Deck 2: Head spaces, Vascular Supply to neck
1/86
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
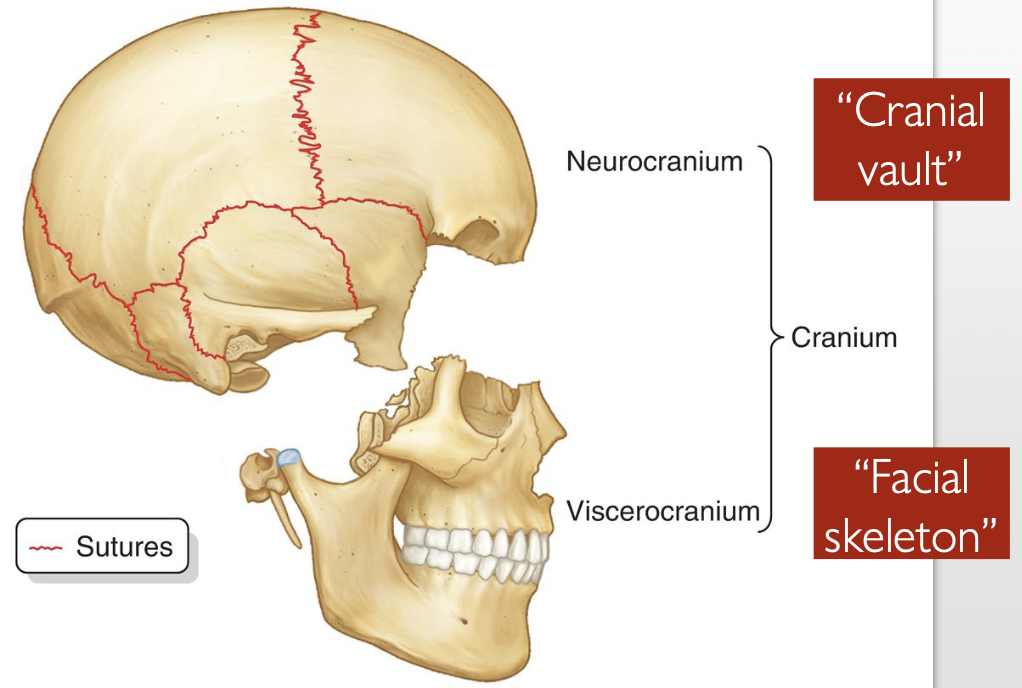
List the 2 parts of the Cranium/skull.
Neurocranium - “Cranial vault”
Viscerocranium - “Facial skeleton”
What is the Neurocranium?
→ encases the brain & cranial meninges
contains proximal parts of the cranial nerves & brain vasculature
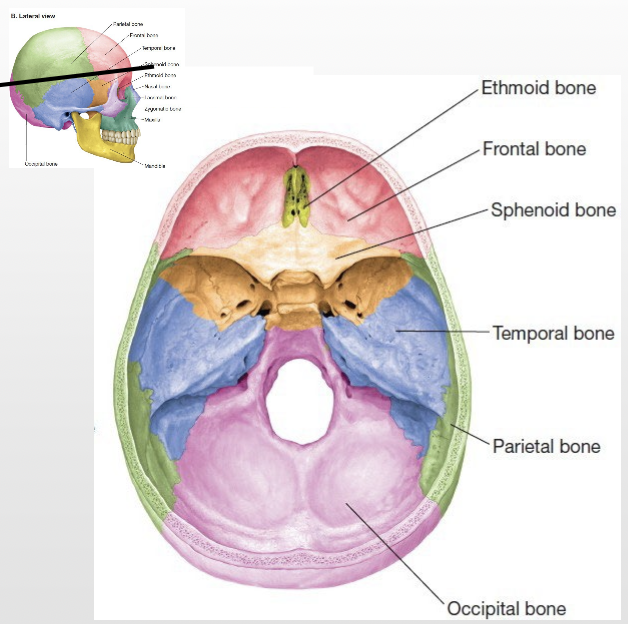
How many bones form the Neurocranium? List them.
8 bones
4 singular (midline) bones:
Frontal
Ethmoid
Sphenoid
Occipital
2 paired bones (bilateral):
Temporal (2)
Parietal (2)
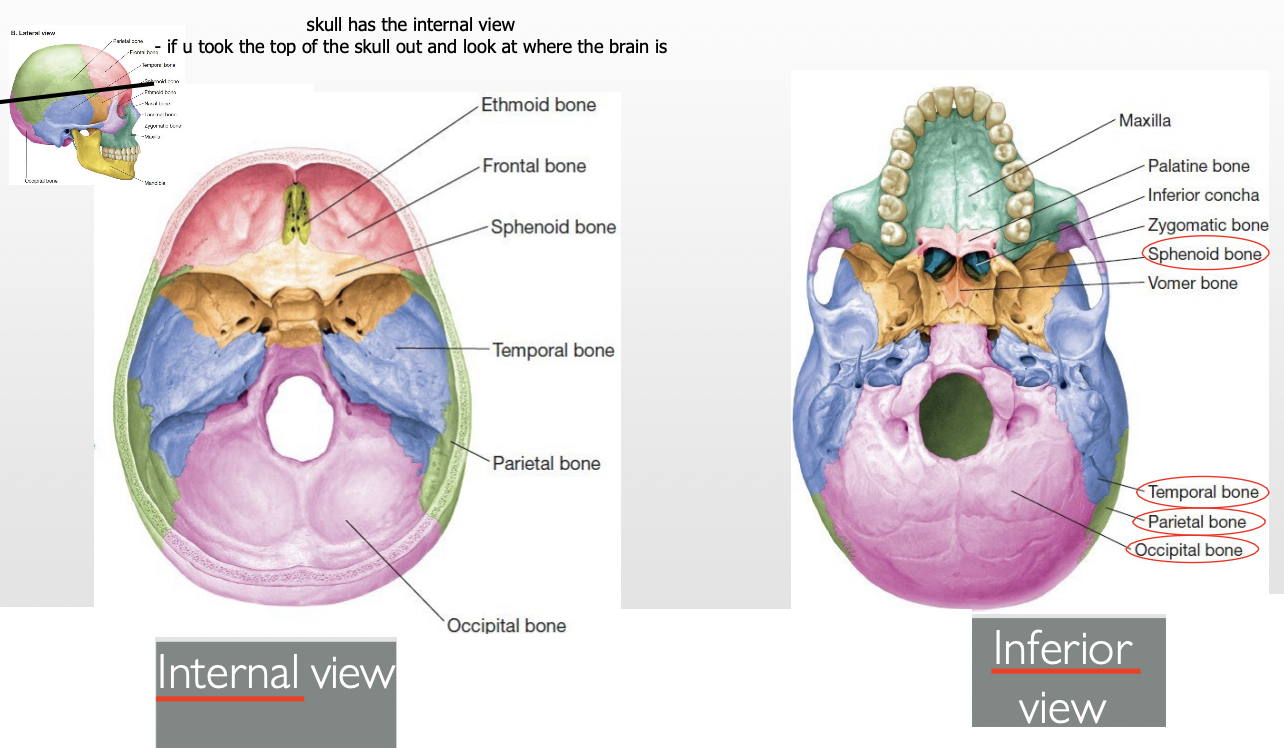
How many bones form the Viscerocranium? List them.
“My pal zoe likes indoor vacations.. never mind”
Maxilla (x2)
Palatine (x2)
Zygoma (x2)
Lacrimal (x2)
Inferior nasal concha (x2)
Vomer
Nasal (x2)
Mandible
Ethmoid*→ this appear in Neurocranium too
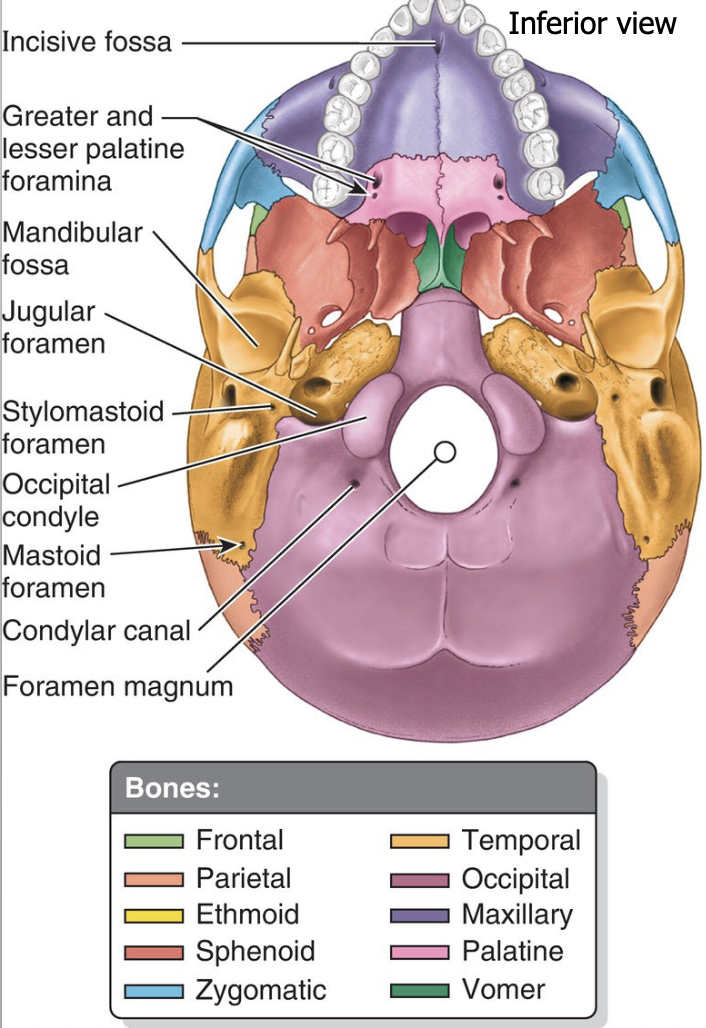
What’s the difference b/w an internal view vs inferior view?
What are cranial sutures?
Strong fibrous joints holding the bones of the skull together
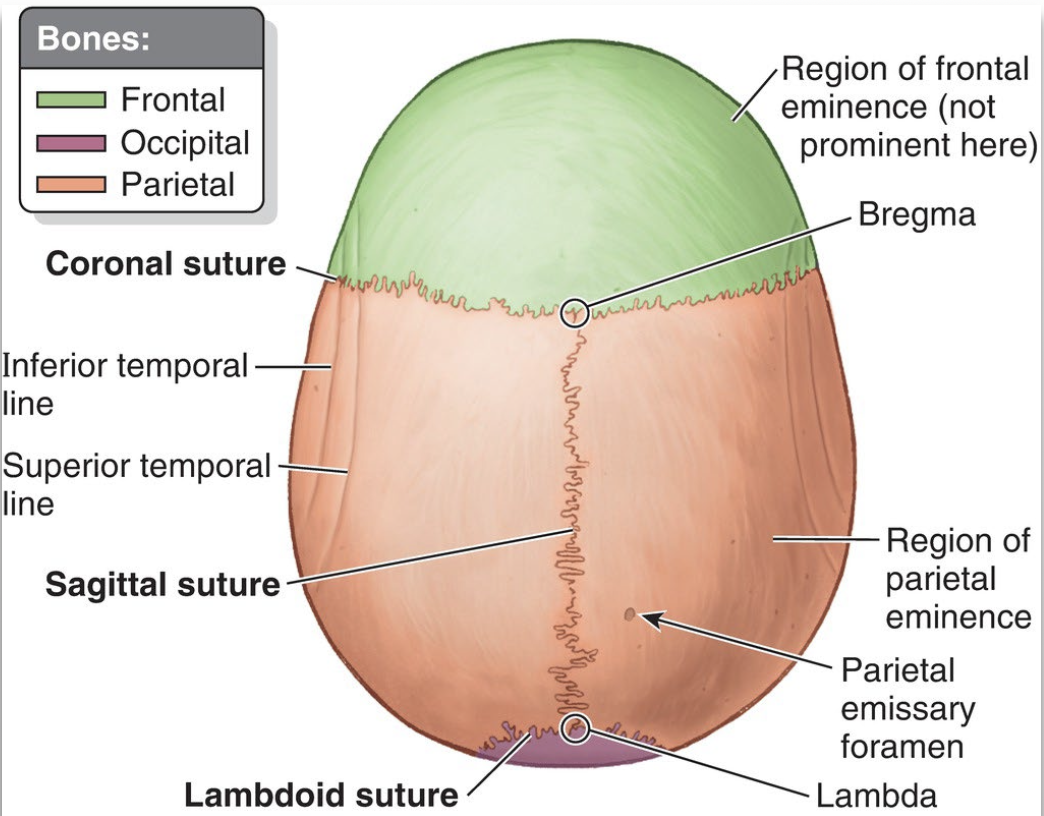
List the major sutures.
