Diagnostic Imaging Exam 2
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
150 Terms
what are some examples of advanced imaging
-CT Scan
-MRI
-Diagnostic Ultrasound
-Bone Scan
-PET scan
-Fluoroscopy
which of the following would NOT be considered advanced imaging?
a. Diagnostic Ultrasound
b. Conventional Radiograph
c. MRI
d. CT scan
conventional radiograph
T/F: a radiograph is more sensitive than a CT scan
False
what does CT stand for in CT scan?
a. Computed Topography
b. Cranial Typography
c. Caudal Thermography
d. Computed Tomography
Computed Tomography
how is an axial CT scan viewed?
a. patient is supine and the viewer is at their feet looking caudocephalad
b. patient is supine and the viewer is at their head looking cephalocaudal
c. patient is prone and the viewer is at their feet looking caudocephalad
d. patient is prone and the viewer is at their head looking cephalocaudal
patient is supine and the viewer is at their feet looking caudocephalad
how is a sagittal CT scan viewed?
a. left to right
b. right to left
left to right
what are the clinical uses of a CT scan?
-subtle fractures and/or complex fractures
-degenerative changes
-serious trauma
-spinal stenosis
-IVD
-loose bodies in a joint
-osseous alignment in any place
CT Scans are best for evaluating which of the following:
a. Nerve Conduction
b. Soft Tissue
c. Bone
d. Venous Perfusion
Bone
what are the pros of CT Scan
-less expensive than MRI
-less claustrophobic
-can image soft tissue and osseous structures in one series
-less time consuming
what are the cons of CT scan
-utilizes ionizing radiation
-high radiation exposure
-more expensive than a plain film radiograph
Joey comes into your clinic for an evaluation of acute ankle pain. He hurt his ankle playing a game of tennis two weeks ago. He went to Urgent Care, where they took an x-ray of his ankle and found a possible fracture or osteochondral imaging. You want to recommend advanced imaging as the next step for this patient, which of the following would be the BEST option?
a. Ultrasound
b. CT Scan
c. MRI with IV contrast
d. CT Scan with IV contrast
CT Scan
what is a CT myelogram?
a CT scan with a contrast media in the spinal fluid
CT scan
what type of imaging is this?
a. T2 MRI
b. Bone Scan
c. CT scan
d. conventional radiography
CT Scan
what type of imaging is this?
a. CT scan
b. MRI with IV contrast
c. PET scan
d. Bone Scan
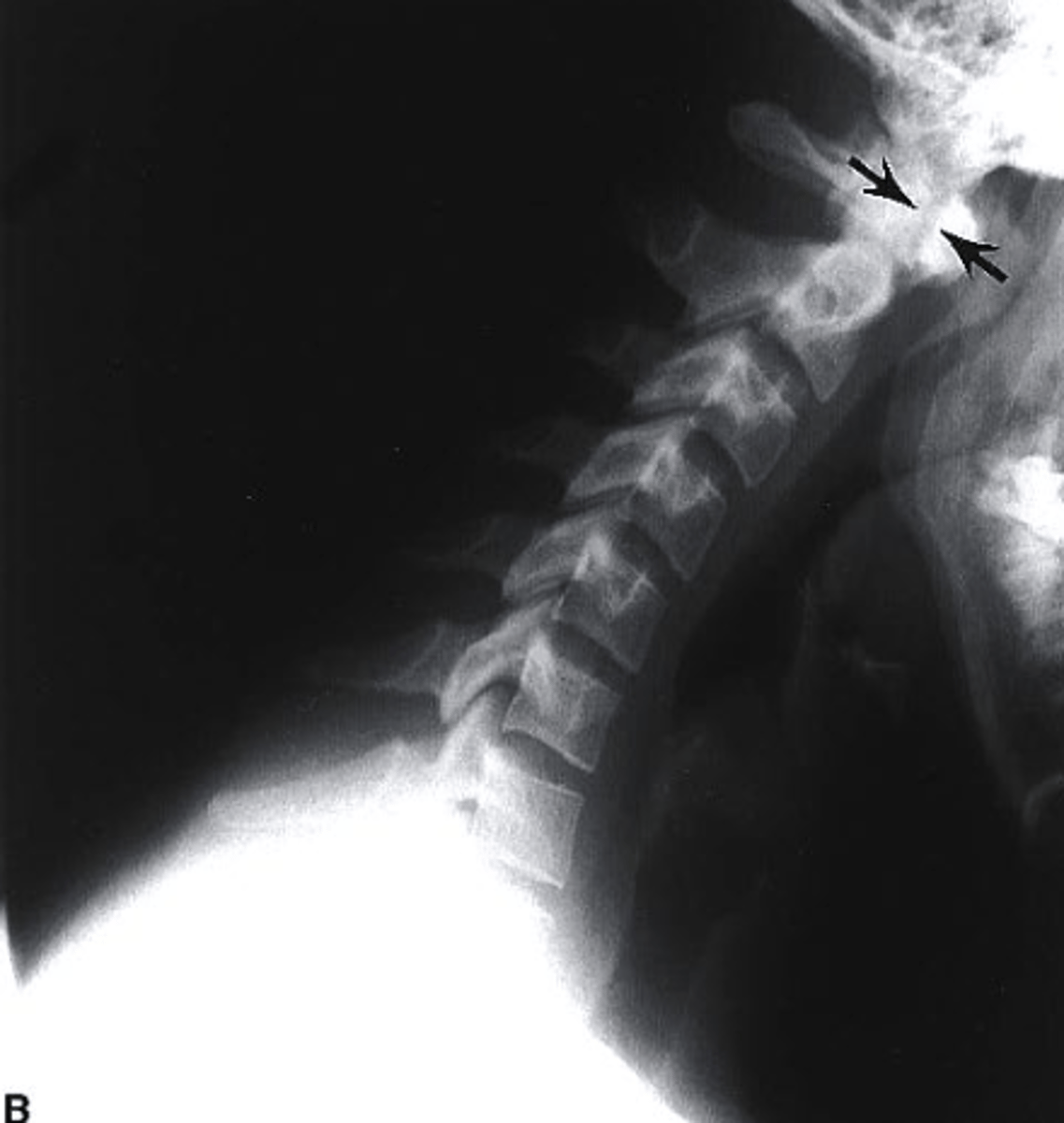
what type of patients are most likely to receive a CT myelogram?
pre surgical patients with spinal stenosis
how does MRI work
energy emitted from hydrogen nuclei after their stimulation by radiofrequency signals
T/F: MRI works with non ionizing radio waves
True
MRI will best view what structures?
-Soft Tissue Detail
-Changes in Bone Marrow
-Staging neoplasm in bone and/or soft tissue
T/F: MRI can not be used to diagnose bony pathologies
False
Danny comes into your clinic with acute shoulder pain. His doctor recommended him to physical therapy after his x-rays came back unclear of pathology. As you perform the exam, you suspect he may have a labral tear and want to recommend him back for advanced imaging. Which of the following would be the best option?
a. PET scan
b. MRI with IV contrast
c. MRI without IV contrast
d. Diagnostic Ultrasound
MRI without IV contrast
what clinical presentations would indicate an MRI?
-localized or regional symptoms suspicious for bone lesion
-radiographs negative or findings do not explain symptoms
-bone lesion on radiographs. would be the next radiographic study
-incidental bone finding on CT; not clearly benign
-soft tissue mass
-potential stress fracture
what are some disadvantages of MRI
-high cost
-claustrophobia of the patient
-length of time to complete
-pt needs to sit still to get adequate images
-cannot be performed with ferrous metal in the body
-findings do not always correlate to symptoms
what are contraindications to MRI?
-any metal implants
-ortho hardware that will distort the imaging
-pacemakers
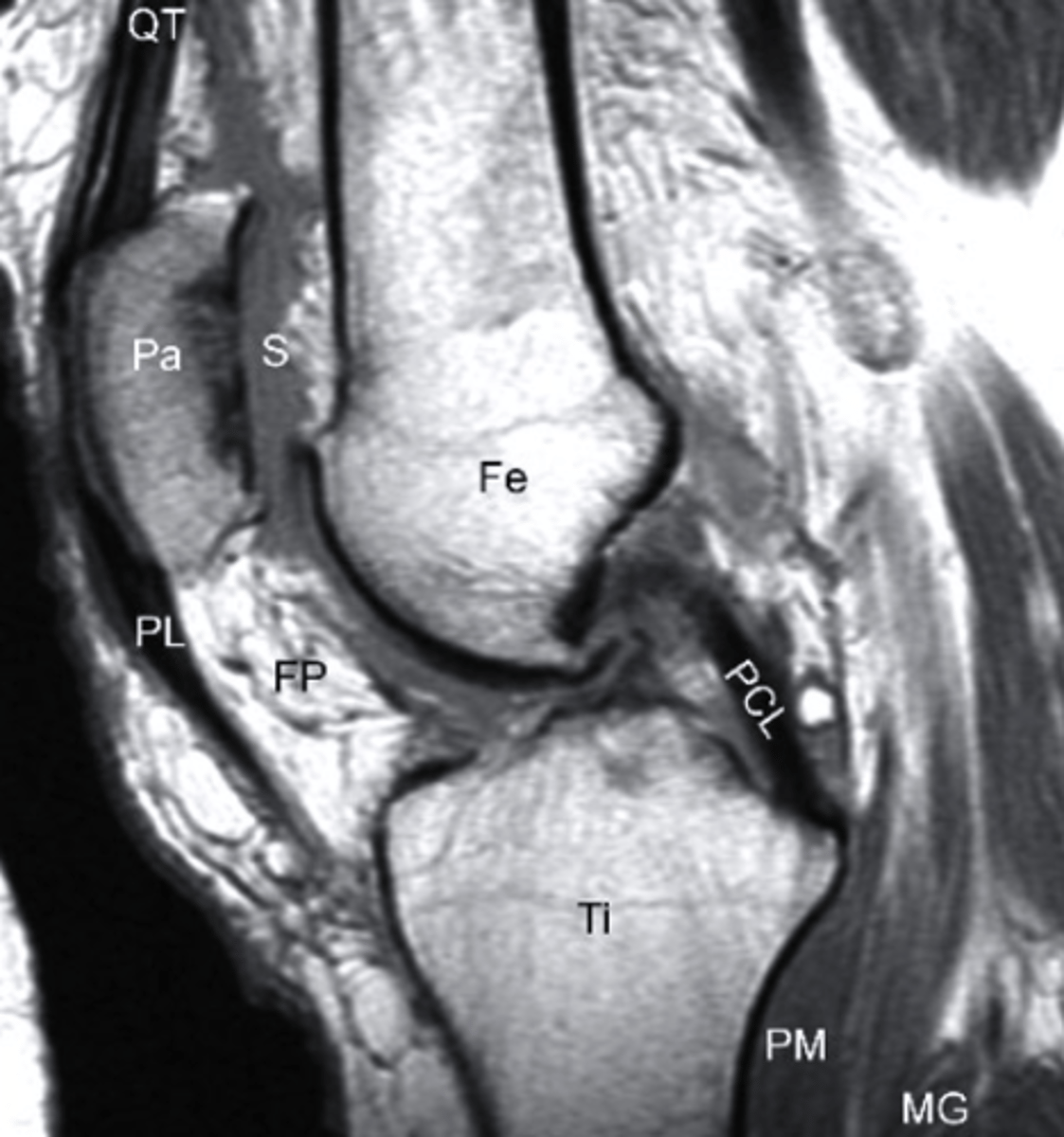
T1 MRI
what type of imaging is this?
a. T2 MRI
b. CT Scan
c. Radiograph
d. T1 MRI
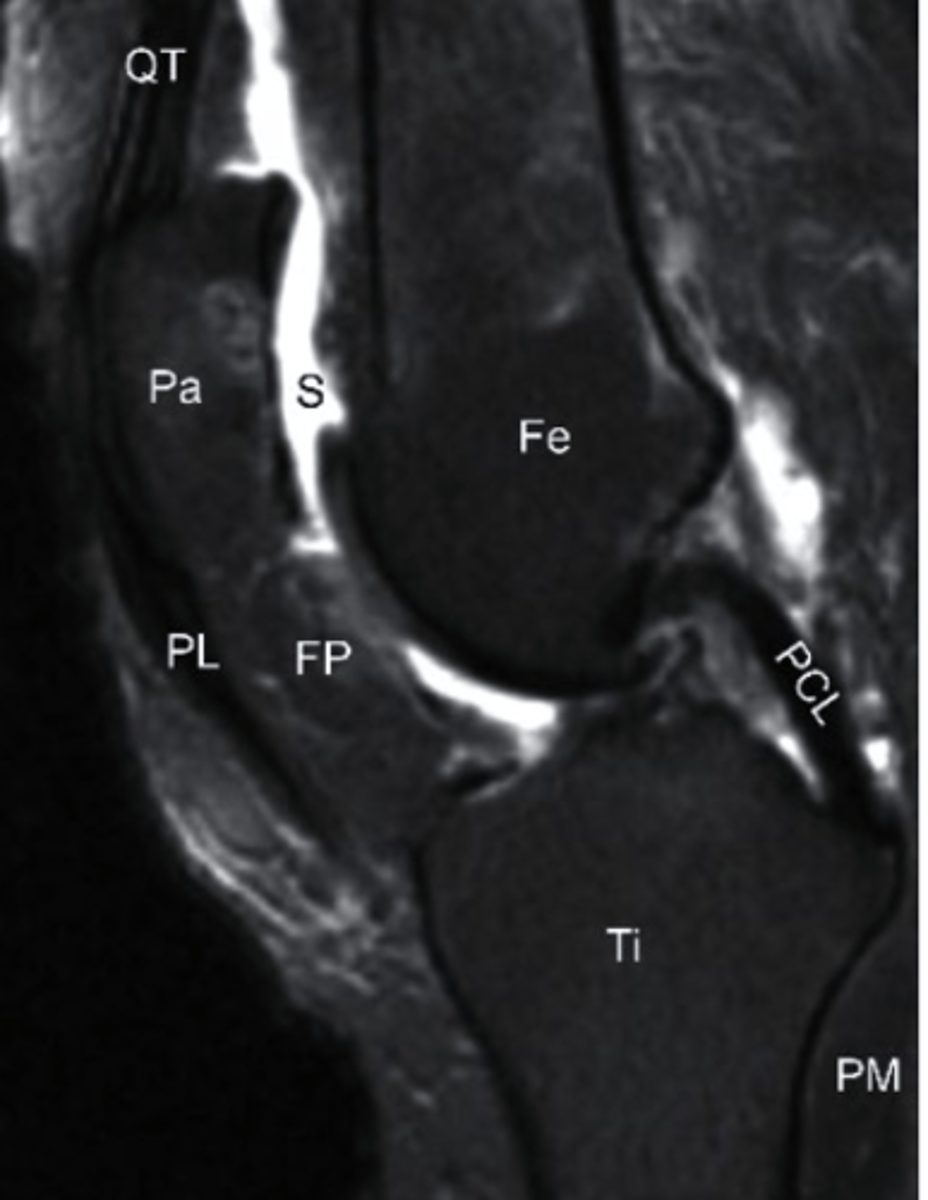
T2 MRI
what type of imaging is this?
a. T2 MRI
b. CT Scan
c. Radiograph
d. T1 MRI
bone marrow edema
what can be seen in this MRI?
a. bone tumor
b. bone marrow edema
c. fracture in the bone
d. bone bruising
is anatomic detail better seen in T1 or T2 MRIs?
T1
what type of MRI is better able to detect water and swelling?
