AP Human Geography Unit 4 Exam Review
Introduction to Political Geography
Other Political Entities
City-State was the first type of political organization (Mesopotamia)
Nation is a group of people who are united by a shared culture, heritage, language & possibly other belief systems
Usually want to have an independent territory
Flemish, Walloons, Irish & Danish
Nation-states are countries made up of one nationality
Homogeneity: countries that are mostly made up of one ethnic group
Iceland, Denmark, Mongolia & Japan
99% of the people that live in Japan are Japanese due to strict immigration policies & strong national identity
Multinational states are countries made up of many nationalities
Canada, Russia & U.S. are among the world’s largest
Often have one majority group with a lot of political power, but being a diversity nation
Usually reflected with national languages where there either isn’t one or there are multiple
Multistate nations are nationalities that spread among many states.
Ex: Koreans live in North & South Korea
Another example Hungarians
Most live in Hungary, but many also live in the Transylvania region of Romania
Stateless Nations are nationalities without a recognized home country
Kurds (largest) & Palestinians
Often been fighting for a state
For decades Palestinians & Israelis have been in conflict
Palestinians have not yet been granted a sovereign state
Autonomous region self ruled region within another country
Hong Kong in China, Northern Ireland in the UK
Semi-autonomous regions having a degree of, but not complete, self-government
American Indian Reservations
Defining Political Boundaries
Defining Political Boundaries
Before defined boundaries, frontiers or zone where no state exercises complete political control separated states or countries
Types of Boundaries
Defined boundaries are established by a legal document
Delimited boundaries are drawn on a map
Demarcated boundaries are identified by physical objects
Walls, signs & fences
Boundaries are determined by:
Natural boundaries are based on physical features
Rivers, mountains & coastlines
Ex: border of Arkansas is formed along the Mississippi River
Geometric boundaries are straight lines drawn by people
Ex: Berlin Conference carving up Africa
Many of the boundaries in Africa are straight because people
Antarctica is the only land masses that has only geometric boundaries
Political boundaries are usually clear, cultural boundaries are more fluid
Cultural boundaries are based on human traits or behaviors & don’t have to be official borders
One region may have more people that practice a religion than another
Will see religious buildings or religious clothing
No definitive boundary
Sometimes, there are cultural boundaries based on cultural traits such as language, religion, or ethnicity
Often referred to consequent boundaries
Economic boundaries exist within one city
Seeing wealthy & poor areas
Sometimes obviously divided by one street
Nothing official & not on a map
See deterioration on one side while the other side is thriving
Function of Political Boundaries
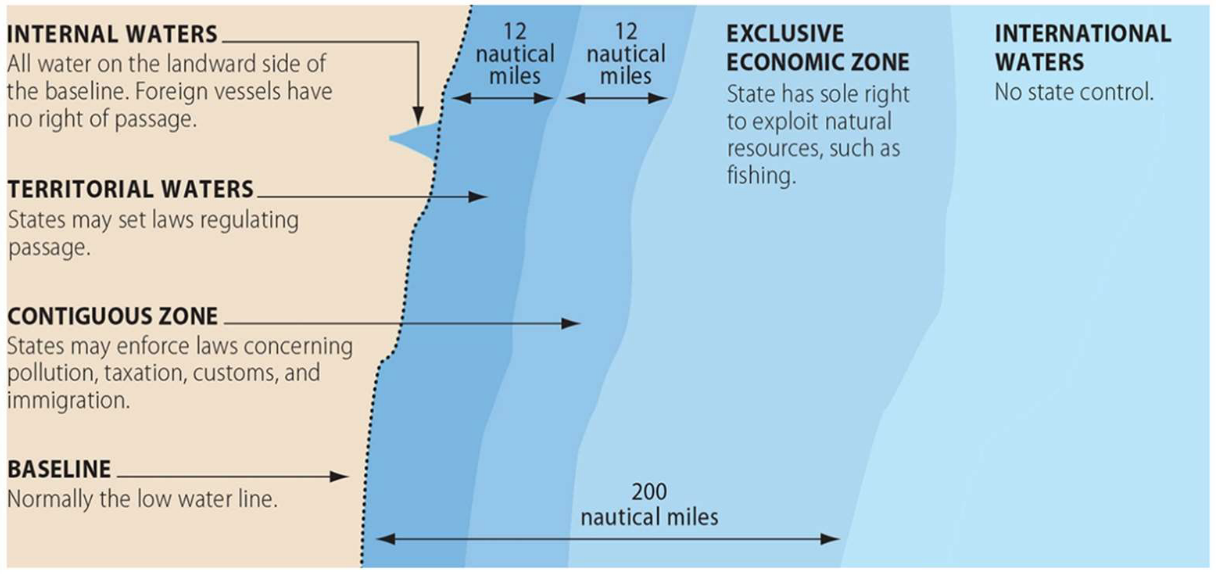
Internal Boundaries
Gerrymandering
Process of redistricting can lead to dramatic manipulations.
