Imaging
5.0(1)Studied by 18 people
Card Sorting
1/69
Earn XP
Last updated 3:57 PM on 11/16/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
70 Terms
1
New cards
DIP
Digital Image Processing
2
New cards
PACS
Picture Archiving & Communication Systems
3
New cards
Image processing
manipulating an image to enhance the image/extract useful information from it
4
New cards
Analog
Continuous-tone images produced by analogue optic + electronic devices that vary continuously over all dimensions of the image
For an analogue image to be processed or displayed by a computer, first its converted into a computer-readable form (digital format)
For an analogue image to be processed or displayed by a computer, first its converted into a computer-readable form (digital format)
5
New cards
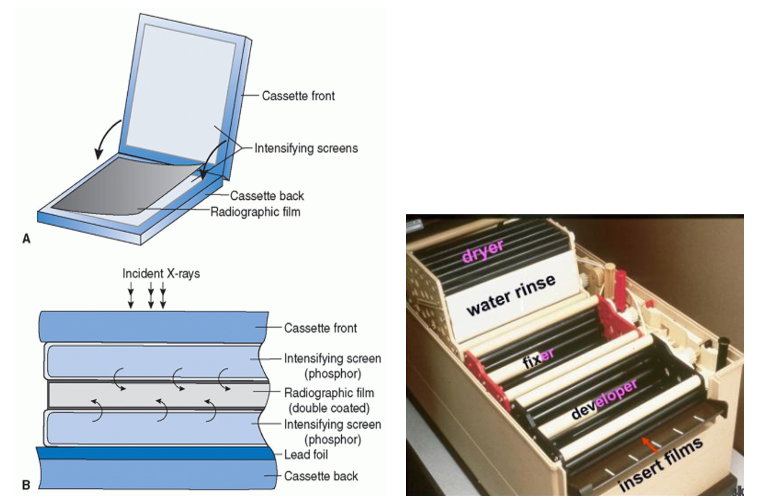
Screen/Film Radiography
process of taking image and processing for result
6
New cards
A digital image
matrix of many small bits- pixels (picture elements)
Each pixel is represented by a numerical value
The pixel value is related to the brightness/colour we see when the digital image is converted into an analogue image for display and viewing
Each pixel is represented by a numerical value
The pixel value is related to the brightness/colour we see when the digital image is converted into an analogue image for display and viewing
7
New cards
DIP
use of a digital computer to process digital images through an algorithm
8
New cards
development of DIP affected by
-Computers development
-Mathematic algorithms development
- demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science
-Mathematic algorithms development
- demand for a wide range of applications in environment, agriculture, military, industry and medical science
9
New cards
Computer language
Binary: 1 or 0 (on or off, black or white)
Bit: binary digit
limitations- the range of values that can be written with a specific number of bits is limited
Bit: binary digit
limitations- the range of values that can be written with a specific number of bits is limited
10
New cards
Binary values-
The number of bits that have been made available in the digital system to represent each pixel in the image
4 bits- limited to 16 different values (brightness levels or shades of grey)
4 bits- limited to 16 different values (brightness levels or shades of grey)
11
New cards
Digital Image Post-Processing
Film-based radiology is now obsolete,
all imaging modalities produce digital images that can be post-processed/ manipulated with relative ease
Main aim in rad imaging is to alter/change an image to enhance diagnostic interpretation
all imaging modalities produce digital images that can be post-processed/ manipulated with relative ease
Main aim in rad imaging is to alter/change an image to enhance diagnostic interpretation
12
New cards
Pre-Processing vs post-Processing
pre-processing operations apply appropriate corrections to the raw data
Post-processing intends to change the image contrast, reduce image noise and enhance the sharpness to enhance diagnostic interpretation
post-processing varies between modalities
Post-processing intends to change the image contrast, reduce image noise and enhance the sharpness to enhance diagnostic interpretation
post-processing varies between modalities
13
New cards
CR and DR
-Grey scale processing
-Spatial filtering
-Dynamic range control
-Spatial filtering
-Dynamic range control
14
New cards
Fluoroscopy
-Digital subtraction angiography (DSA)
-Subtraction of images out of a sequence
-Grey scale processing
-Temporal frame averaging
-Edge enhancement
-Subtraction of images out of a sequence
