AP Bio Units 1 and 2
1/99
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Independent Variable
The variable that is being changed by the scientist
Dependent Variable
The variable that’s being measured by the scientist and is affected by a change to the independent variable
Monomers
Simplest unit of macromolecules
Polymers
Large macromolecules, made of repeating monomers linked with covalent bonds
Free vs bound ribosomes
Free ribosomes float in the cytosol while bound one are attached to the ER or nuclear envelope
How are molecules built?
Through dehydration synthesis
Dehydration synthesis
The building of complex molecules by bringing two smaller ones together, removing an H2O molecule and replacing it with a bond
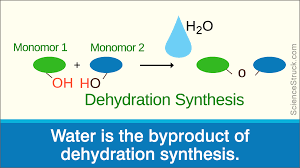
Hydrolosis
The reverse of dehydration synthesis, when water is added to break the bonds between a molecule
What atoms are carbohydrates built from?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
What ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen is present in carbohydrate monomers?
1:2:1
What are carbohydrates used for?
Short-term energy storage and structure
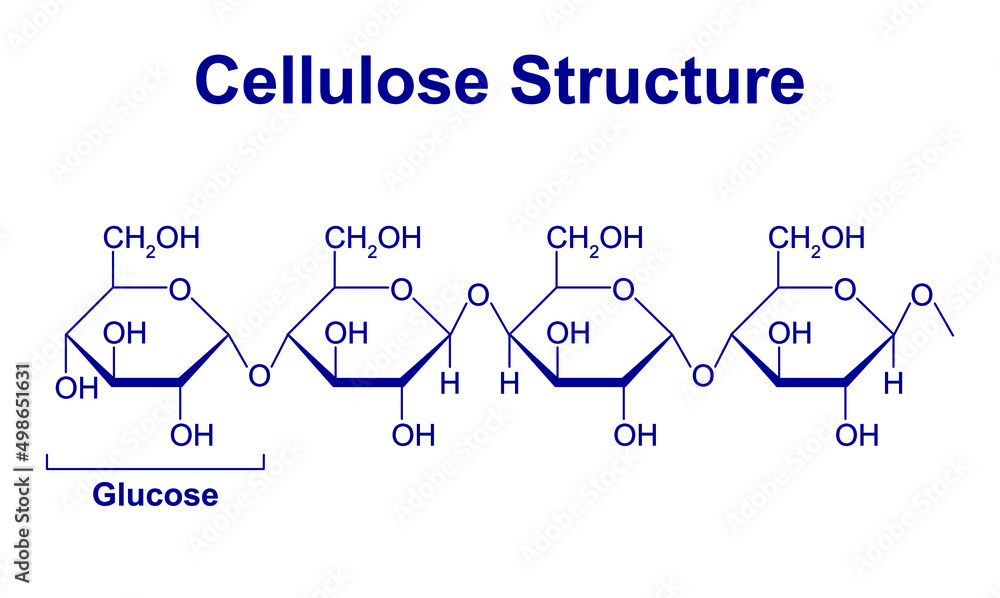
What’s the difference between starch and cellulose?
Starch is alpha linked; cellulose is beta linked.
How do plants store polysaccharides?
In starch
How do animals store polysaccharides?
In glycogen
How do cells use polysaccharides for structural support?
They use cellulose for stability in cell walls
How do fungi and insects use polysaccharides for structural support?
Fungi use chitin for support in cell walls, insects use it for structure in exoskeletons.
What atoms make up lipids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
What are lipids used for?
Long-term energy storage and insulation.
What are triglycerides?
1 glycerol and 3 fatty acids connected through dehydration synthesis.
