Pulmonary function and medical diagnostics
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Medical diagnostics
-chest x-ray
-MRI
-CT scan
-V/Q scans (ventilation/perfusion)
-Bronchoscopy
-PFT and ABGs
-Oximetry
Pulmonary function testing provides info about
-integrity of airways
-function of respiratory musculature
-condition of lung tissues
Most common pulmonary function tests
-spirometry
-diffusing capacity of the lung for CO (DLCO)
-helium lung volumes
spriometry
-max inhalation followed by max exhalation
-measures volume of air and time
-data obtained: FVC, FEV1, FEV1/FVC,VC
Diffusing capacity of the lung for CO
-inhalation of fixed concentration of CO and helium, breath holding for 10 sec, then expiration with measurement of end-tidal CO and helium
-data obtained: uptake and diffusing capacity of CO
Helium lung volumes
-Maximal expiration, then inhalation of a known concentration of helium until steady state is reached
-data obtained: RV, ERV, IRV, TV with calculation of TLC, VC, FRC, IC
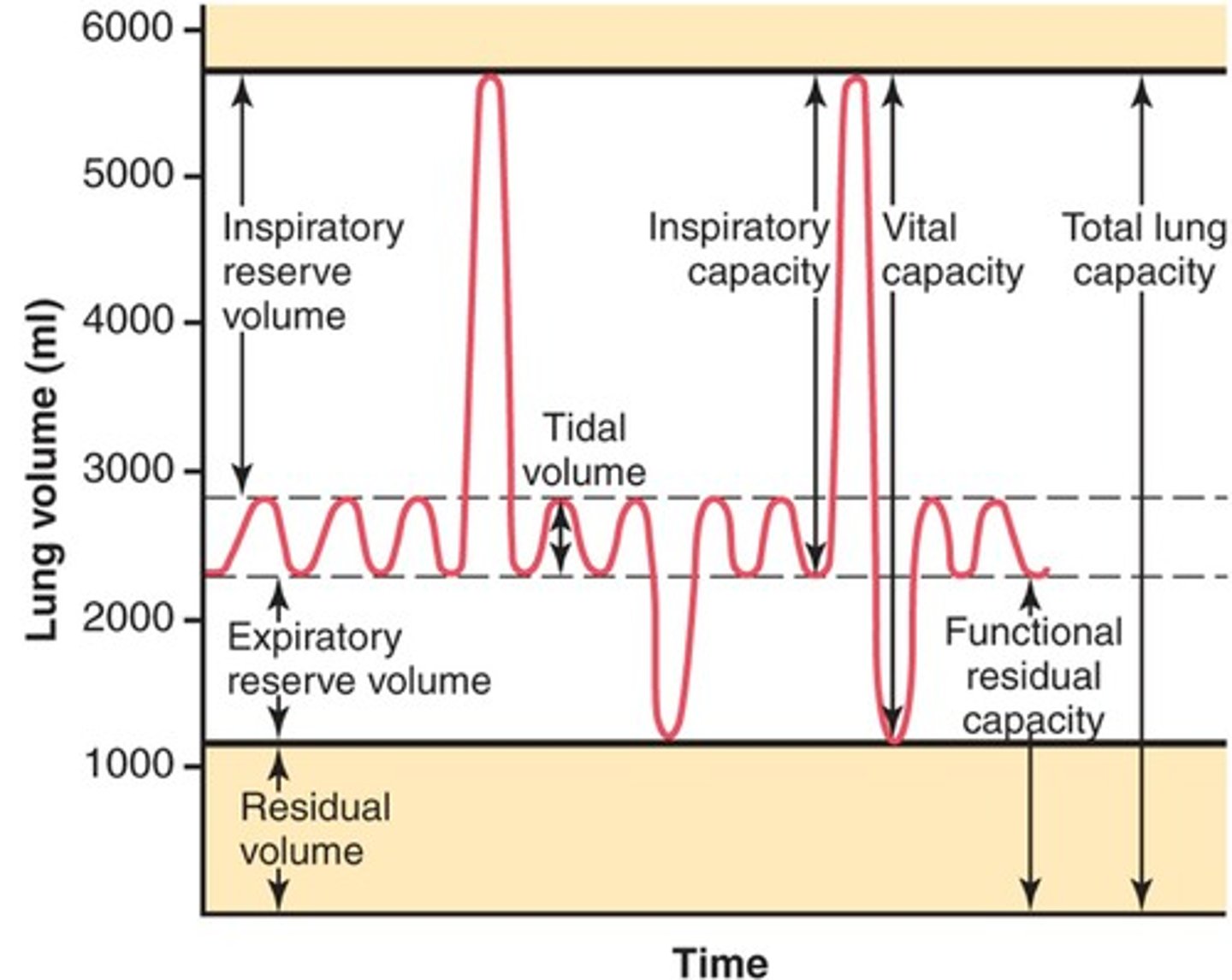
Lung volumes and capacities
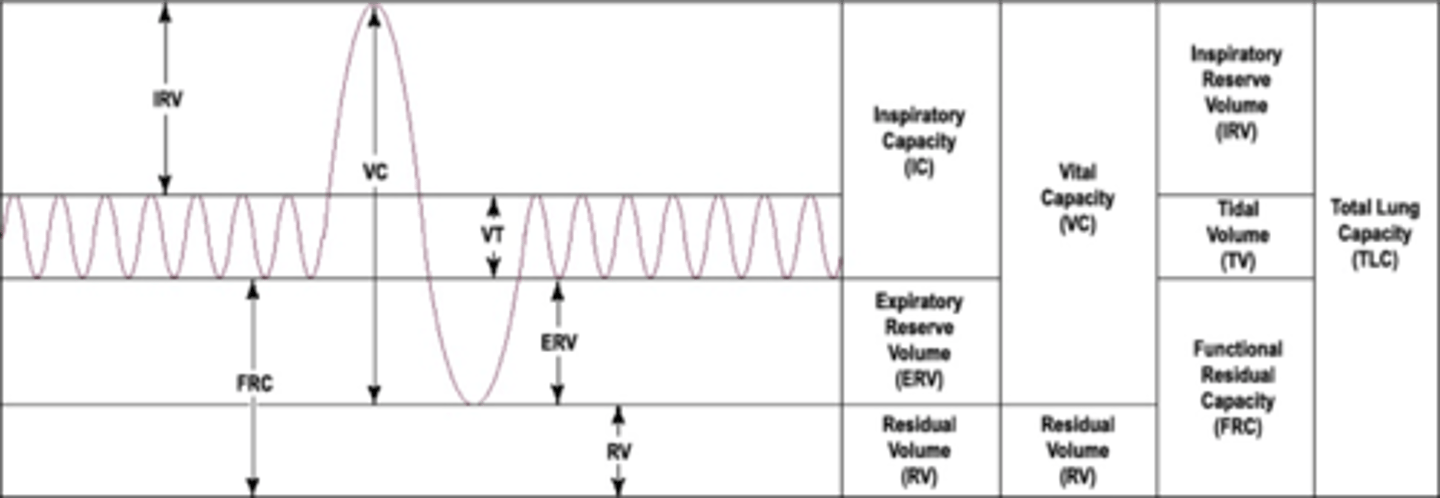
Inspiratory Reserve Volume (IRV)
-amount of air that can be forcefully inhaled after a normal tidal volume inspiration
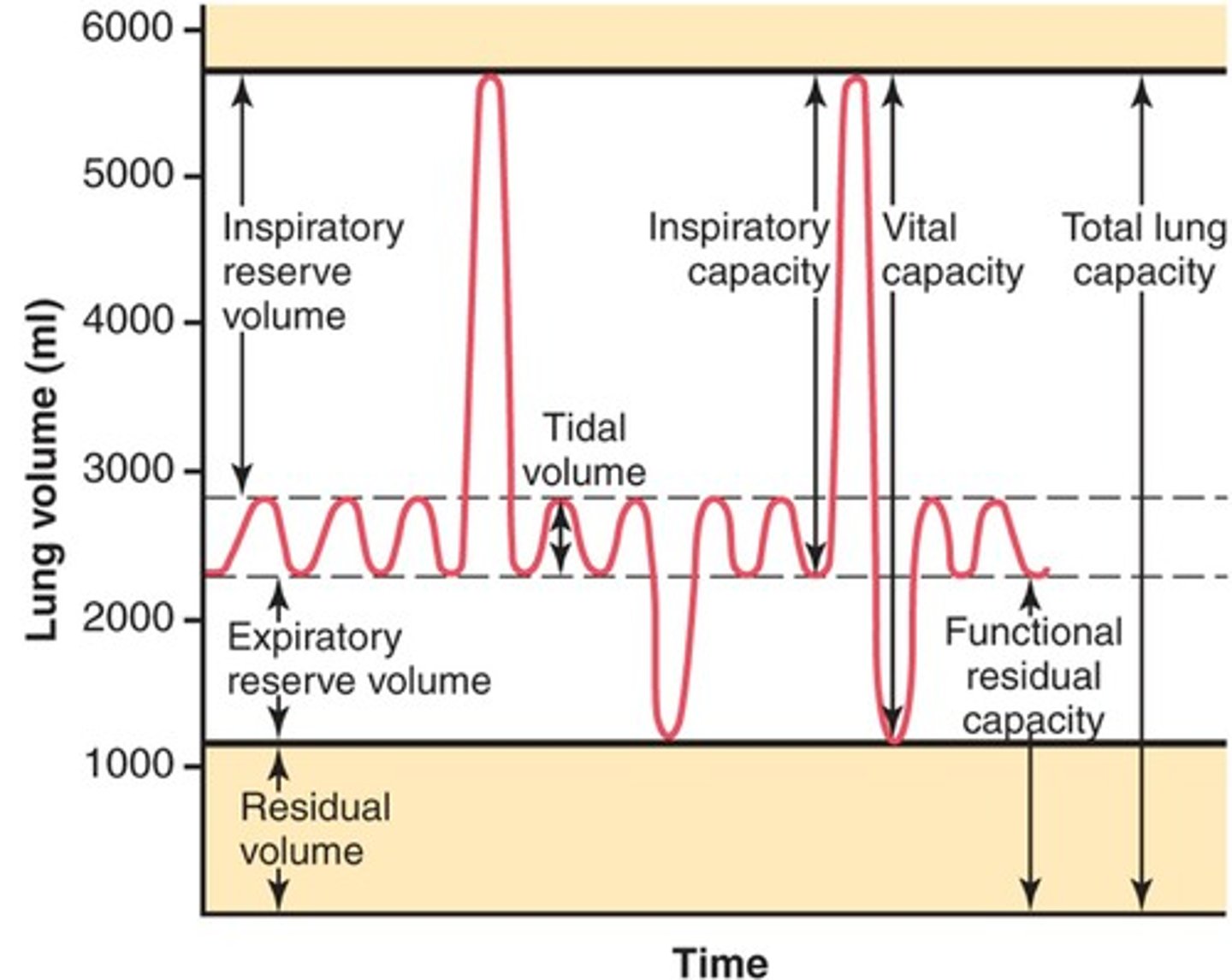
Functional Residual Capacity (FRC)
-volume of air remaining in the lungs after a normal tidal volume expiration
-ERV+RV
Vital capacity
-The total volume of air that can be exhaled after maximal inhalation.
-ERV+IC
Tidal volume
-Amount of air that moves in and out of the lungs during a normal breath
-~500 mL