-Grey scale processing
-Temporal frame averaging
-Edge enhancement
15
New cards
CT
-Image plane reformatting
-Windowing
-Region of interest (ROI)
-3D volume rendering
--Multi-planar reformatting (MPR)
-Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP)
-Windowing
-Region of interest (ROI)
-3D volume rendering
--Multi-planar reformatting (MPR)
-Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP)
16
New cards
Imaging Processing Algorithms
Point processing operations e.g., grey scale processing (windowing, image subtraction, and temporal averaging)
Local processing operations (such as spatial filtering, edge enhancement, and smoothing)
Global operations such as the Fourier Transform (FT)
Local processing operations (such as spatial filtering, edge enhancement, and smoothing)
Global operations such as the Fourier Transform (FT)
17
New cards
Grey scale processing
Contrast stretching, Contrast enhancement, Histogram modification, Histogram stretching + Windowing (most commonly used across all modalities)
18
New cards
LUT
LUT= numerical info/ enhancing image contrast
Lookup tables are pre-calculated data (numeric info) stored in the computer: used to substitute new values for each pixel during the processing
Lookup tables are pre-calculated data (numeric info) stored in the computer: used to substitute new values for each pixel during the processing
19
New cards
Dynamic Range
Digital radiographic detectors have wide exposure latitude
The latitude (or dynamic range) is the range of receptor exposures over which an image and contrast will be formed
The latitude (or dynamic range) is the range of receptor exposures over which an image and contrast will be formed
20
New cards
Exposure index
EI is the measure of the amount of exposure received by the IR
-provides useful feedback to the rad about the accuracy of the exposure utilised
-Vendor specific but there is an international standard for EI
-provides useful feedback to the rad about the accuracy of the exposure utilised
-Vendor specific but there is an international standard for EI
21
New cards
Image Windowing
windowing is a way of adjusting the brightness and contrast of an image to visualise specific anatomy
selecting a segment of the total pixel value range (the wide dynamic range of the receptors) and then displaying the pixel values within that segment over the full brightness (shades of grey) range from white to black
selecting a segment of the total pixel value range (the wide dynamic range of the receptors) and then displaying the pixel values within that segment over the full brightness (shades of grey) range from white to black
22
New cards
Spatial Frequency Processing
Series of different algorithms used to post-process the image:
Edge enhancement-sharpness
Unsharp Masking- uses DSA to sharpen
Smoothing/blurring- reduce noise/graininess
Edge enhancement-sharpness
Unsharp Masking- uses DSA to sharpen
Smoothing/blurring- reduce noise/graininess
23
New cards
Geometrical Processing
Techniques allowing user to change the position/orientation of pixels in the image rather than the contrast/brightness of the pixels--> enhanced diagnosis
24
New cards
Image Reconstruction (CT)
-Multiplanar Reformatting (MPR)
-Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP)
-Volume Rendering/3D Reconstruction
-Maximum Intensity Projection (MIP)
-Volume Rendering/3D Reconstruction
25
New cards
Digital Breast Tomosynthesis - DBT
Imaging technique that allows a volumetric reconstruction of the whole breast from a finite number of low-dose two-dimensional projections obtained by different X-ray tube angles
26
New cards
Why health informatics?
