SN2, SN1, E1, E2 Reactions
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ALL MY NOTES
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Second Order Reaction because it depends on the concentration of 2 species
R = k[RX][-OH]
An SN2 is an example of what order of reaction and why?
Occurs in a single step
How many steps for an SN2 reaction
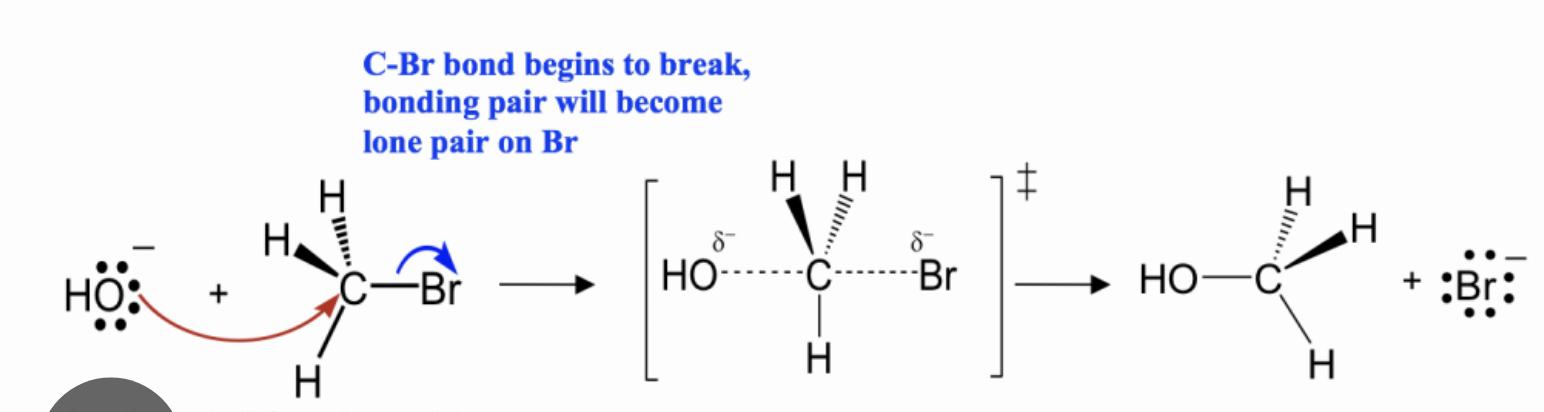
Mechanism for SN2 reaction
Lowering reactant energy or increasing transition-state energy
What increases the activation energy for an SN2 reaction? (Slows down reaction)
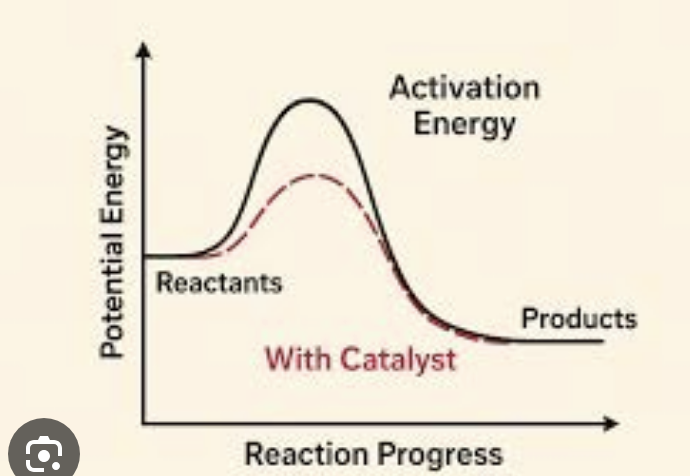
Increasing reactant energy or decreasing transition-state energy (pictured)
What decreases the activation energy for an sn2 reaction? (Catalyzes reaction)
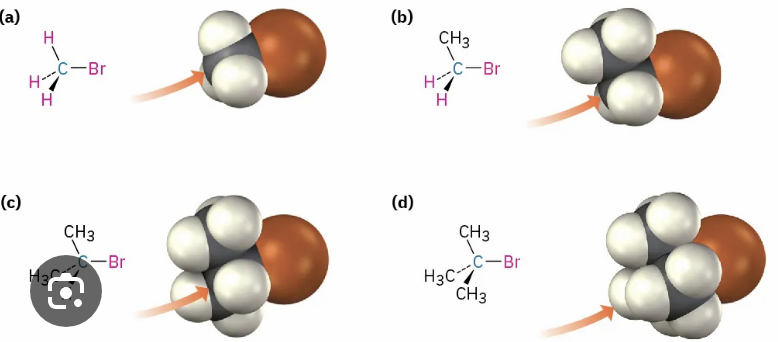
A hindered, bulky substrate prevents easy approach of Nucleophile - D is impossible, C is sometimes possible
Steric effects in an SN2 reaction
Unreactive toward SN2 displacement due to steric factors
How do vinylic halides and aryl halides act in an SN2 reaction?