T2
How does fat and bone marrow appear _______, and water appears _______ on a T1 MRI image?
a. dark; bright
b. dark;dark
c. bright; dark
d. bright; bright
bright; dark
fat and bone marrow have a _______ signal density in T1 MRI.
a. low
b. high
c. moderate
high
T1 MRI
what type of image is this?
a. T2 MRI
b. CT Scan
c. T1 MRI
d. conventional radiograph
T2 MRI
what type of image is this?
a. T2 MRI
b. CT Scan
c. T1 MRI
d. conventional radiograph
Synovial Fluid, T2 MRI
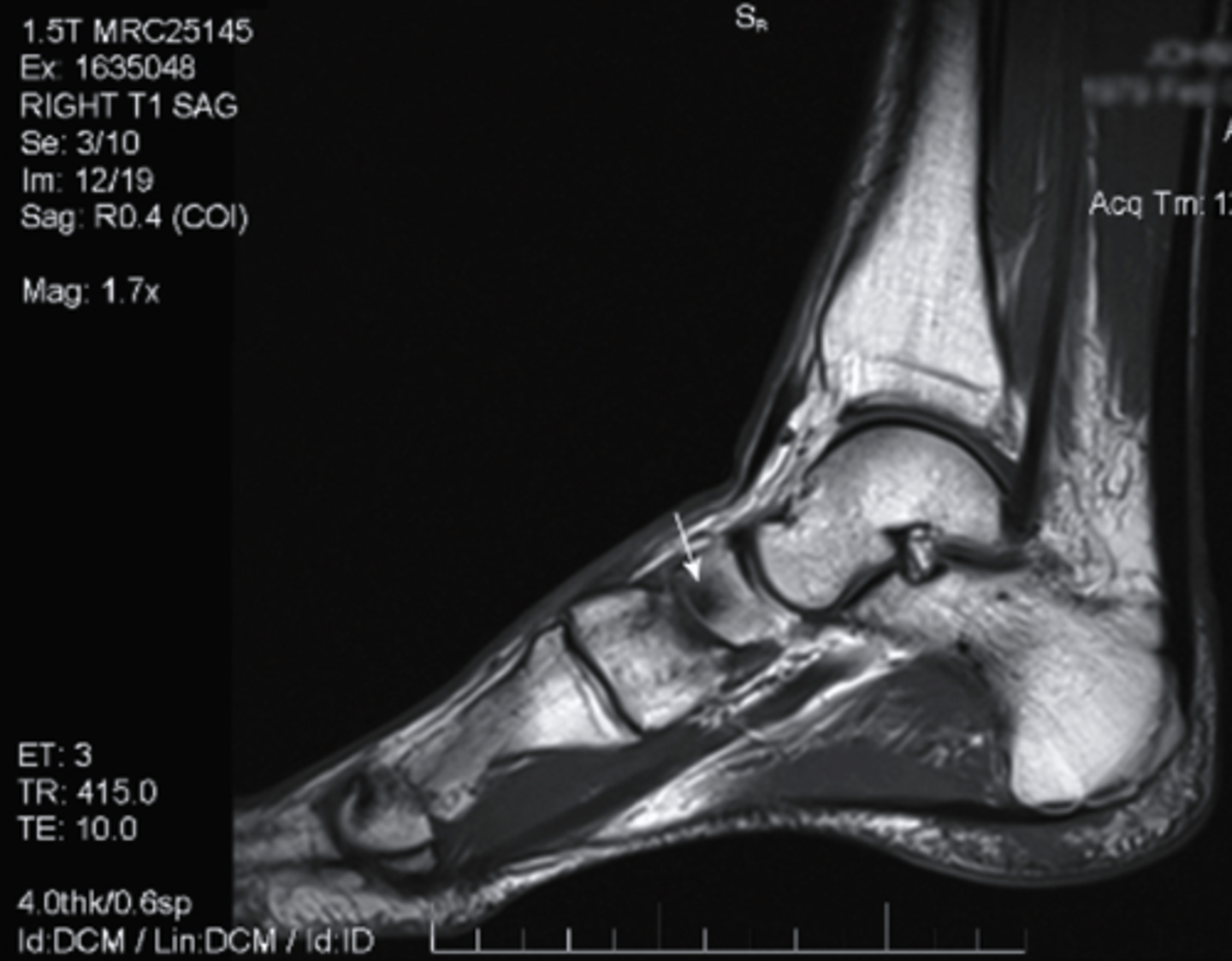
what does the S represent on this image and what type of image is this?
a. Swelling, T1 MRI
b. Sclerosis, T1 MRI
c. Synovial Fluid, T2 MRI
d. Sartorius, T2 MRI
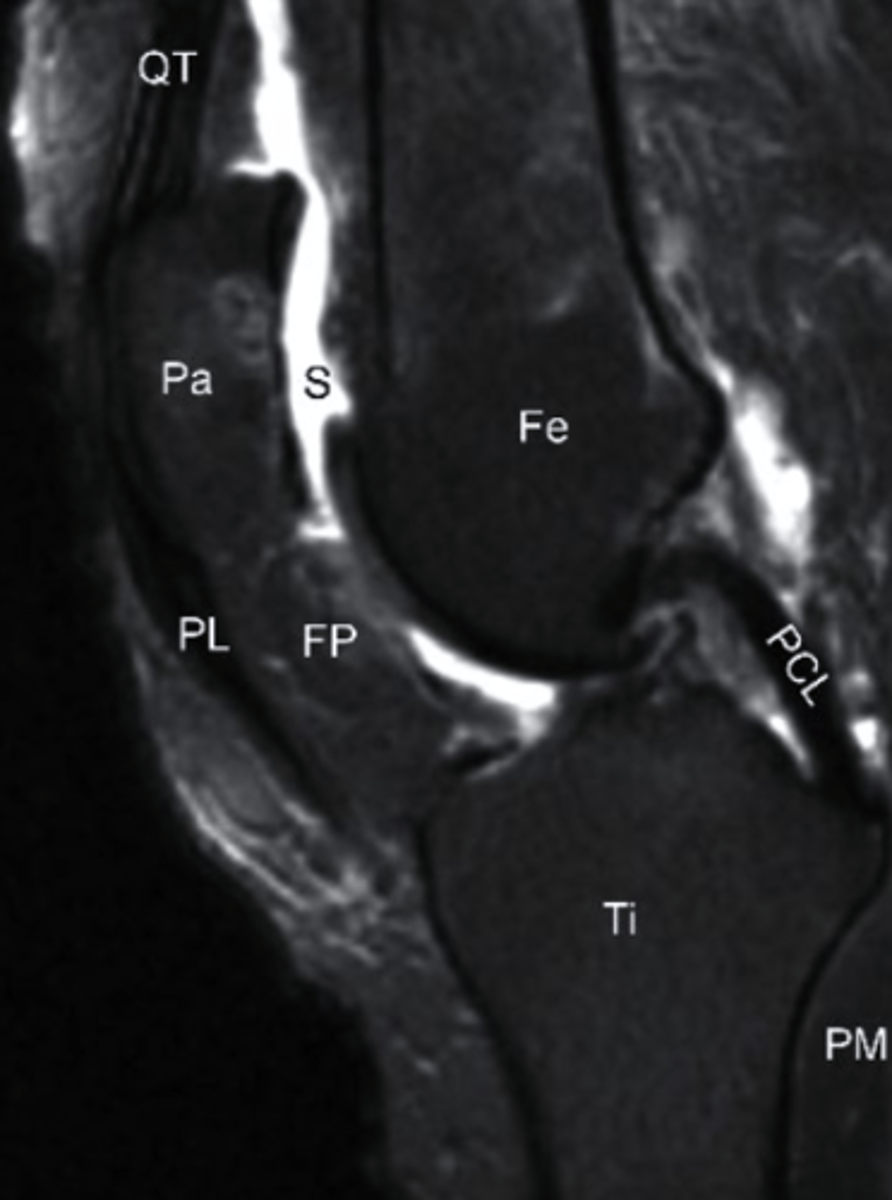
sagittal
what is the view of this image?
a. coronal
b. axial
c. frontal
d. sagittal
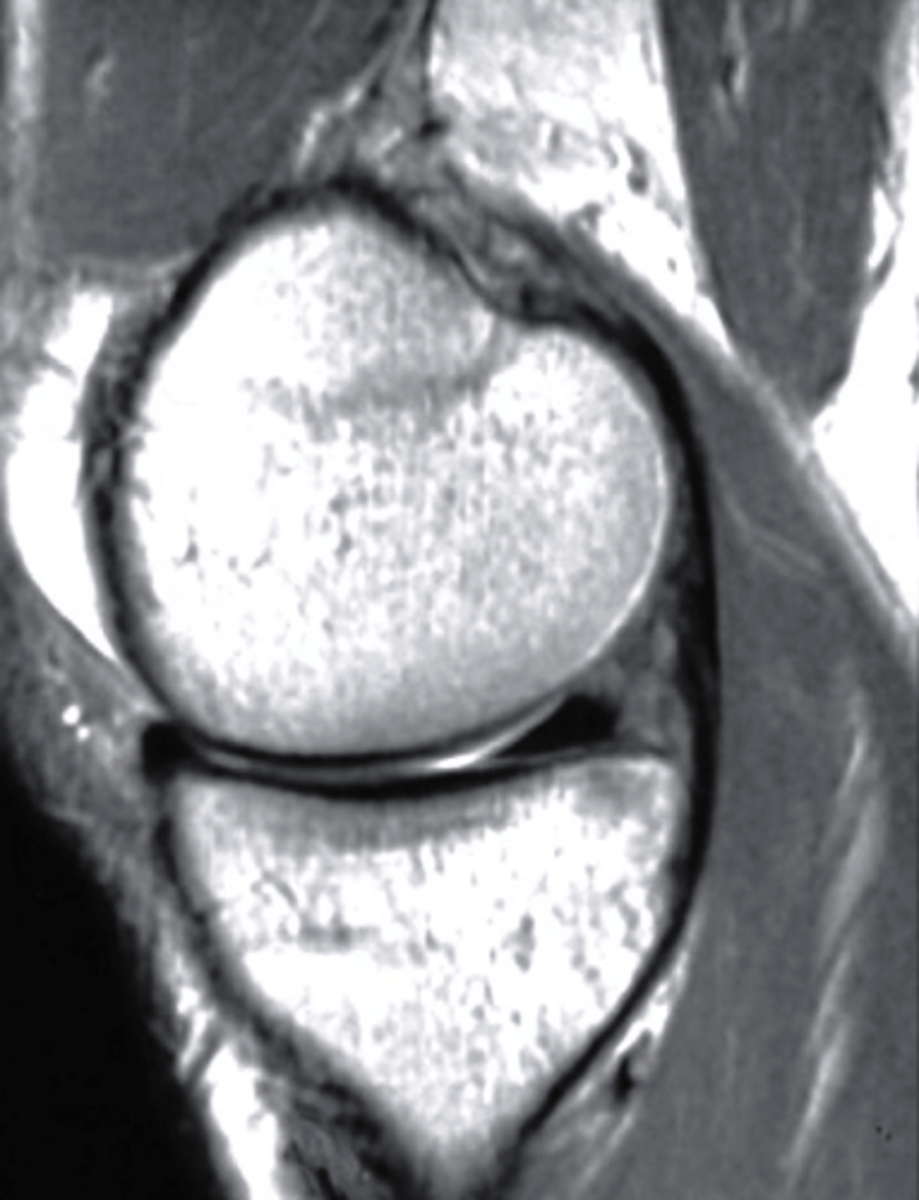
bone bruise, T2 MRI
what can be seen on the medial tibial plateau in this image and what type of image is this?
a. tumor, T1 MRI
b. complex fracture, CT scan
c. bone bruise, T2 MRI
d. AVN, conventional radiograph
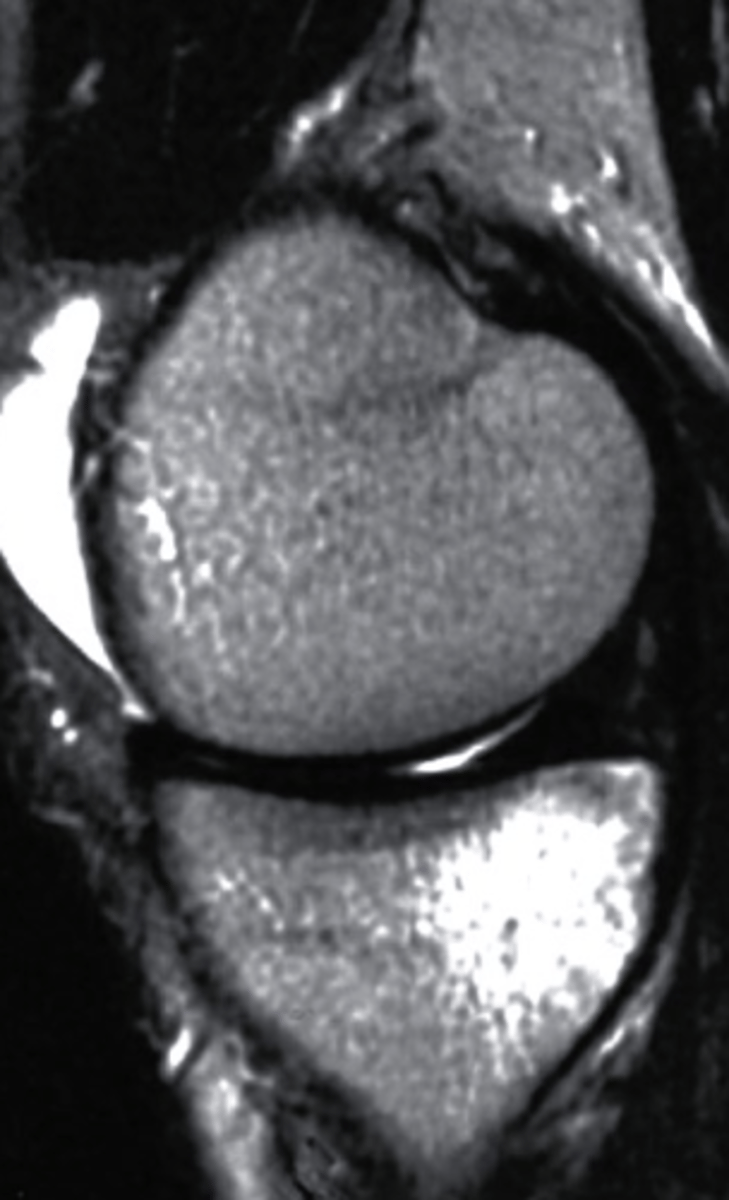
Your patient Erin is a 23 year old female who has been referred to PT after identification of a stress fracture in her L knee. She is showing signs of delayed healing and you want to refer her for some more imaging. Her PMH includes an implanted pacemaker and prev sx on her L knee in which she completed pre-op and post-op PT for ACL reconstruction. Which would be the best option for the next imaging study?
a. MRI without IV contrast
b. CT without IV contrast
c. Ultrasound
d. Bone scan
CT without IV contrast
what MRI sequence is best for detection of fractures?
a. Proton Density
b. STIR
c. MRA
d. fMRI
STIR
what are some different techniques for DMUS
-palpating for tenderness to guide transducer placement
-placing the affected joint in a symptom provoking position
-using resisted muscle contractions or passive stretching
-stress-testing ligaments
-applying traction or compression
what are the advantages of Ultrasound Imaging?
-lower cost and greater availability relatively
-portability
-quick scanning time; <12 mins
-high patient tolerance
-increased diagnostic accuracy
-real-time patient interaction
-no ionizing radiation
what are the disadvantages of ultrasound imaging?