Healthcare generates a vast amount of data that needs to be used, organised, stored, communicated and managed efficiently
27
New cards
Data
facts, observations or measurements (e.g., pts BP is 120/80mmHg)
28
New cards
Information
the relationships between data (eg pt's BP is considered high as its been greater than 135/95mmHg on 3 separate occasions)
29
New cards
Knowledge
application of information (eg pts BP has now measured 125/85mmHG + is now under control)
30
New cards
Digital data
Computers only work with digital data.
info 1st turned into a digital signal either: 'on' or 'off'
computer processor -collection of switches
Transistors= switches which can either be on or off
Info from input devices must be digitised so the info can be processed.
info 1st turned into a digital signal either: 'on' or 'off'
computer processor -collection of switches
Transistors= switches which can either be on or off
Info from input devices must be digitised so the info can be processed.
31
New cards
Digital Data Organisation - Databases
An organised collection of data stored and accessed electronically from a computer system/A Database Management System (DBMS) is the software that interacts with end users, applications, and the database itself to capture and analyse the data
32
New cards
Information Sharing
-Internet
-A global system of interconnected computer networks to communicate between networks and devices
-A global system of interconnected computer networks to communicate between networks and devices
33
New cards
Computer Networks
Allows different computers to share resources and exchange information
34
New cards
Info systems
An integration of components for collection, storage and processing of data
35
New cards
Health Information Systems- HIS
System designed to collect, store, manage and transmit healthcare data
tasks such as booking in pts + appointment scheduling
Manage a pt's electronic record + Analyse data to support healthcare policy decisions
tasks such as booking in pts + appointment scheduling
Manage a pt's electronic record + Analyse data to support healthcare policy decisions
36
New cards
Data analytics
Help gather, compile and analyse health data to help manage population health, reduce healthcare costs and improve patient care
37
New cards
Collaborative care
When patients need treatments from different healthcare providers, exchange of information between HIS, allow healthcare facilities to access common health records
38
New cards
cost control
Using digital networks to exchange healthcare data creates efficiencies and cost savings
39
New cards
Population health management
Aggregate pt data, analyse it and identify trends in populations. Clinical decision support systems can use data to help diagnose individual patients and treat them
40
New cards
Health Information Systems (HIS)
Main hospital system where pt is registered and is connected to all other systems. Manages all pt data
41
New cards
Radiology Information System (RIS)
System for the electronic management of imaging departments. Manages pt scheduling, resource management, examination performance tracking, reporting, results distribution etc.
42
New cards
Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)
A system connected to various imaging modalities that allows storage, viewing, manipulation and sharing of diagnostic images and reports
43
New cards
Electronic Health Record (EHR)
A longitudinal record of a patient's health and healthcare from cradle to grave (it is not associated with just one institution)
44
New cards
Electronic Patient Record (EPR)
A longitudinal record of a pts heath provided mainly by one institution (typically this relates to the healthcare provided by 1 hospital or a GP)
45
New cards
Electronic Medical Record (EMR)
An electronic record of an episode of medical care, whether inpatient, outpatient, A&E etc.
46
New cards
Interoperability
Characteristic of a system whose interfaces are completely able to work with other systems, at present or the future, in either implementation or access, without restrictions
47
New cards
Interoperability standards
Integrating the Healthcare Enterprise (IHE)-non-profit organisation: improve the way computer systems in healthcare share information
use of established standards such as DICOM and HL7 to address specific clinical needs in support of optimal patient care
use of established standards such as DICOM and HL7 to address specific clinical needs in support of optimal patient care
48
New cards
HL7 (Health Level 7)
International standards for transfer of clinical and administrative messaging data between software applications used by various healthcare providers- ‘layer 7’ in the OSI model
49
New cards
DICOM
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine- international standard to transmit, store, retrieve, print, process and display medical imaging information (medical jpeg/png)
50
New cards
Unique Identifiers (UID)
An identifier that is guaranteed to be unique among all identifiers used for those objects (in a database) and for a specific purpose
51
New cards
Terms, Codes and Classifications