The most well-known example of this is gerrymandering
When politicians use redistricting to cement their power.
Often based on race, voting patterns, class, etc.
Gerrymandering today in the U.S
In 1985 made illegal by Supreme Court
Allowed to keep existing boundaries
Limits the shift of Congressional seats
Types of Gerrymandering
Five types of gerrymandering & they all rhyme!
Cracking is when legislatures disperse a group into several districts in order to prevent a majority
Packing combines similar voters into one district to prevent them affecting another district
What we see in Louisiana.
Stacking is when minority voting groups are “stacked” together, but alongside higher turnout majority groups which dilute their power
Hijacking involves redrawing districts to force two representatives in the same party to run against each other
Kidnapping is when redistricting moves a supported elected official to an area they are no longer supported
Forms of Governance
The most today national governments today are classified as democracies
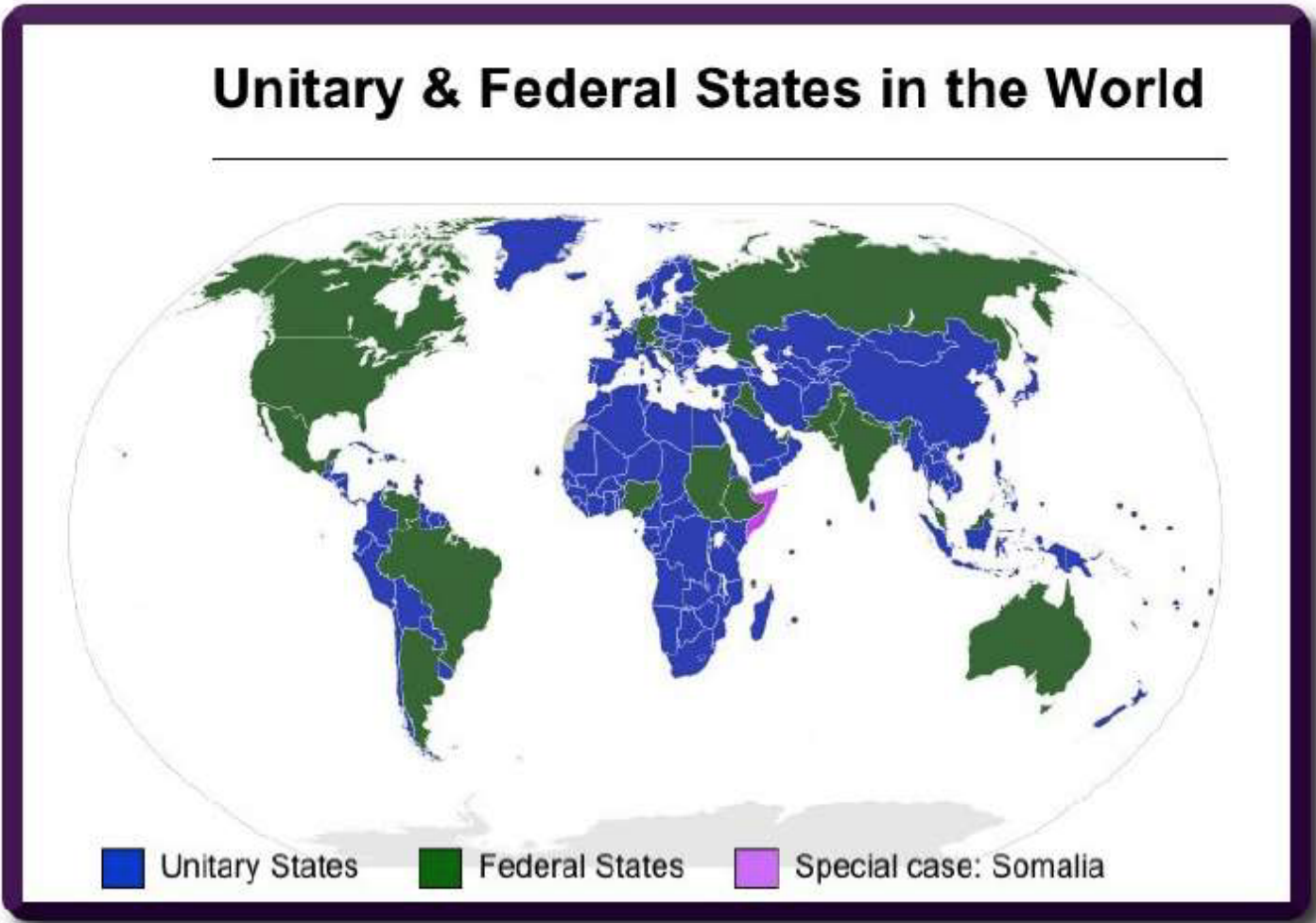
Federal State
Power is shared between the central government & state or local governments
Works well on multiple ethnic group with significant minorities, especially large countries
U.S., Germany, Australia, India, , Brazil, Russia or Canada
Exception: Belgium is the small country
Unitary State
Power is held primarily by the central gov’t without much power given to local gov’ts
Local gov’ts are usually just an extension of the central gov’t without much power of their own
Can be democratic (France) or undemocratic (China)
Few cultural differences or homogeneous & small minorities
France, North Korea, Japan, Saudi Arabia, Iran, Egypt or Spain
Exception: China is a large country
Theocracies are gov’ts ruled by religious laws
Iran & Saudi Arabia
Defining Devolutionary Factors
Devolution is the transfer of power from one central government to many local or regional governments
Fall of the Soviet Union
Happened many times before as an empire or country breaks up into several countries, but it’s not super common
It’s a big deal when it happens because several new states could be created
Forces that Lead to Devolution
Physical geography can cause isolation due to natural features
Kashmir area between India & Pakistan can feel isolated
Separated by the Himalayan & Pir Panjal mountains
These areas have some local autonomy because the physical barriers make it difficult for a central government to rule
Other physical features that can lead to devolution include deserts and large bodies of water
Ethnic separatism occurs when minority groups fight for independence
In Spain, the Basques & Catalans are groups that have a unique culture/ language & desire independence
Spanish government has appeased these groups by giving them more freedoms & representation
The will for independent is strong & the continue to protest for separation
Sometimes, ethnic separatists use terrorism to reach their goal of independence
Basques in Spain have organized a terrorist organization, the ETA, that has used violence to escalate the issue