Coronal - “crown”
Sagittal - splits left and right
Lambdoid
The cranial base is divided into 3 regional depressions called _______. They are:
1)
2)
3)
The cranial base is divided into 3 regional depressions called fossa
Anterior
Middle
Posterior
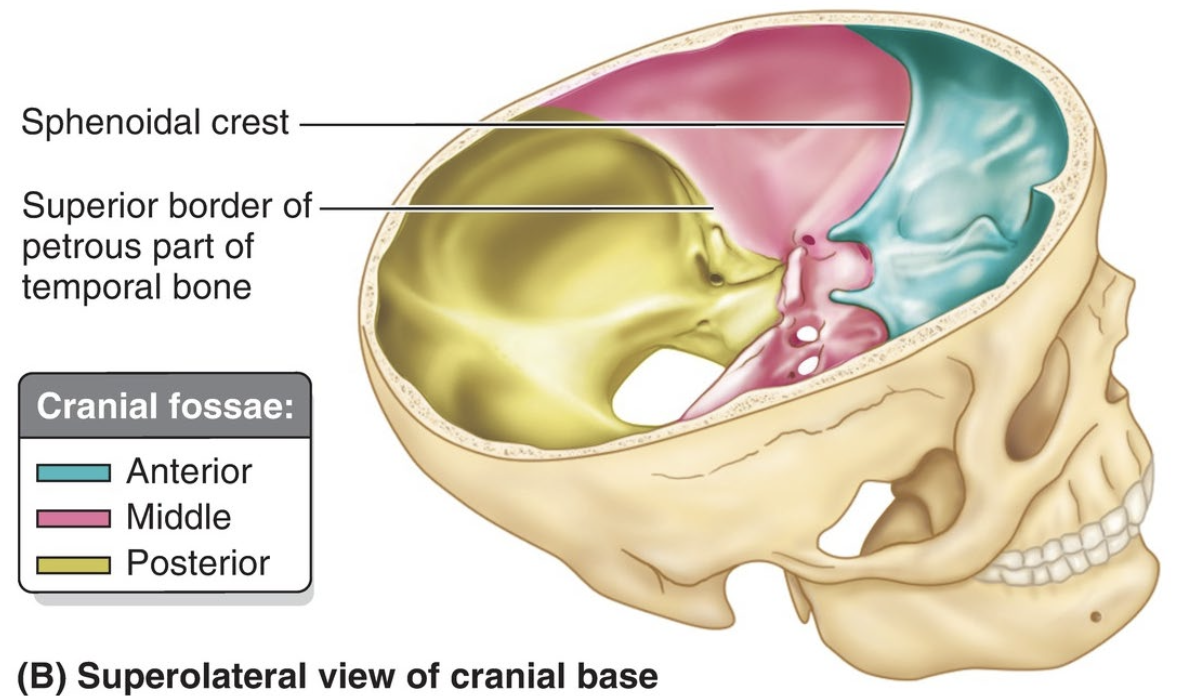
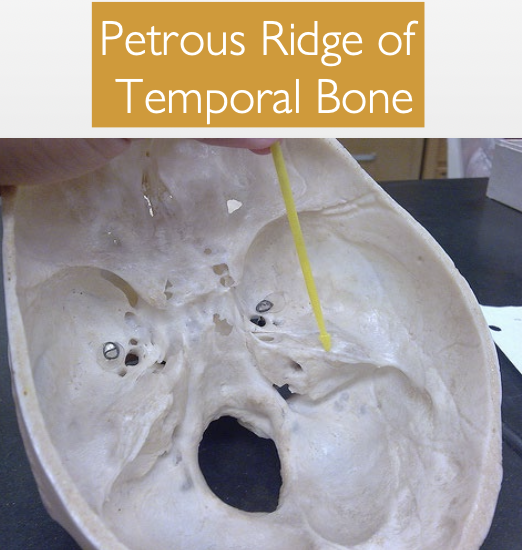
What 2 bony landmarks delineate the boundaries between the cranial fossae, and which fossae do they separate?
1) Sphenoid lesser wing → separates the anterior & middle fossae
2) Temporal bone petrous ridge → separates the middle & posterior fossae
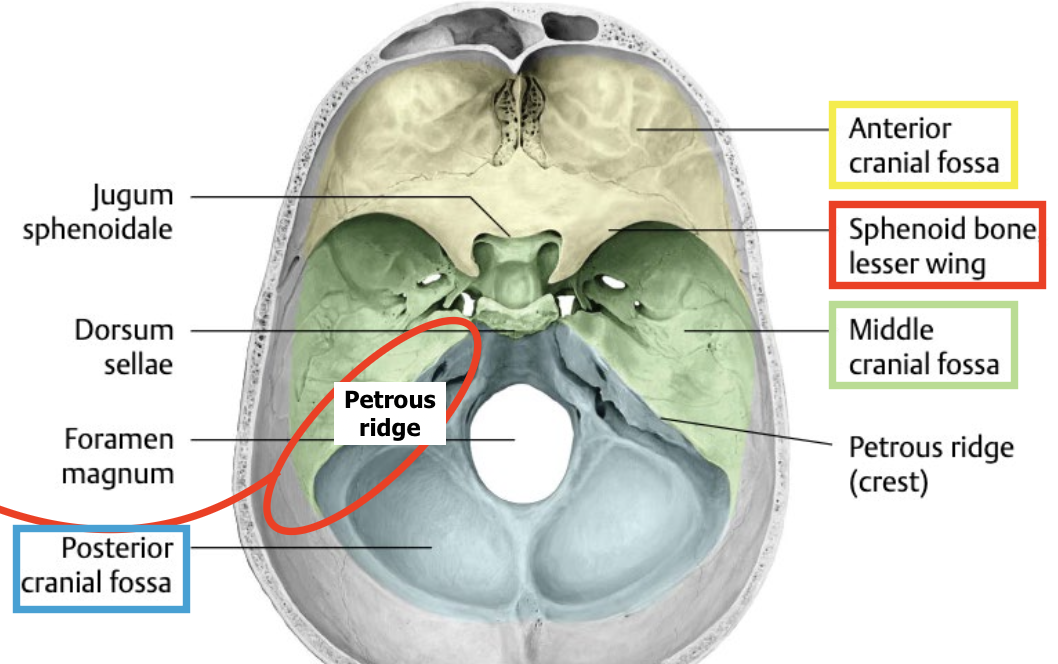
“solid” portion)
What is a foramen, and what is its function in the skull?
→ Opening or hole in a bone
allows passage of nerves, blood vessels, and other structures
connects the brain with other parts of the body
List the main rooms of the house.
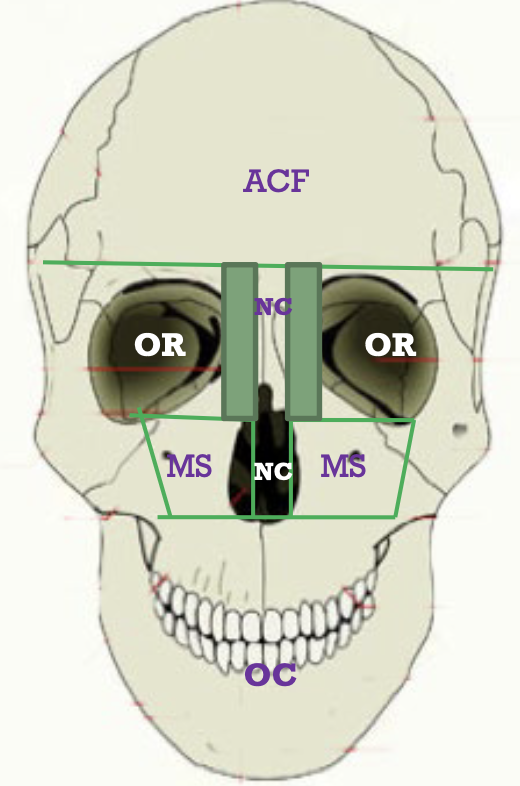
ACF – Anterior Cranial Fossa
MCF – Middle Cranial Fossa
PCF – Posterior Cranial Fossa
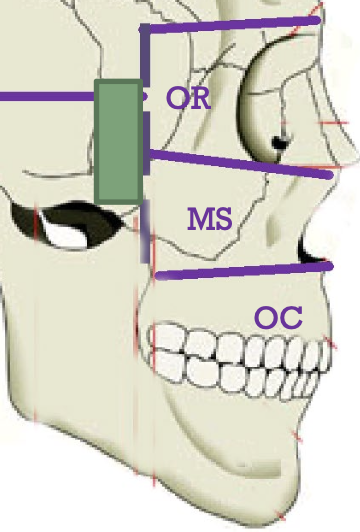
MS – Maxillary Sinus (paranasal sinus inside maxilla)
OC – Oral Cavity
NC – Nasal Cavity
OR – Orbit
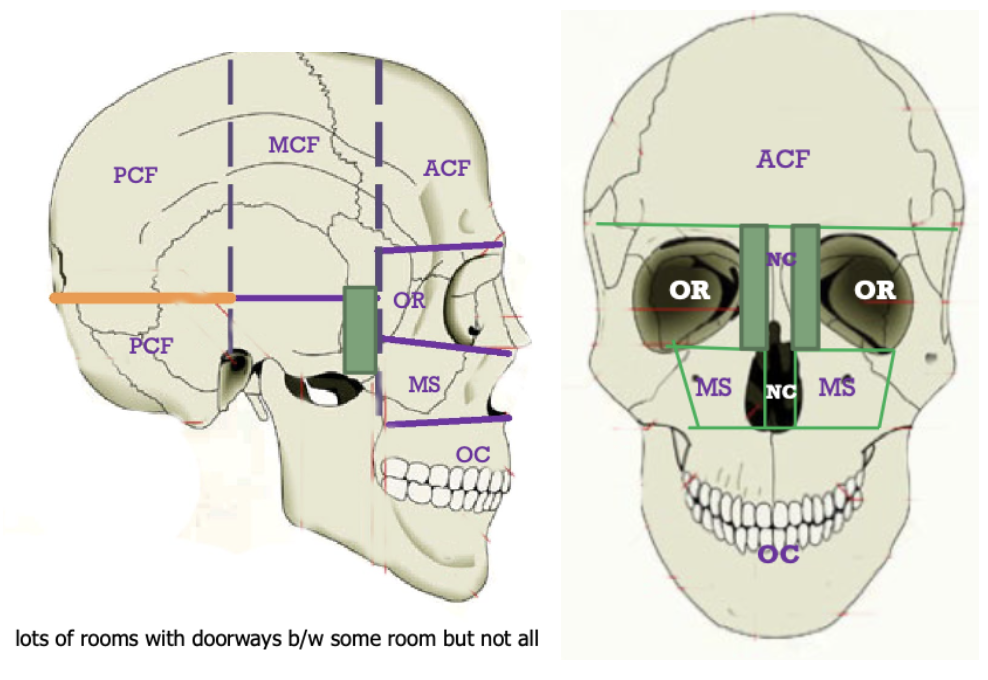
Label the main rooms of the house laterally and frontally. Mentions which rooms the 3 main rooms (ACF, MCF, PCF), can’t directly connect to.
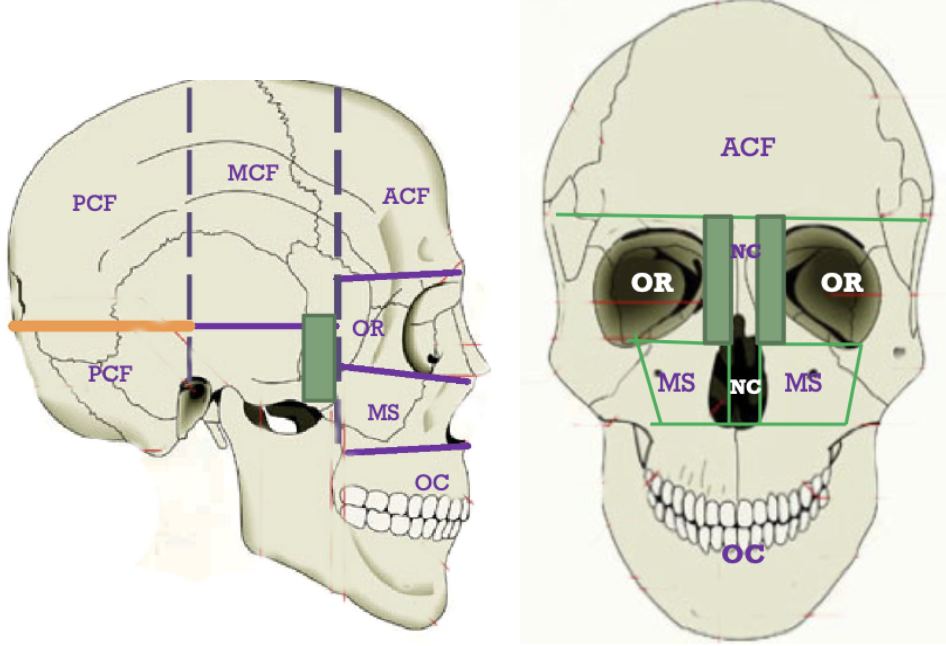
ACF = Middle or Posterior fossae
MCF = Nasal cavity, Oral cavity
PCF = Orbit, Nasal cavity, Oral cavity
What’s the only way the Pterygopalatine Fossa be viewed?
can only be viewed laterally
What are Ethmoid Air cells?
has multiple air spaces; considered a sinus
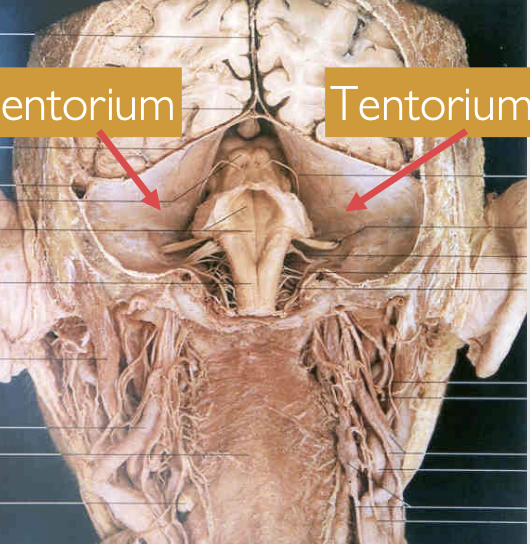
What is the Tentorium Cerebelli? Where is it attached?