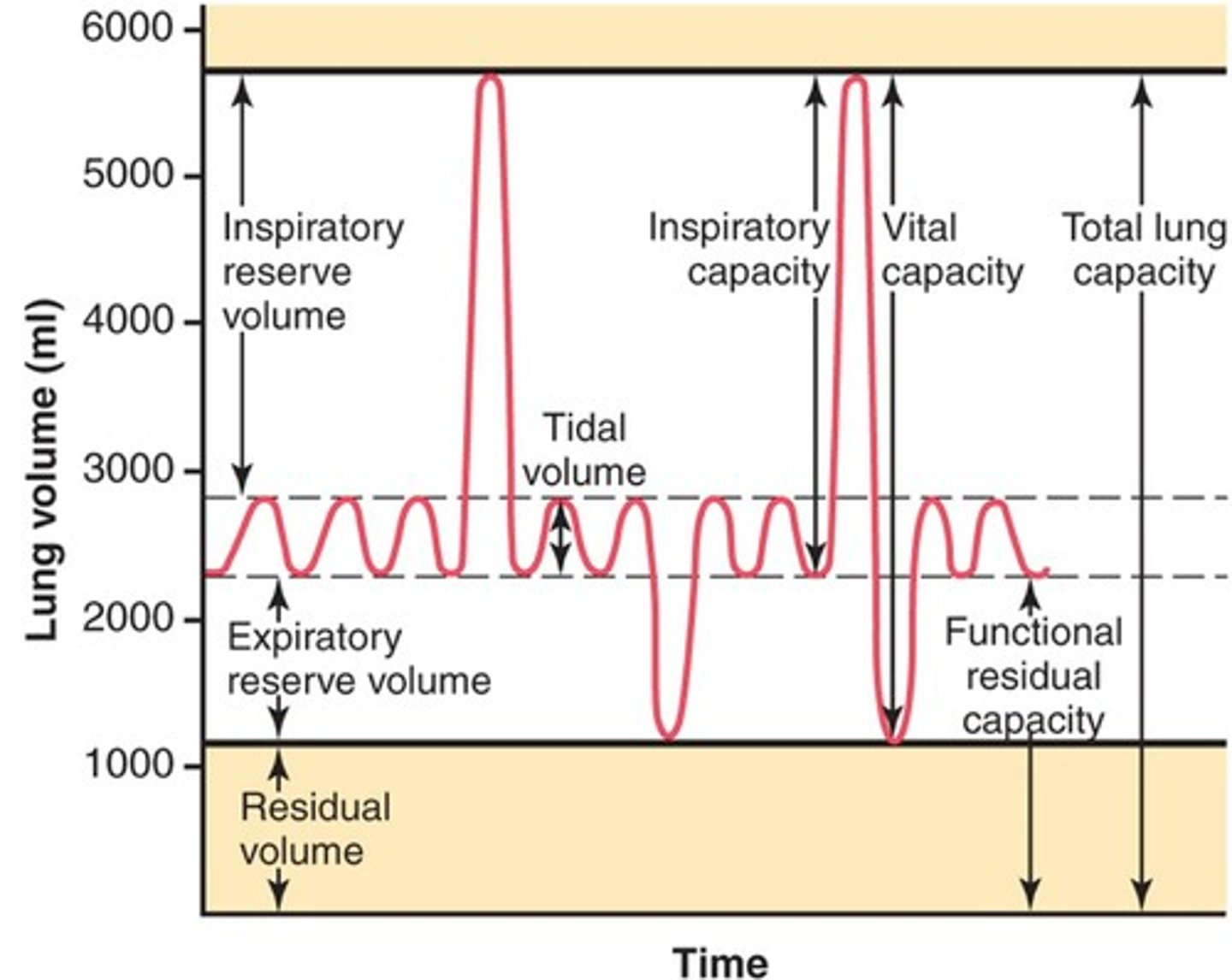
Expiratory reserve volume
-Amount of air that can be forcefully exhaled after a normal tidal volume exhalation
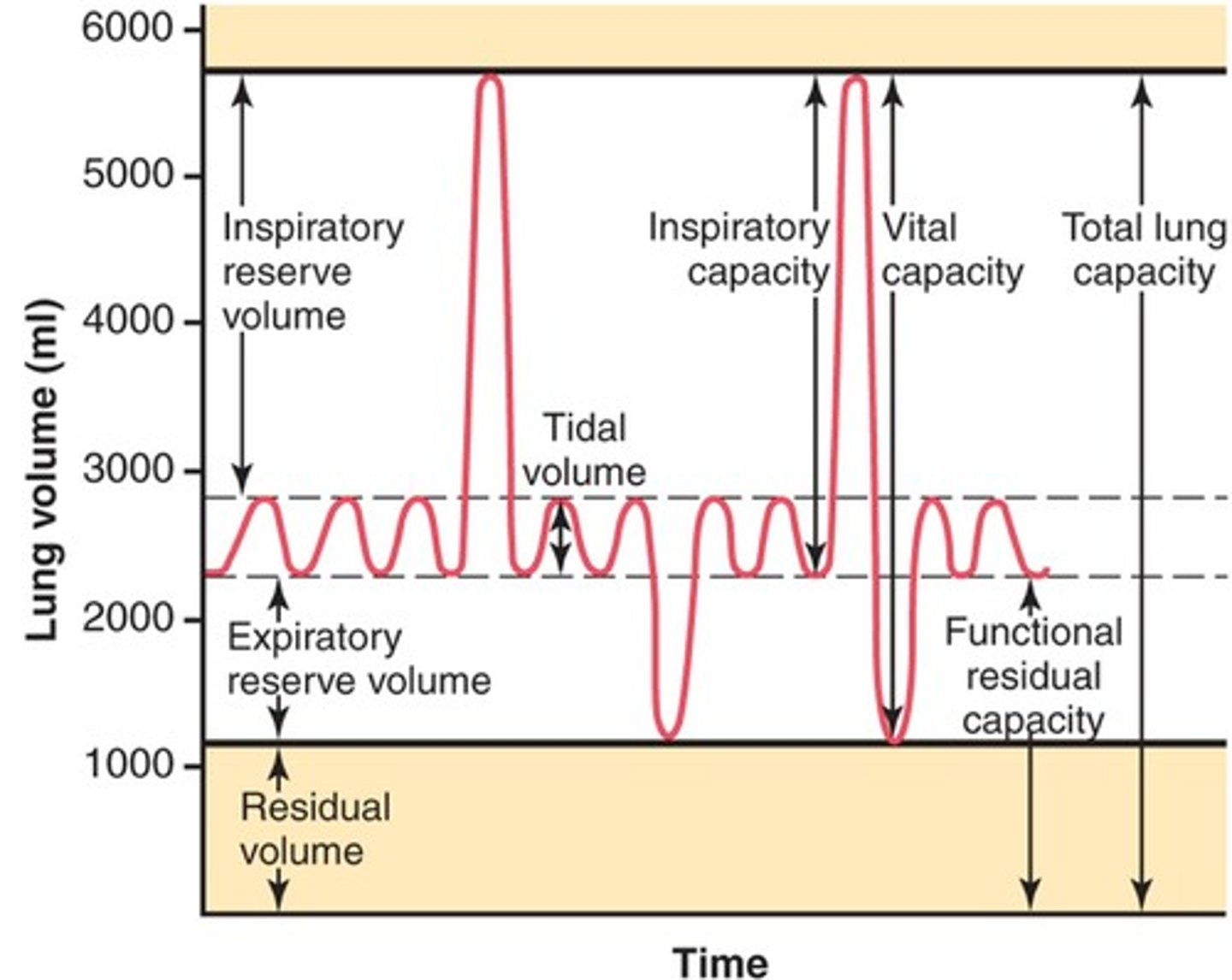
Residual volume
-Amount of air remaining in the lungs after a forced exhalation
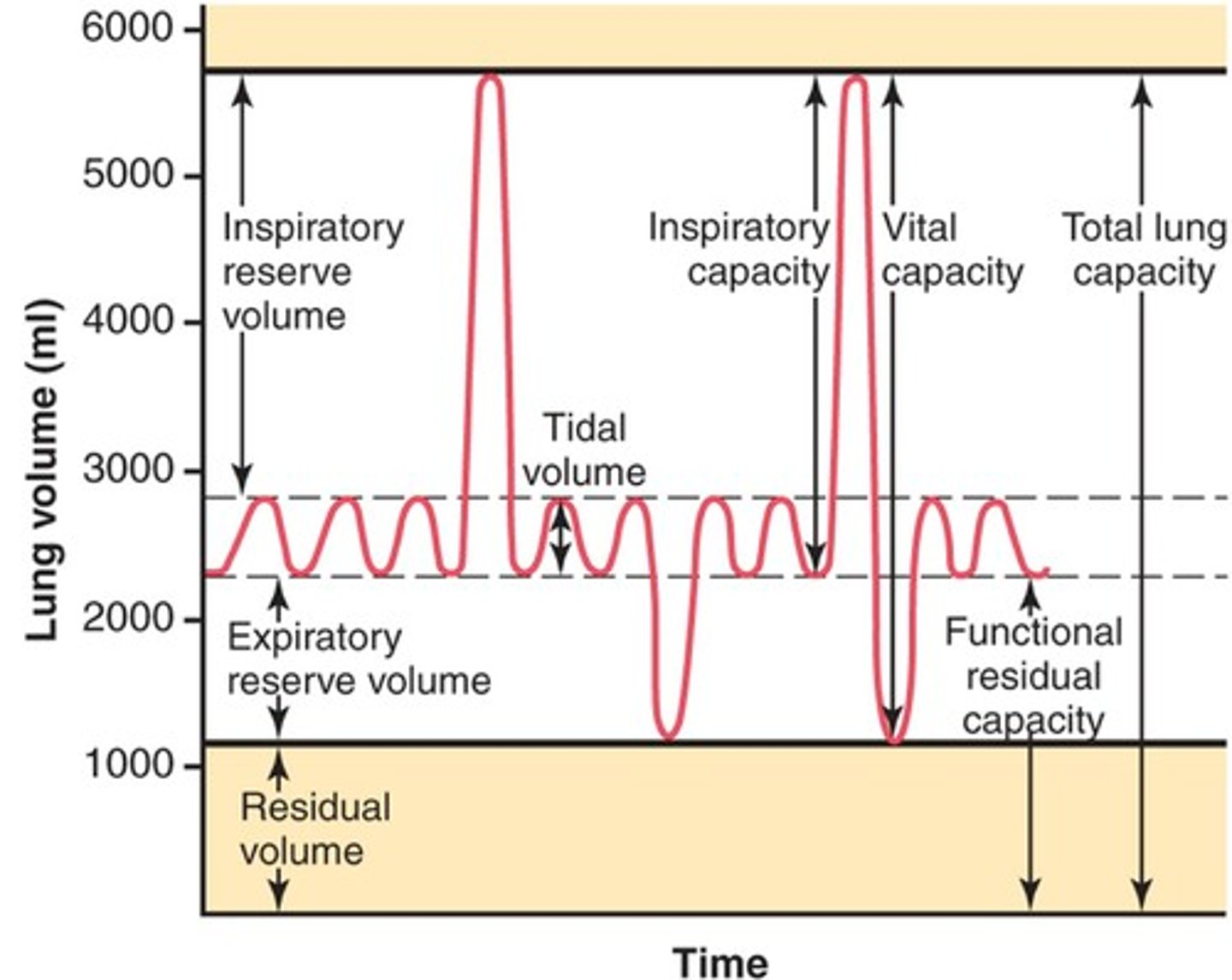
Total lung capacity
-vital capacity + residual volume
Normal IRV
-1.9-2.5 L
Normal TV
-0.4-0.5L
Normal ERV
-1.1-1.5L
Normal RV
-1.5-1.9L
Normal TLC
4.9-6.4L
Normal IC
-2.3-3.0L
Normal FRC
-2.6-3.4L
Normal VC
-3.4-4.5L
Spirogram
-graphic tracing related to lung function
-performed using spirometers
-often conducted at bedside using simple equipment
Body Plethysmography (Body Box)
-Measures gas volume within the lungs indirectly by using a modification of Boyle's law
-pt sits in airtight chamber
