AP Econ Unit 4
1/53
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
54 Terms
financial sector
network of institutions that link borrowers and lenders
includes banks, mutual funds, pension funds & other financial intermediaries
3 tasks of financial system
reduce transaction cost
reduce risk
provide liquididy
assets
anything tangible or intangible that has value
interest rate
the amount a lender charges borrowers for money, the price of a loan or cost of money
interest-bearing assets
assets that earn interest over time eg bonds
investment
always refers to businesses increasing capital stock (machinery & tools)
liquidity
the ease with which an asset can be converted to cash
stocks
aka “equities”
represent ownership of a corporation
stockholder hopes value of equity rises & they can make a capital gain (sell for more than they purchased it for)
bonds
aka “securities”
loans issued by gov, business, or individual
issuer of debt must repay to the lender for a specific period of time
the bond holder has no ownership of the company & is paid interest on the bond
a bond is issued at a specific interest rate that doesn’t change throughout the life of the bond
higher liquidity than stocks
investors always consider new interest rates to older bonds
bond prices & interest rates are inversely related
savings account
bank/credit union keeps your $ safe while sometimes paying low variable interest rate
sometimes have min balance requirement
aka “demand deposits because depositor can claim $ at any time
Certificate of Deposit
type of savings account that pays a fixed interest rate on your set deposit for a set period of time
*lower liquidity & higher interest rate than savings account
Nominal interest rates
% increases in $ that the borrower pays (not adjusted for inflation)
nominal = real interest rate + inflation
real interest rates
the % increase in purchasing pwr that a borrower pays (adjusted for inflation)
real=nominal interest rate - expected inflation
first form of money
barter system
goods & services traded directly no “medium of exchange”
problems
double coincidence of wants necessary (both parties must want what the other has)
some goods cannot be split
what is money
anything that is generally accepted in payment for goods & services or in the repayment of debts
wealth
accumulation of assets over time
income
flow of earnings per unit of time
functions of money
medium of exchange
unit of account
store of value
medium of exchange
used to buy goods & services with no complications of barter system
a medium of exchange must be
standardized
accepted
divisible
portable
long lasting
unit of account
used to measure value in the economy
store of value
allows you to store purchasing power for the future
evolution of money
commodity money: item performs the function of money & has intrinsic value
fiat money: something that serves as money due to government decree but has no other value or uses
M1
most liquid assets - $ used in everyday transactions
currency in circulation
checkable bank demand deposits (checking account)
savings deposits (ex money market account)
M2
less liquid- short term savings vehicles
M1
time deposits (Certificate of deposits)
terms >7 days $<100000
money market funds
money market accounts
type of bank account that earns higher interest than a savings account & allows checks/debit card options
usually limits # of withdrawals per month
money market funds
type of mutual fund (pools investors money together)
invests in short-term bonds
not FDIC insured
monetary Base (M0)
all physical currency in circulation & the reserves held by commercial banks @ the federal reserve
M0 grows when the federal reserve buys bonds from banks or when more ppl hold cash/coins
assets
what a bank owns
required reserves
excess reserves
loans
securities/bonds
physical assets
liabilities
what a bank owes
demand deposits
other deposits
debts/liabilities
owner equity (profit owed to bank’s owners)
balance sheet
a record of a bank’s assets liabilities & net worth
reserves
the portion of deposits that banks have not lent out
required reserves (rr)
% of deposits banks must hold by law
excess reserves
the amount the bank can loan out
fractional-reserve banking
a system in which banks hold a fraction of their deposits as reserves
money multiplier
1/rr
Why do ppl demand money?
