Microeconomics - Chapter 13
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Monopoly
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
what is a monopoly
an industry controlled by a monopolist
def of market power
the ability of a firm to raise prices
what does a monopolist do
reduces the quantity supplied and moves up the demand curve which raises the price
why do monopolies exist
because there are barriers to entry
5 types of barriers to entry
control of a scarce resource or input, increasing returns to scale, technological superiority, network externalities, and government-made barriers
explain control of a scarce resource or input
a monopolist that controls a crucial resource or input can prevent other firms from entering its market
explain increasing returns to scale (economies of scale)
when the average total cost falls as output increases, firms then to grow larger. increasing returns to scale can give rise to and sustain a monopoly
explain technological superiority
a firm that maintains a consistent technological advantage over potential competitors can establish itself as a monopolist
explain network externality
the value of a good or service to an individual increases as more individuals use the same good or service
explain government-made barrier
a patent gives an inventor a temporary monopoly in the use or sale of an invention. a copyright give the creator of a literary or artistic work sole rights to profit from that work.
can monopolists choose the price
yes
all firms follow the same profit-maximizing rule
profit is maximized at the Q where MR=MC
what is the equation for marginal revenue
the change in total revenue / the change in quantity outputed
MR is _____ the demand curve because _______
below; of the price effect
when a monopolist increases production what effects happen?
the quantity effect and the price effect
explain the quantity effect