-determines how much air is in lungs after taking a deep breath
-also measure air left in lungs after max exhale
Test of gas flow rates (PFT)
-measure of airflow rates during forced breathing maneuvers
PFT provide info on
-lung function
-degree of impairment
-general location of problem
Forced Vital Capacity (FVC)
-max volume of gas exhaled as forcefully and quicklyb as possible
Normal FVC is
- ~4L
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1)
-volume of air exhaled during first second of the FVC
FEV1 reflects airflow in _______ airways.
-large
Peak expiratory flow (PEF)
-max flow that occurs at any point in time during FVC
Normal PEF
-9-10 L/sec
DLCO assess what?
-lungs ability to transfer gas from inspired air to the blood stream
What does DLCO measure?
-uptake of CO per unit time per mm of driving pressure of CO
DLCO is used to evaluate _________ and _________ lung disease
-parenchymal
-non-parenchymal
Abnormal values of DLCO are attributed to what 3 factors
-decreased qty of hemoglobin per unit vol of blood
-increased thickness of the alveolar-capillary membrane
-decreased functional surface area avail for diffusion*** main reason
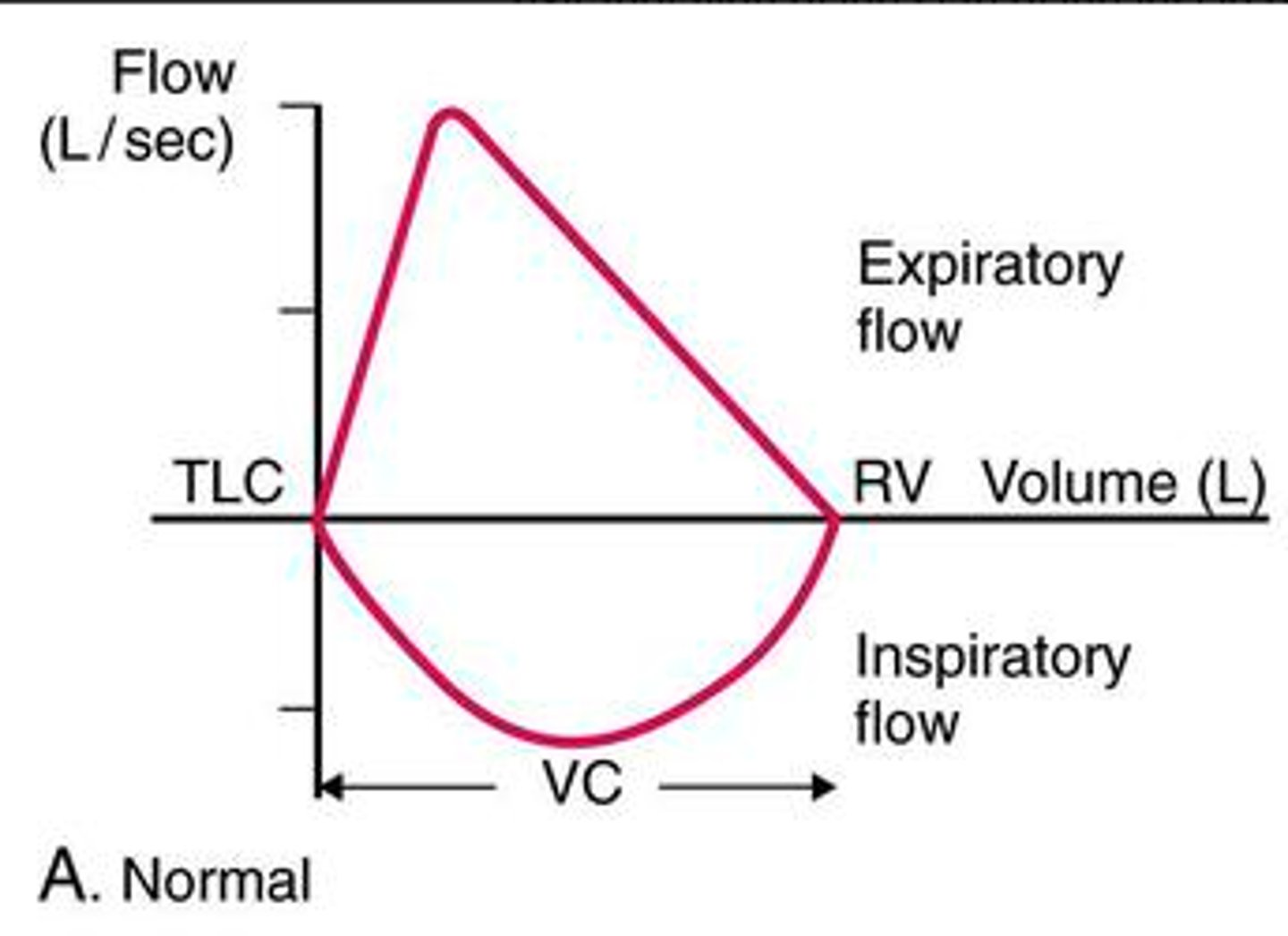
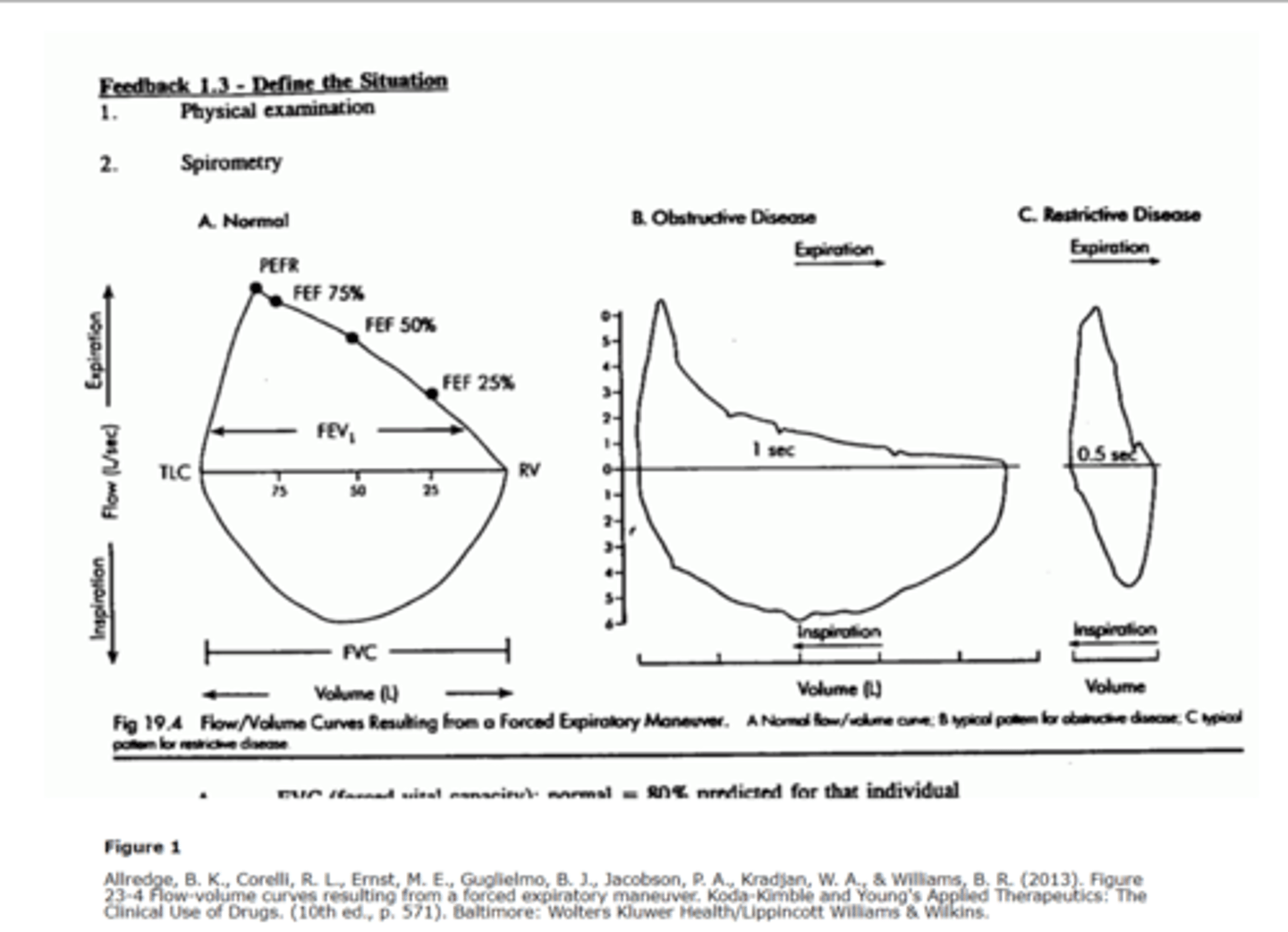
Flow volume loop
-Graphic presentation of FVC maneuver followed by forced inspiratory volume (FIV) maneuver
Normal flow volume loop
-Upsidedown ice cream cone
Flow volume loop of obstructive lung disease
-graph B
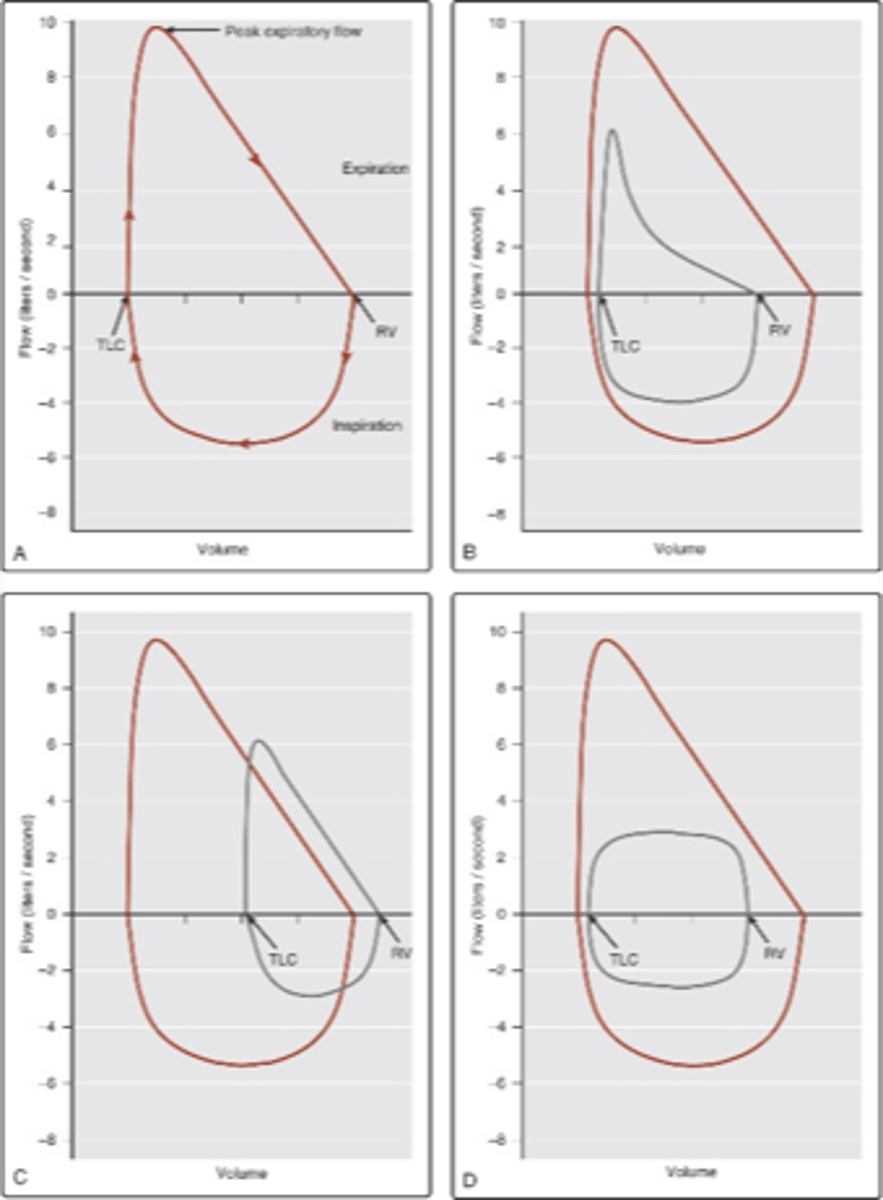
Flow volume loop of restrictive lung disease
-Graph C
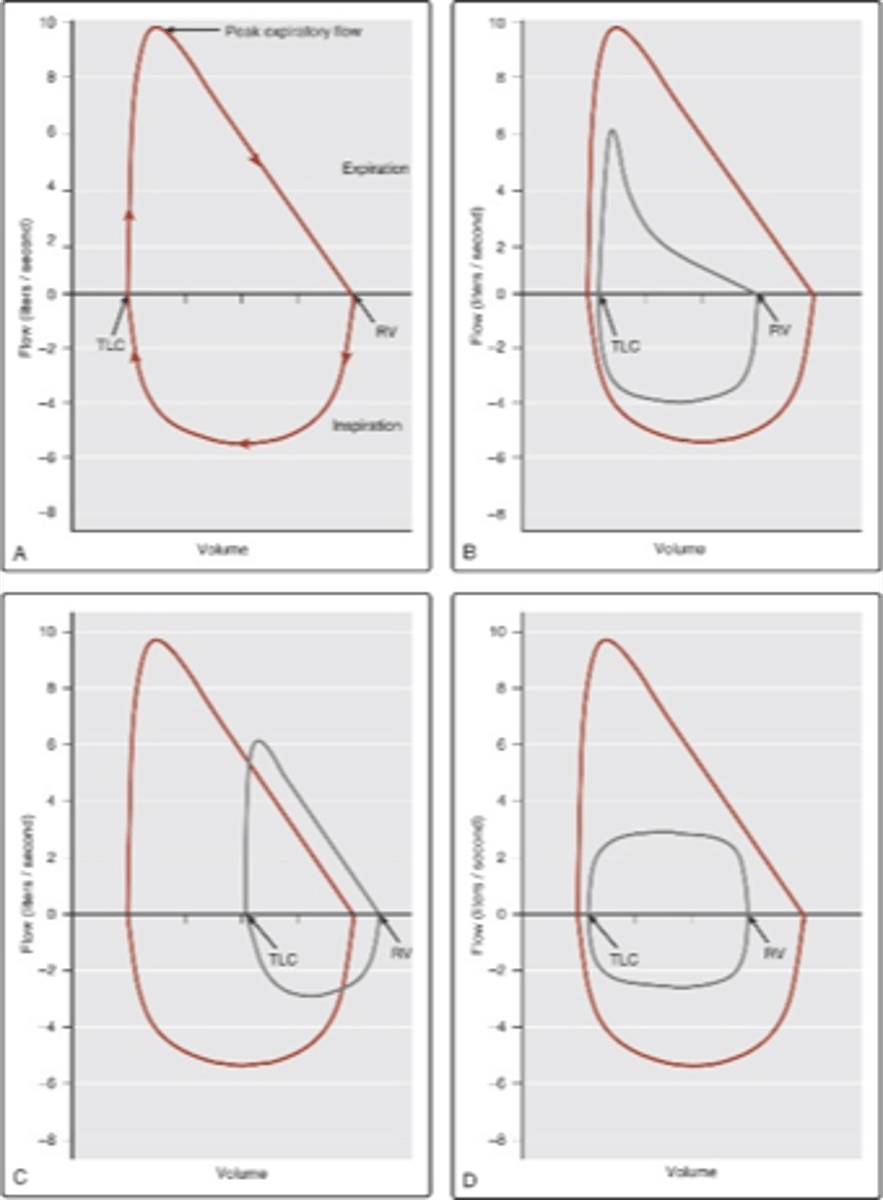
Flow volume loop of tracheal stenosis
