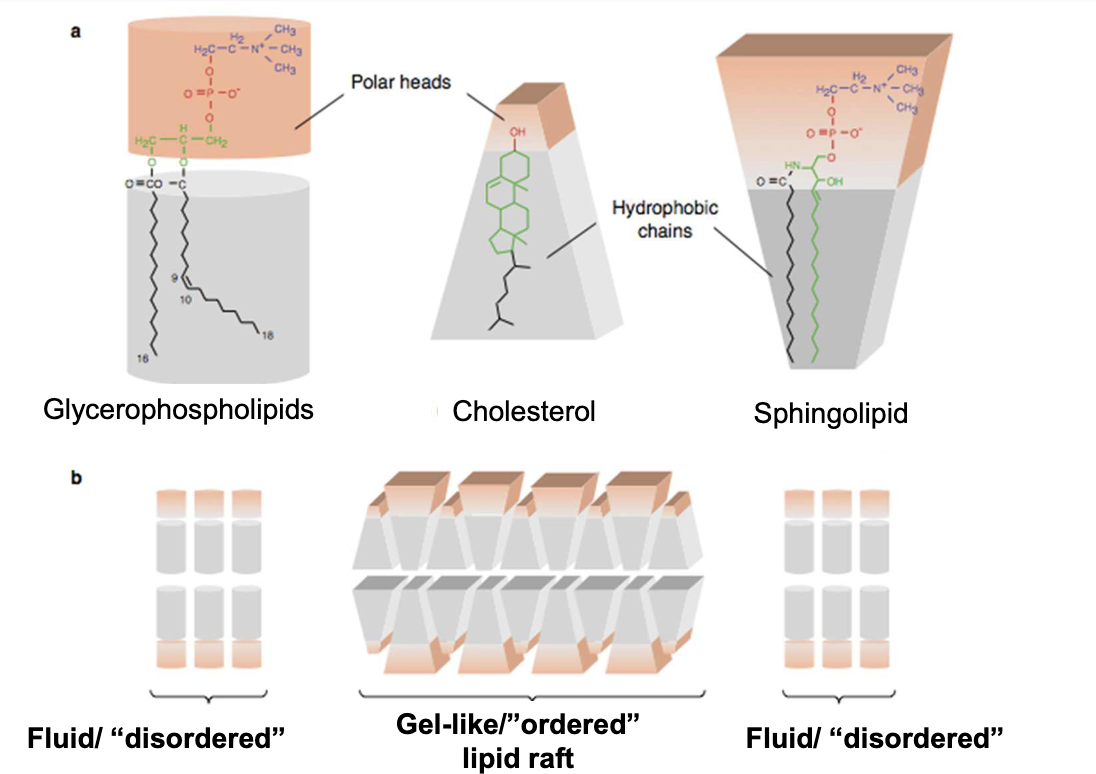
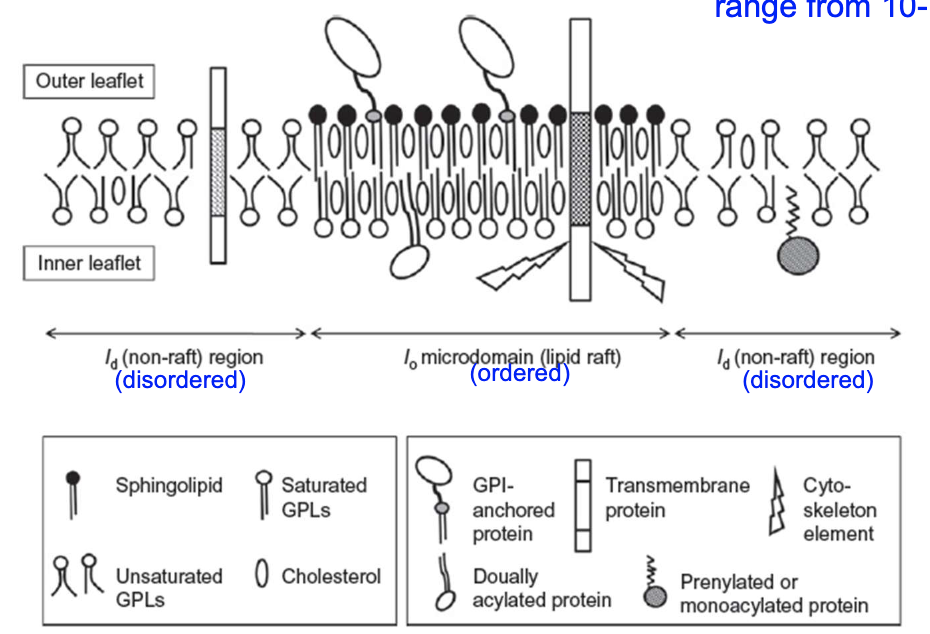
So what are lipid rafts now that we know about sphingolipids and cholesterol?