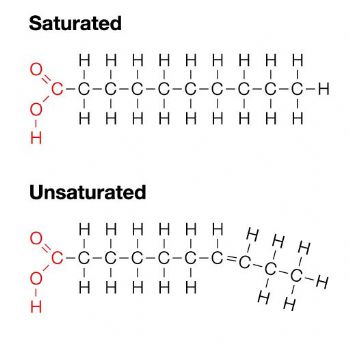
Saturated Fatty Acids
Single bonds between the carbons, they stack and are difficult to break. Solid at room temperature
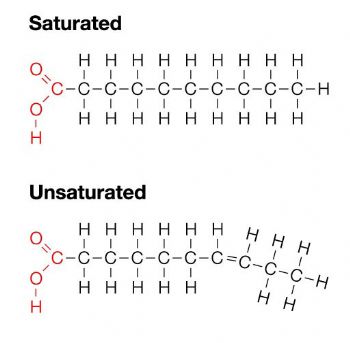
Unsaturated Fatty Acids
At least one double bond between the carbons. Liquid at room temperature
Phospholipids
Modified triglycerides with a polar head and two non-polar tails
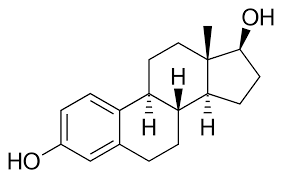
Steroids
Characterized by 4 fused carbon rings. (Cholesterol and some hormones)
What is the most complex group of macromolecules?
Proteins
What atoms make up proteins?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur
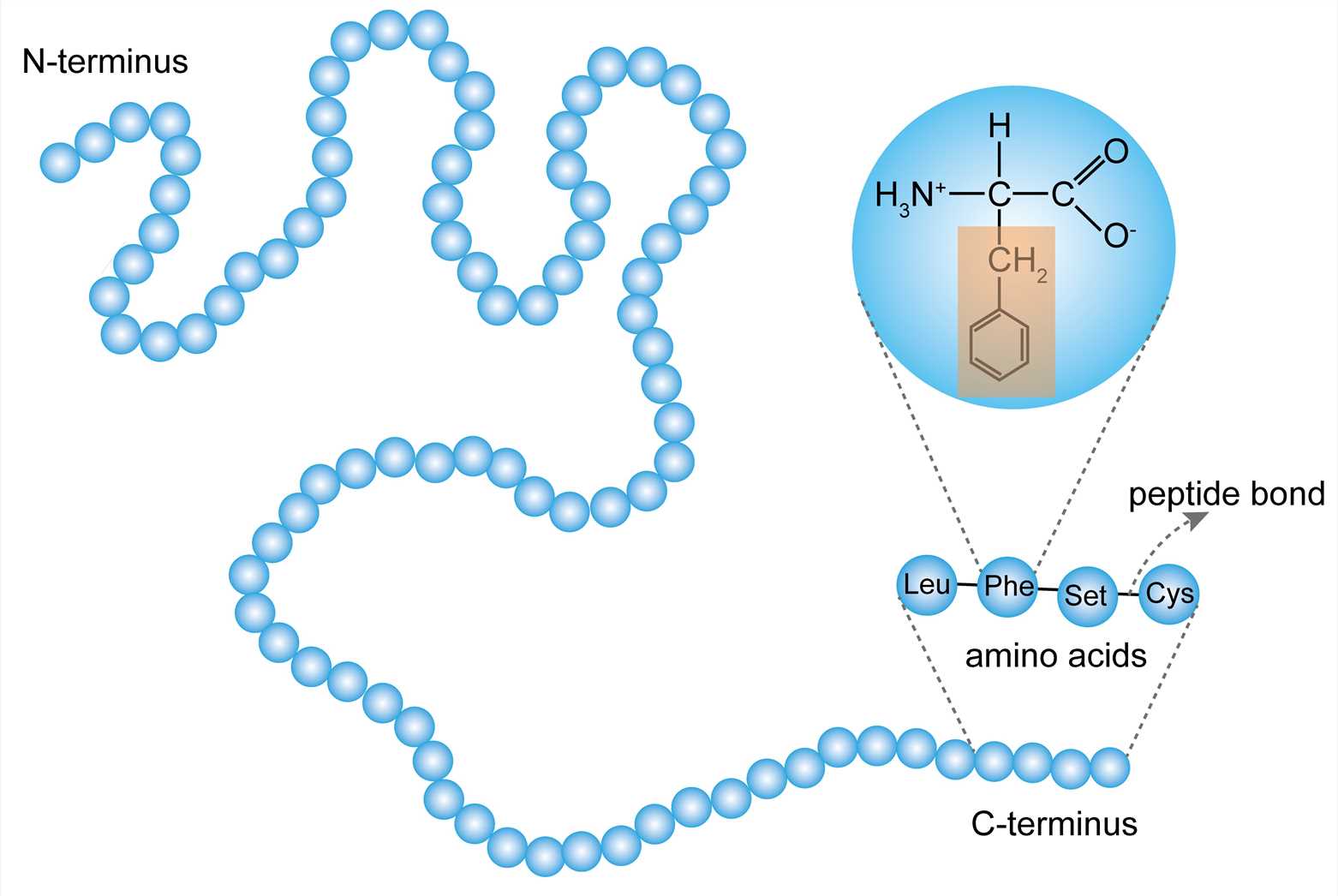
How are amino acids joined?
They’re joined with peptide bonds
What are proteins polymers of?
Amino acid monomers
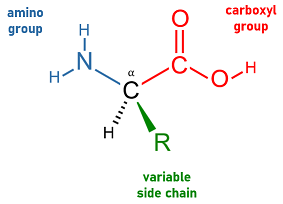
Amino Acids
Compounds that make up proteins and polypeptide chains. They vary based on the ‘R’ group and are characterized by a central carbon atom joining an amino group and a carboxyl group