-operator dependent
-not included in many curriculums
-underutilized
-learning curve
-cost of unit: $10,000+
-efficiency
-bone and metal cannot be adequately imaged
higher frequency transducers will provide _____ resolution, but _____________ depth.
a. worse; increased
b. better, decreased
c. worse, decreased
d. better, increased
better, decreased
when utilizing ultrasound imaging, if a structure that reflexes the waves is bright, what is it called?
a. anechoic
b. high density
c. hyperechoic
d. low density
hyperechoic
when using diagnostic ultrasound, how do different structures rank on most to least reflective?
a. ligament > nerve> bone > tendon > muscle
b. tenon > ligament > nerve >bone > muscle
c.nerve > bone >ligament > tendon >muscle
d. bone > ligament > tendon > nerve > muscle
bone > ligament > tendon > nerve > muscle
what is a normal finding for cortical bone tissue on ultrasound
a. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
b. thin hyperechoic line
c. hyperechoic relative to muscle
d. hyperechoic, smooth, continuous
hyperechoic, smooth, continuous
what is a normal finding for tendons and ligament tissue on ultrasound
a. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
b. thin hyperechoic line
c. hyperechoic relative to muscle
d. hyperechoic, smooth, continuous
hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
what is a normal finding for bursa on ultrasound
a. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
b. thin hyperechoic line
c. hyperechoic relative to muscle
d. hyperechoic, smooth, continuous
thin hyperechoic line
what is a normal finding for nerves on ultrasound
a. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
b. thin hyperechoic line
c. hyperechoic relative to muscle
d. hyperechoic, smooth, continuous
hyperechoic relative to muscle
what is a normal finding for muscle on ultrasound?
a. hypoechoic, with parallel fibrous hyperechoic bands
b. hyperechoic compared to nerve
c. anechoic
d. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
hypoechoic, with parallel fibrous hyperechoic bands
what is a normal finding for hyaline cartilage on ultrasound?
a. hypoechoic, with parallel fibrous hyperechoic bands
b. hypoechoic layer next to a hyperechoic layer
c. anechoic
d. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
hypoechoic layer next to a hyperechoic layer
what is a normal finding for cysts on ultrasound?
a. hypoechoic, with parallel fibrous hyperechoic bands
b. hypoechoic layer next to a hyperechoic layer
c. anechoic
d. hyperechoic, distinct parallel fiber pattern
anechoic
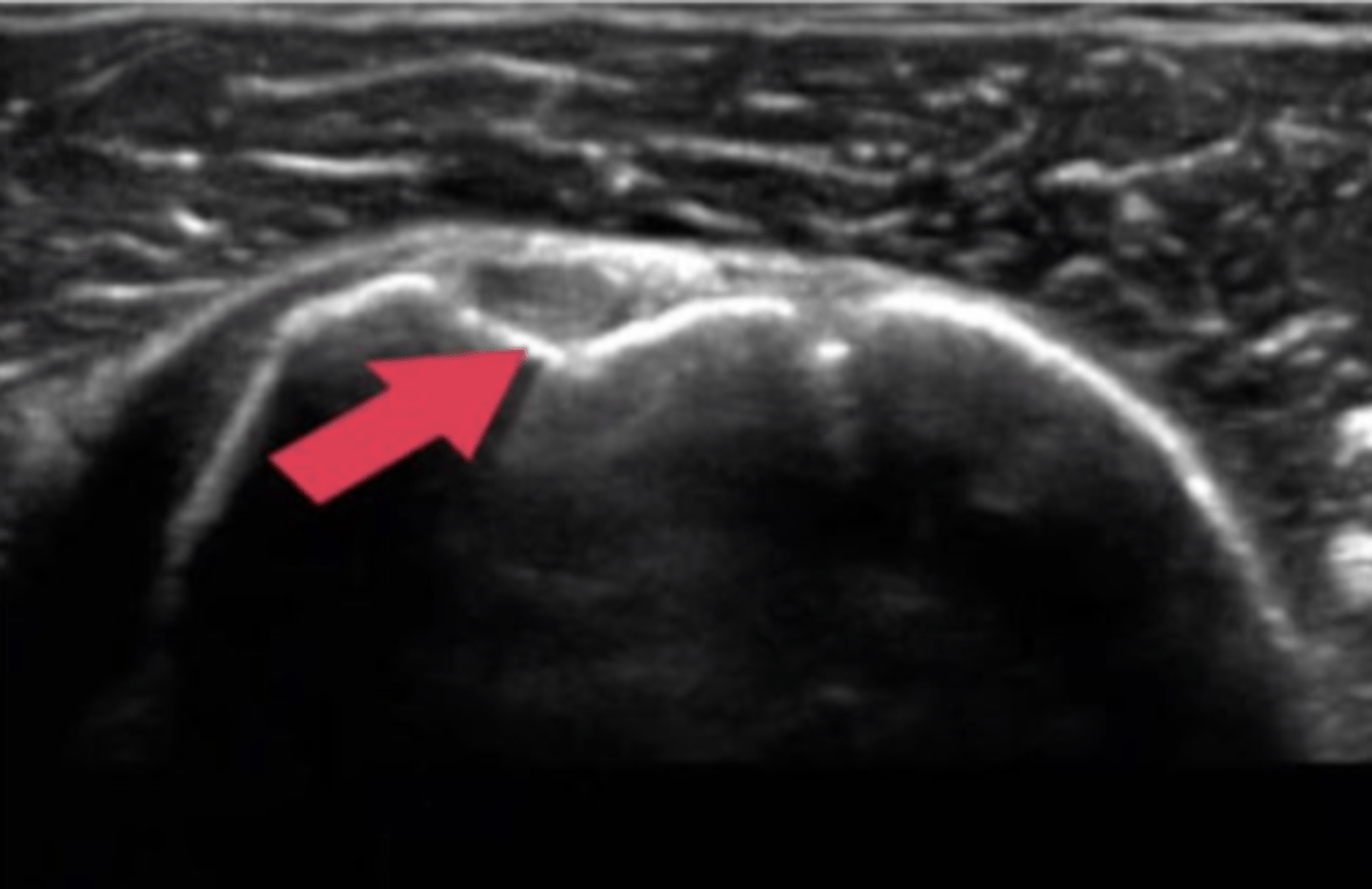
Ultrasound, partial tear
What type of imaging is this and what is identified by the white arrows?
a. CT scan, fracture
b. Ultrasound, partial tear
c. Ultrasound, Swollen Bursa
d. T2 MRI, torn ligament
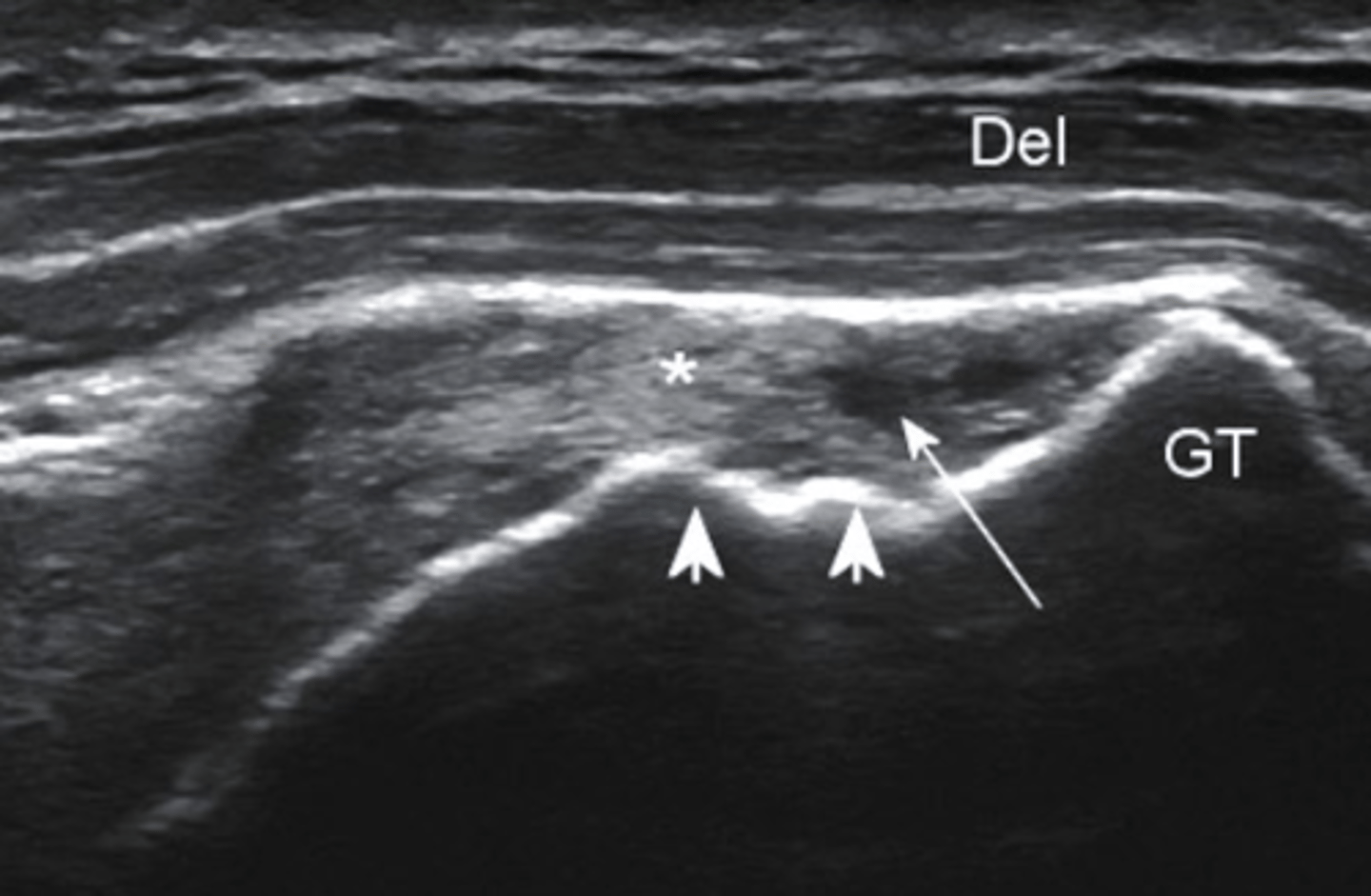
what are the typical indications for use of diagnostic ultrasound?
-soft tissue mass
-potential DVT
-superficial soft tissue foreign body
-muscle integrity, contraction, volume
-soft tissue and joint swelling
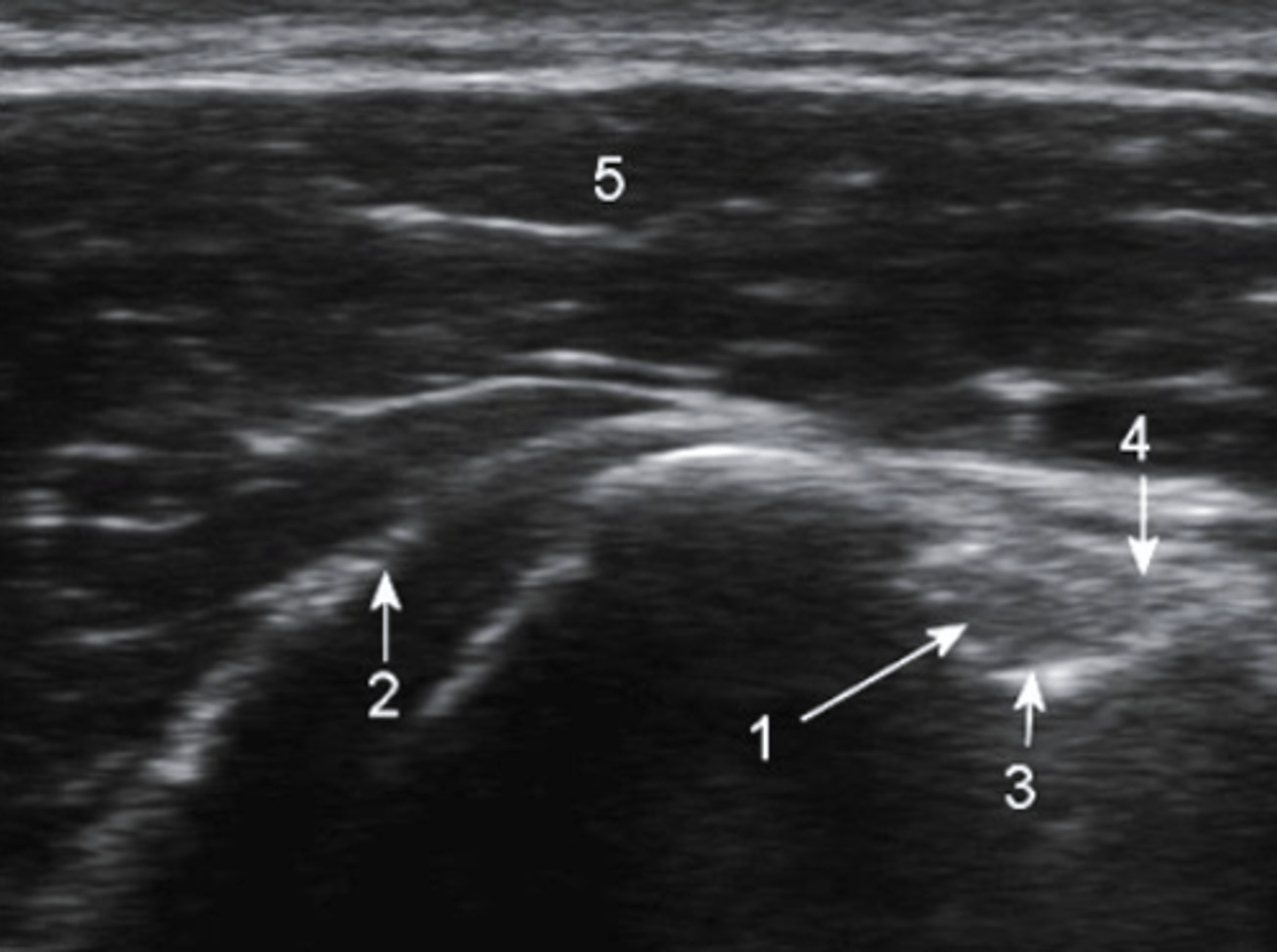
ultrasound, transverse
What type of imaging is this and how is it being viewed?
a. ultrasound, longitudinal
b. T2 MRI, frontal
c. CT Scan, axial
d. ultrasound, transverse
how can Doppler ultrasound be used?