Healthcare organisations often use different software and different terminologies/terms to record health information
E.g., 1 doc records a 'chest infection', other recorda it as 'upper-respiratory infection' so the 2 systems might not be able to match the info
needs to be a commonality to the way illnesses are described/ An agreed set of terms to describe illnesses, pathologies and conditions
E.g., 1 doc records a 'chest infection', other recorda it as 'upper-respiratory infection' so the 2 systems might not be able to match the info
needs to be a commonality to the way illnesses are described/ An agreed set of terms to describe illnesses, pathologies and conditions
52
New cards
SNOMED CT (Systemised Nomenclature of Medicine – Clinical Terms)
A systematically organised computer processable collection of medical terms providing codes, terms, synonyms, definitions used in clinical documentation and reporting
Considered to be the most comprehensive multilingual clinical healthcare terminology in the world- Provides clinical IT systems a single shared language, which makes exchanging information between systems easier,
Considered to be the most comprehensive multilingual clinical healthcare terminology in the world- Provides clinical IT systems a single shared language, which makes exchanging information between systems easier,
53
New cards
ICD 11 (International Classification of Diseases version 11)
medical classification list by World Health Organization (WHO)
contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases
contains codes for diseases, signs and symptoms, abnormal findings, complaints, social circumstances, and external causes of injury or diseases
54
New cards
Terminology server
A terminology server transforms the way in which data is captured, shared and analysed across healthcare, meaning more effective, efficient and safer decision-making
55
New cards
Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS)
A health info tech system- provides clinicians with knowledge and person-specific info, intelligently filtered/presented at appropriate times, to enhance health and health care
Links health observations with health knowledge to influence health choices by clinicians for improved health care
Links health observations with health knowledge to influence health choices by clinicians for improved health care
56
New cards
Picture
any medical image acquired through the various imaging modalities (DR, fluoro, US, CT, MRI, RNI, mammo etc.)
57
New cards
Archiving
storage of images (short + long term) via image archive servers, VNA or cloud based solutions
58
New cards
Communication
images need to be shared and visualised both internally within the organisation (hospital) and externally with other organisations
59
New cards
System
All the various components are connected, user can access the images via an application program
60
New cards
PACS
A computerised means of replacing the roles of conventional radiological film: images are acquired, stored, transmitted, and displayed digitally/allows the digital images generated by imaging modalities to be visualised, shared and stored. Revolutionised the practice of radiology/medical imaging + rad profession
61
New cards
VNA and Cloud Storage
Most healthcare organisations looking for a new PACS installations or upgrades will opt for a VNA and/or cloud storage solutions
62
New cards
Vendor Neutral Archive
Application that stores medical images in a standard format with a standard interface. Images stored in VNA can be accessed through any workstation, irrespective of the vendor
63
New cards
Advantages of VNA
PACS features can often vary between individual vendors, even if images are stored in the standard DICOM format. Despite the brand of software, VNA’S open on anything and file can be accessed on anything
64
New cards
VNA function
When image is stored in PACS, several ‘tags’ are added which vary between vendors, so final medical image file may open on other applications
VNA ‘uncouples’ the pure DICOM image from the surrounding fluff, ensuring that the image is standardised and compatible with all workstations
VNA allows healthcare providers to migrate from 1 vendor to another without worrying about imaging data loss
65
New cards
Web based PACS VS Client based PACS
66
New cards
systems used by rads
HIS, RIS + PACS
67
New cards
Display Moniter
Flat panel liquid crystal displays (LCDs) are the main types of monitors used offering high spatial resolution, low distortion, high luminance and high contrast ratios
68
New cards
Medical monitors
must allow custom measurement and adjustment of their colour and grayscale tonal representations to allow for calibration towards recognised reference standards (DICOM GSDF)
69
New cards
DICOM viewer
Within a hospital environment, PACS workstations are utilised to review radiographic images and examinations/ essential to view dicoms as they wont open on MACS/WINDOWS
70
New cards
Managing PACS
-Radiology Systems Manager
-PACS Manager
-PACS Administrator
-IT Support
-Vendor/Service Provider Support
-PACS Manager
-PACS Administrator
-IT Support
-Vendor/Service Provider Support