transaction demand for money
asset demand for money
transaction demand for money
ppl hold money for everyday transactions
asset demand for money
ppl hold money since its less risky than other assets
money demand shifters
changes in aggregate price level
if inflation increases…
changes in real GDP
if someone gets more $…
changes in tech
ATM’s affect on society
changes in banking institutions
invention of interest bearing checking account
demand for money graph
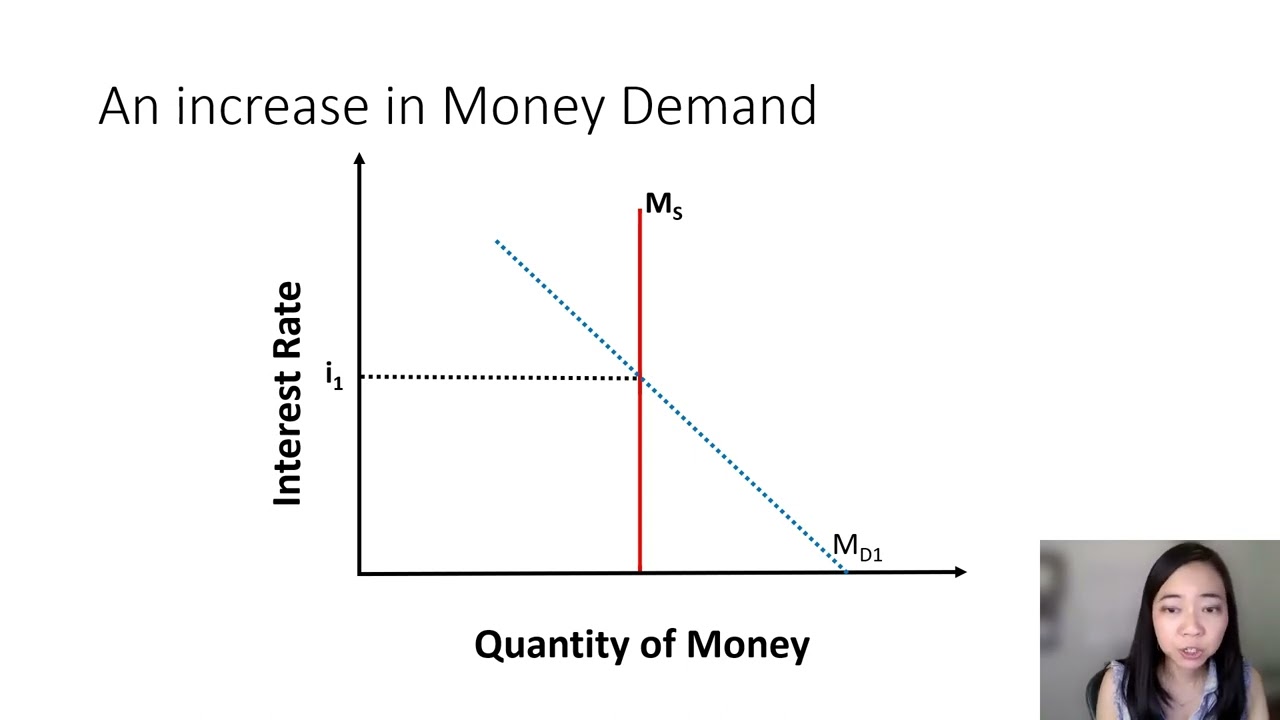
supply of money is…
set by central bank independent from the interest rate
Money supply ~
monetary base
*monetary policy
when MS increases…
interest rates decrease → investments increase → AD, GDP, & PL increase
when MS decreases…
interest rates increase → investments decrease → AD, GDP, & PL decrease
federal reserve
created in 1913 as 12 regional banks spread across US
independent of gov & w/o a single bank controlling all policies
structure of the fed
board of governors
chairman
12 federal reserve districts
board of governors
7 members appointed for 14 year terms
governors guide the fed’s policy actions
chairman
1 member of the board is selected by the president to serve as chairman for a 4 year term
12 federal reserve districts
1 federal reserve bank per district which reports economic activity in its district
3 Shifters of Money Supply
reserve requirement
discount rate
open market operations
reserve requirement
the % of deposits banks must hold in reserve
discount rate
the interest rate the fed charges commercial banks
to increase money supply the fed should decrease the discount rate
to decrease money supply the fed should increase the discount rate
open market operations
the fed buys or sells government bonds (securities)
to increase the money supply the fed should buy bonds
to decrease the money supply the fed should sell bonds
*buy→big sell→small
Federal funds rate
the interest rate banks charge each other for one-day loans of reserves (if a bank has insufficient funds to meet the fed’s reserve requirement")