-measure blood flow to diagnose arterial stenosis or vessel constriction
-used during injections to avoid blood vessels during invasive procedures
-used to guide dry needling to deeper structures
what occurs with a radionuclide bone scan
radiopharmaceutical substance is injected into the patient and collects in areas of increased bone activity and will appear as black/dark for a hot spot of activity
Radionuclide bone scan
what type of imaging study is this?
a. Radionuclide bone scan
b. ultrasound
c. PET scan
d. mammogram
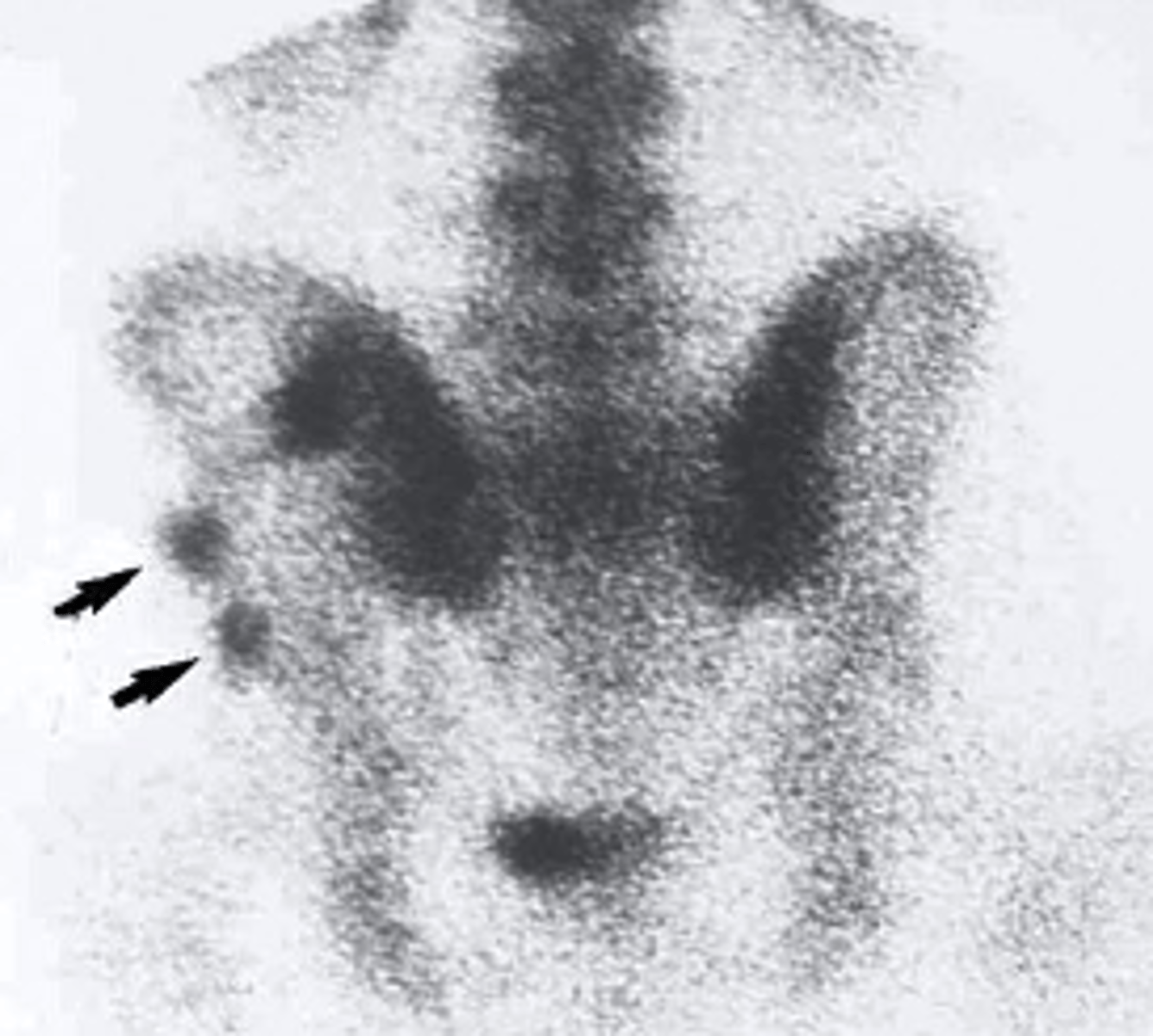
what is a radionuclide bone scan used to view
-subtle fx
-primary and metastatic tumors
-infections
-AVN
-metabolic bone disease
-unexplained bone pain
-epiphyseal growth plates
-areas of arthritis
how does a PET scan occur
radiopharmaceutical is injected into the patient and the radioactive decay products are detected by gamma rays. These are capable of imaging metabolism at the molecular level.
what can a PET scan view
-quantification of blood flow and perfusion
-anatomical mapping of brain function
-study diseases such as dementia
-metabolic activity of tumors
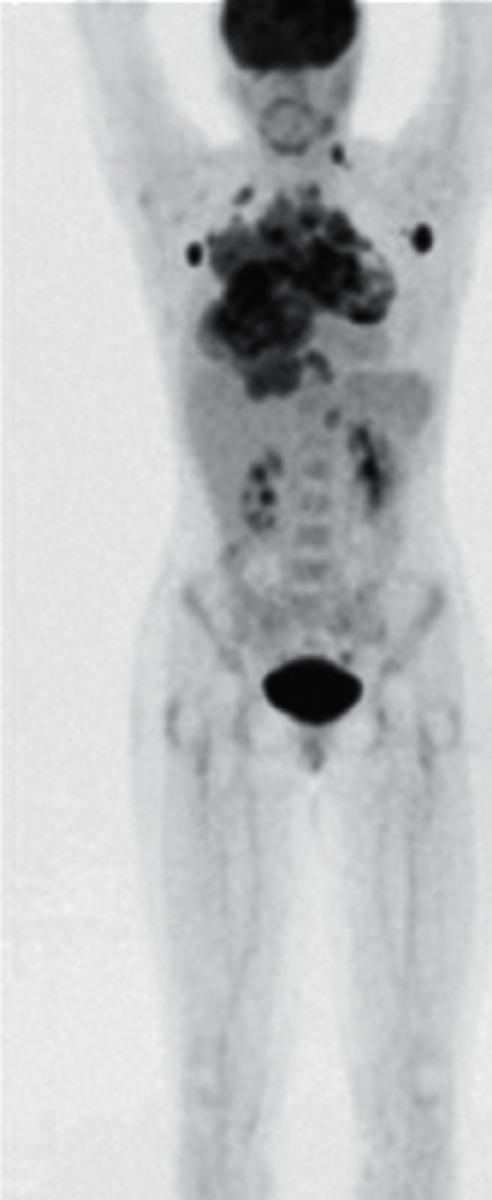
PET scan
what type of imaging study is this?
a. Bone Scan
b. CT scan
c. PET scan
d. MRI
what is fluoroscopy
a dynamic or continuous beam of x-ray sometimes called an x-ray movie
Fluoroscopy
What type of imaging study is this?
a. PET scan
b. Bone Scan
c. T1 MRI
d. Fluoroscopy
what does fMRI measure
regional blood flow and metabolic changes associated with function-related changes in neural firing level
what does a Nerve conduction velocity test measure
how fast an electrical impulse moves through a nerve
what does EMG measure
muscle response or electrical activity in response to a nerve's stimulation of the muscle
a patient sustains a meniscus tear of the knee. Which type of imaging method would be most appropriate to visualize the pathology?
a. CT
b. MRI
c. conventional radiograph
d. ultrasound
MRI
CT
what type of imaging study is this?
a.MRI
b. CT
c. Bone Scan
d. diagnostic ultrasound
Which statement is most accurate of CT imaging as compared to MRI?
a. CT is more expensive
b. CT is more time consuming
c. CT is less claustrophobic
d. CT is not as preferred for evaluating complex fractures
CT is less claustrophobic
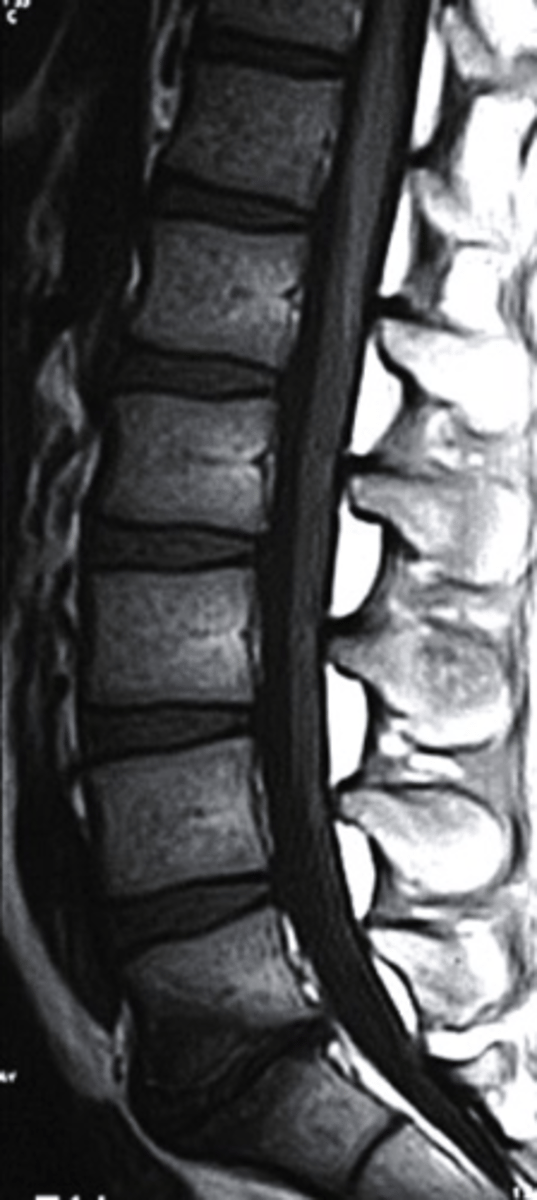
sagittal
What plane is this MRI?
a. sagittal
b. coronal
c. axial
d. AP
Which of the following is accurate of ultrasound imaging?
a. There is minimal learning curve
b. Patient interaction during the procedure is not attainable
c. Ionizing radiation is used.
d. It is highly portable.
It is highly portable.
The main advantages of CT lie in:
a. Its ability to differentiate between malignant and benign tumors
b. Showing the histological makeup of tissues
c. Low radiation
d. Displaying fine detail of cortical bone
Displaying fine detail of cortical bone
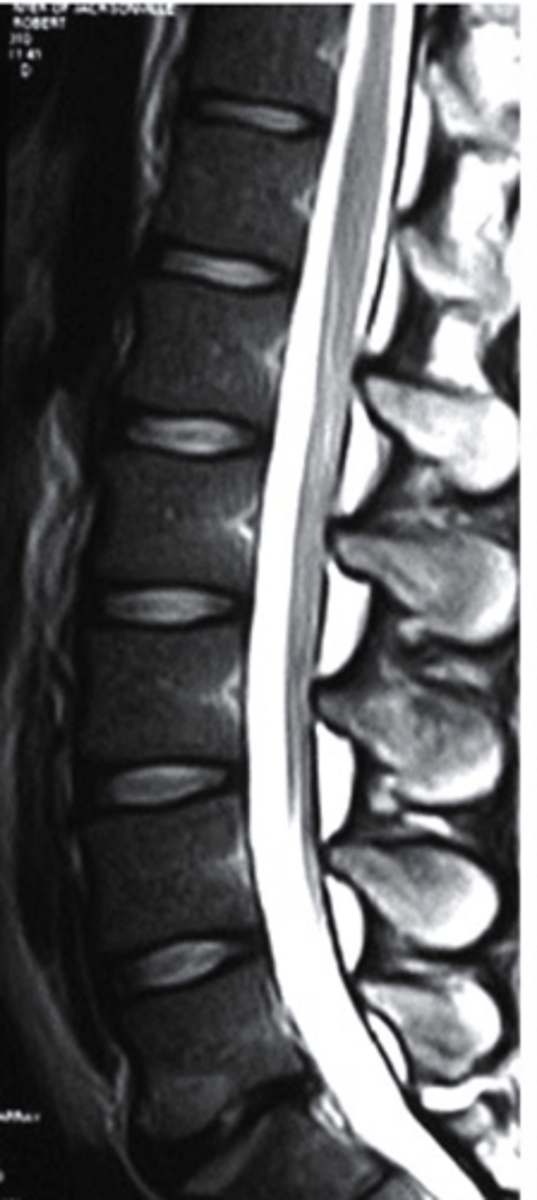
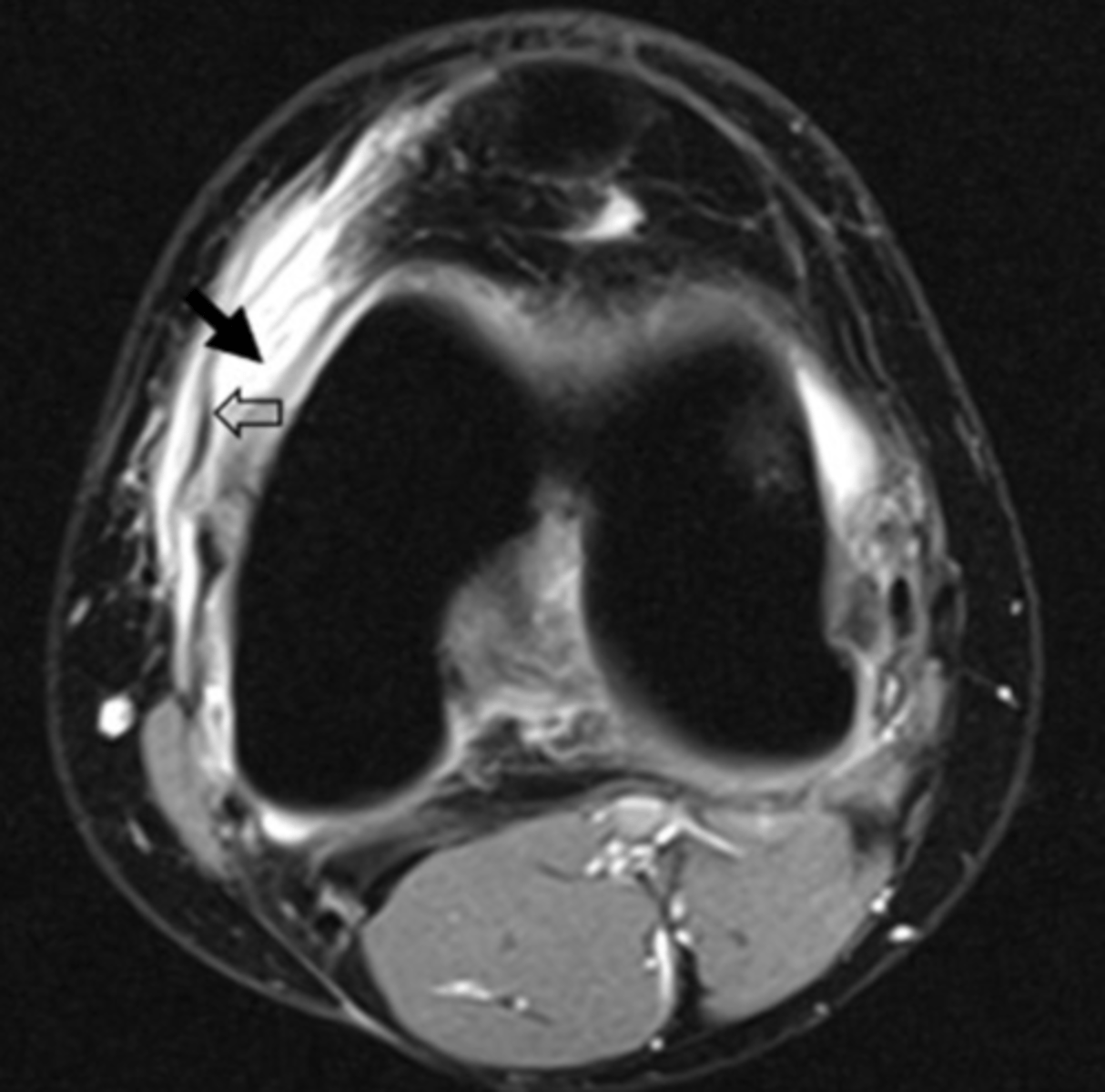
edema
This is an axial T2 image at the level of the femoral condyles. The open arrow points to the medial patellar retinaculum. What does the solid arrow point to?
a. Edema
b. Fatty tumor
c. Hemorrhage
d. Osteogenic tumor
ultrasound
what type of imaging is shown here?
a. fluoroscopy
b. ultrasound
c. bone scan
d. CT
no
Is there ionizing radiation associated with this type of imaging procedure?