one more unit is sold, increasing total revenue by the price at which the unit sold
explain the price effect
to sell the last unit, the monopolist must cut the market price on all units sold; this decreases total revenue

C
recreate the monopolist’s profit-maximizing output and price graph
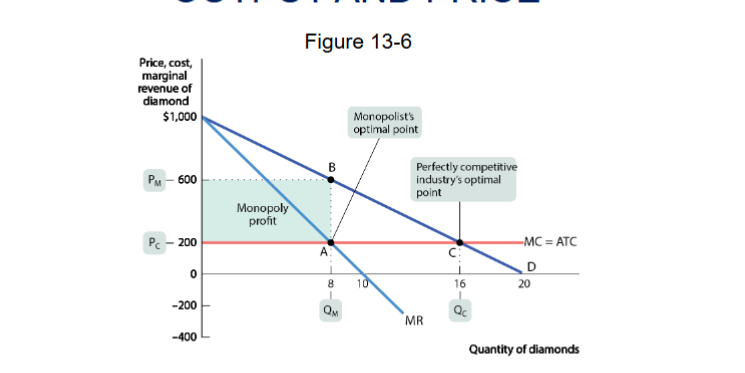

B
how is a monopoly a source of inefficiency
the losses to consumer from monopoly behavior are larger than the gains to the monopolist
recreate the graph the shows how a monopoly causes inefficiencies
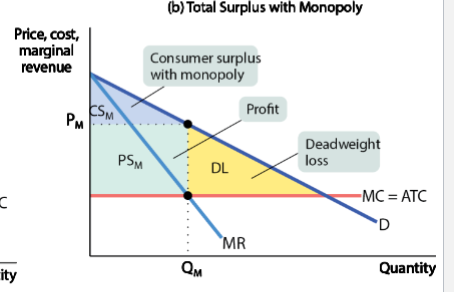
what are policy options to deal with natural monopolies
public ownership and regulation
explain public ownership
the government establishes a public agency to provide the good and protect consumers’ interest. (These are usually poorly run)
explain regulation
a price ceiling imposed on a monopolist does not create shortages if it its not set too low
recreate an unregulated and regulated natural monopoly graph
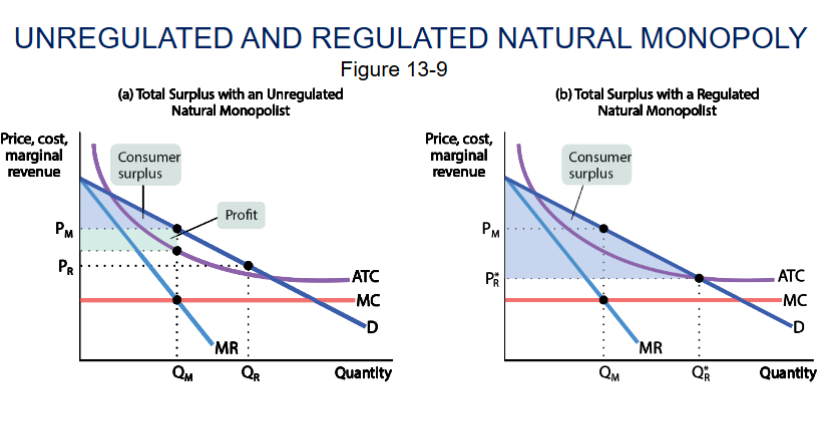
recreate the graph of logic of price discrimination
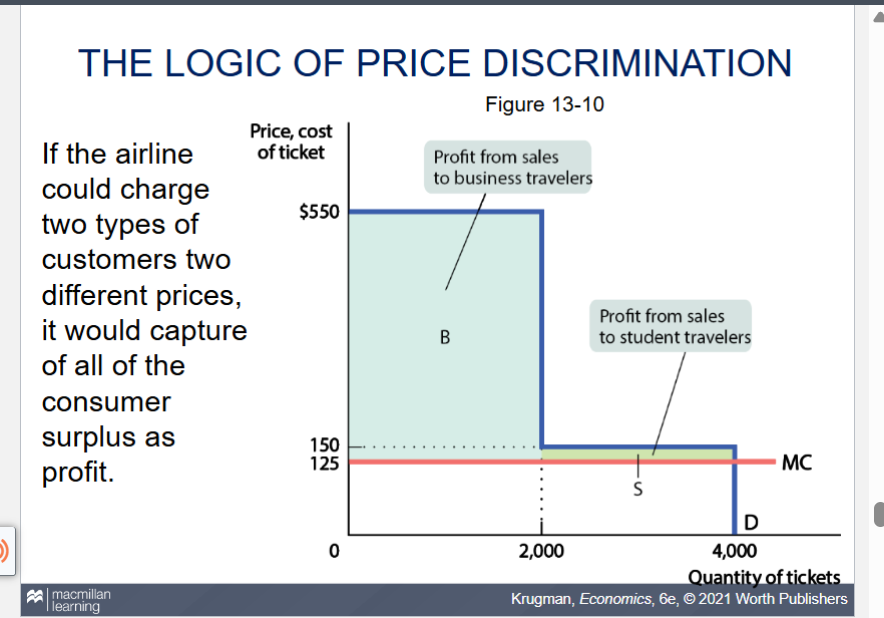
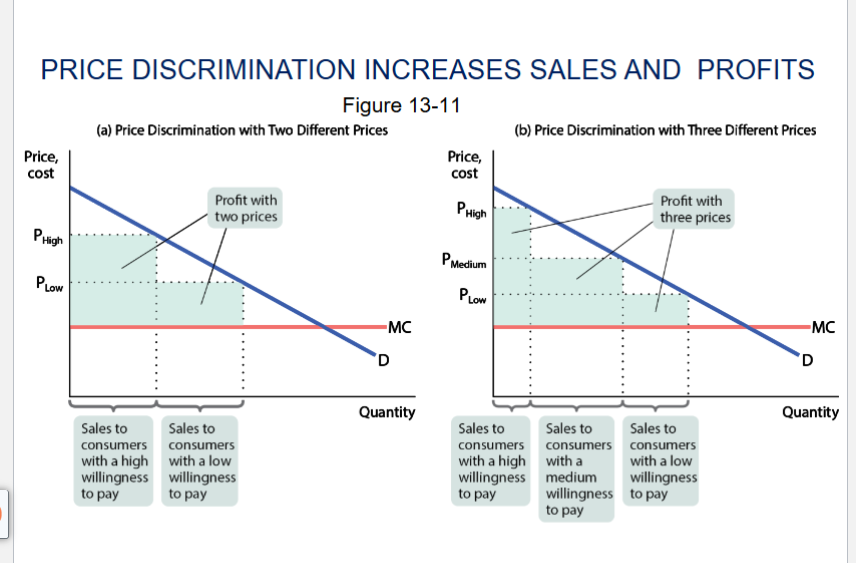
what is price discrimination
firms charge different prices to different consumers for the same good
recreate price discrimination increases sales and profits graph
perfect price discrimination=
the maximum price each group is willing to pay
what is a firm able to do under perfect price discrimination
the firm captures all consumer surplus as profit
recreate the perfect price discrimination graph
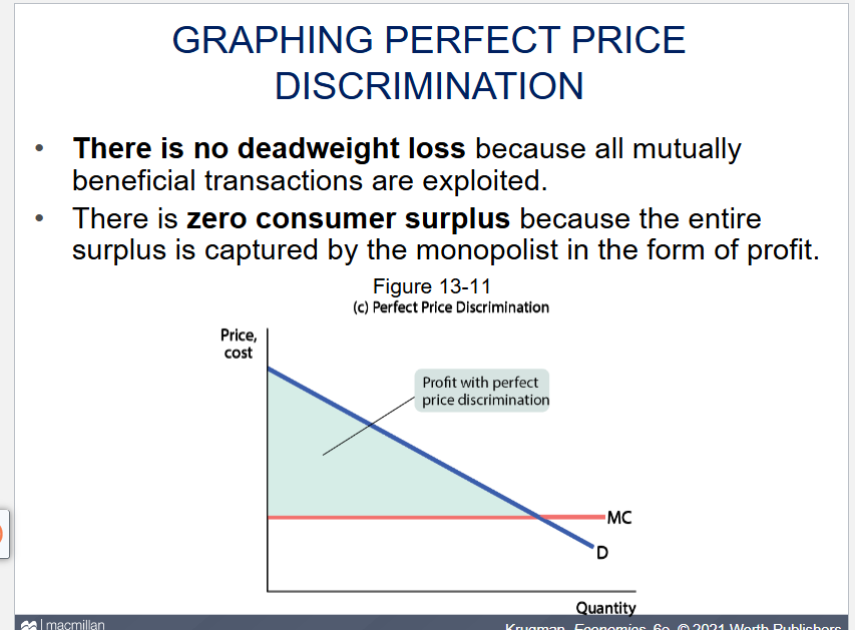
what are features of the perfect price discrimination graph
there is no deadweight loss and there is zero consumer surplus
what are common techniques for price discrimination
advance purchase restrictions, volume discounts, two-part tariffs, sales and outlet stores, and digital personalized pricing