→ a fold of the dura mater that separates the occipital and temporal lobes from the cerebellum and brainstem
also separates the posterior cranial fossa
attached along the petrous ridge of the temporal & occipital bone
looks like a “tent”
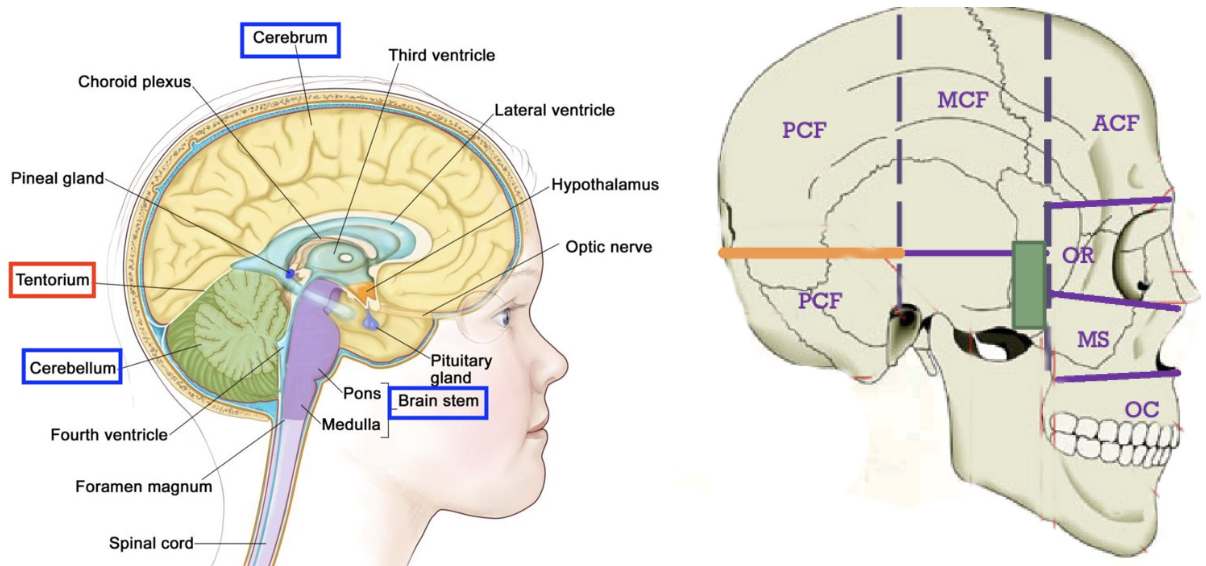
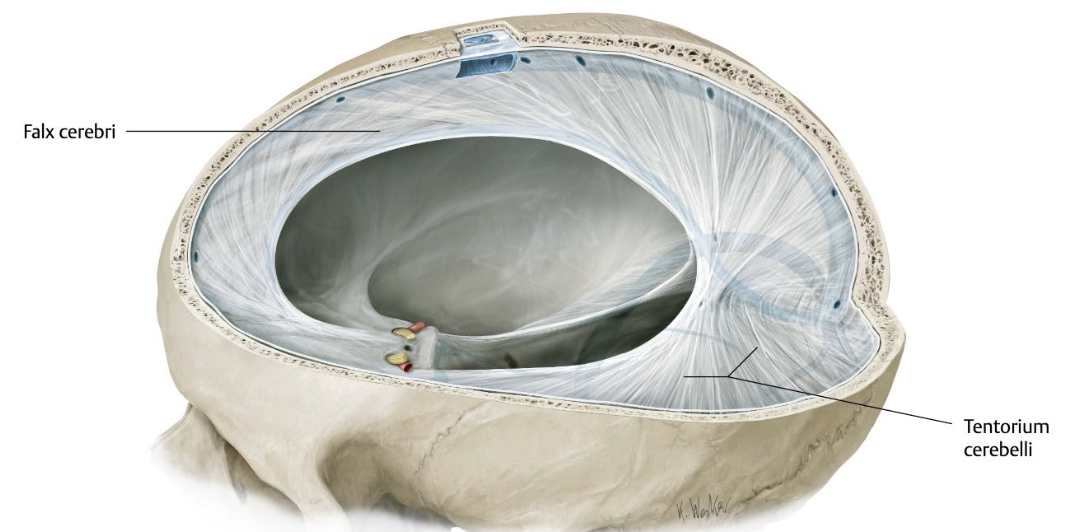
What is the falx cerebri?
→ fold of dura mater that divides the brain hemispheres into left and right, running along the sagittal plane
create spaces within the dura, which form part of the venous drainage system
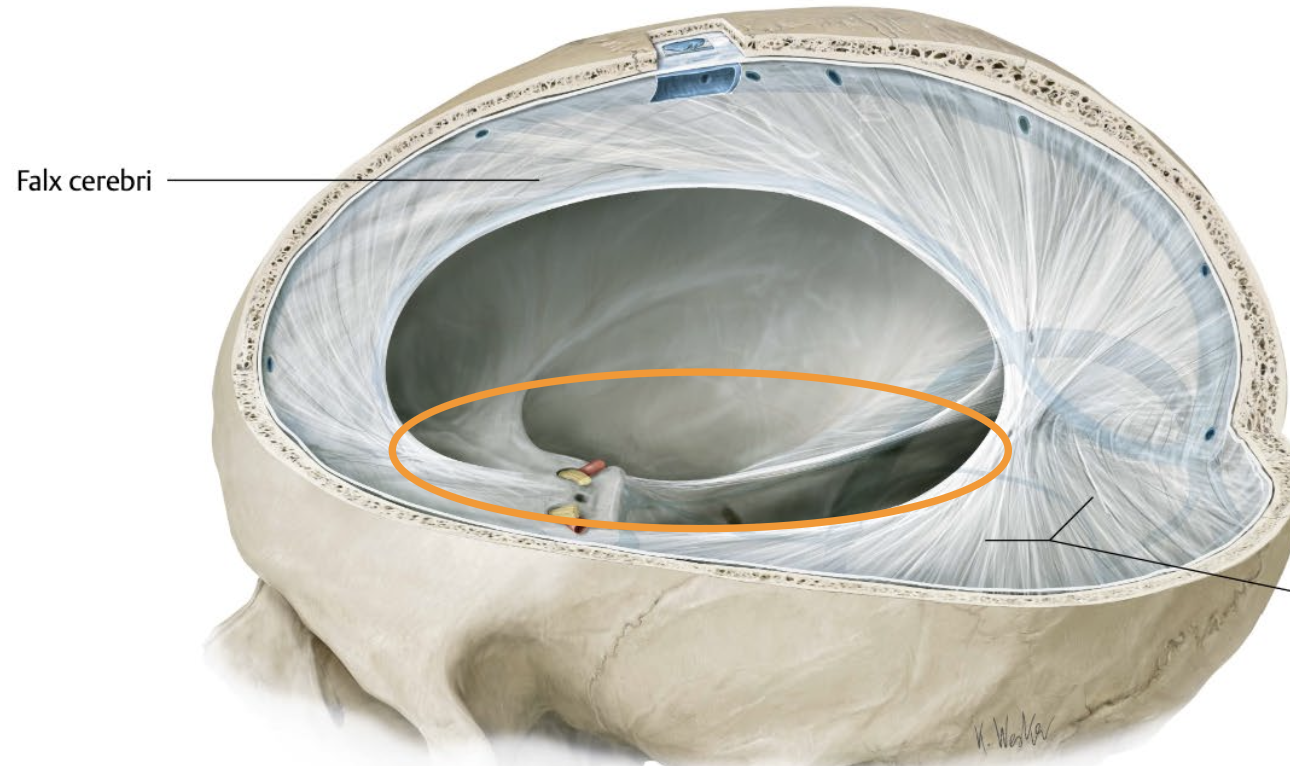
Note: Orange part shows the part of the Falx Cerebri that split the hemispheres into 2.
it’s also near the front (whereas tentorium is near the back)
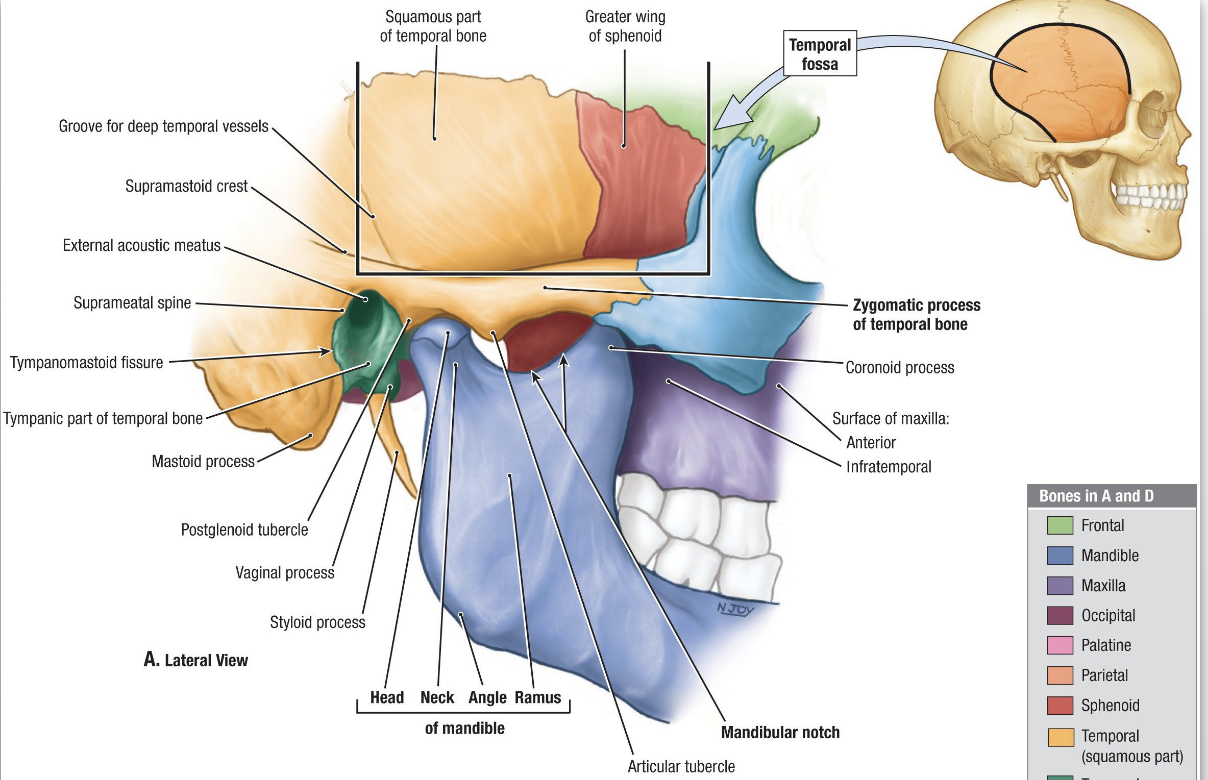
What is the Temporal Fossa?
→ contains the upper portion of the temporalis muscle
Location: area above the cheekbone
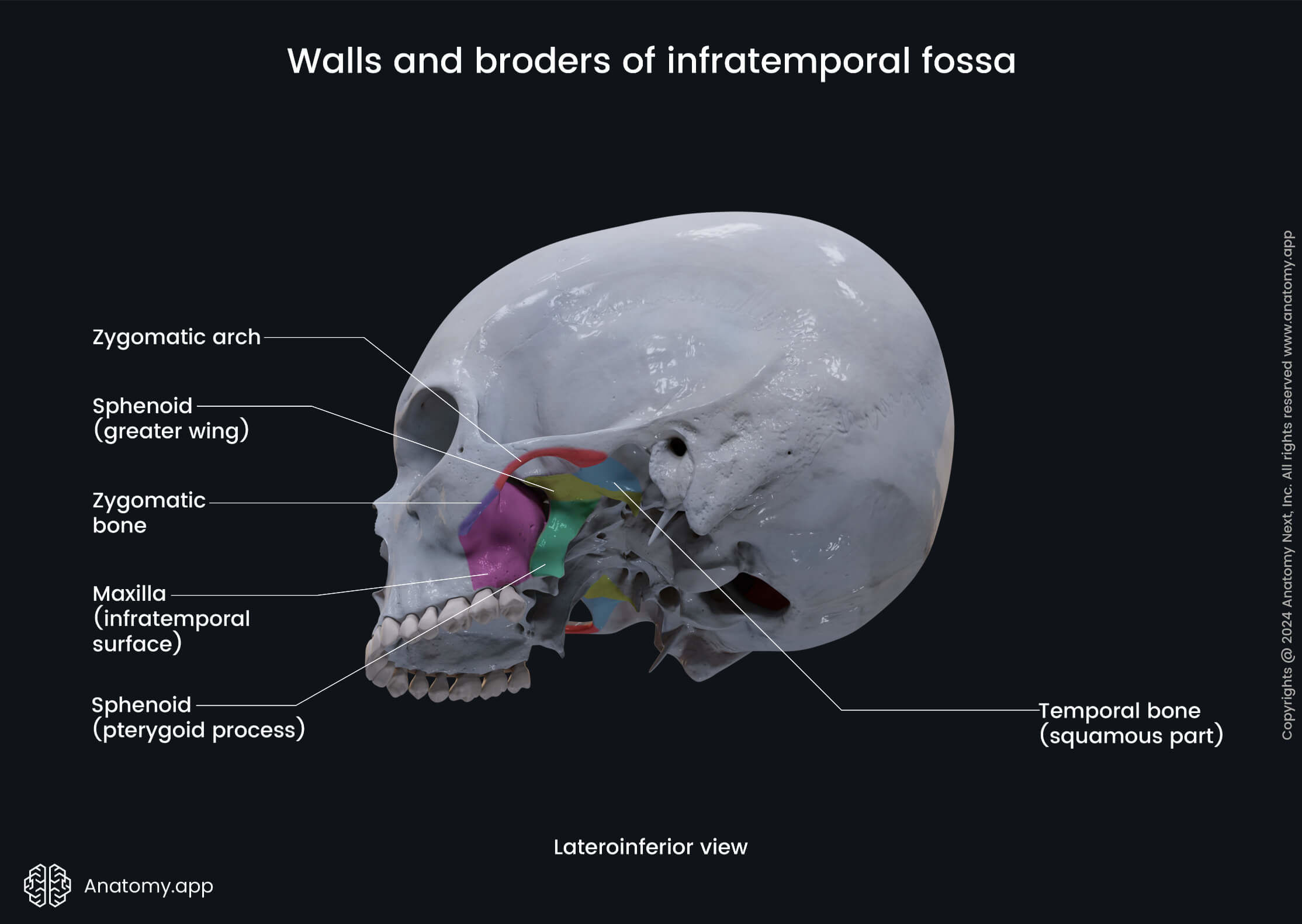
What is the Infratemporal Fossa?
→ Irregularly shaped space
Location:
deep and inferior to the zygomatic arch (cheekbone)
under the temporal fossa
deep to the ramus of the mandible (jawbone)
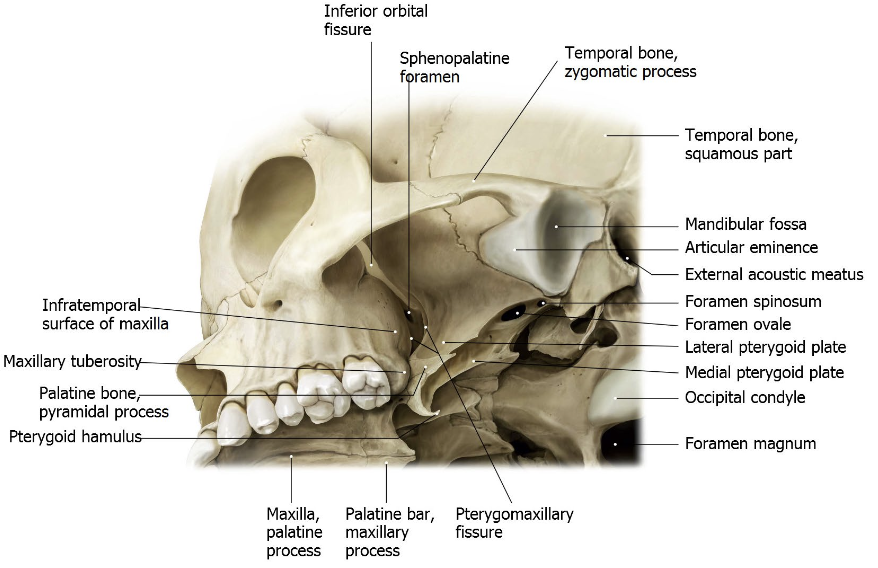
What are the arteries that make up the Infratemporal Fossa?