a. yes
b. no
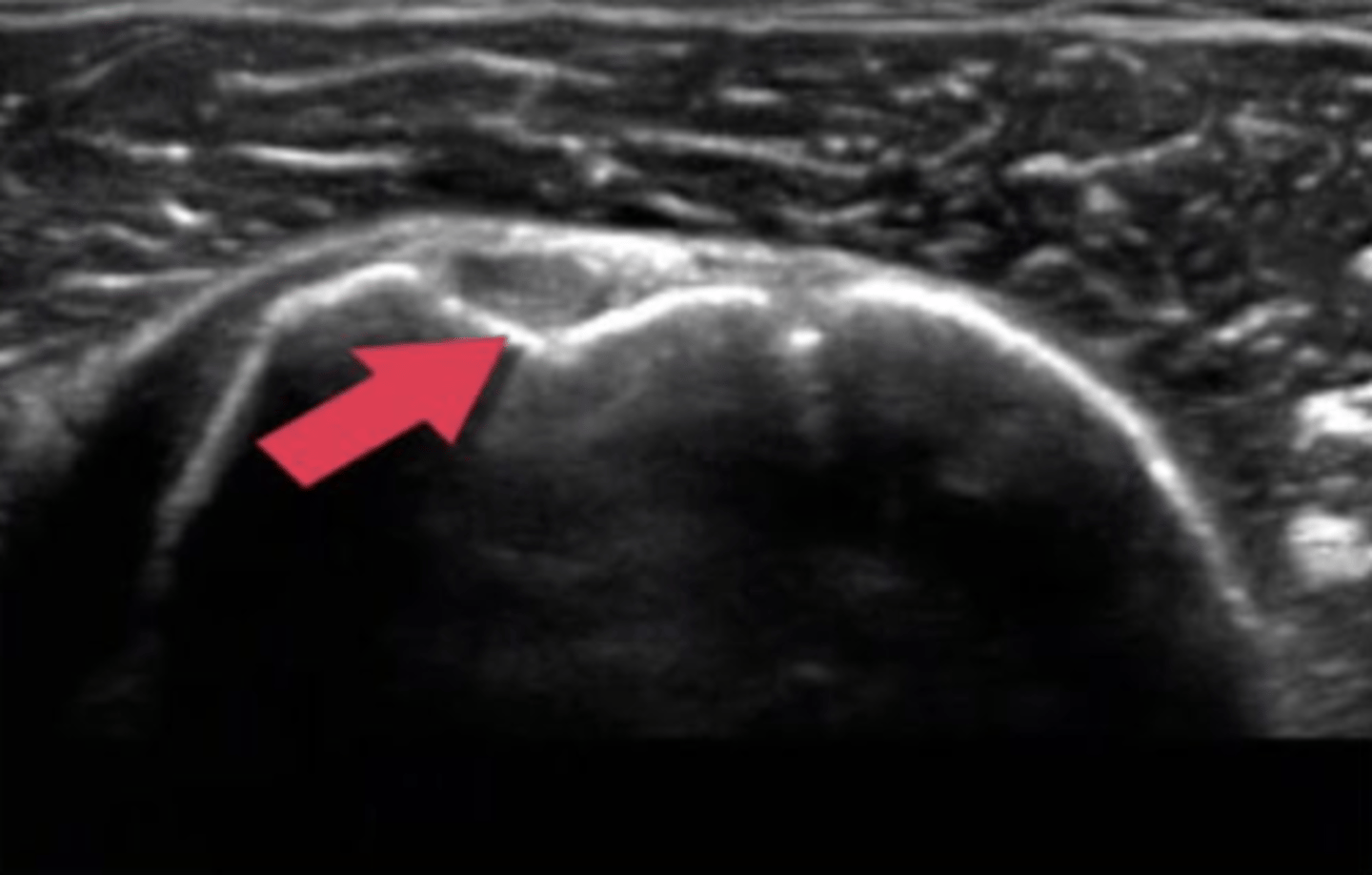
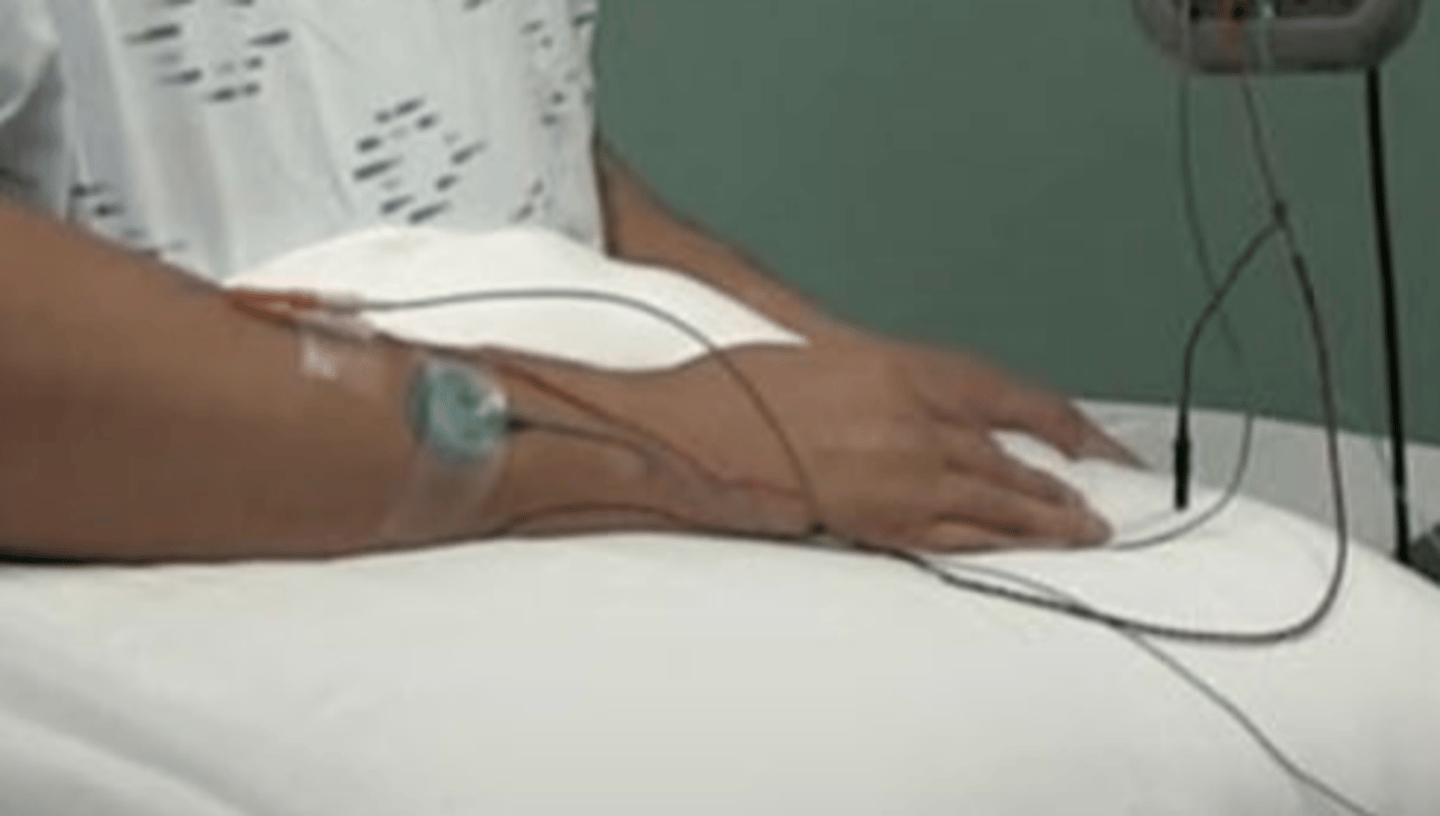
EMG study
By using a needle in this procedure, we know that this is likely a(n) ______________.
a. nerve conduction study
b. dry needling exam
c. EMG study
d. dermatomal screen
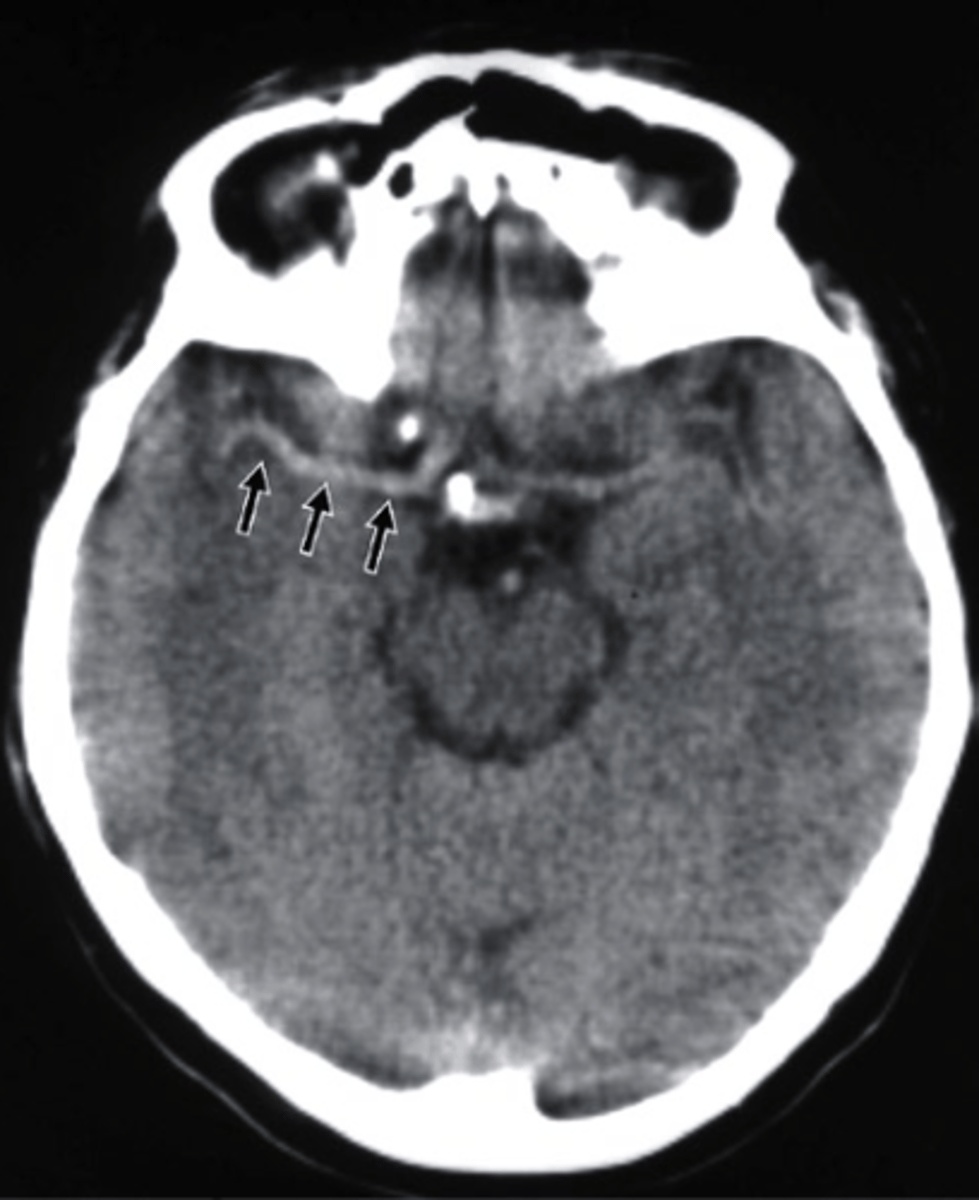
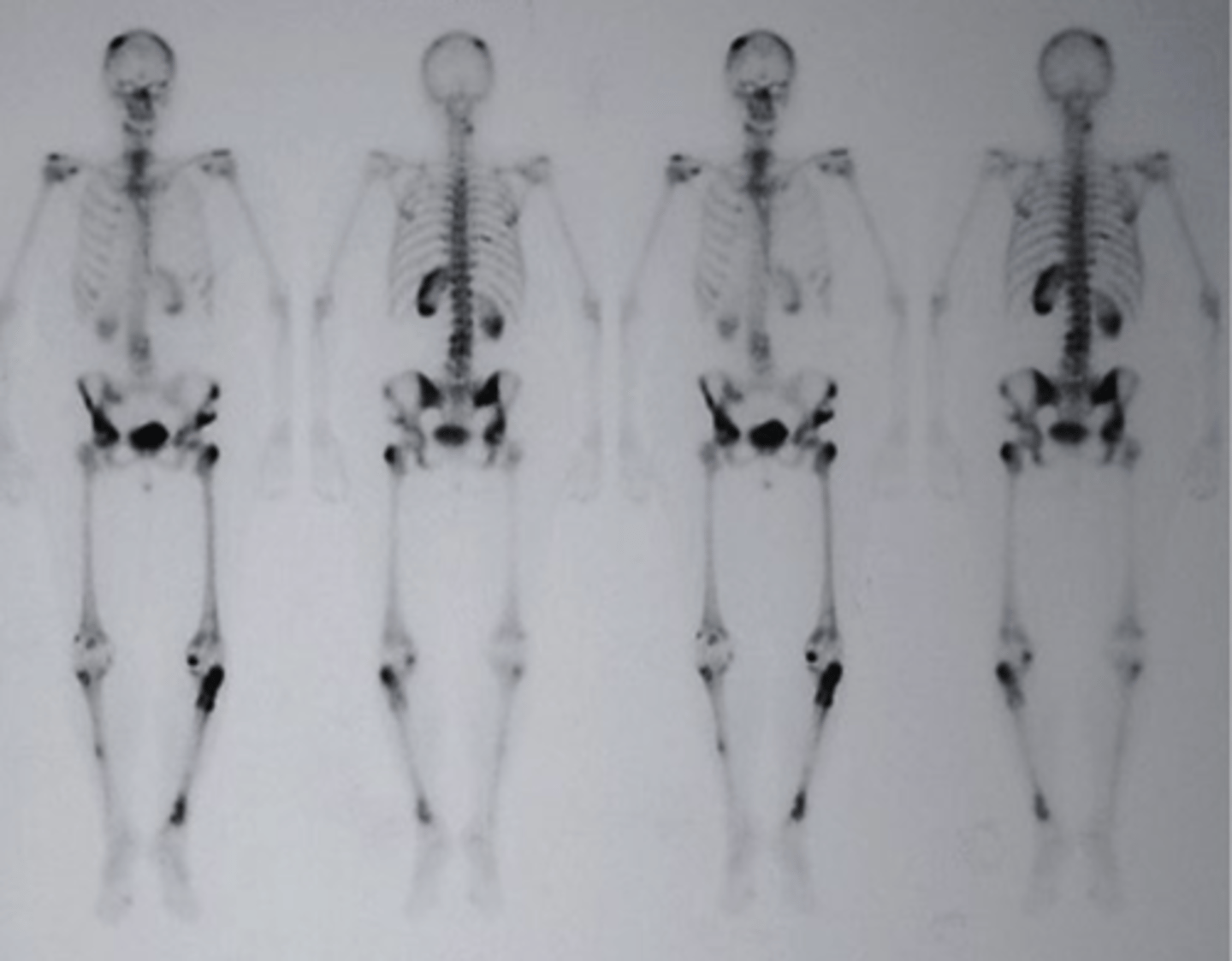
multiple skeletal metastases
which of the following would be the correctly associated image findings?