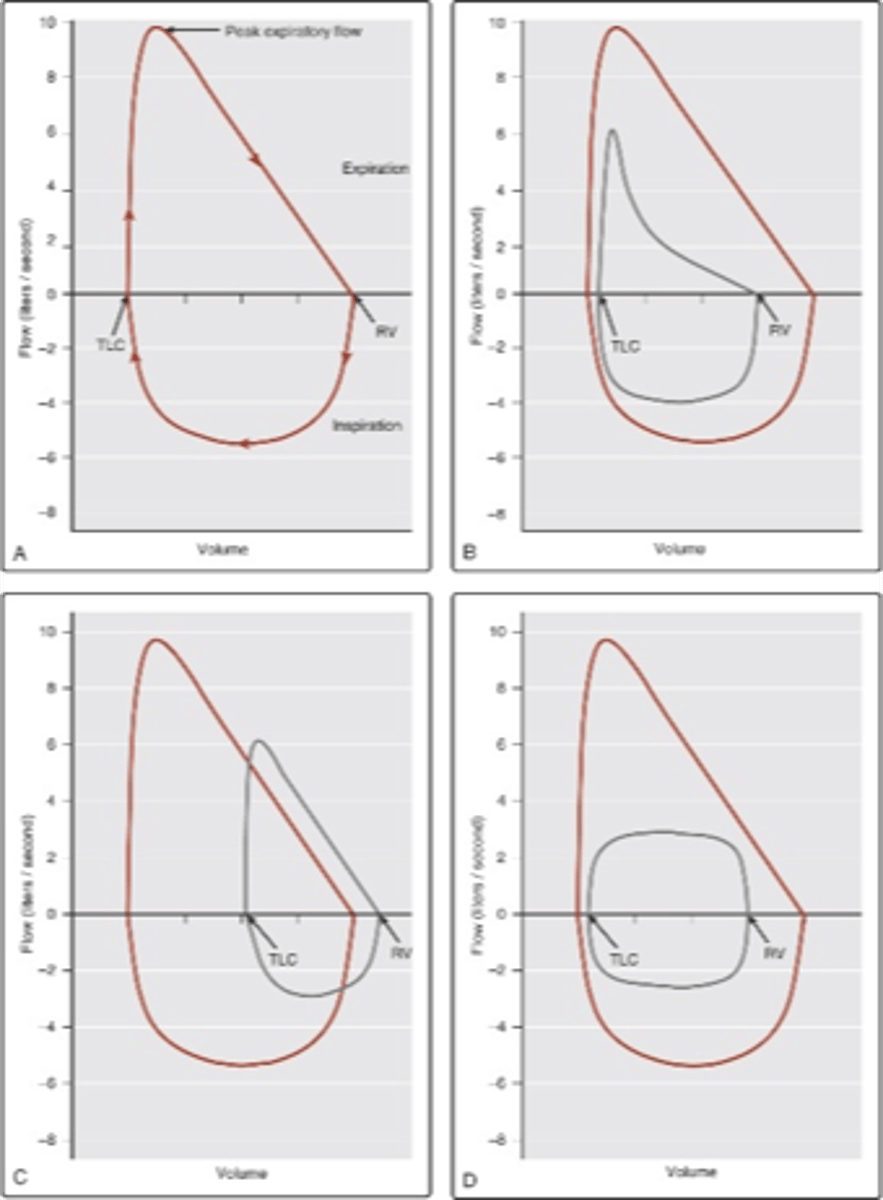
Another flow-volume loop
GOLD
-Global initiative for chronic obstructive lung disease
Mild COPD (I)
-FEV1/FVC <0.7
-FEV1 >/= 80% predicted
-pt may not be aware that their lung function is abnormal
Moderate COPD (II)
-FEV1/FVC <0.7
-50%
Severe COPD (III)
-FEV1/FVC <0.7
-30%/= FEV1<50% predicted (btwn 30-50%)
-SOB worsens and limits ADLs.
-Exacerbations begin in this stage
Very severe COPD (IV)
-FEV1/FVC <0.7
-FEV1 <30% predicted
-QOL very impaired
-exacerbations may be life-threatening
Interpretation of basic PFTs
-determine if results are normal
-determine whether results indicate OLD or RLD
-if OLD, determine reversibility
-consider hx and phys exam along with PFTs to determine disease progression
-be cautious of results if poor pt effort existed