Branches of the Maxillary Artery:
Middle meningeal artery
Inferior alveolar artery
Deep temporal artery
Buccal artery
What are the veins that make up the Infratemporal Fossa?
Pterygoid venous plexus
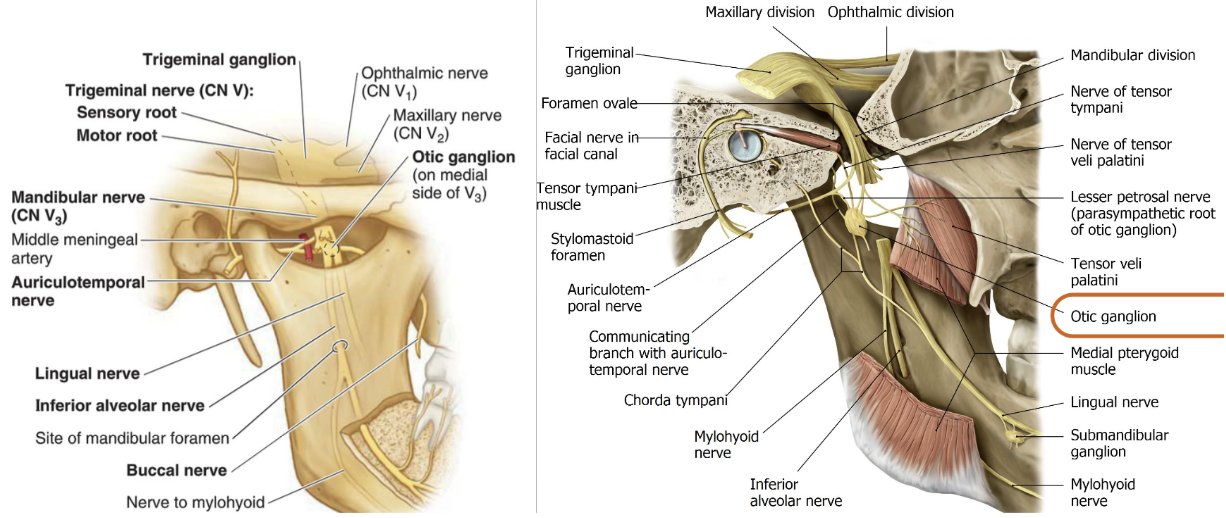
What are the nerves that make up the Infratemporal Fossa?
1) Mandibular nerve (CN V3)
Auriculotemporal nerve
Buccal (long buccal) nerve
Lingual nerve
Inferior alveolar nerve
6) Chorda tympani nerve (CN VII)
7) Otic ganglion (PNS)
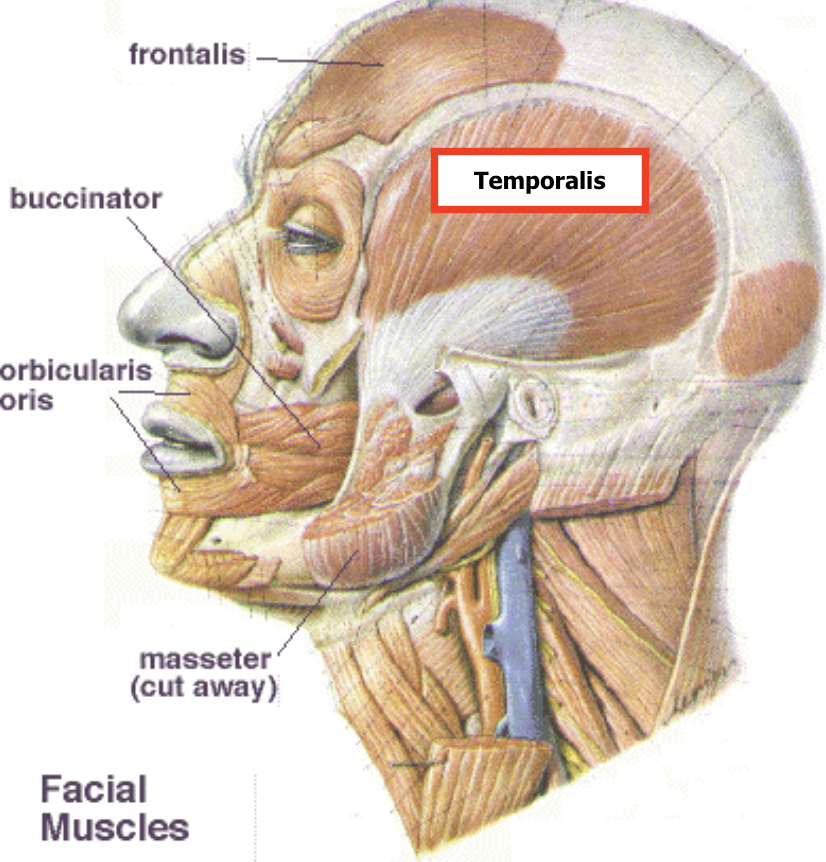
What are the muscles that make up the Infratemporal Fossa?
Temporalis muscle (inferior)
Pterygoid muscles (lateral & medial)
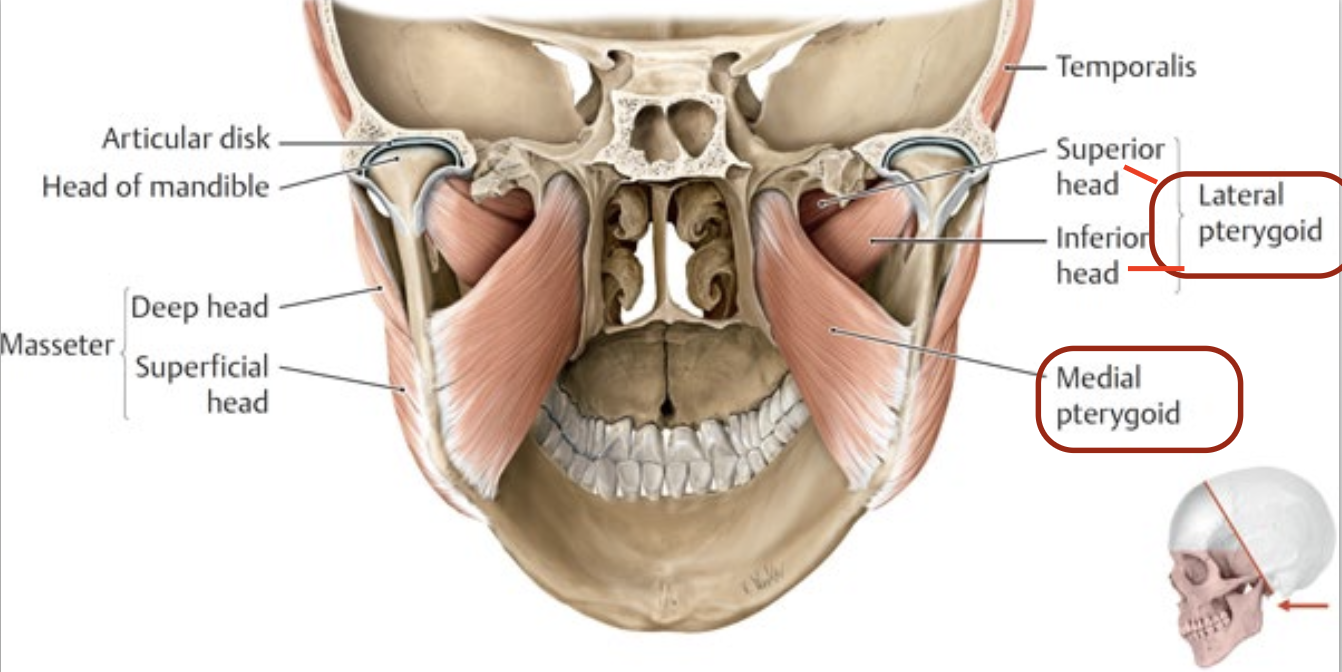
What are the joints that make up the Infratemporal Fossa?
Temporomandibular joint (TMJ) - allows for chewing, but also the first jaw that feel painful when ur stressed
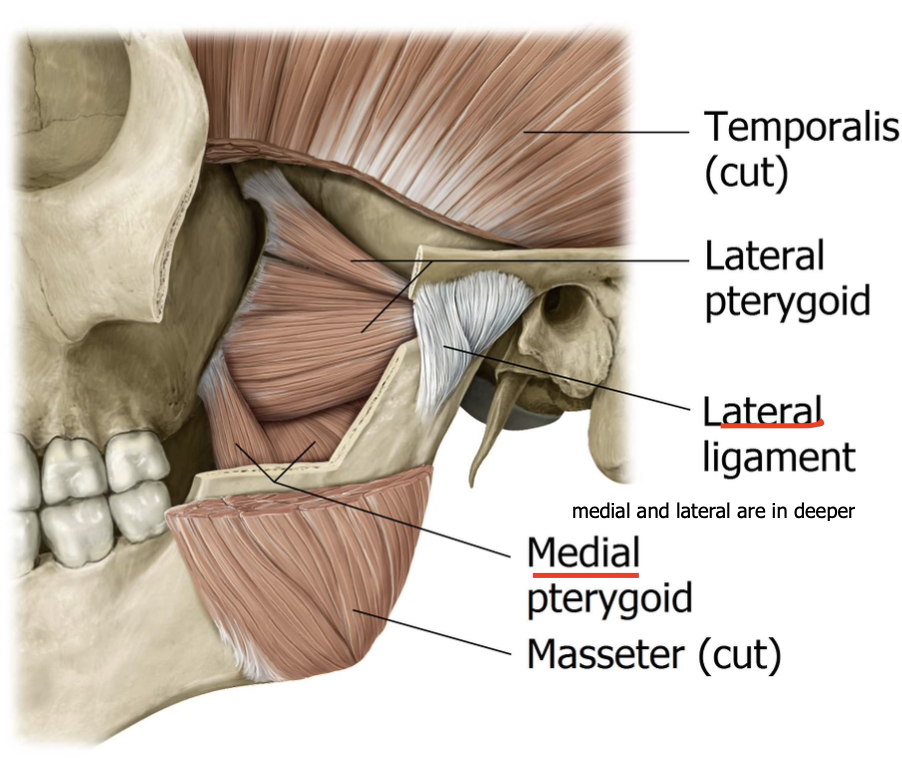
List the muscles used for Mastication (chewing).
Masseter
Temporalis
Lateral pterygoid
Medial pterygoid
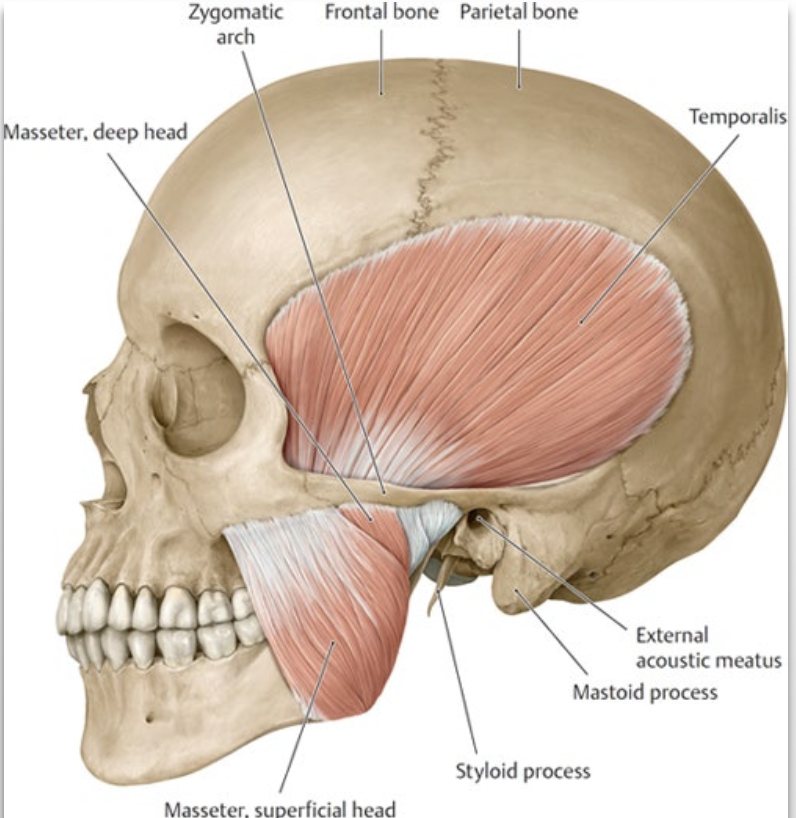
Where do the muscles used for mastication attach?
attach to the mandible creating the TMJ
List the nearby spaces the Infratemporal fossa is connected with. Mention the fissure
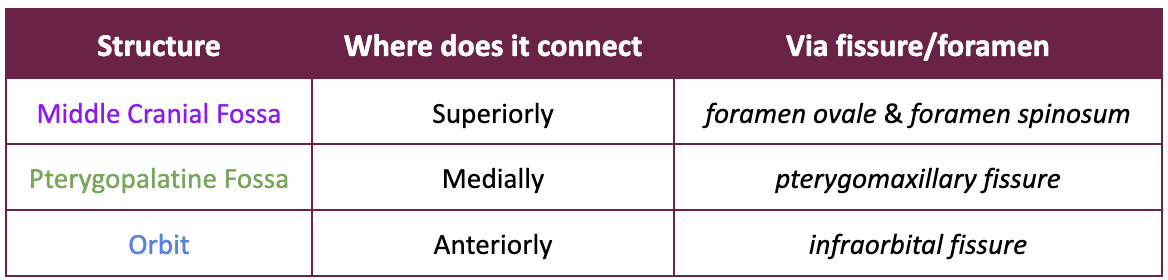

What’s the downside to these interconnected spaces within the Infratemporal fossa?
Infections (such as dental or deep facial infections) can spread from the teeth or jaw into deeper regions, potentially reaching the cranial cavity
What bones is Pterygopalantine fossa (PPF) bounded by?