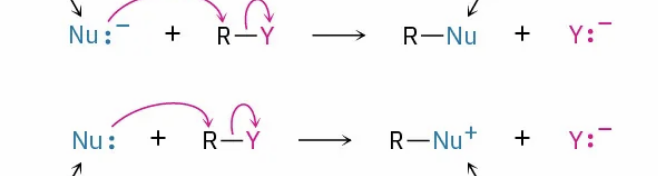
Nucleophile negative = neutral product
Nucleophile neutral = positive product
What are the products of a negative nucleophile or neutral nucleophile?
Any species, neutral or negative charge can act as nucleophile as long as it has unshared pair of electrons (MUST BE LEWIS BASE - donate e- to form covalent bond)
Describe a nucleophile in an sn2 reaction?
H2O
CH3O2-
NH3
Cl-
-OH
CH3O-
I-
-CN
-SH
List these 9 nucleophiles from weakest to strongest:
-SH, CH3O-, NH3, Cl-, I-, H2O, CH3O2-, -CN, -OH
As you move down a column in periodic table
EX: HS more nucleophilic than OH > I- > Br- > Cl-
Nucleophilicity increases as you move?
Usually carried out in basic conditions
SN2 reactions are usually in what type of conditions?
Weak bases are best leaving group because they best stabilize the negative charge
Describe the best kind of leaving group for SN2 reactions
(-OH, -NH2, -OR) bad leaving groups
F- (very weak)
Cl-
Br-
I-
TosO-
List the following leaving groups by reactivity going worst to best:
I-, Br-, -OH, TosO-, -NH2, F-, -OR, Cl-
alkyl fluorides, alcohols, ethers, and amines
What types of molecules typically do not do SN2
Favor polar aprotic solvents - have no -OH or -NH — solvate metal cations, not Nucleophile anions
Describe the best solvent for an SN2 reaction
CH3OH
H2O
DMSO
DMF
CH3CN
HMPA
List the solvents from worst to best for an SN2 reaction:
DMF, HMPA, CH3OH, CH3CN, H2O, DMSO
Protic solvents (contain -OH or -NH) like methanol or ethanol slow down SN2 by solvation of nucleophile (H-bond to it)
Describe the worst kind of solvents for an SN2 Reaction
First order reaction
R = k[RX]
The rate-limiting step does not involve the nucleophile
An SN1 reaction is what type of order? What is its equation?