What are the four stages of protein structure?
Primary, Secondary, Tertiary, and Quaternary structure
Primary Structure
Sequence of Amino Acids joined by peptide bonds. The order of the amino acids is dictated by DNA
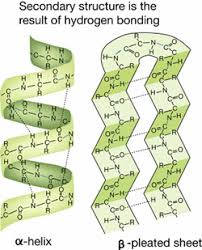
Secondary Structure
The result of hydrogen bonding of atoms in the Carbon-Nitrogen backbone of the polypeptide chain, causing the protein to fold into and alpha helix or beta pleated sheet
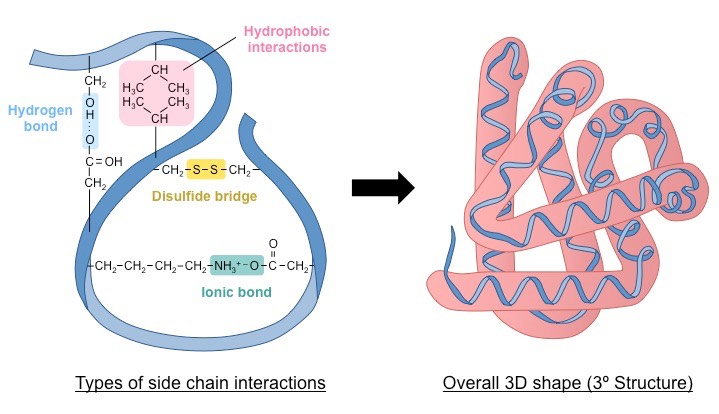
Tertiary Structure
The specific 3-D shape the protein folds itself up into. It happens through interaction between R-group atoms. The structure is generally stabilized by outside polar hydrophilic hydrogen and ionic bond interactions, and internal hydrophobic interactions between non-polar amino acid side chains. The way the protein folds determines its function.
Quaternary Structure
The only optional step of protein structure. When the polypeptide chains combine with non-covalent bonds to form one functional protein.