a. bone fracture
b. epiphyseal plates
c. multiple skeletal metastases
d. Blood Clots
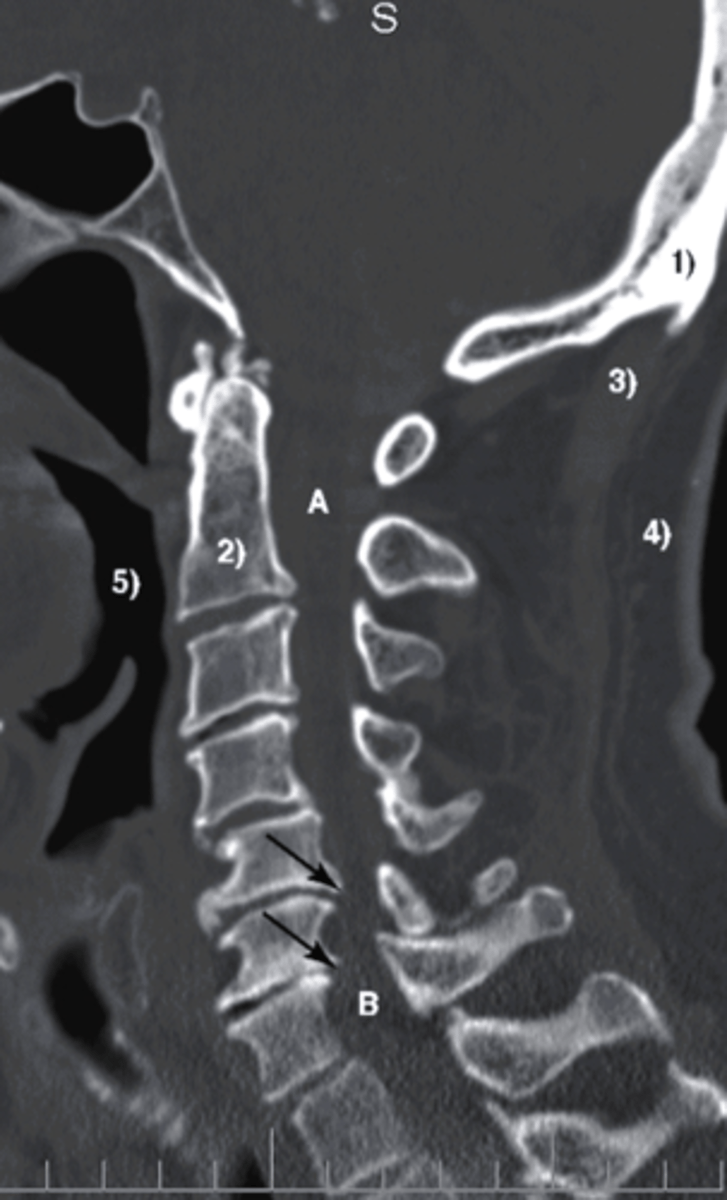
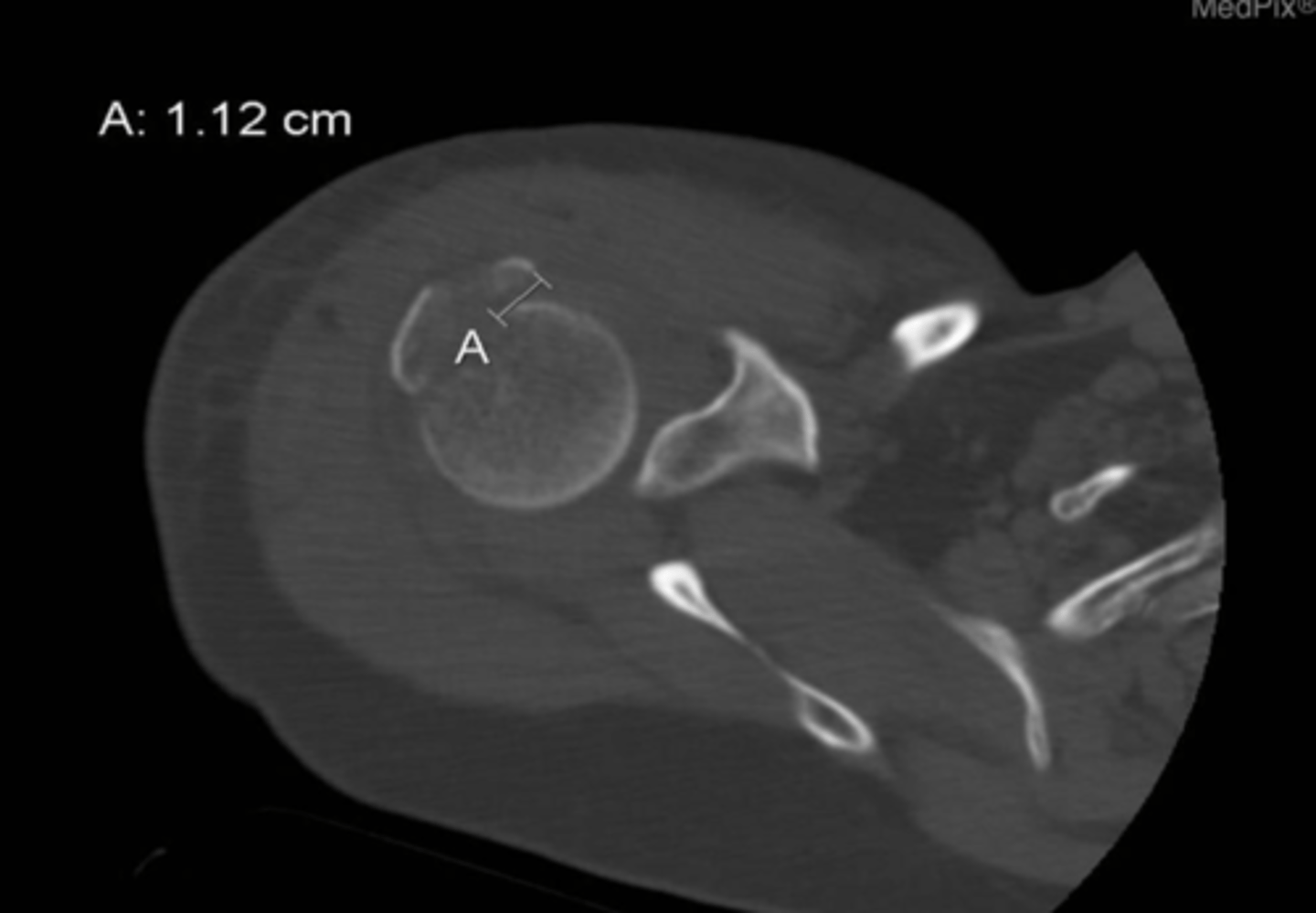
displacement
What is identified by A in this image?
a. edema
b. displacement
c. bruising
d. osteophyte
what are indications for C-Spine Imaging
-trauma
-shoulder or arm pain
-occipital headache
-limitation in motion
-planned or prior surgery
-evaluation of primary and secondary malignancies
-arthritis
-suspected congenital anomalies
-syndromes associated with spinal abnormality
-follow up of known abnormality
-suspected spinal instability
You've been seeing your patient Bill (72, male) for the last 2 months for hip pain. He comes in complaining of new onset of neck after falling on some ice over the weekend. What is your best recommendation as a PT?
a. D/C hip case to start treating the neck
b. Recommend Bill for some cervical radiography due to a high risk factor
c. Give Bill some neck exercises for home, and continue with PT as normal
d. Ignore the neck pain, since you only have a referral for hip pain
Recommend Bill for some cervical radiography due to a high risk factor
You are evaluating Christine (24, female) for recent onset of neck pain following a rear-end MVC where another car hit her at 30mph. During the history she tells you she immediately felt some pain in the neck. When measuring her ROM you notice she is able to rotate to the L 70 deg, but to the R 50 deg. How should you proceed with Christine's exam?
a. terminate the exam and refer to the emergency room
b. refer for conventional radiograph
c. refer for advanced imaging
d. continue exam as normal
continue exam as normal
You are evaluating Cait (23, female) for neck pain. She was performing in a cheer competition over the weekend and fell while performing a stunt. The following day she started to experience some intense neck pain. How should you proceed with the exam?
a. terminate the exam and refer to the emergency room
b. refer for conventional radiograph
c. refer for advanced imaging
d. continue exam as normal
refer for conventional radiograph
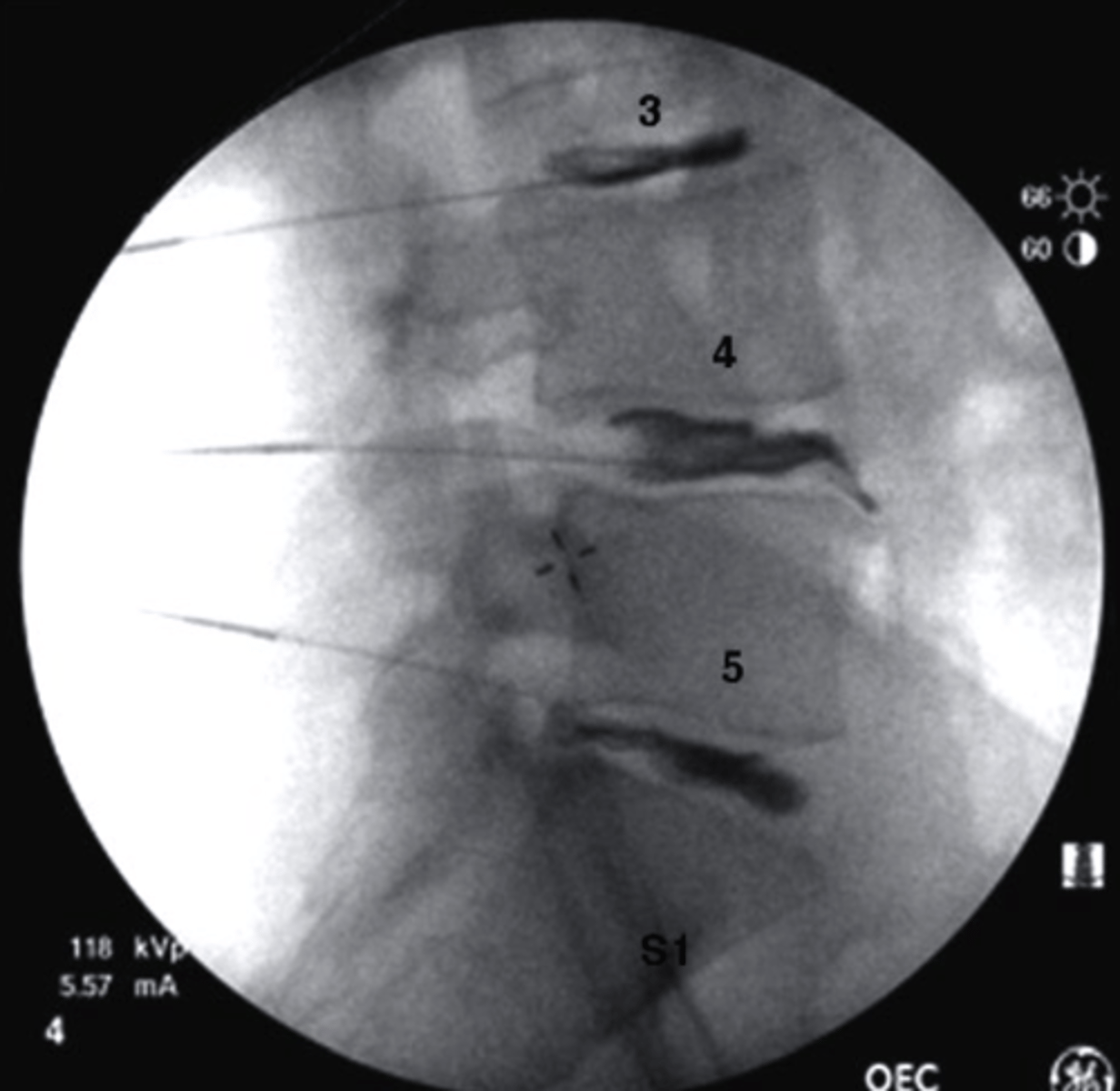
what are the standard projections of the C-spine
-AP lower C-Spine
-lateral
what are the additional projections you can obtain for the C-spine
-AP open mouth
-R and L oblique
what can be seen in an AP lower C-Spine radiograph?
-vertebral bodies of C3-T1
-Spinous processes at some levels
-large transverse process of T1
-First Ribs and costotransverse joints
-clavicles
-air-filled trachea
True or False: You can see the uncinate process in an AP Lower C-Spine Radiograph?
True
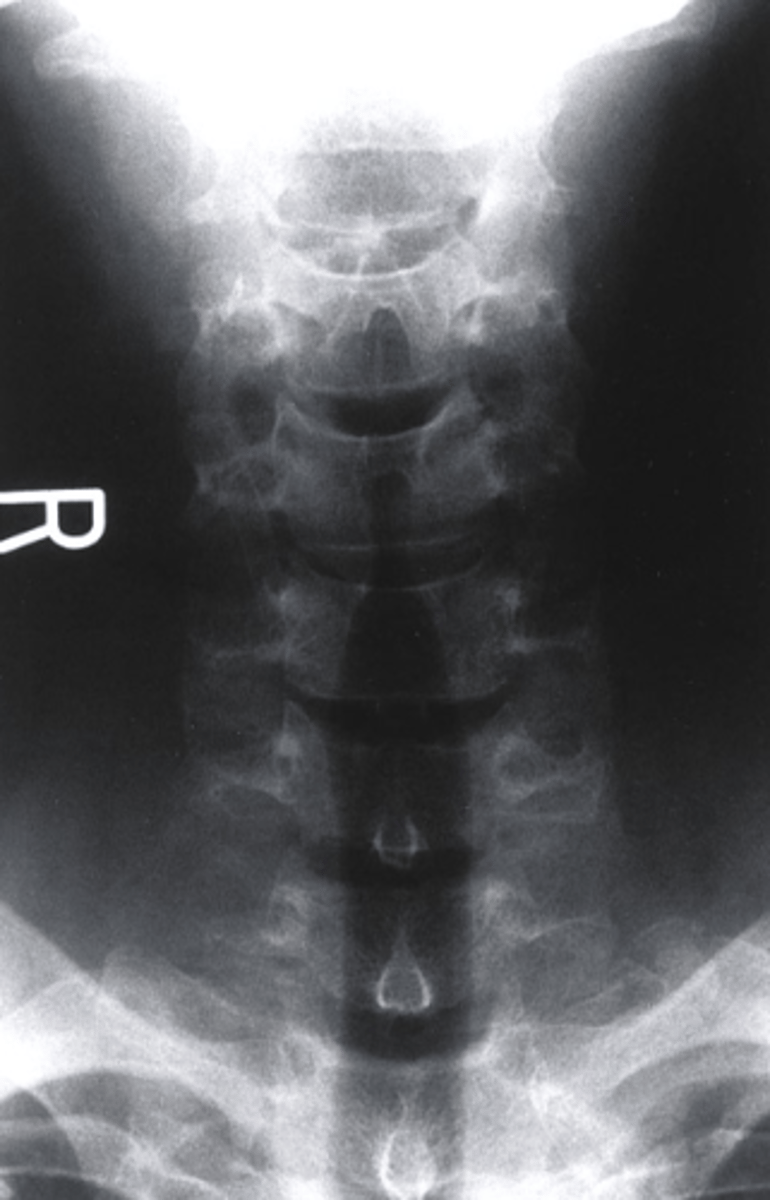
AP Lower C Spine
what view is this?
a. AP Lower C Spine
b. AP Lumbar Spine
c. R oblique
d. L Lateral
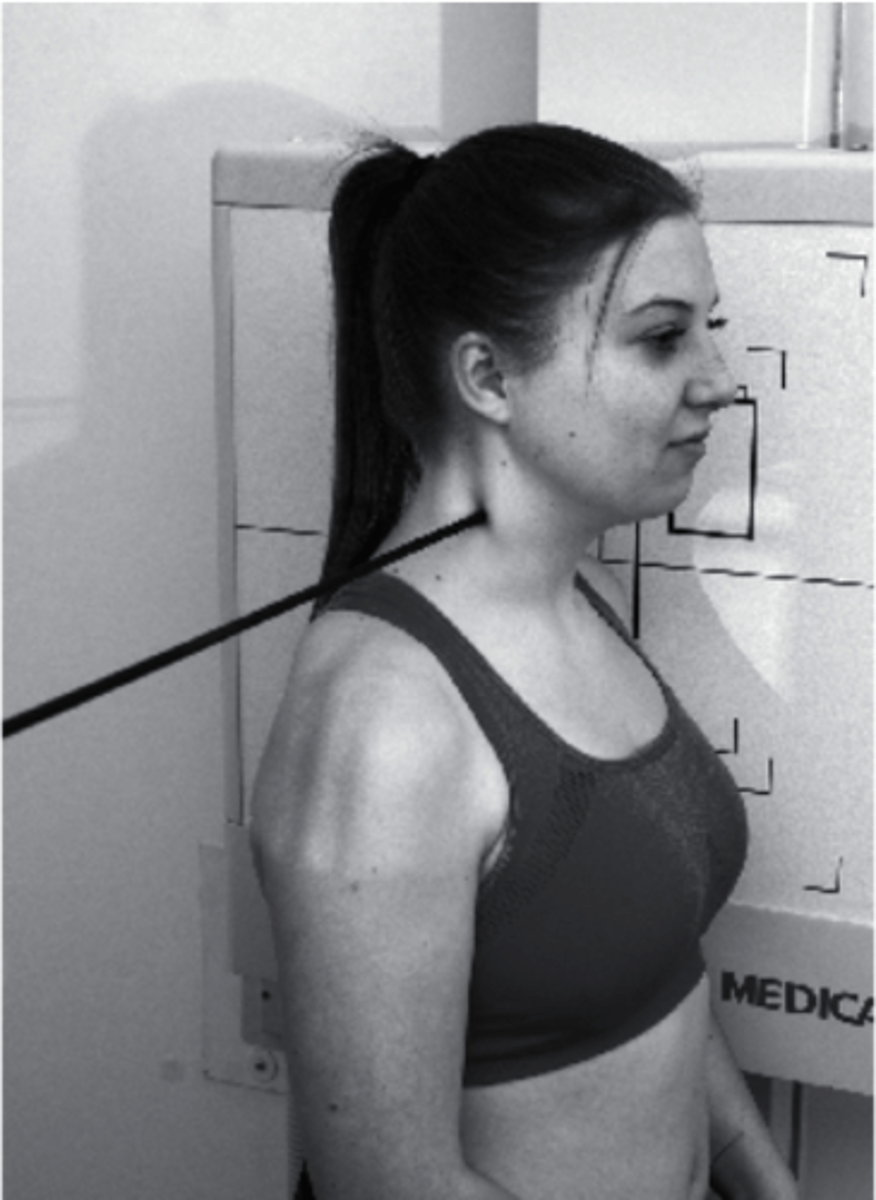
Lateral
What view is being captured on this patient?
a. AP Lower C Spine
b. Oblique
c. Lateral
d. PA Lower C Spine
what can be identified on a lateral view of the C spine?