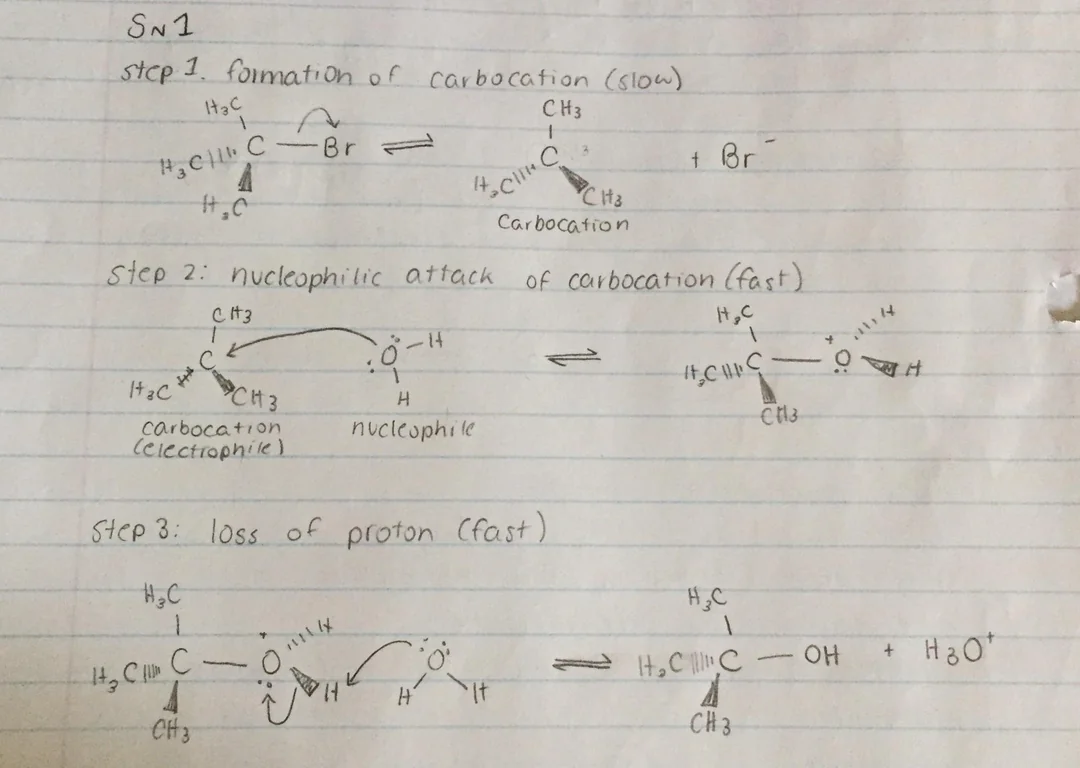
Has 3 steps
Spontaneous dissociation of alkyl bromide (slow rate-determining step)
Carbocation reacts with nucleophile in fast step to get protonated alcohol
Loss of proton = neutral alcohol product
Mechanism for SN1 reaction
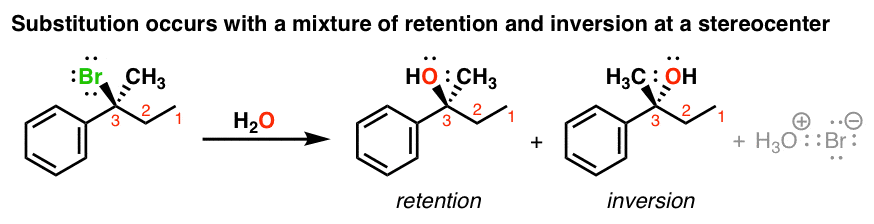
Racemic mixture (not usually 50:50 because of ion pairs — still loosely associated thus blocking rxn on one side (prefers inversion, attacking from backside)
Describe the products of an SN1 reaction… why does this happen what does it prefer?
More stable carbocation formed = faster SN1 rxn
tertiary > secondary > primary (never occurs)
Describe the substrate for an SN1 reaction
Allyl (2 resonance structures) and benzyl (5 resonance structures) cations are unusually stable — increasing rate of rxn
Allyl and benzyl cations in Sn1 reaction do what to the reaction rate?
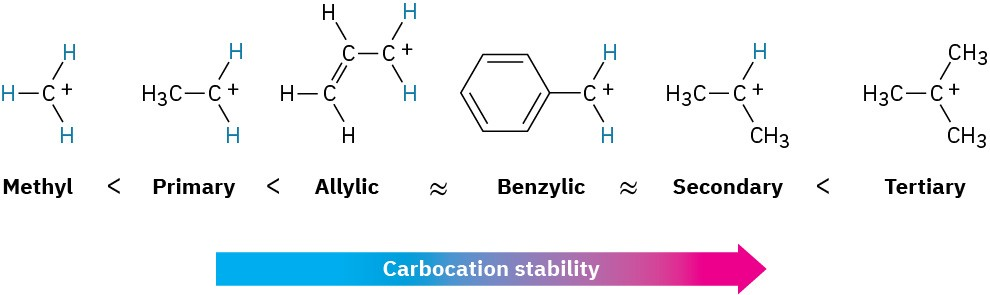
List carbocations in order of increasing stability (include primary allyl and primary benzyl)
Primary allylic and primary benzylic substrates are also involved in SN2 rxns
What is important to remember about primary allylic and primary benzylic substrates?