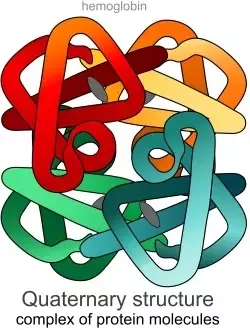
8 protein functions
Storing amino acids
Building structure/Fibrous framework
Hormones (coordinating organism activity)
Defense
Transport of Substances
Receptor of cell-cell chemical stimuli
Movement (contraction and motor proteins)
Enzymes (acceleration of chemical reactions)
Denaturation
Change in structure of the protein due to high temperature, high acidity, high salinity, etc. Protein becomes biologically inactive.
Nucleolus
Found within nucleus and produces ribosomes
What are nucleic acids used for?
Information storage
What atoms make up nucleic acids?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Phosphorous
What do nucleotides consist of?
A phosphate, pentose sugar, and one of the four nitrogenous bases.
Nucleotides
The monomer that makes up nucleic acids
Prokaryote Cells
Cells with no organelles but ribosomes and DNA clusters. (bacteria cells)
Eukaryote Cells
Cells subdivided with internal membranes into various membrane-enclosed organelles (plant and animal cells)
Why is cell size important?
Because a small size helps maintain a high surface-area-to-volume ratio.
Why is a high surface-area-to-volume ration important for cells?
Because it ensures the rate of chemical exchange is adequate for the cell’s survival as only a limited amount of substances can cross the membrane per second.
What are organelles?
They’re specialized structures with specialized functions that partition the cell into compartments and provide membranes to act as sites for reactions.
What organelles are involved with building proteins?
The nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, Golgi apparatus, and vesicles.
Fluid Mosaic Model
A way of describing the cellular membrane, due to the phospholipid bilayer, it’s fluid and studded with various proteins.
Protein assembly line
Nucleus (mRNA) → Ribosomes (protein is made) → ER and Golgi Apparatus → (protein structures are formed) → Vacuole (delivers protein to where it’s needed)
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death, lysosomes break open and kill cells.
Vacuole
Large vesicles derived from the ER and Golgi Apparatus, used in transport and storage of materials
Lysosomes
Only found in animal cells, they digest large molecules with enzymes and clean up broken-down molecules. They can fill with undigested material if enzymes don’t work, which can disrupt cell function.
Phagocytosis
The engulfing of molecules by the cell membrane
Endomembrane System
Group of organelles in eukaryotic cells which forms a network
What two organelles are not part of the endomembrane system?
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts
How do mitochondria and chloroplasts differ from other organelles?
They have separate DNA and grow and reproduce on their own within the cell.
Endosymbiosis theory
This theory states that mitochondria and chloroplasts were once free living bacteria that were engulfed by an ancestral eukaryote.
Endosymbiont
A cell that lives within another cell. One provides energy, the other supplies raw materials or protection
Water potential
The potential energy of water; its tendency to move
Solute potential
determined by the solute concentration, as amount of solute increases, the solute potential decreases
Pressure potential
The amount of pressure exerted on the cell by the cell wall
Water potential equation
φ=φs+φp
What is the φ of pure water?
Zero, it has the highest water potential, all other water potential is negative.
How does water flow in respect to water φ?
Water flows from areas of high potential to those of low potential
What is the equation for solute potential (will be provided; not necessary to memorize)
φs= -iCRT
i= ionization constant, for all sugars it’s one, for salts it’s two
C= molecular concentration of solute
R= pressure constant (.0831 liters/bars/moles for sucrose)
T= Temperature in Kelvin (273+ temp C)
What are the characteristics of the structures of monosaccharides?
They have a carbonyl group (C=O) and multiple hydroxyl groups (-OH). The location of the carbonyl group determines whether the sugar is a aldose or ketose.