-arches of C1
-Dens
-vertebral bodies of C2-C7
-articular pillars and lamina
-IVD spaces from C2-C3 through C6-C7
-spinous processes
-transverse processes
-facet joint surfaces
Posterior Arch of C1
What structure is circled in blue?
a. Dens
b. Spinous Process of C2
c. Spinous Process of C3
d. Posterior Arch of C1
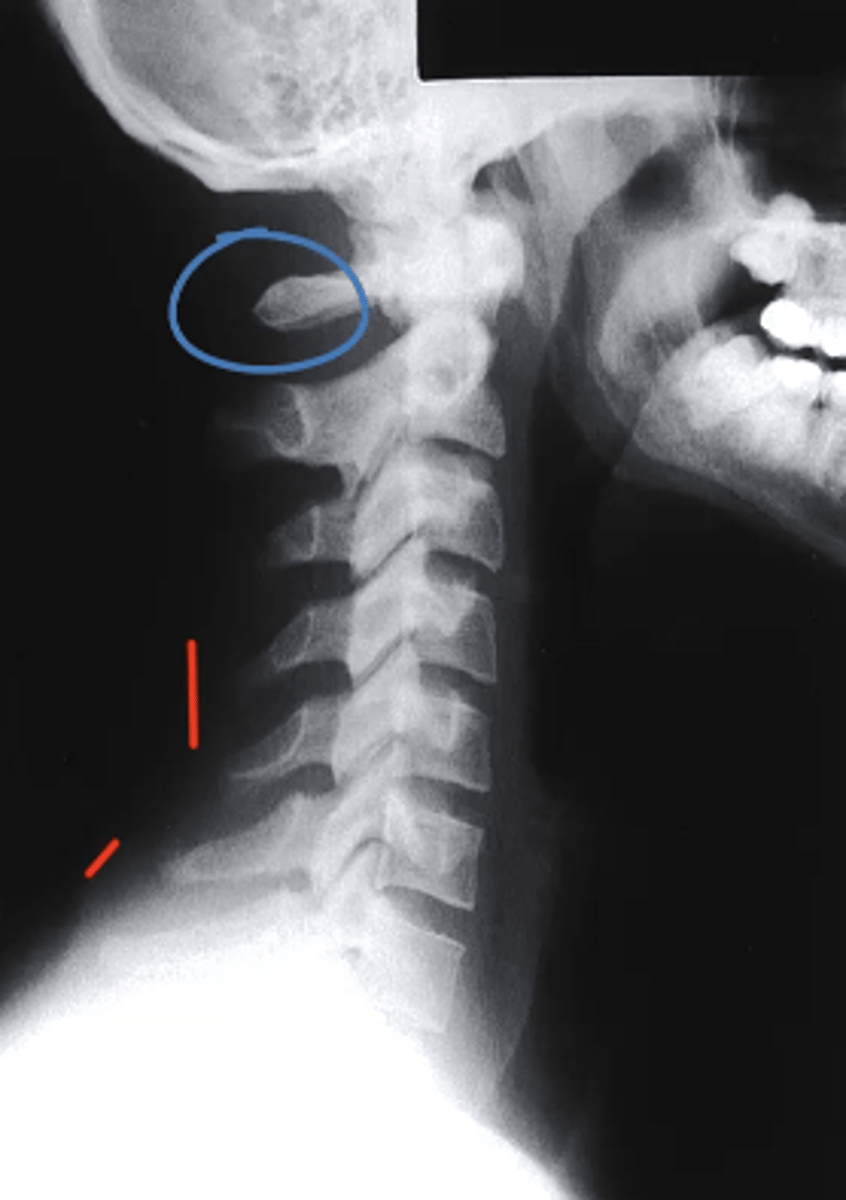
D
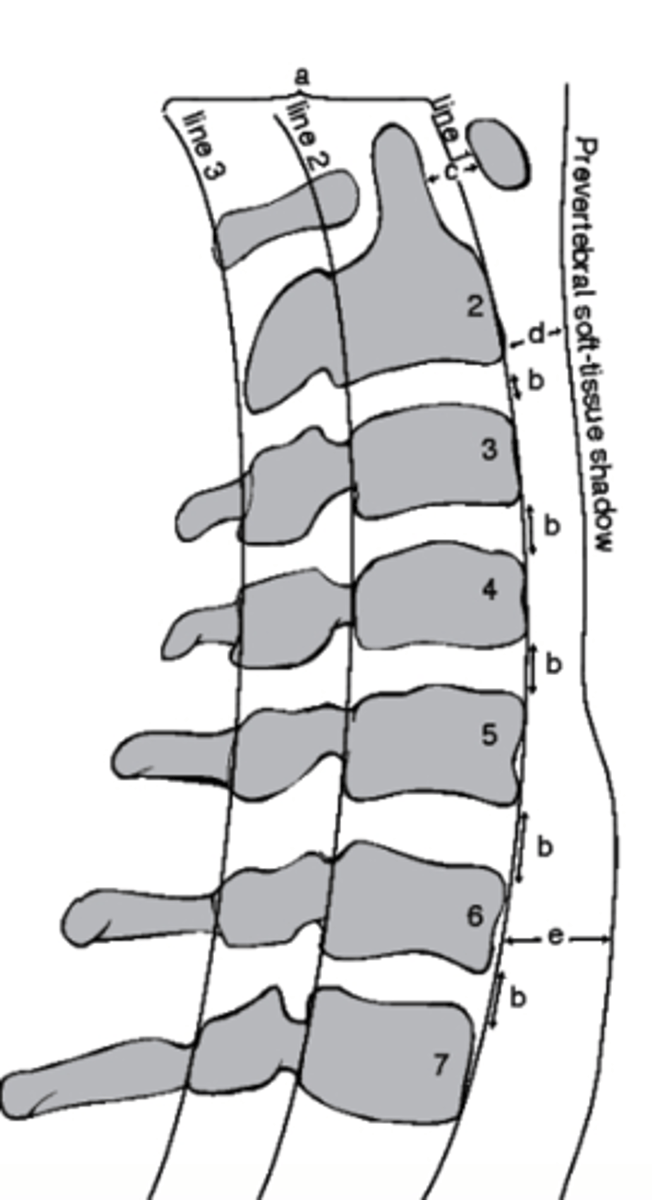
which structure corresponds with the retropharyngeal space?
a. Line 1
b. D
c. Line 3
d. E
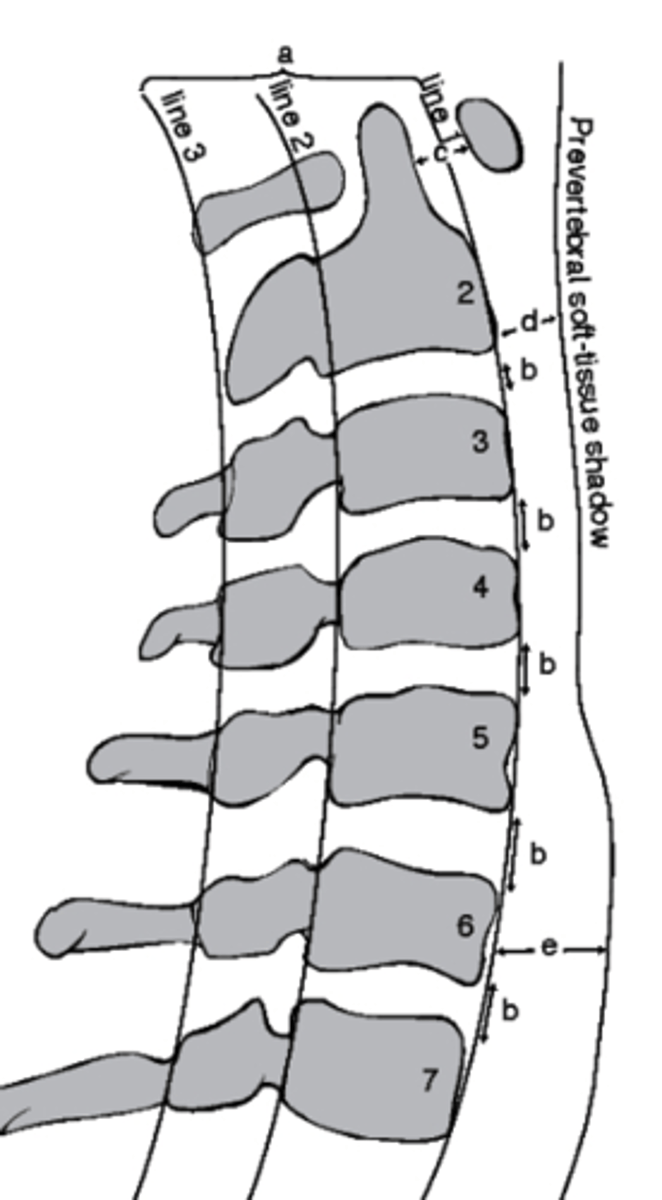
E
which structure corresponds with the retrotracheal space?
a. Line 1
b. D
c. Line 3
d. E
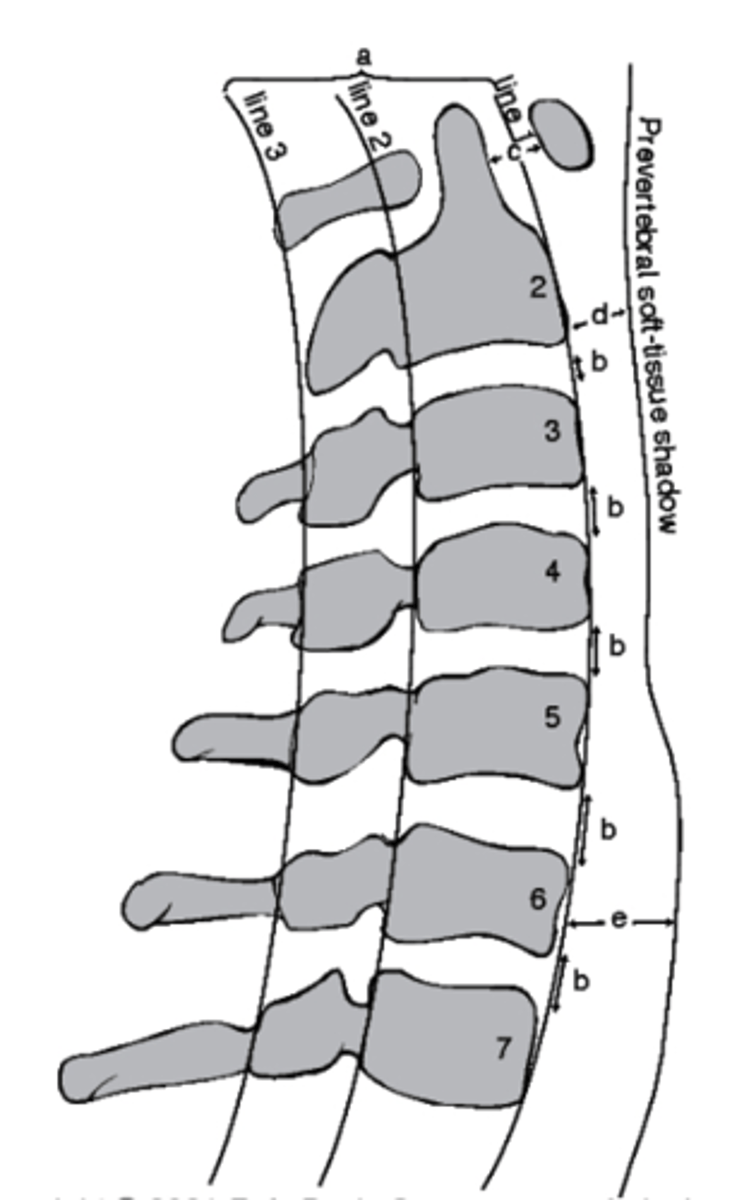
Between Line 2 and Line 3
Where would the spinal cord run in this image?
a. Between line 1 and Line 2
b. Between Line 3 and Line 1
c. Between Line 1 and the soft tissue
d. Between Line 2 and Line 3
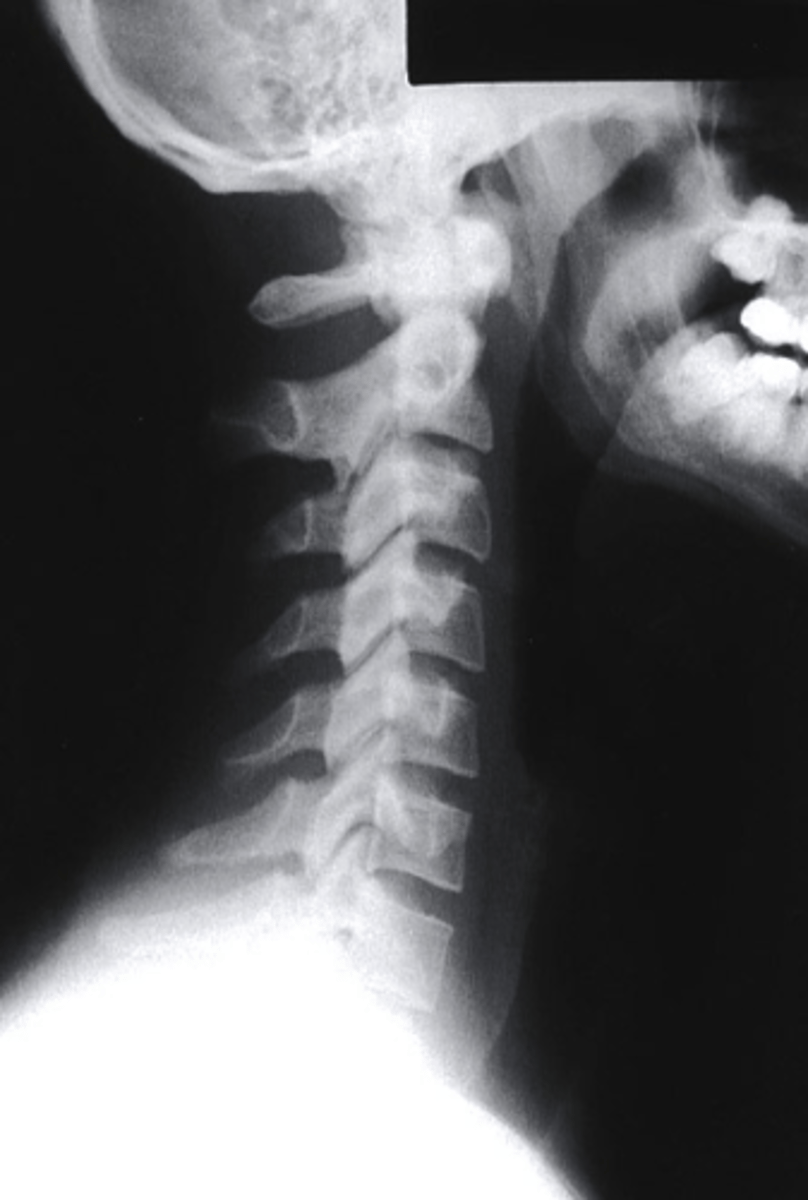
Lateral
which view is this?