Maxilla
Sphenoid
Palantine
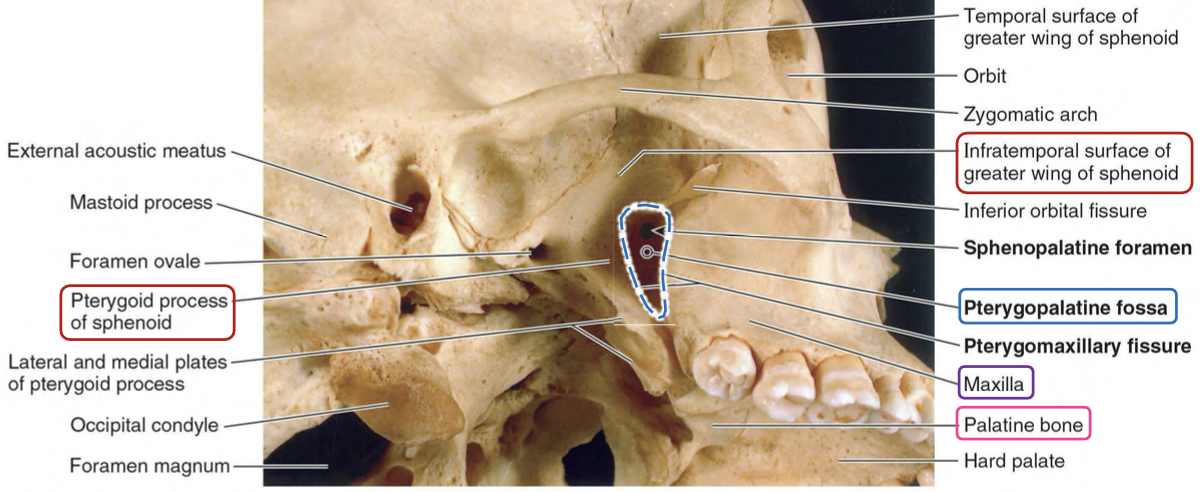

List the contents of the Pterygopalantine fossa (PPF)?
→ major neurovascular hub in the deep face
1) Maxillary nerve (CNV2) + its branches
2) Maxillary artery (terminal) + its branches
3) Nerve of the pterygoid canal (Vidian nerve)
Greater superficial petrosal nerve → preganglionic PNS fibers
Deep petrosal nerve → postganglionic SNS fibers
4) Pterygopalatine ganglion
5) Accompanying veins (tributaries of the pterygoid venous plexus)
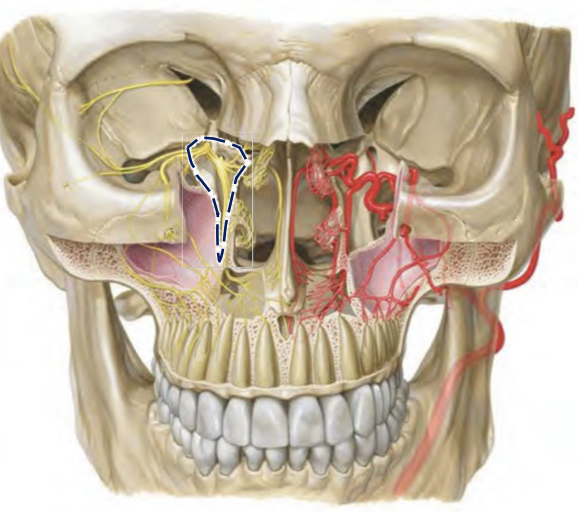
Which nerve and artery pass through the Pterygopalatine fossa, and what do they supply?
Maxillary nerve (CN V2) & Maxillary artery course through the PPF → supply the nasal cavity & palate
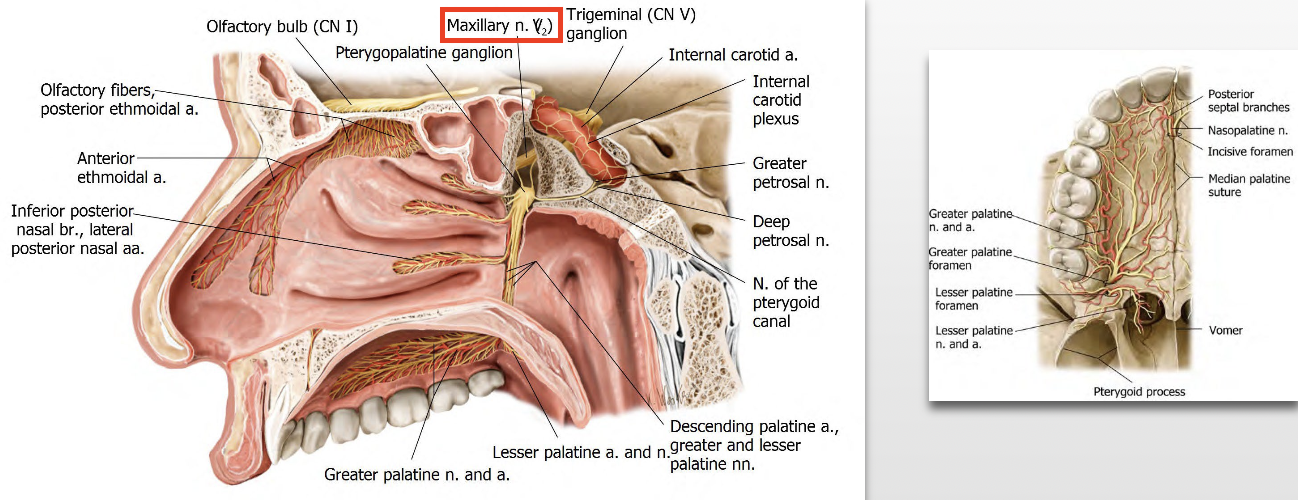
Which fibers synapse in the pterygopalatine ganglion?
pre-ganglionic PNS fibers from the Facial nerve (CNVII) via the greater petrosal nerve
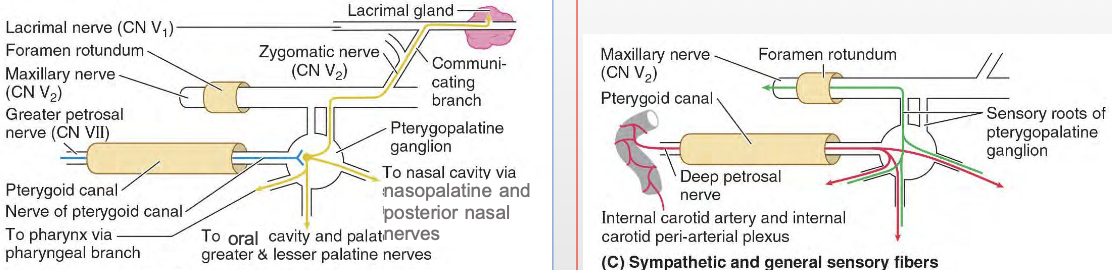
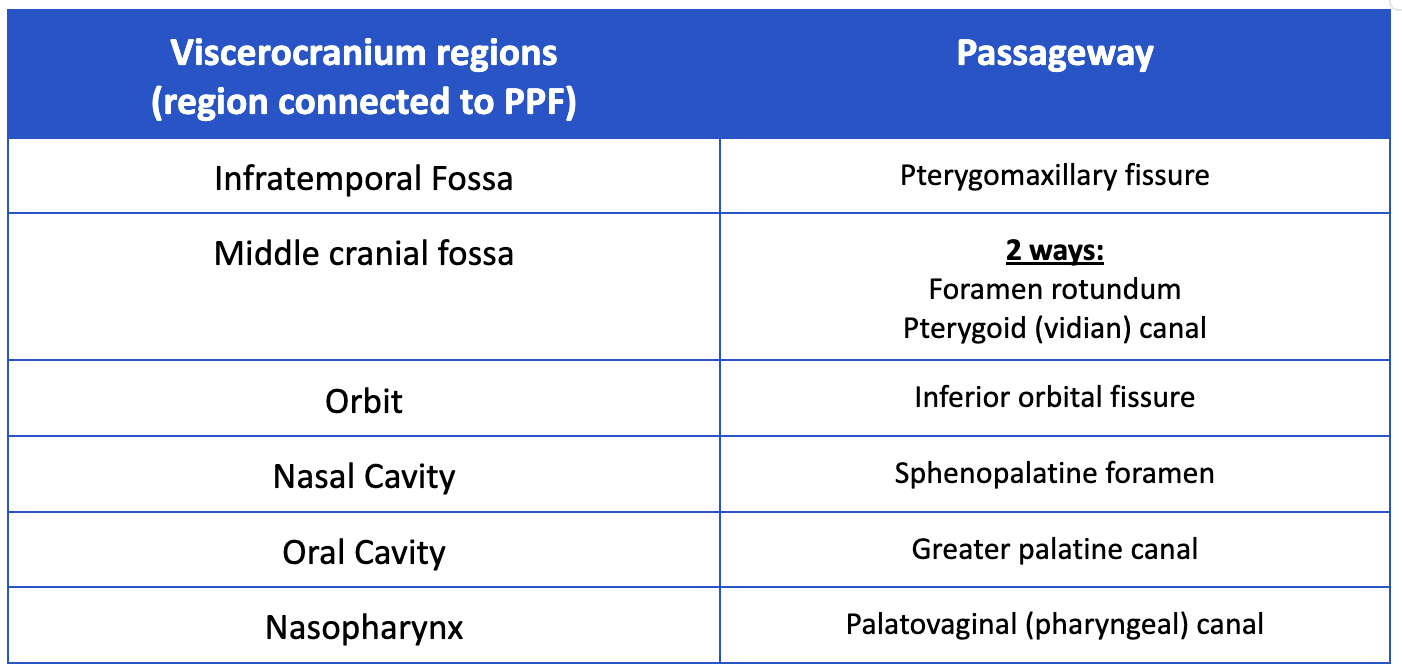
What major regions does the Pterygopalatine fossa (PPF) communicate with? How?
Major regions of the viscerocranium
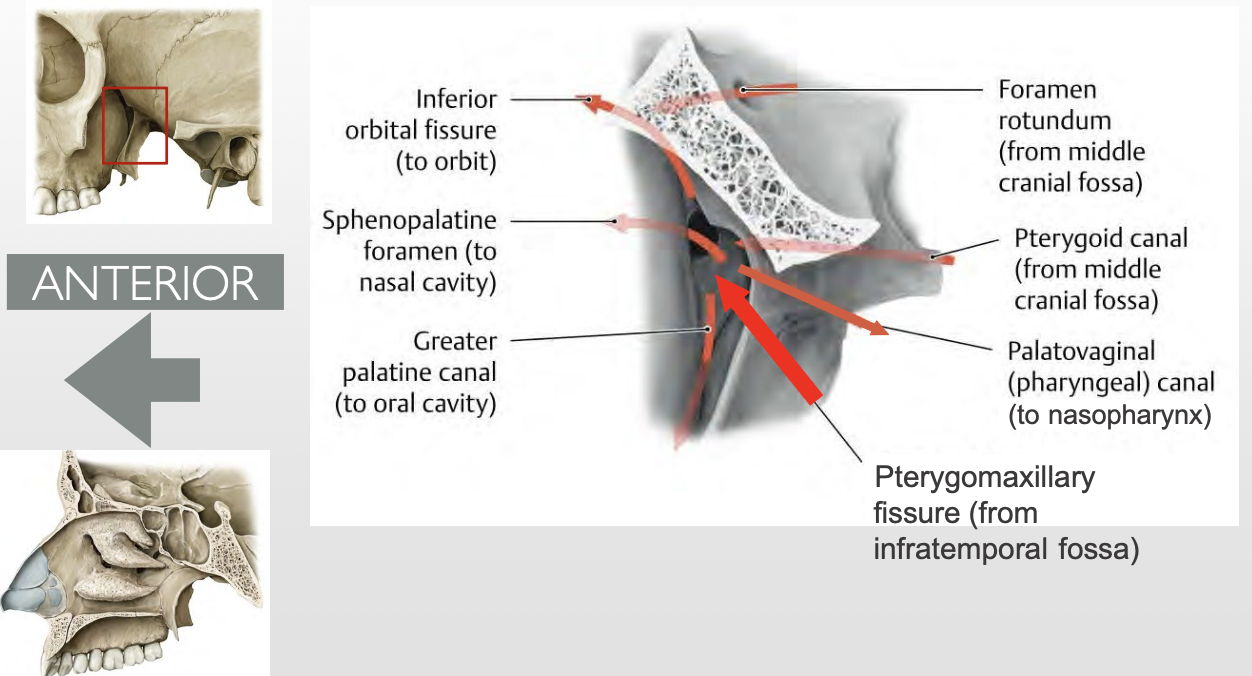
Which muscles connect the head to the thoracic skeleton and form boundaries of the neck regions? How are these muscles innervated?
1) Sternocleidomastoid (SCM)
2) Trapezius muscles
→ innervated by the spinal accessory nerve (CN XI), which exits the jugular foramen and passes deep to the SCM toward the trapezius to provide motor innervation
What are the actions of the sternocleidomastoid (SCM)?
Unilaterally: Tilts the head to the same side and rotates it to the opposite side
Bilaterally: Moves the neck in the sagittal plane (head moves down)
What are the actions of the trapezius?
Upper fibers: Elevate the scapula
Middle fibers: Retract the scapula
Lower fibers: Depress the scapula
Where are the SCM and trapezius located relative to each other?
SCM = anterior
Trapezius = posterior
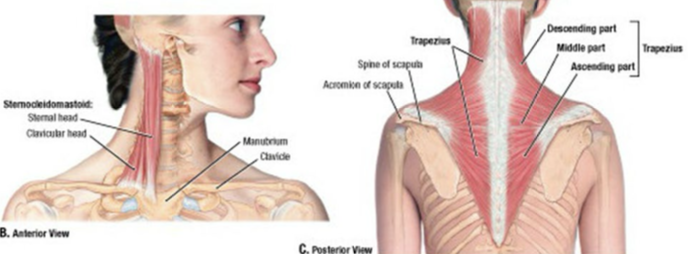

What is the Platysma?
is a thin muscle of facial expression that overlies the deeper structures of the neck
What are Neck triangles?
→ musculoskeletal landmarks divide the neck into cervical triangles

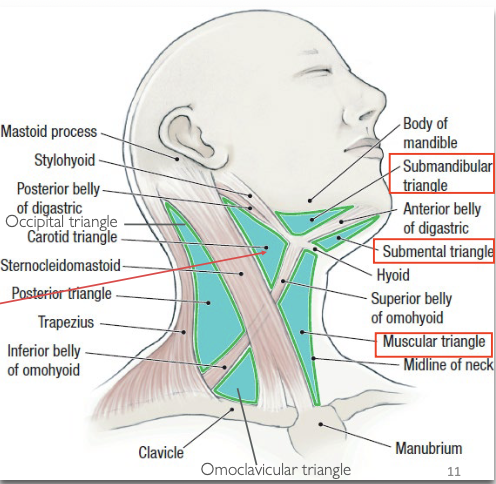
What forms the palpable borders of the Posterior triangle of the neck?
