OCHEM I pKA values, names, conjugate base
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Exam I
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
HI
-10
Hydroiodic Acid
I-
6 Common Strong Acids
HBr
-9
Hydrobromic Acid
Br-
Six Common Strong Acids
HCl
-8
Hydrochloric Acid
Cl-
Six Common Strong Acids
HF
+3.2
Hydrofluoric Acid
F-
H2SO4
-3
Sulfuric Acid
HSO4-
6 Common Strong acids
H3O+
-2
Hydronium Ion
H2O
Amphoteric
HNO3
-1.4
Nitric Acid
NO3-
6 Common Strong Acids
H2S
+7
Hydrogen Sulfide
HS-
Weak, Inorganic
NH4+
+9
Ammonium
NH3
Weak, Inorganic
H2O
+16
Water
OH-
Amphoteric
ROH2+
-2
“R” is generic for an alkyl group; generic alcohol
ROH
ROH
+16
“R” is generic for an alkyl group; generic alcohol
RO-
The smaller the pKA value…
the more acidic and stronger the acid
The more acidic/stronger an acid…
the more stable/weaker it’s conjugate base is
The less acidic an acid…
The stronger, and more unstable it’s conjugate base is
The more stable/weaker the base…
The more acidic its conjugate acid will be

In proton transfer reactions, which side does equilibrium favor?
The side with the weaker, more stable base and the weaker weaker acid (higher pKA value)
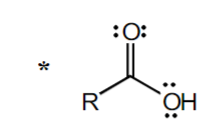
+5
“R” is CH3—> pKA= +4.7
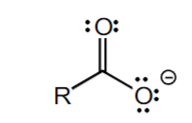
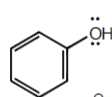
+10
Benzenol
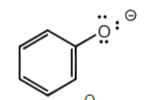
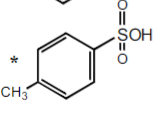
-3
4-methyl sulfonic Acid
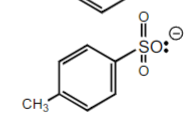
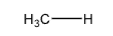
+50
Methane
H3C-
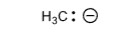
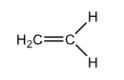
+44
Ethene
H2C=CH-
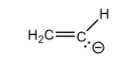
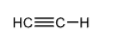
+25
Ethyne
HCCH
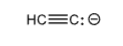
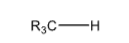
>+60
Tertiary Carbon, or Methine Carbon
R3C-
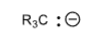
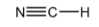
+9.2
Hydrogen Cyanide
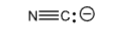
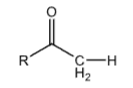
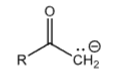
+20
Acetyl Group
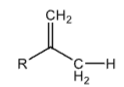
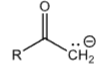
+40
Ethyl Group
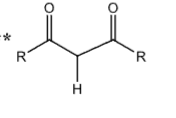
+10
Anhydride
NH3
+35
Ammonia
NH2-