Lipid rafts are microdomains of predominantly sphingolipids + cholesterol, in the outer (exoplasmic) leaflet of the membrane.
Recall what does leaflet mean?
a leaflet is one layer of the bilayer.
T/F: Lipid rafts are TYPICALLY in the outer leaflet of the membrane, but ofc its composition can change.
true!
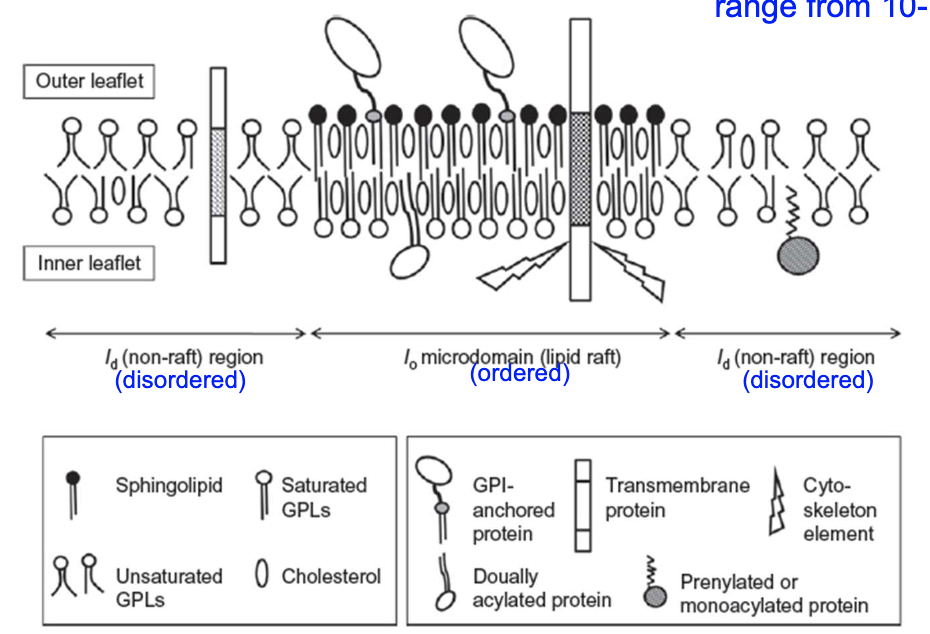
T/F: Cholesterol and GPLs are NOT present in the inner leaflet.
false! they are!
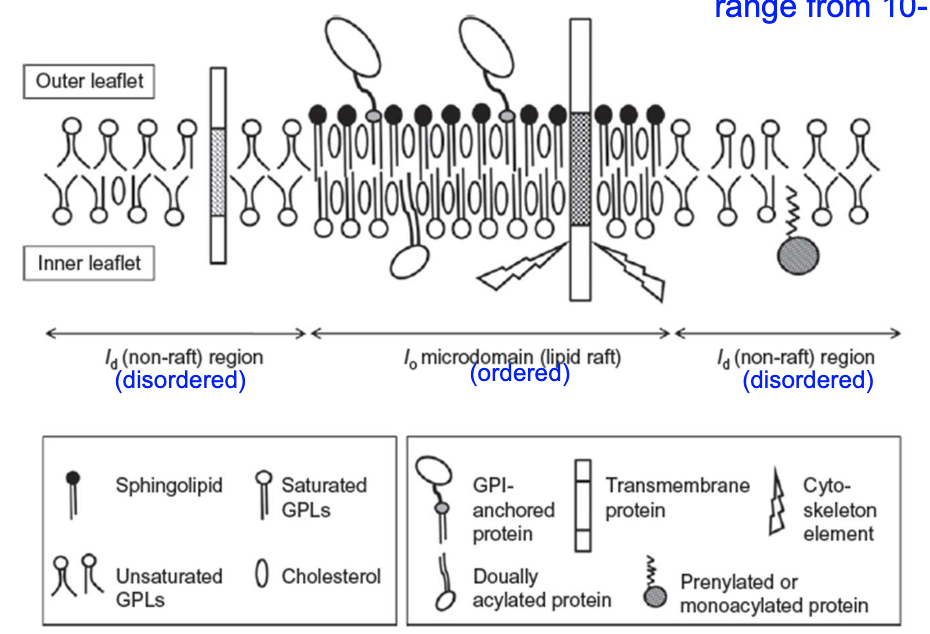
Other than sphingolipids and cholesterol, what else is present in the raft?