Clavicle (base)
Trapezius muscle (posterior border)
SCM (anterior border)
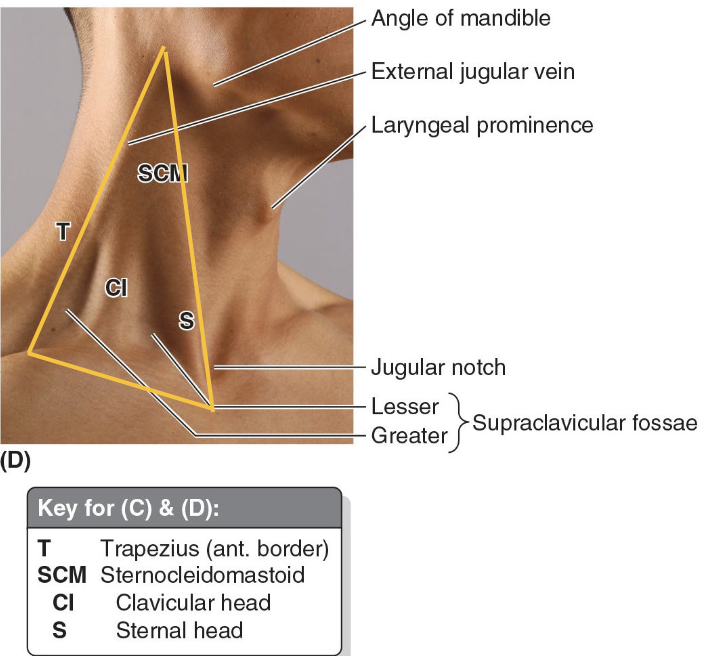
What are the main palpable landmarks in the neck region?
Mastoid process
Angle of mandible
Laryngeal prominence (Adam’s apple)
Jugular notch

List borders of the Carotid Triangle.
Superior – Digastric muscle
Lateral – SCM muscle
Inferior – Omohyoid muscle
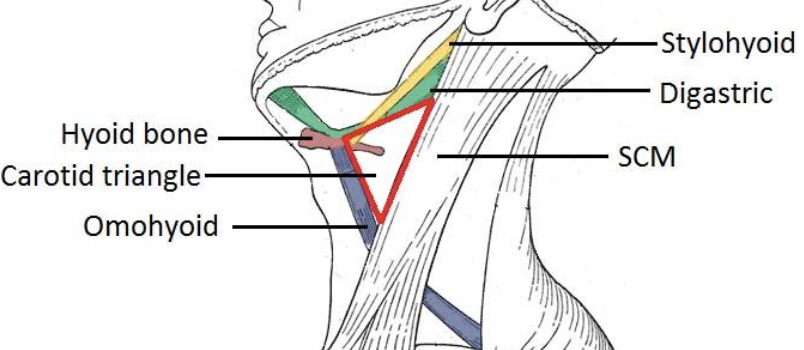
Carotid Triangle
List the arteries of the Carotid Triangle.
1) Common carotid
2) Internal carotid
3) External carotid + its 5 branches:
Superior thyroid artery
Ascending pharyngeal artery
Lingual artery
Occipital artery
Facial artery
Carotid Triangle
List the veins of the Carotid Triangle.
1) Internal jugular vein
2) IJV Tributaries:
Superior/Middle thyroid vein
Lingual vein
Pharyngeal vein
Common facial vein
Carotid Triangle
List the nerves of the Carotid Triangle.
1) Cranial nerves - Vagus, Spinal Accessory & Hypoglossal
2) Other nerves - Ansa cervicalis + sympathetic chain (cervical part)
Carotid Triangle
List the lymph nodes of the Carotid Triangle.
Deep cervical lymph nodes
Carotid Triangle
List the other structures of the Carotid Triangle.
Carotid sinus
Carotid body
Where do the vertebral arteries originate and how do they travel?
Origin: Subclavian arteries
Ascends through the transverse foramina of the cervical vertebrae
Enter the cranium via the foramen magnum to supply the brain
After entering, they fuse to form the basilar artery
it’s formed along the medulla oblongata’s ventral surface
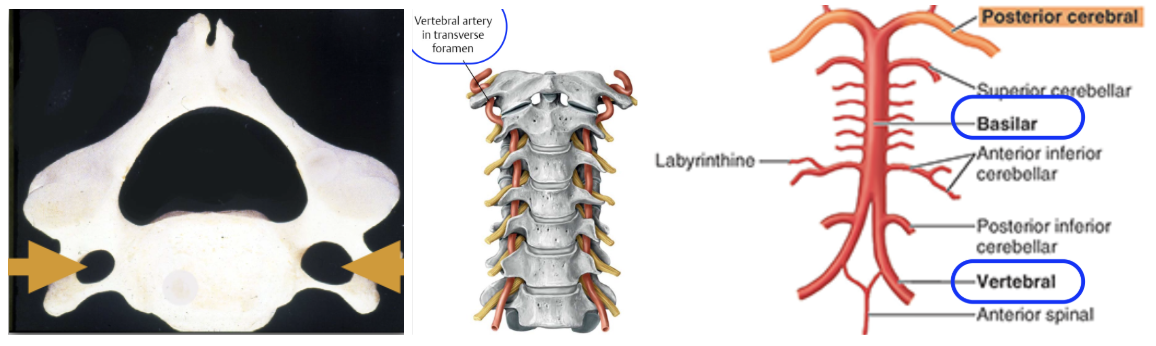
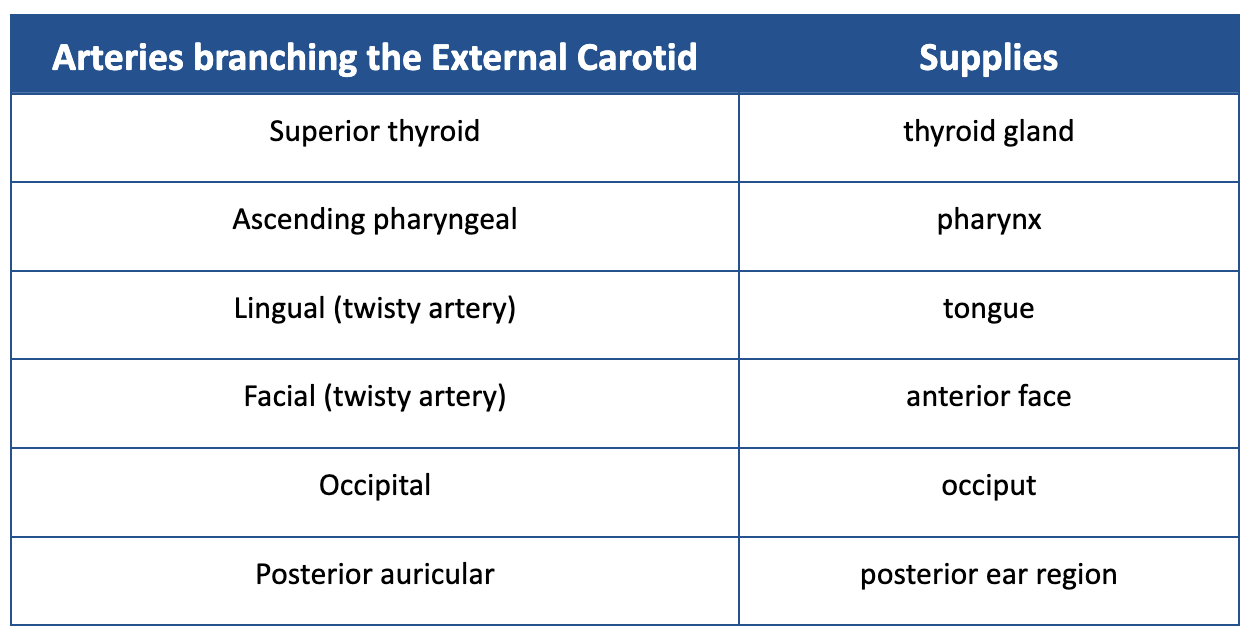
What does the Common carotid artery branch into? What do these branches supply?
External carotid - supplies the neck, lower jaw, and face
Internal carotid - supplies the brain
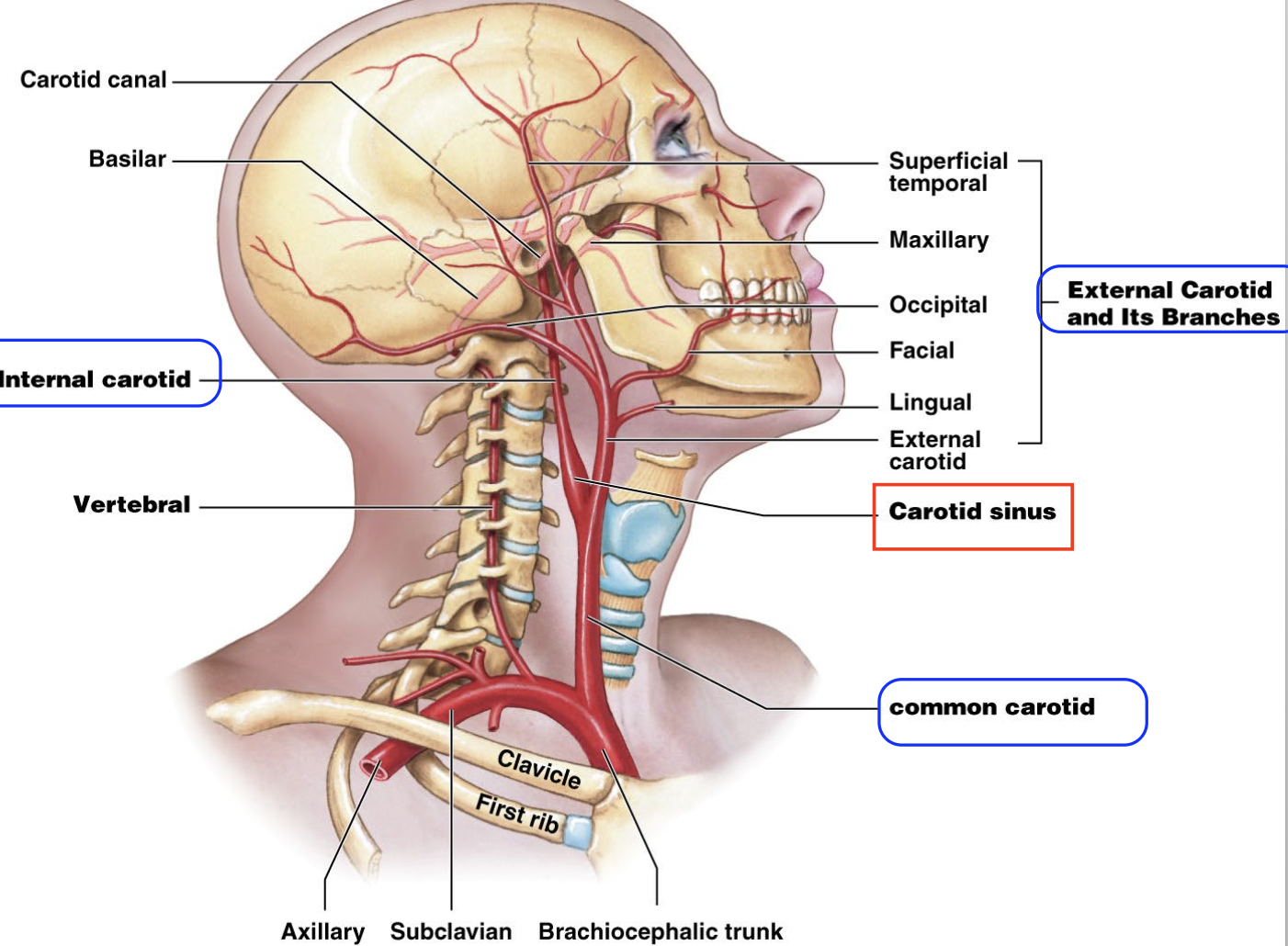
Where is the Common carotid artery enclosed?
enclosed within the carotid sheath in the neck
What is the Carotid sheath?
→ a fascial compartment that extends from the cranial base to the root of the neck
sheath ends at the inferior opening of carotid canal
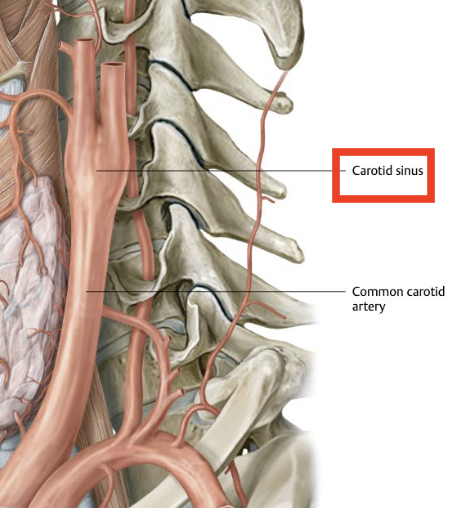
What is the Carotid Sinus? Where is it found?
→ “Blood pressure sensor” - contains baroreceptors to monitor BP in the brain
Action: Reads BP & stimulates reflex vasoconstriction if blood supply to brain drops (e.g., when standing up)
- it’s a “dilation” at the base of the internal carotid artery

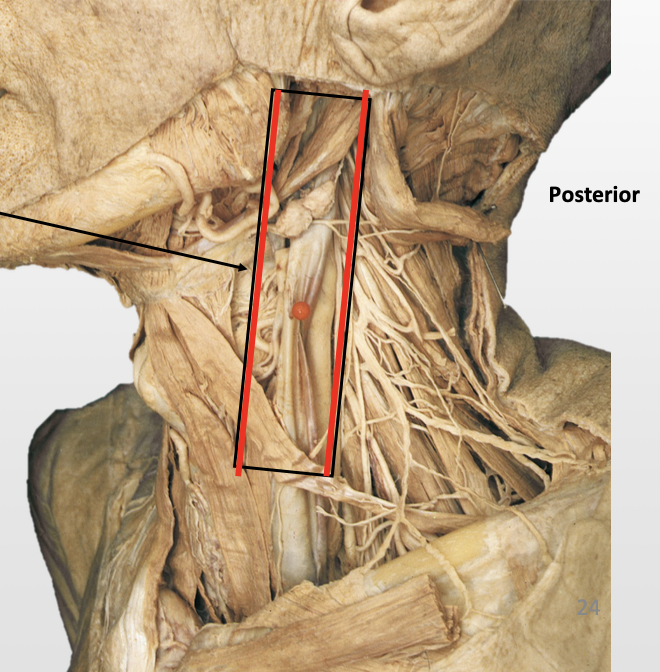
What are the contents of the Carotid sheath?