-OH
Cl-
Br-
I- = TosO-
H2O
List the following in order of increasing leaving group reactivity for SN1 reactions:
Br-, I-, H2O, -OH, Cl-, TosO-
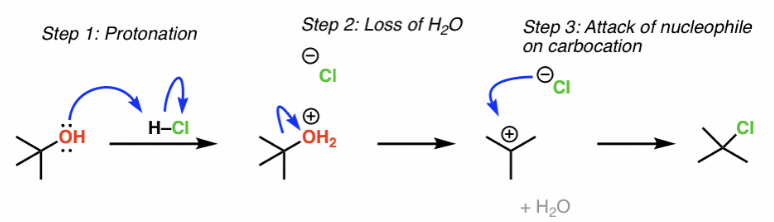
Sn1 - works best for tertiary alcohols because they give the most stable carbocation intermediates
what mechanism type is involved in the conversion of alcohols to alkyl halides?
Nucleophile does not matter, can’t affect reaction rate in SN1
What role does the nucleophile play in an sn1 reaction?
Neutral or acidic conditions
What are the best conditions for an SN1 reactions?
Ethanol
40% H2O/60% ethanol
80% H2O/20% ethanol
H2O
List solvent reacitivty from least to greatest for sn1 reaction:
H2O, 80% H2O/20% ethanol, ethanol, 40% H2O/60% ethanol
Favor polar solvents - lower transition state energy to carbocation by solvation
vs less polar solvents like ethers or CHCl3 (chloroform) are slower
What type of solvents favor sn1 reactions?
Protic solvents lower the ground state of the nucleophile due to solvation
Why do SN2 reactions dislike polar protic solvents?
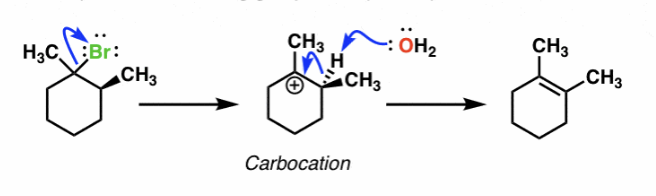
E1 reaction mechanisms
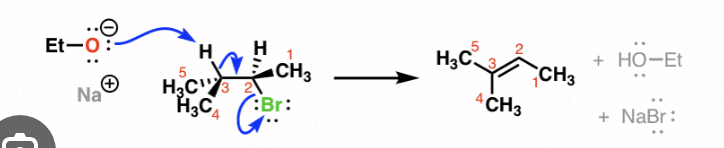
E2 reaction mechanisms
E2
Examples: NaH, DBN, DBU
Strong base/weak nucleophile
For primary: E2 (major) or SN2
secondary and tertiary: E2
Examples: -OH, CH3O- (methyl oxide), EtO- (ethyl oxide)
Strong base/strong nucleophile
For primary and secondary: SN2
Tertiary: SN1
Examples: I-, Br-, Cl-, RS-, HS-, RSH, H2S
Weak base/Strong nucleophile
no reaction for primary or secondary…
tertiary: SN1 or E1
Examples: H2O, MeOH, EtOH
Weak base/Weak nucleophile
methyl substrate and bulky base = SN2
primary, secondary, and tertiary substrate and bulky base = E2
Example of bulky base: tertBuO-
Bulky Base and primary, secondary, or tertiary substrate
methyl substrate + strong base = SN2
primary substrate + strong base = SN2/E2
secondary substrate + strong base = E2 (Favors)/SN2
tertiary substrate + strong base = E2
Examples of strong bases = -OH, Ch3O-, EtO-
Strong base and primary, secondary, or tertiary substrate
Methyl/primary/secondary substrate + aprotic solvent = SN2
tertiary substrate + aprotic solvent = SN1/E1
Examples of aprotic solvents = DMF, DMSO, I-, CN-, RS-
Aprotic solvent and primary, secondary, tertiary substrates
methyl, primary substrate + protic solvent = SN2
secondary substrate + protic solvent = SN1/E1 (favors)/SN2
tertiary substrate + protic solvent = SN1/E1
Examples of protic solvents: H2O, MeOH
protic solvent plus primary, secondary, or tertiary substrate…
![<p>second order</p><p>rate = k[RX][Base]</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/a9433b45-e877-4e40-8a23-3e2820a3e07e.png)
second order
rate = k[RX][Base]
E2 is what type of reaction order?