GPI-anchored proteins, acylated proteins, and transmembrane proteins are also present!
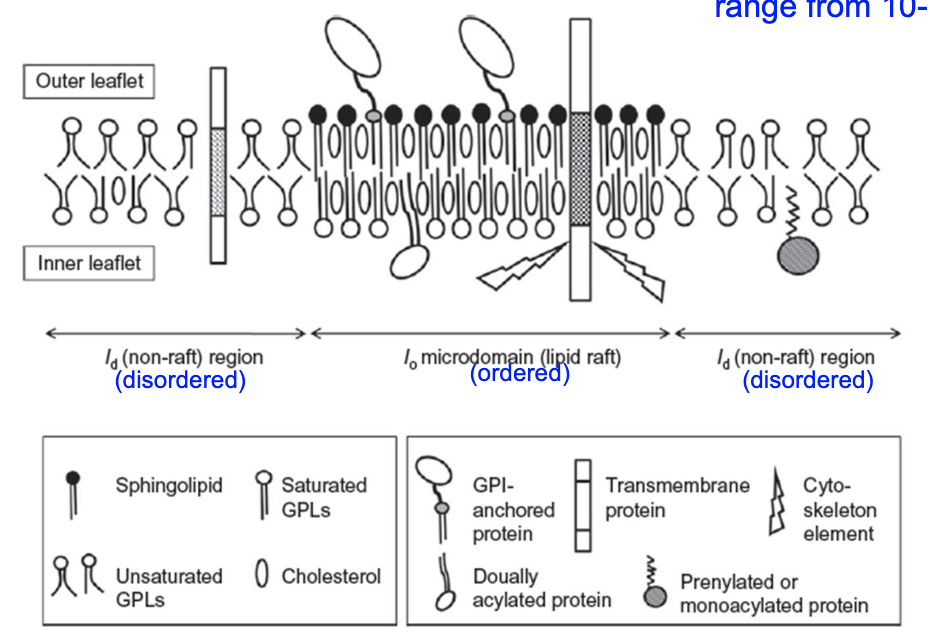
Lipid raft platforms can range from 10-_____ nm.
Lipid raft platforms can range from 10-1000 nm.
The lifetime of a raft can range from nanoseconds to __________.
The lifetime of a raft can range from nanoseconds to minutes. since it may need to stay in place longer for signalling purposes.
How can we study lipid rafts?
detergent-resistant membrane fraction isolation
cholesterol depletion w/ cyclodextrins
microscopy
Explain detergent-resistant membrane fraction isolation.
we take a membrane and try to fractionate it (break it apart) using a detergent.
the detergent will break apart shit that’s packed more loosely and isolate parts that are packed tightly and orderly (such as lipid rafts).
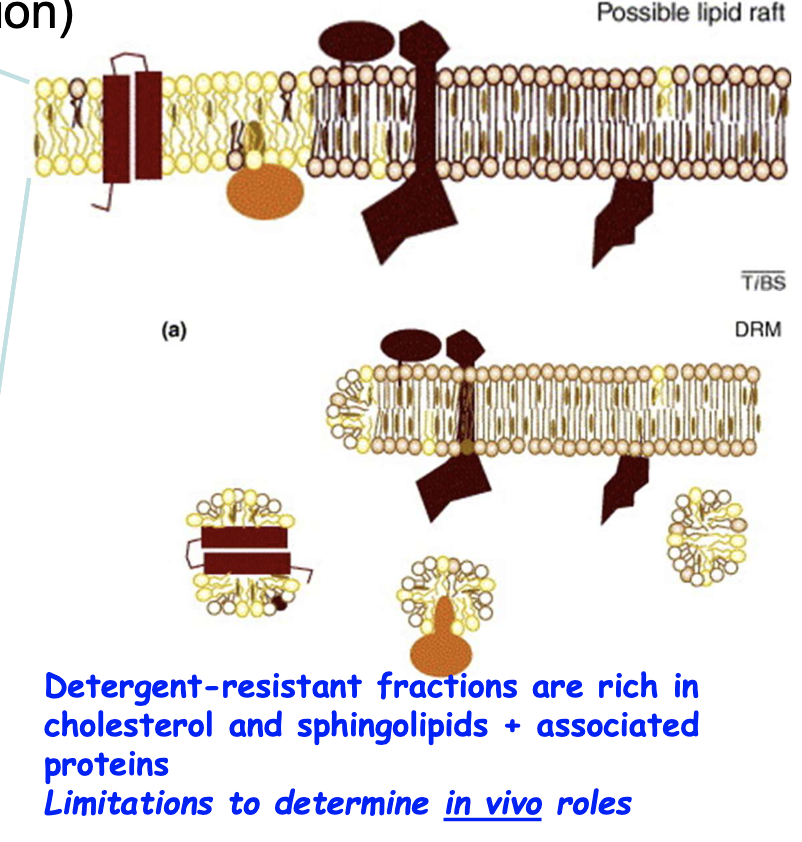
So detergent-resistant membrane fraction isolation helps us to isolate and confirm the EXISTENCE of lipid rafts. But why do we need to go into a further level of detail?