Medial: Common & internal carotid arteries
Lateral: Internal jugular vein
Posterior: Vagus nerve (CN X)
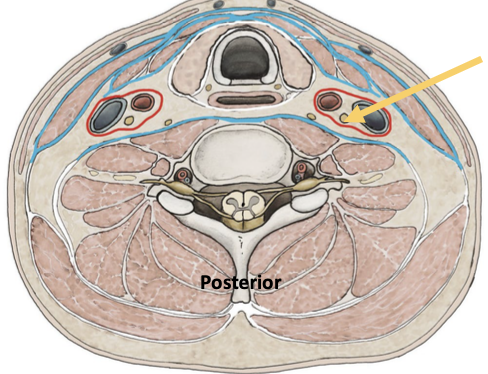
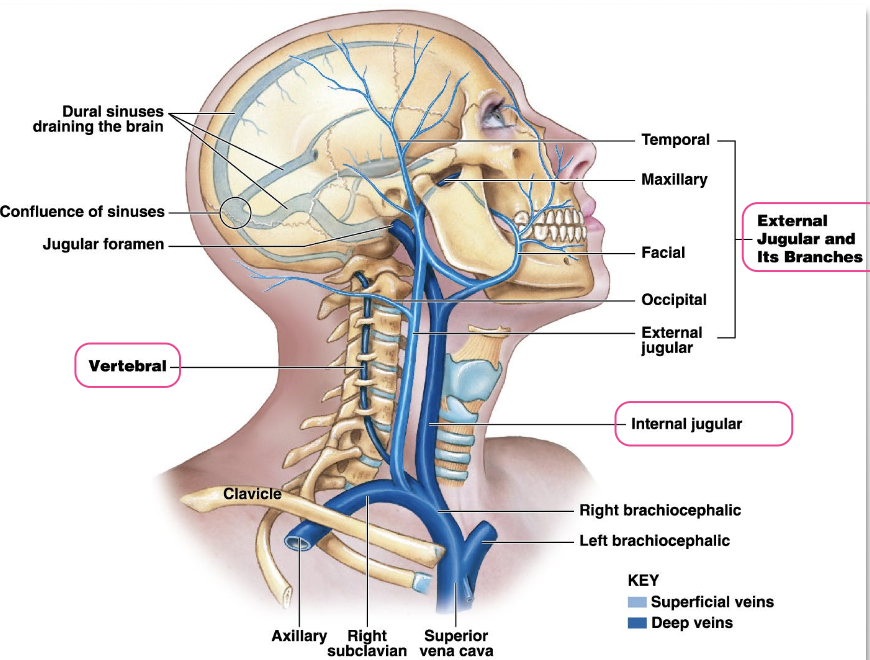
List all the veins of the neck.
External jugular vein - drains superficial structures of the head and neck
Internal jugular vein - drains deep structures of the head and neck
Vertebral vein - drains the cervical spinal cord & posterior surface of the skull
What do the veins of the neck merge with, and what do they form?
All 3 veins merge with the subclavian vein → form the brachiocephalic vein
What is the Carotid body?
→ small piece of tissue b/w origins of the internal & external carotid
chemoreceptor = mainly reads pO2 (less pCO2 and pH)
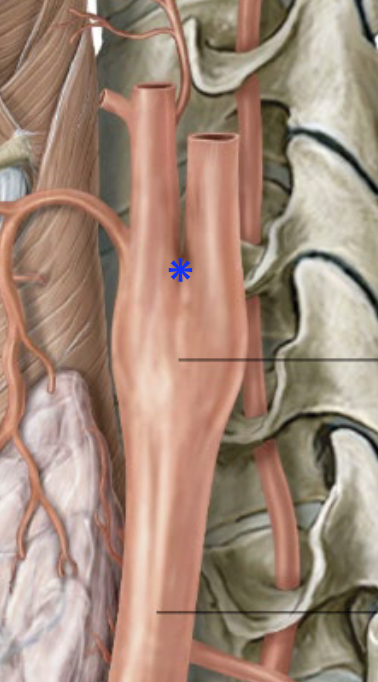
Which nerve primarily innervates the carotid sinus and carotid body? Describe the innervation path
Glossopharyngeal nerve
1) Sensory signals from the carotid body and carotid sinus travel through the sinus nerve (of Hering)
2) Signals reach the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) → brainstem
What happens when glomus cells in the Carotid body detect ↓pH, ↑CO₂, or ↓O₂?
Sympathetic activation leading to:
↑BP
↑ HR
↑ respiratory rate
How does the Carotid body respond to changes in BP?
↓ BP → afferents stimulate vasoconstriction
↑ BP → afferents stimulate vasodilation
List the branches of the External Carotid Artery. Mention what they supply.
SALFOP
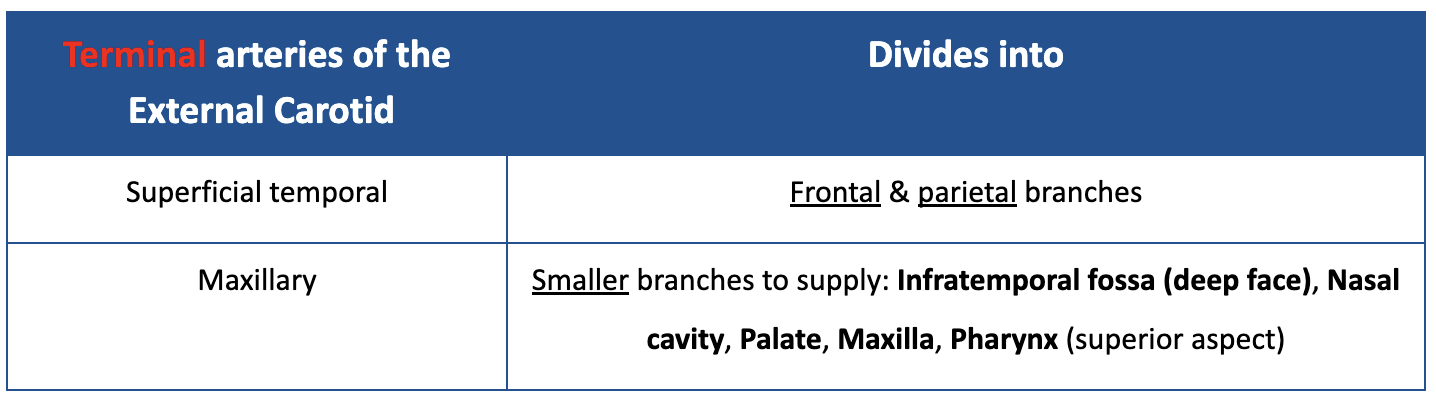
List the Terminal branches of the External Carotid Artery. Mention what they supply.
“Terminal” - don’t anastomose
What is the course of the internal carotid artery as it enters the cranial cavity?
Each internal carotid artery enters the cranial cavity via the carotid canal found in the temporal bone (petrous/hard part)

What is the Cavernous Sinus?
→ venous sinus located on either side of the pituitary gland
“vein with contents” — meaning many important structures pass through or along it
portion of the dura mater
Which cranial nerve travels alongside the internal carotid artery in the cavernous sinus?
Abducent nerve (CN VI)
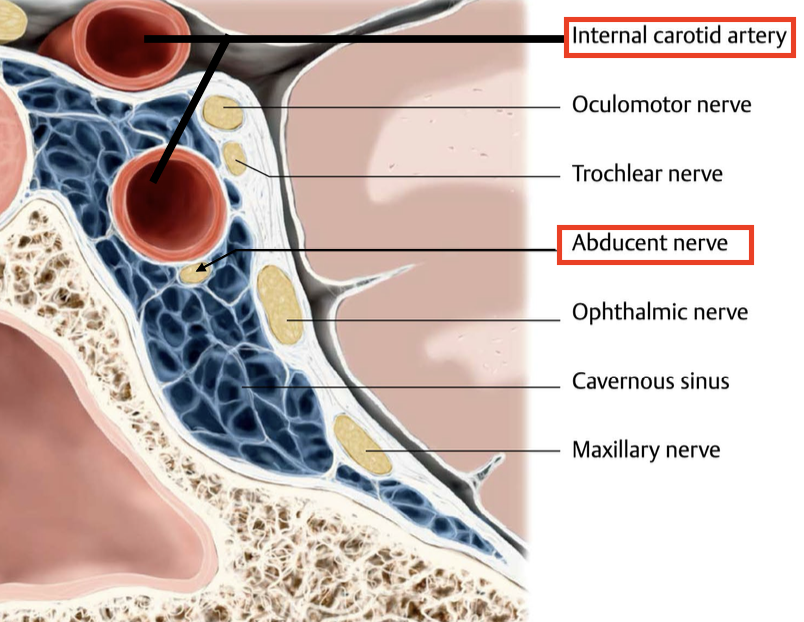
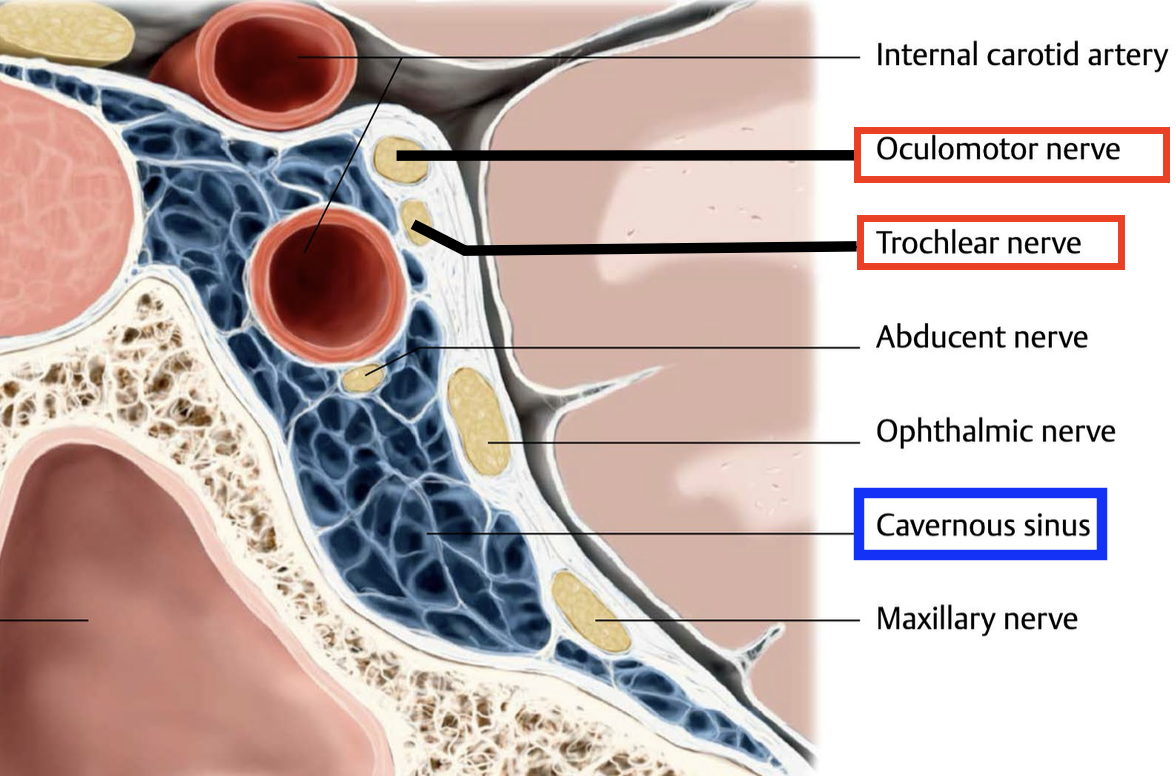
Which cranial nerves are located in close proximity to the cavernous sinus, within its lateral wall?
Oculomotor nerve (CN III)
Trochlear nerve (CN IV)
What part of the brain do the internal carotid arteries supply?
anterior half of the cerebrum
Name the 3 branches of the Internal Carotid artery & what they supply. What is the internal carotid artery + its branches collectively referred to as?
Ophthalmic artery - eyes
Anterior cerebral artery - frontal and parietal lobes
Middle cerebral artery - midbrain and lateral surfaces of cerebral hemispheres
“Anterior circulation of the brain”
Which arteries supply the rest of the brain (not the anterior half)?
Vertebral arteries
Basilar arteries (comes from vertebral arteries)
List the 3 principal arteries of the brain. What are their origins?
Anterior cerebral artery (L & R)
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior cerebral artery
- Terminal branches of the Internal carotid arteries
-Terminal branches of the Basilar artery from the vertebra

What are the terminal branches of the Internal carotid arteries?
Anterior arteries (left & right)
Middle cerebral arteries
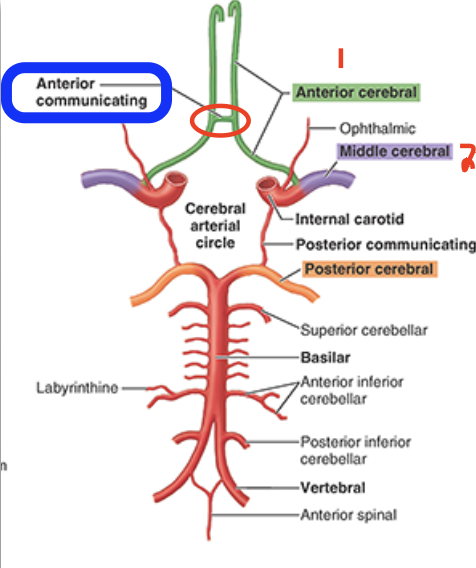
How are the left & right Anterior arteries connected to eachother?
Anterior communicating artery

What is another name for the posterior circulation of the brain?
vertebrobasilar system
How does the posterior circulation connect to the anterior circulation?
via the right and left posterior communicating arteries

Draw out the diagram showing how the following at connected.
Anterior cerebral artery
Anterior communicating artery
Middle cerebral artery
Posterior communicating artery
Posterior cerebral artery
Basilar artery
Vertebral artery
Arterial circle

The Cerebral Arterial Circle (Circle of Willis) reunites 3 vascular systems. What are they?
1) Vertebrobasilar system (posterior circ)
2) Left Internal carotid system (anterior circ)
3) Right Internal carotid system (anterior circ)
Which arteries connect the internal carotid arteries to the posterior cerebral arteries?