Irish Republic Army (IRA) - unofficial nationalist military force seeking independence for Ireland from Great Britain
Ethnic Conflicts
Stem from a number of common causes:
Demand for ethnic/ cultural autonomy (self-rule)
Competing demands between ethnicities for land, money & power
Long-standing rivalries between ethnic groups
Other factors that set places up to have conflict:
Structural factors (weak state, interior security concerns, ethnic geography)
Political factors (elite politics, discriminatory institutions, exclusive national ideologies)
Economic/social factors (economic problems, discriminatory systems, modernization)
Cultural/perceptual factors (patterns of discrimination, problematic group histories)
Balkanization occurs when a state fragments into smaller, often hostile, states based on language/ ethnic lines
Self Determination: Concept that nations or ethnicities have the right to govern themselves
Ethno-nationalism: desire of an ethnic community to have absolute authority over its own political, economic & social affairs
When the Balkan region experienced ethnic conflict & split into several states
Yugoslavia was ruled by Tito for decades after WWII as a member of the non-aligned movement
It was a communist state, but was not aligned with the Soviets
Tito died in 1980, led to years of uncertainty & unrest
Region includes several ethnicities: Serb, Bosnia, Croat, Albanian & Macedonian
There were divisions between the religions of Christianity & Islam
Consequences to Centrifugal and Centripetal Forces
Centripetal Forces
Centrifugal- forces people farther apart / Centripetal- pulls people together.
Sovereignty is initially achieved because the people of a region are linked by common characteristics
Centripetal force, unifies people within a state
Shared religion, external threats, stable government & common language
National holidays bring people together
Shared traditions around religion, clothing, food & language
Keeping countries together despite the differences that arise & the size of the state
Political: Nationalism or strong feeling of patriotism
Cultural: Homogeneous or share a common trait
In the U.S., there are a lot that divide us, but we share a common history, democratic values & national identity as Americans
Centripetal Forces broke up Yugoslavia then led to the formation of several new states that were pulled together by centripetal forces
Croatians had a shared history, language & religion that differentiated them from the Bosnia's
Resulted in the formation of two states rather than one
Centrifugal Force
Forces that pushes people away from each other
Differing religion or languages, an unstable government, internal conflict, & geographic features that physically divide people (mountain ranges, etc.)
India became independent from Britain, forces that divided the Indian people were the differing religions of Islam & Hinduism
Resulting in a mass conflict & eventually a two-state solution was adopted
Tensions still continue between India & Pakistan.