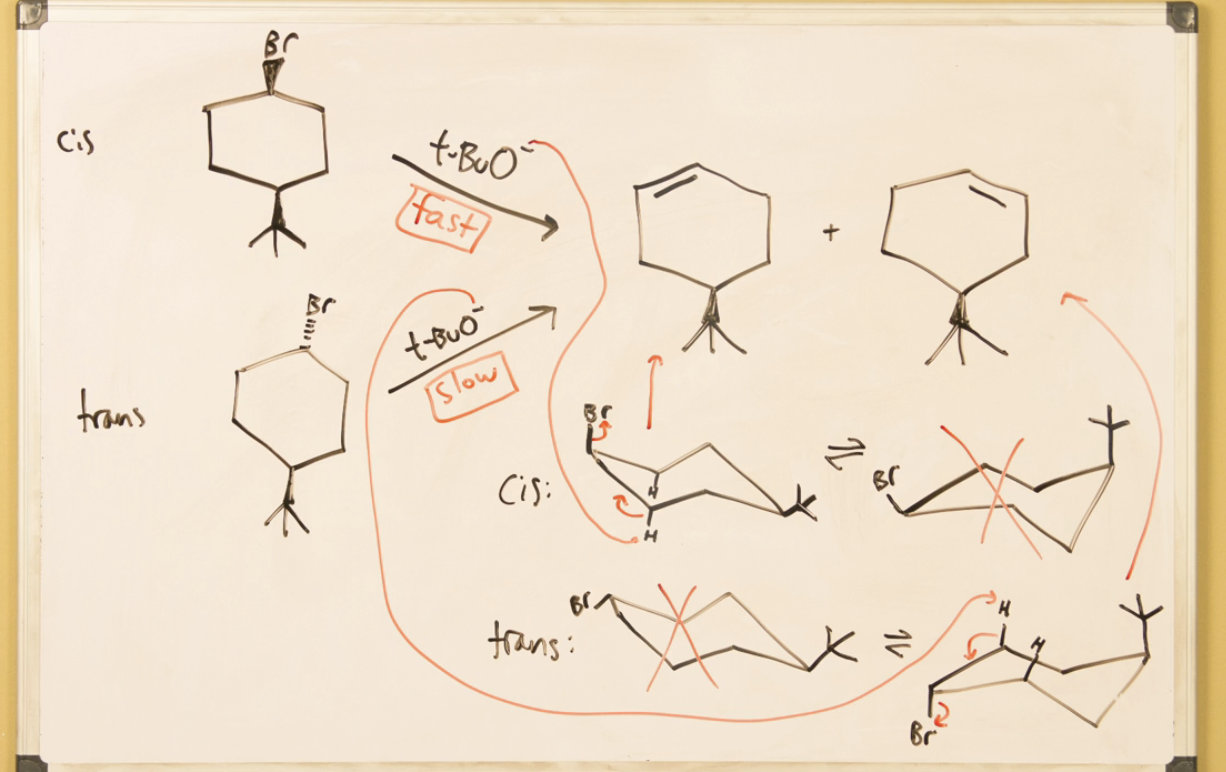
Leaving group and H must both be axial for anti periplanar elimination to occur
E2 in cyclohexane rings