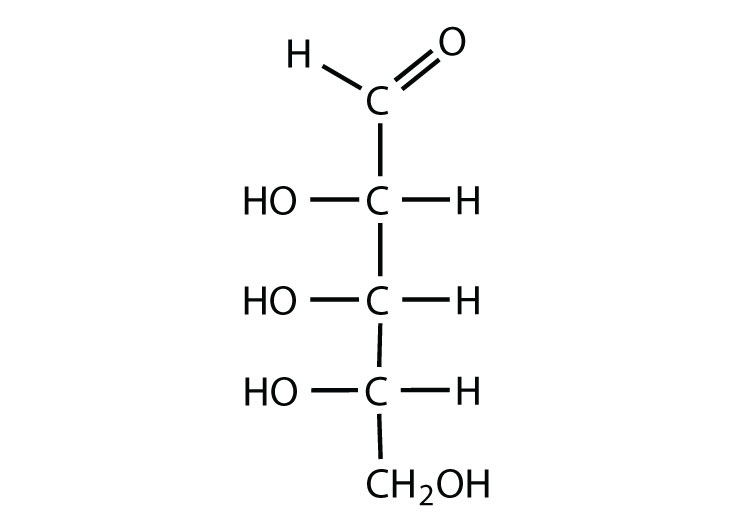
What joins the monosaccharides in a disaccharide?
A glycosidic linkage or covalent bond formed by dehydration synthesis
How do plants store starch?
As granules within cellular structures, or plastids
Where do animals store glycogen?
Mostly in liver and muscle cells
What’s different about the glucose monomers of cellulose compared to those of starch?
In cellulose, every other glucose monomer is “upside down”
When added to water, why do phospholipids automatically form a bilayer?
To shield their hydrophobic tails from the water.
Polypeptide
A polymer of amino acids
Amino Acid structure
Possess both an amino group and a carboxyl group
Sickle-Cell Disease
An inherited blood disorder caused by the substitution of one amino acid for the normal one at a particular position in the primary structure of hemoglobin resulting in the deformation of the cell
Chaperonins (Chaperone proteins)
Protein molecules that assist in the proper folding of other proteins.
Common features of cells
All are bound by a plasma membrane, contain cytosol, chromosomes, and ribosomes.
Cytosol
Semifluid substance within all cells that suspends all subcellular components
What kind of molecules are impermeable to the cell membrane?
Polar molecules (except water), charged ions, and large molecules
What functions do membrane proteins perform?
Transport, enzymatic activity, signal transduction, cell-cell recognition, intercellular joining, and attachment to cytoskeleton.
What role does cholesterol play in the cell membrane?
It allows it to be fluid and for molecules to pass through
Why must carbohydrates anchor to proteins?
Because they’re non-polar so they must covalently bond to a phospholipid head or protein in order to not be repelled from the cell membrane.
Simple Diffusion
The passive transport of non-polar hydrophobic molecules that follows the concentration gradient
Facilitated diffusion
The passive transport of polar, hydrophilic molecules through a protein channel; follows the concentration gradient.
Active transport
The diffusion against the concentration gradient using a protein pump and ATP
Membrane potential
The voltage across a membrane. The cytoplasmic side has a negative change with respect to the extracellular side due to the unequal distribution of anions and cations. Because of this, membrane potential favors the passive transport of cations into the cell and anions out.
Endocytosis
Bringing large molecules into the cell by engulfing them using ATP
Exocytosis
The release of large molecules from the cell
Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a semi-permeable membrane
Tonicity
The ability of a solution to cause a cell to gain or loose water
Isotonic
The solution has equal amounts of solute as the cell, so there’s no net water gain or loss by the cell
Hypertonic
The solution has more solute that the cell, cell looses water and shrivels
Hypotonic
Solution has less solute than the cell, cell gains water and swells
Lyse
When the cell bursts due to a large influx of water
Turgid
The healthy state for plant cells, full of water
Solute
The particles dissolved in a solution
Rough ER
Has attached ribosomes; involved in the producing and transporting of proteins
Smooth ER
synthesizes lipids like cholesterol or phospholipids; aids in detoxification.
Golgi Apparatus
Receives proteins from ER, further modifies, sorts, and transports molecules.
Mitochondria
Make ATP through cellular respiration using glucose and O2
Chloroplasts
Make glucose using light energy