cuz we want to preserve the raft iin its functional form. to see the in vivo roles and functions of the proteins in the raft.
the detergent usually kills the function and renders it like a historical artifiact.
Explain cholesterol depletion w/ cyclodextrins.
use cyclodextrins (molecules with a hydrophobic cavity inside) as a vacuum to cholestrol (sucks up cholesterol) to examine lipid rafts inside LIVE cells.
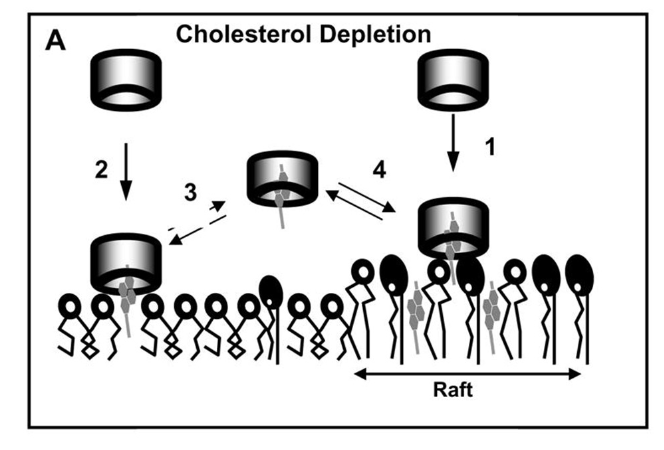
Why is it beneficial for cyclodextrins to suck up cholesterol?
since cholesterol is what is holding these rafts tg. so sucking it away helps to examine the other proteins inside the rafts.
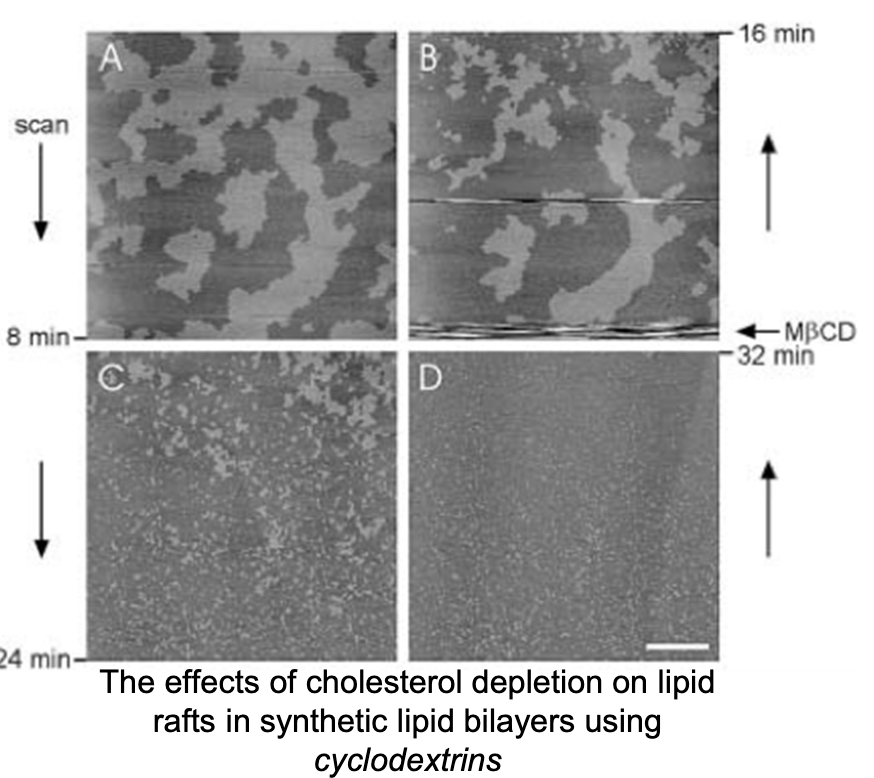
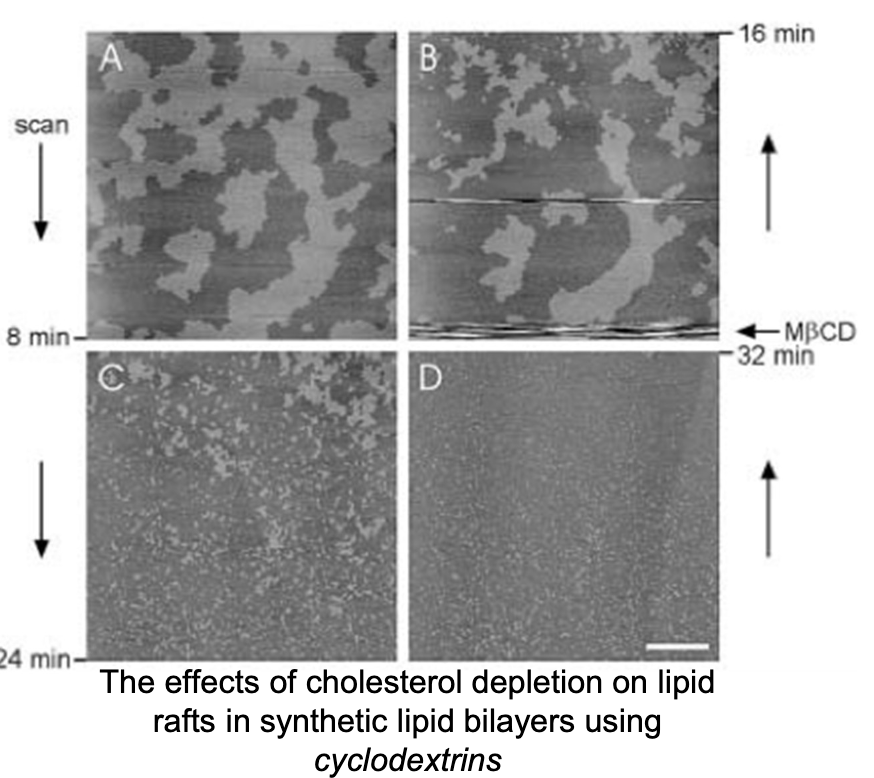
Explain what has happened in these microscopic slides of a raft:
The light grey regions are lipid rafts.
Cyclodextrins suck up the cholesterol.
As you can see in B, C, and D, the rafts disperse cuz they’re no longer bound tg.
So what do we think lipid rafts have an important role in?
signal transduction
help form blood-brain barrier
for adhesion and changes in shape during migration
WHY do we think lipid rafts have an important role in lots of aspects of health? Why did we come to that conclusion?
-cancers have a higher level of lipid rafts
-may be involved with amyloid plaque accumulation (rem. this is what causes Alzheimer’s etc)
-lipid rafts can be targets of different pathogens
-raft localization of cellular prion protein which facilitates conversion to the bad prion form.
First we will talk about how lipid rafts apply to the immune response:
…
When your immune system is triggered, what cells go to the regions of infection, interact w/ other cells during antigen presentation, and respond to said inflammation?
leukocytes!