a. Lateral
b. Oblique
c. PA
d. AP
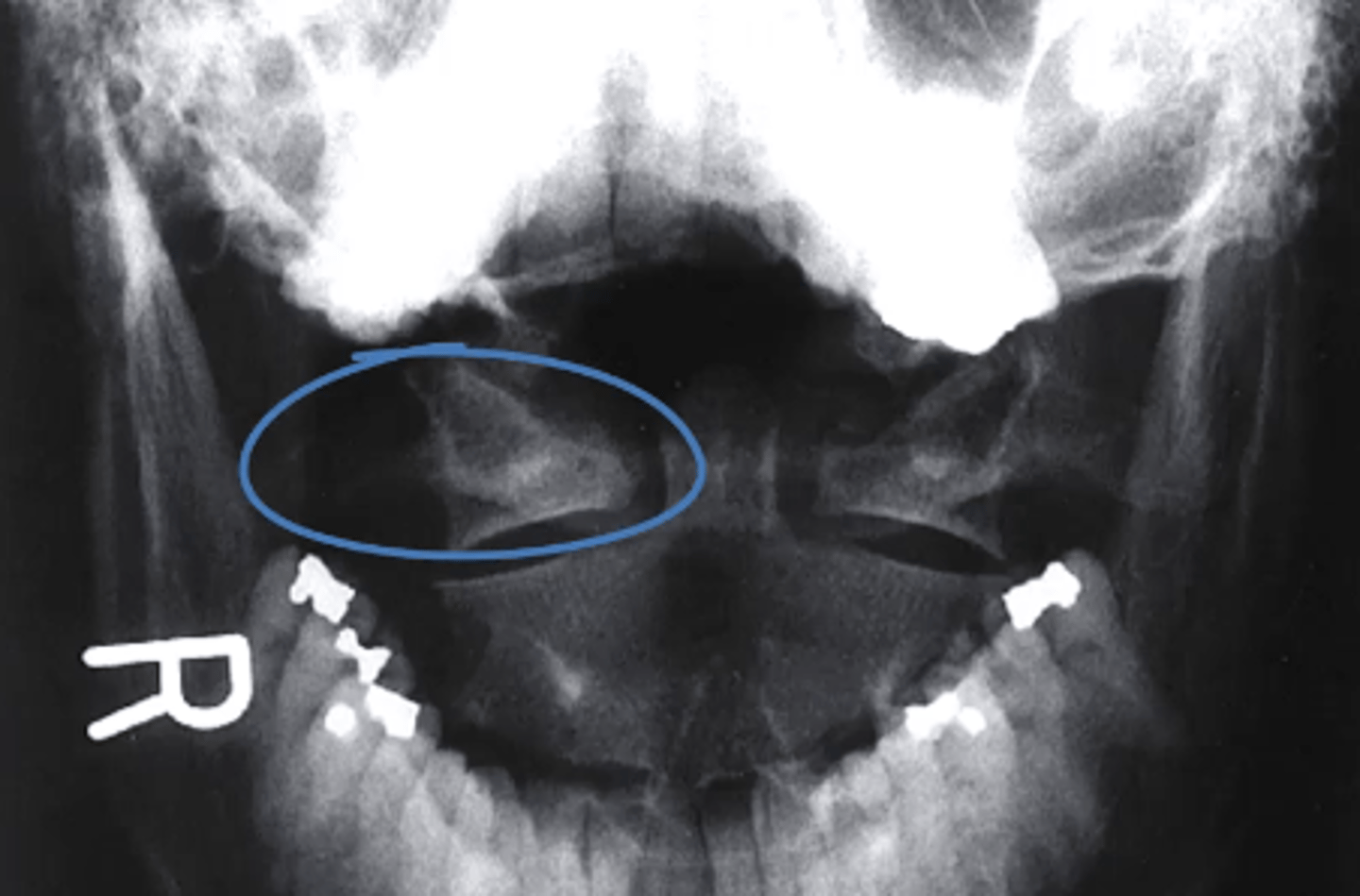
what can you see in an odontoid view?
-base of occiput
-angle of the mandible
-dens and body of C2
-anterior arch of the atlas
-posterior arch of the atlas
-lateral atlantoaxial facet joints
-bodies and spinous processes of C2-T1
Lateral mass of the atlas
what structure is circled in blue?
a. Dens
b. Lateral mass of the atlas
c. Body of C2
d. condylar process
oblique
What view is being captured here?
a. lateral
b. Odontoid
c. oblique
d. AP

what can be viewed in an oblique view of the c-spine
-vertebral bodies
-pedicle, lamina, and spinous processes
-inferior and superior articulating processes of the facet joints
-intervertebral foramina
-contralateral pedicle
-angle of the mandible
-thoracic ribs
oblique
what view is this?
a. lateral
b. odontoid
c. AP
d. oblique
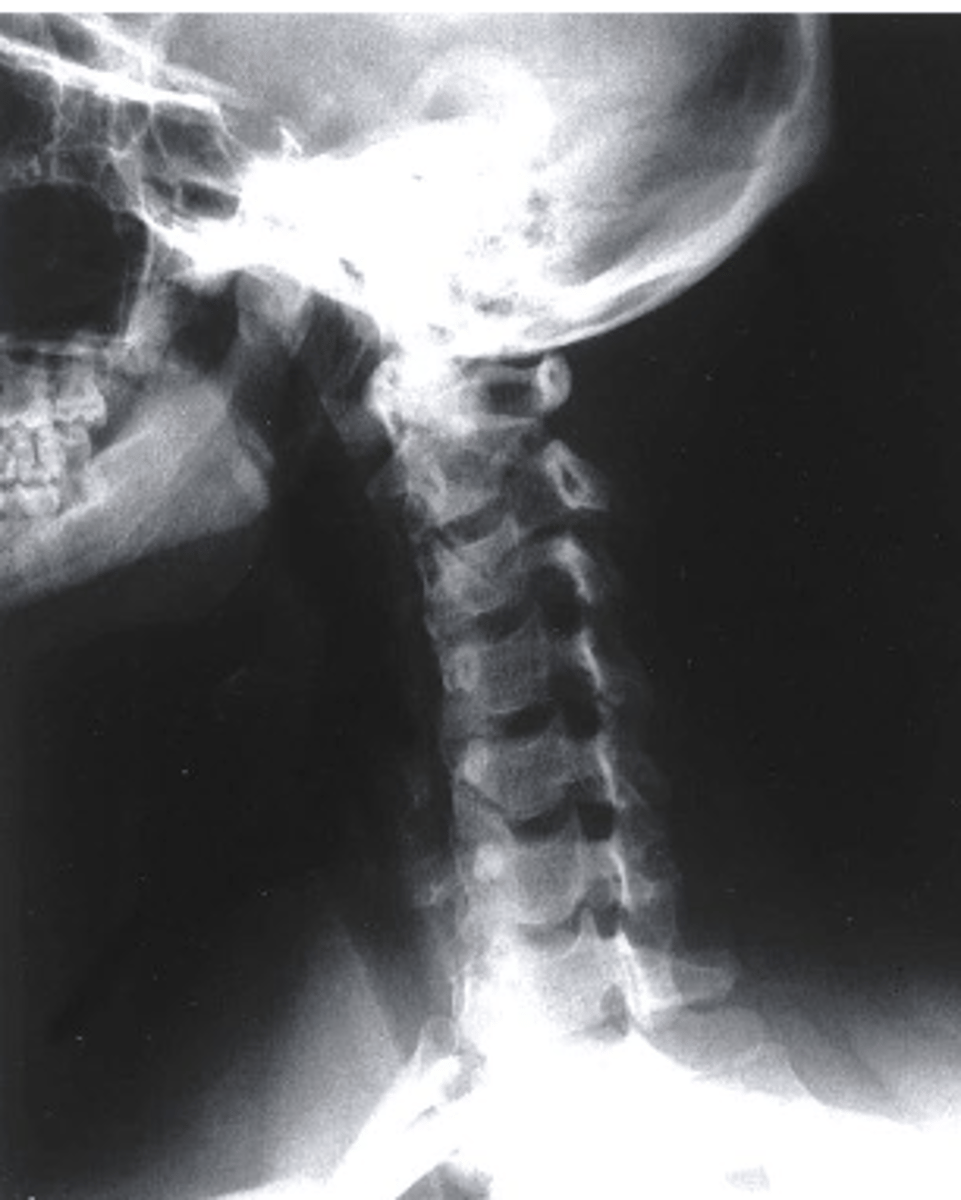
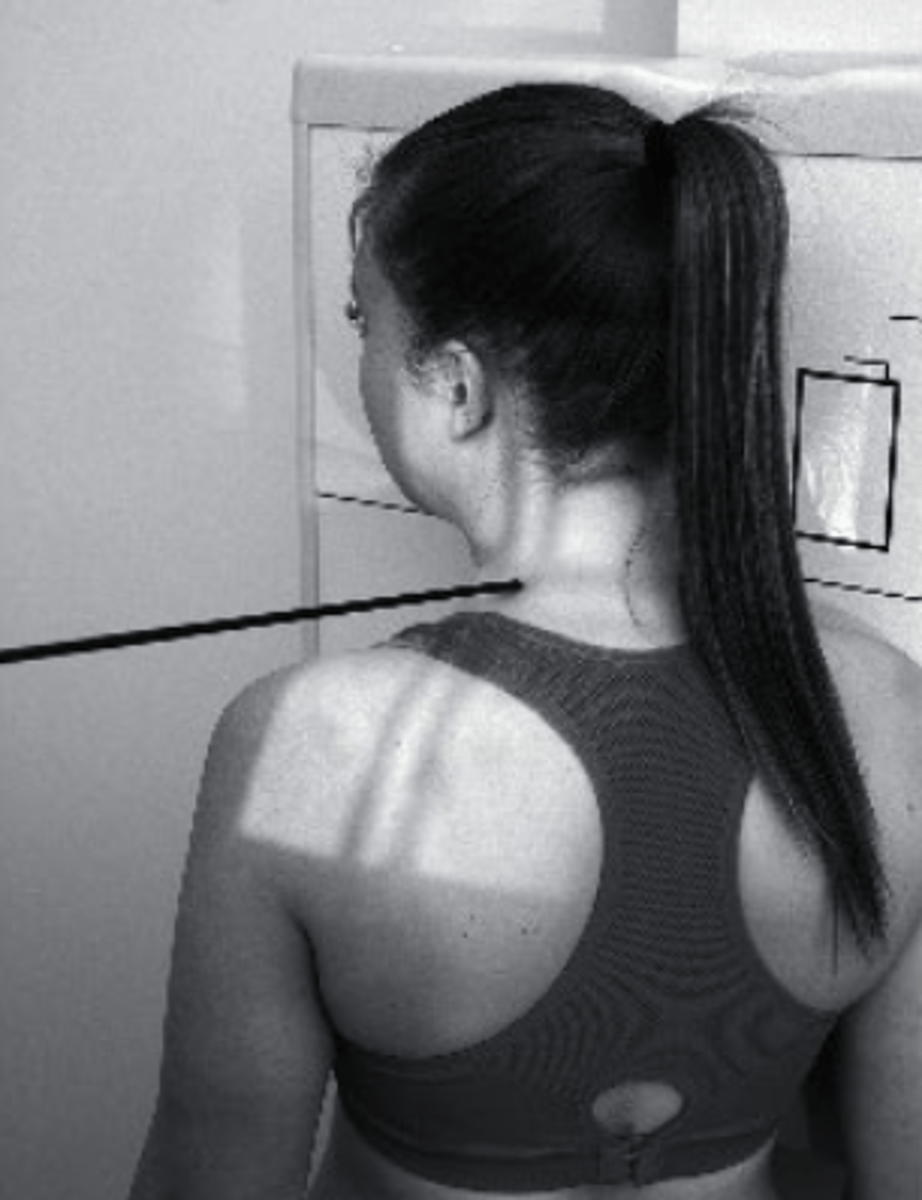
extension stress
what view is this?
a. extension stress
b. flexion stress
c. lateral
d. oblique
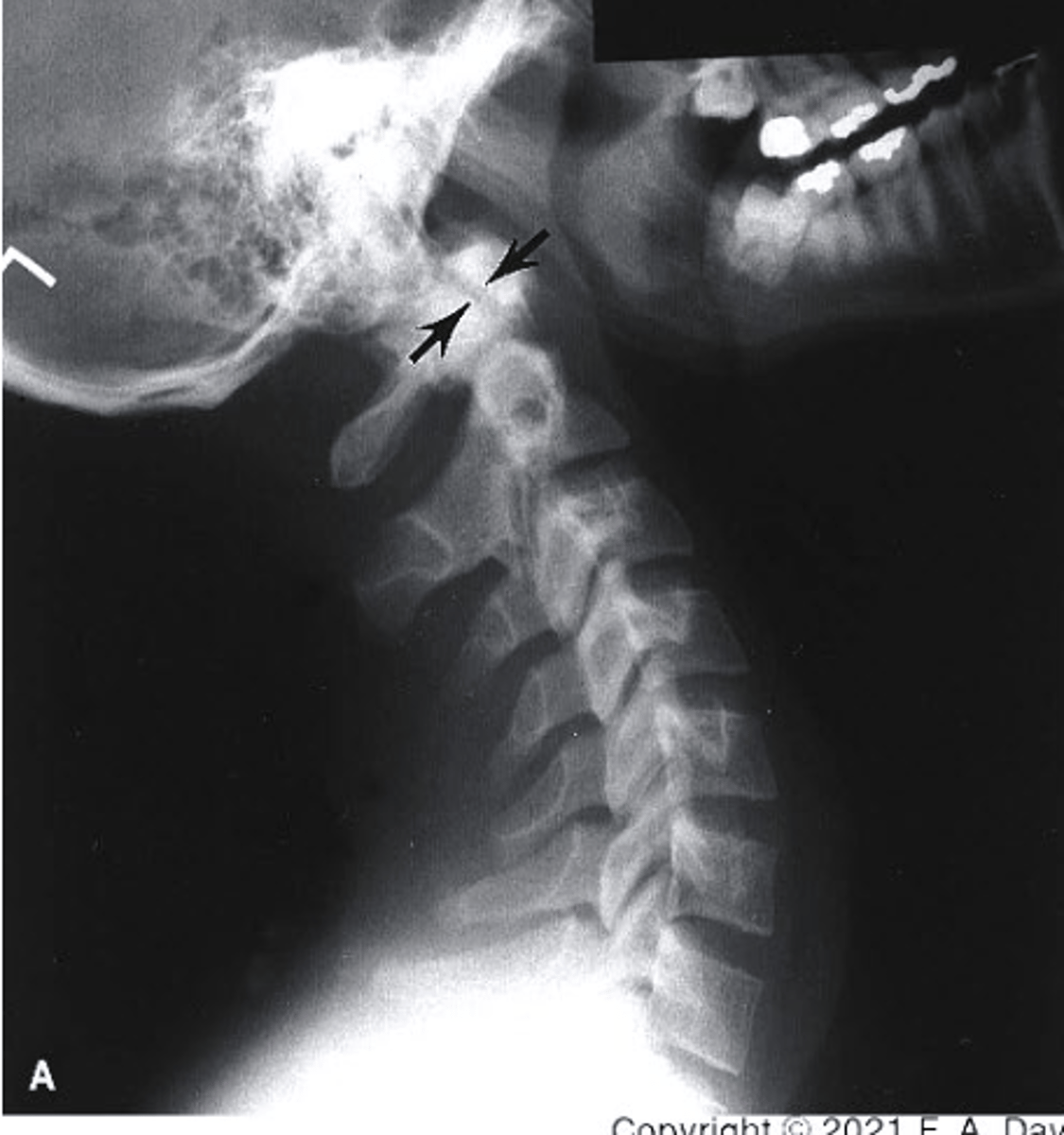
flexion stress
what view is this?
a. extension stress
b. flexion stress
c. lateral
d. oblique