Posterior communicating arteries → allow the posterior and anterior circ (internal carotid) to form an anastomosis and complete the cerebral arterial circle (Circle of Willis)
If symptoms appear on both sides/bilateral of the body, what does that suggest about the artery supply?
1 artery supply (vertebrobasilar)
b/c vertebral arteries anastomose into a single central vessel (basilar artery) → bilateral symptoms
If symptoms appear on only one side/unilateral, what does that suggest about the artery supply?
2 artery supply (internal carotids)
b/c internal carotid arteries remain separate → unilateral symptoms
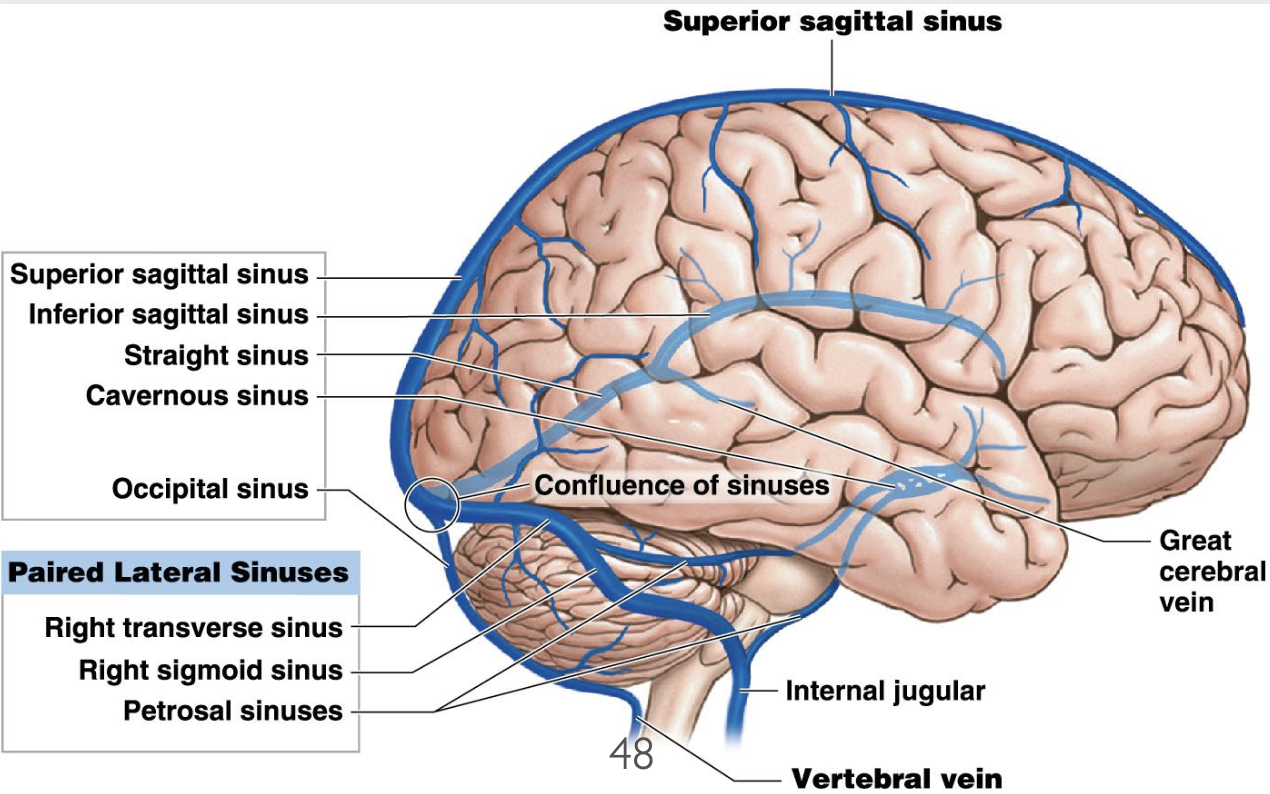
What does venous drainage from the brain occur via?
occurs via cerebral and cerebellar veins that drain into the adjacent dural venous sinuses
What is the function of the Meninges?
Line the skull
Surround, and protect the brain
What is the Dura Mater?
→ Tough, fibrous outermost layer
has 2 layers: Periosteal & Meningeal
layers are fused except where they form dural folds and dural venous sinuses
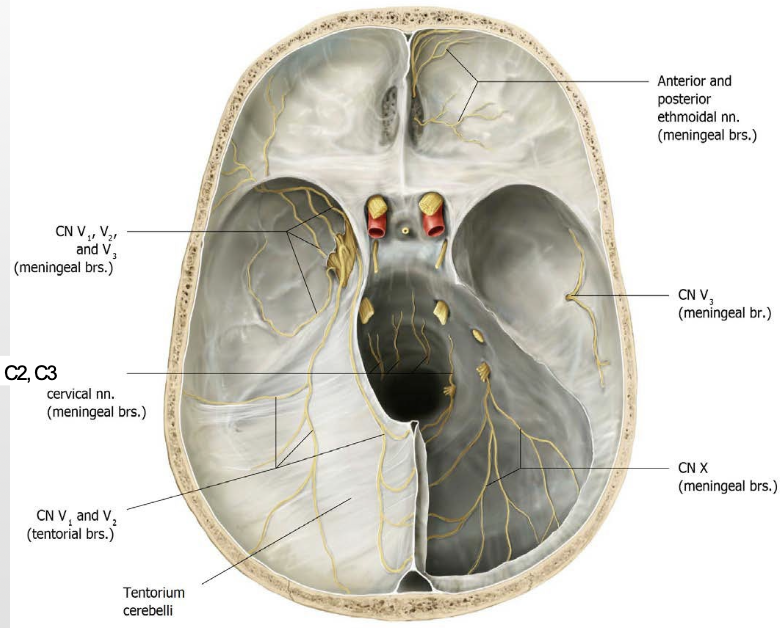
Which nerves transmit pain sensations from the dura mater?
Cervical nerves C2–C3
Trigeminal nerve (main)
Vagus nerve (CN X)
What is the Arachnoid Mater?
Thin, transparent, middle meningeal layer
What is the Pia Mater?
→ Delicate, vascularized innermost layer
adheres tightly to the brain, following its gyri and sulci
What are Dural Venous Sinuses?
→ endothelium-lined venous channels located b/w the 2 layers of dura mater
Drain venous most of the blood from the brain into the internal jugular vein
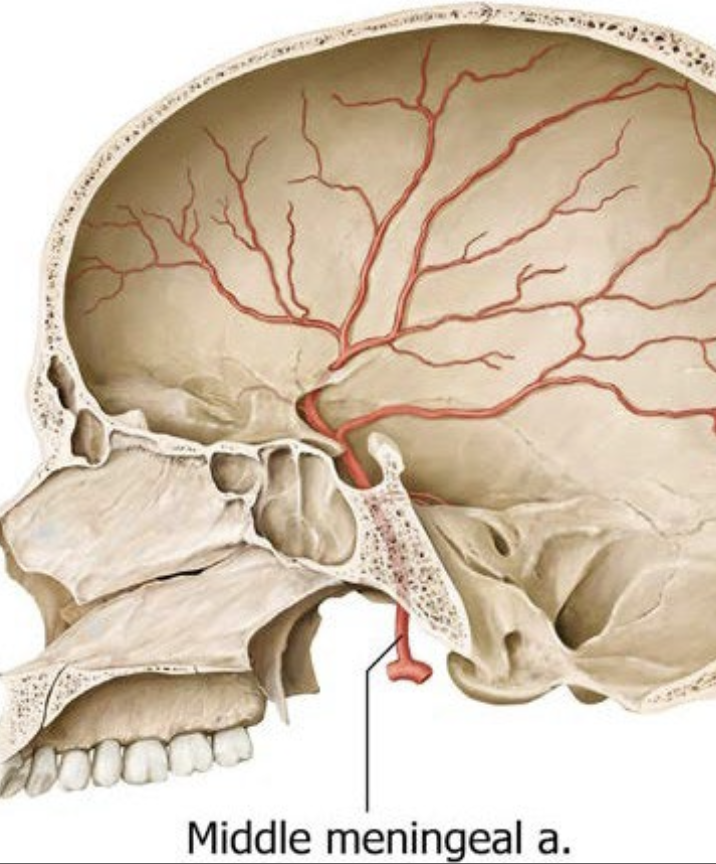
What is the Middle Meningeal Artery?
External carotid artery → Maxillary artery → Middle meningeal artery
main blood supply to the Dura mater
enters the skull through the foramen spinosum
lies in the middle cranial fossa (on internal surface of skull base)
What are grooves on the skull formed by?
Dural venous sinuses
Meningeal arteries (especially the MMA)
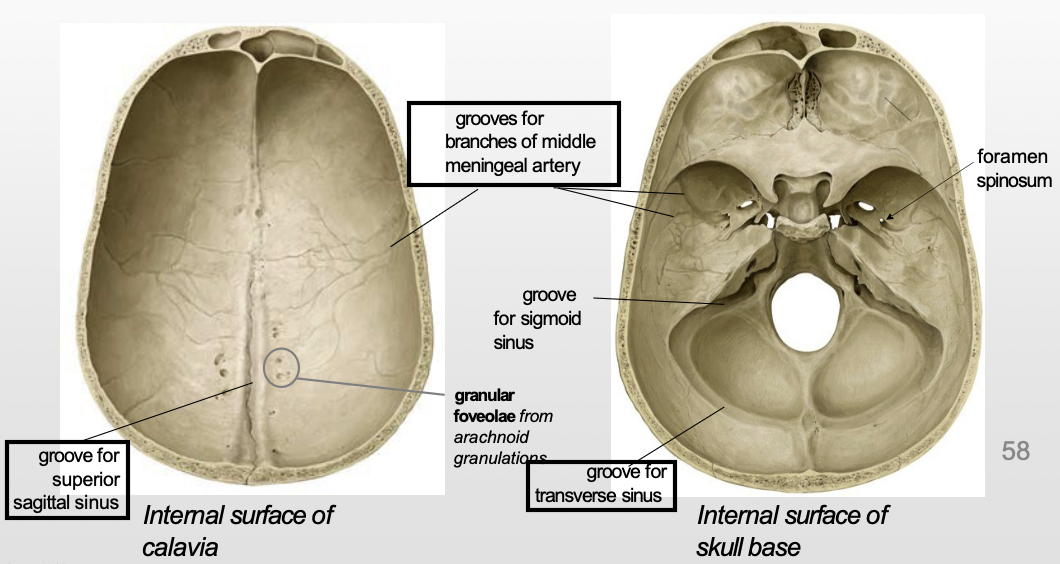
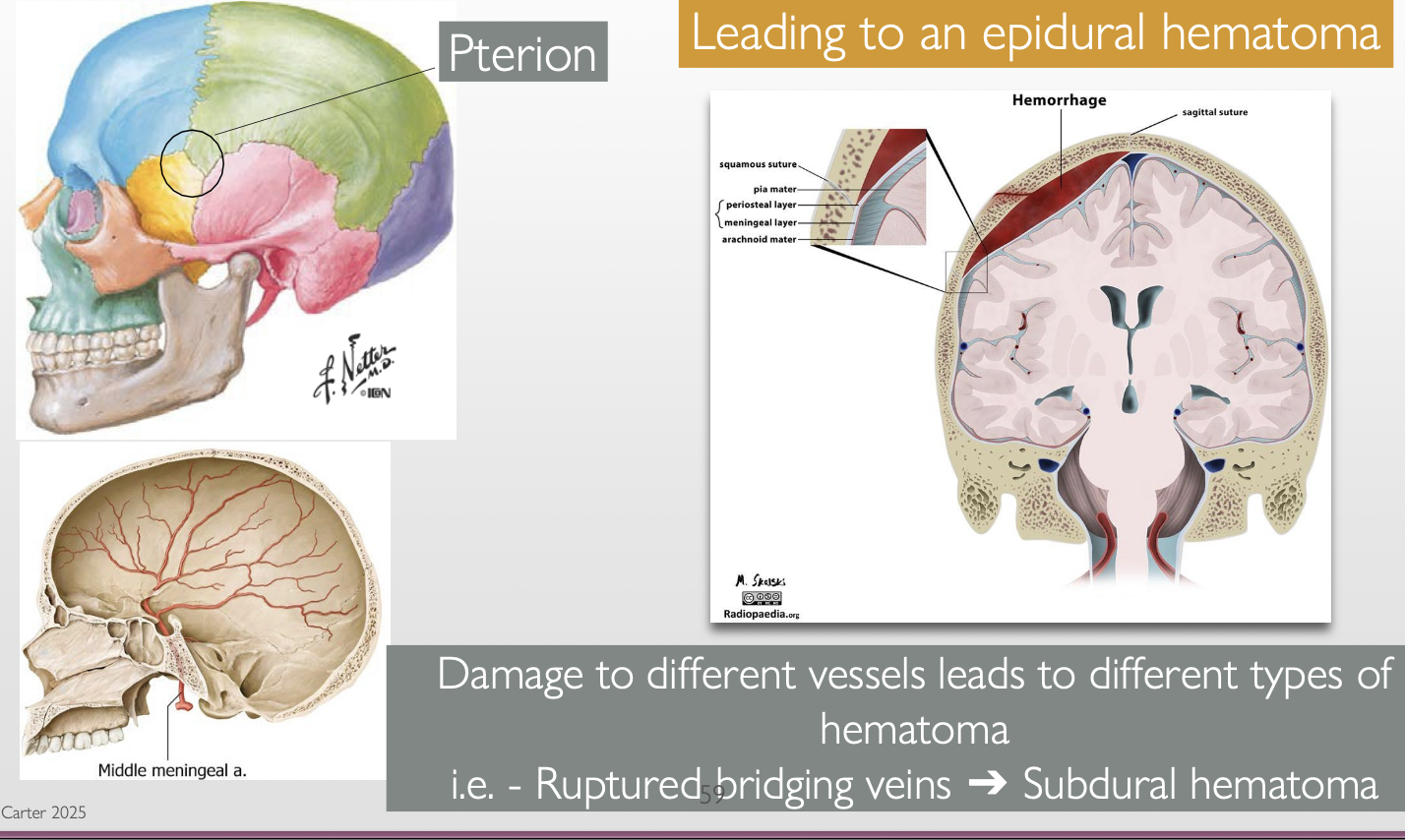
What is the pterion? Why is a fracture at the pterion clinically significant?
Pterion: is where the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid bones meet
MMA runs under it, so a fracture in this area can rupture the MMA → epidural hematoma
Epidural hematoma: bleeding b/w the dura & skull that rapidly ↑ intracranial pressure