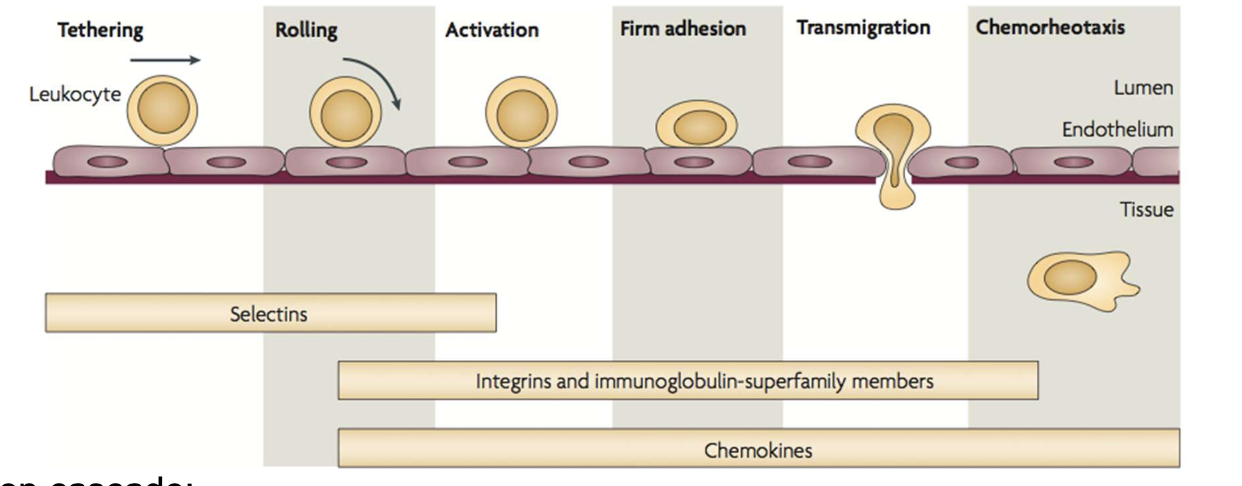
So wtf do lipid rafts got to do with leukocytes/immune response?
lipid rafts come into those regions/membranes, where leukocytes interact with inflamed vascular tissue, and facilitate that interaction!
—> faster immune healing!
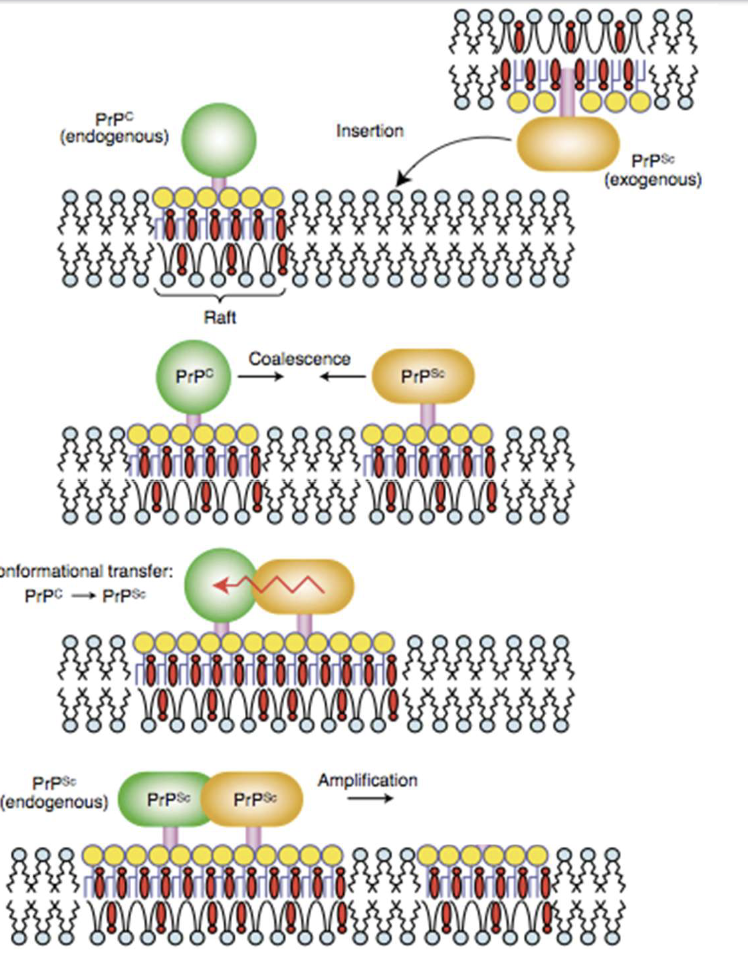
Next we will talk about how lipid rafts apply to prions:
Rem. prions are conversions of PrPC to PrPSc.
This requires the insertion of PrPSc into the continuous membrane.
rem. PrPc IS a membrane protein (typically in neuron synapse membranes)
Wtf do lipid rafts got to do with prions?!
Lipid rafts may coalesce to allow the close contact of PrPC and PrPSc proteins.
—> allows PrPC to convert into PrPSc
So studying lipid rafts may help us DISRUPT that process and prevent prions from propagating.
Lastly how can pathogens interact with lipid rafts?
well viruses like covid-19 (corona) can take advantage of the high receptor concentration within lipid rafts, to enter the cell. and thus infect it.
So lipid rafts could explain why people experience such different symptoms to the same virus?!
yup!! maybe!