OLD is considered reversible if
-there is a 12% increase in post-bronchodilator values in at least 2 parameters (FEV1, FVC or FEF 25-75%)
OLD value recap
-FEV1 decrease
-FVC normal/low
-FEV1/FVC < 0.7
-RV increase
-TLC increase
-DLCO decrease
RLD recap
-FEV1 decreased or normal
-FVC decrease
-FEV1/FVC normal
-RV decrease
-TLC decrease
-DLCO decrease
Blood gas analysis
-assesses problems related to acid-base balance, ventilation and oxygenation
Typical arterial blood gas (ABG) report has
-arterial pH
-PaCO2
-PaO2
-SaO2
-HCO3- (bicarb) concntration
-base excess
ABG chart
-PaO2 normal 80-100 mmHg (hypoxemia/hyperoxemia)
-PaCO2 normal 35-45 mmHg (hypo/hypercapnia)
-H+ concentration (pH) normal 7.35-7.45 (acid/alkalosis)
-SaO2 normal >95% (hypo/hyperoxemia)
-bicarb level (HCO3-) normal 22-26 mEq/L
-Base excess normal-2 to +2 mEq/L-1 (abnormal suggests metabolic process)
base excess measures
-availability of bicarb
- (-) is a base deficit
- (+) is a base excess
- >2 -->alkalosis
- <-2-->acidosis
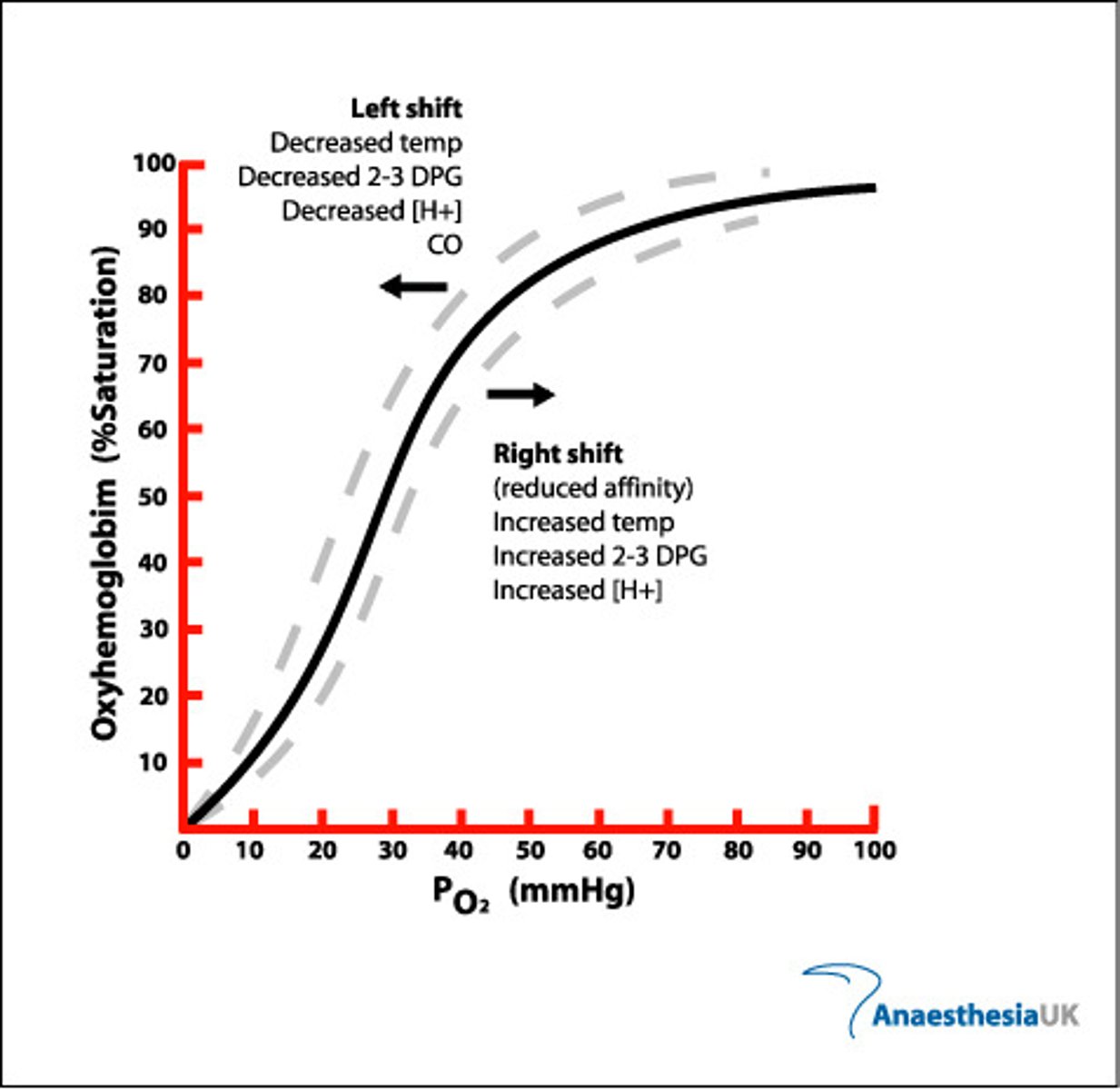
oxyhemoglobin dissociation curve
-increase in temp will cause downward/right shift
hypoxemia (PaO2)
-mild 60-79 mmHg
-moderate 40-59 mmHg
-severe < 40 mmHg
Hyperventilation
- PaCO2<30mmHg
Hypoventilation
-PaCO2 btwn 30-50 mmHg
Ventilatory failure
-PaCO2>50 mmHg
Lung and kidneys regulate 2 types of acids
-volatile: carbonic acid (lung)
-non-volatile: lactic acid (kidney)
Normal human blood pH
-7.4
pH <7.4
-acidic
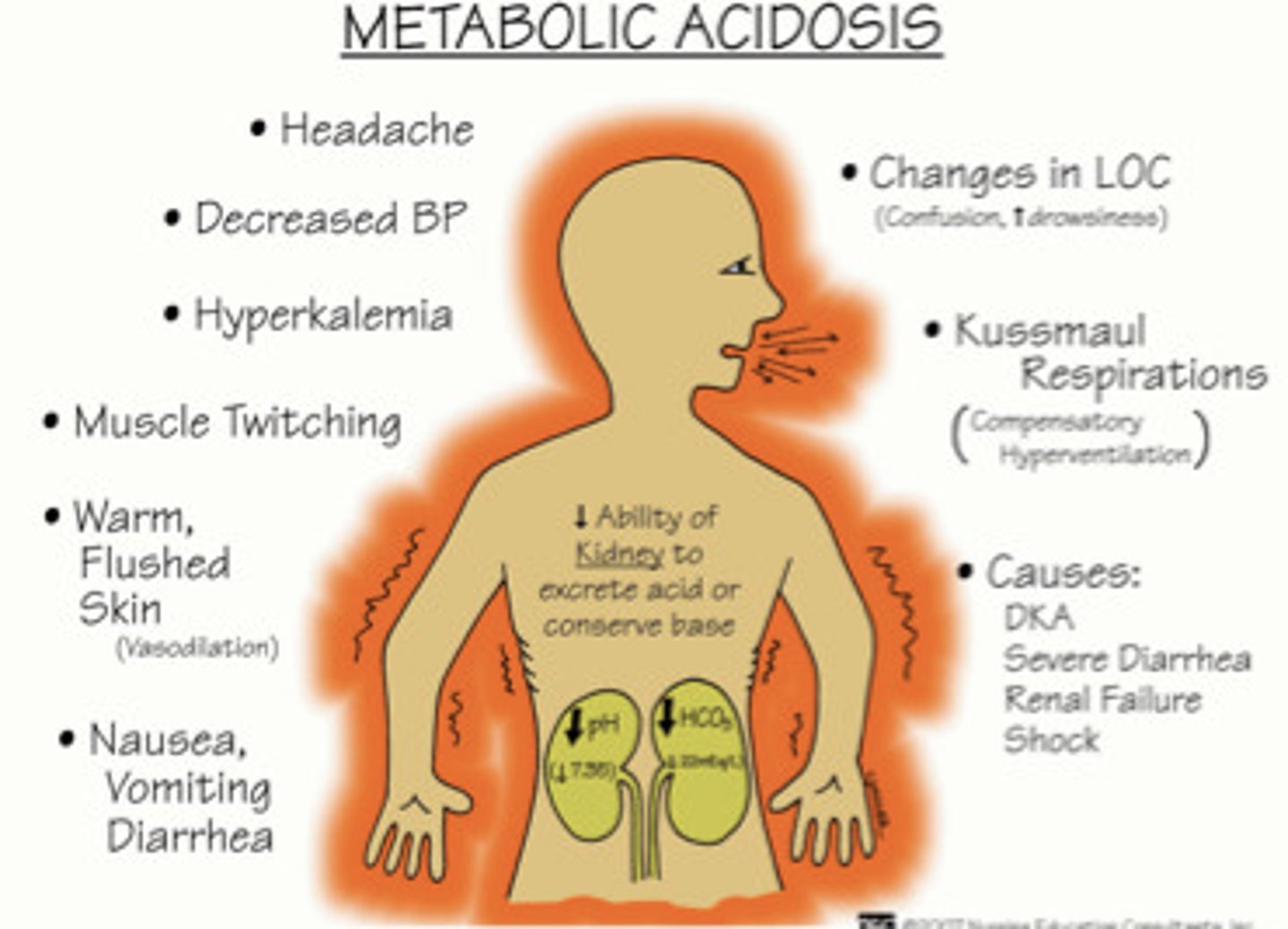
-low HCO3- lead to metabolic acidosis
-high PaCO2: respiratory acidosis
pH of >7.4
-alkaline
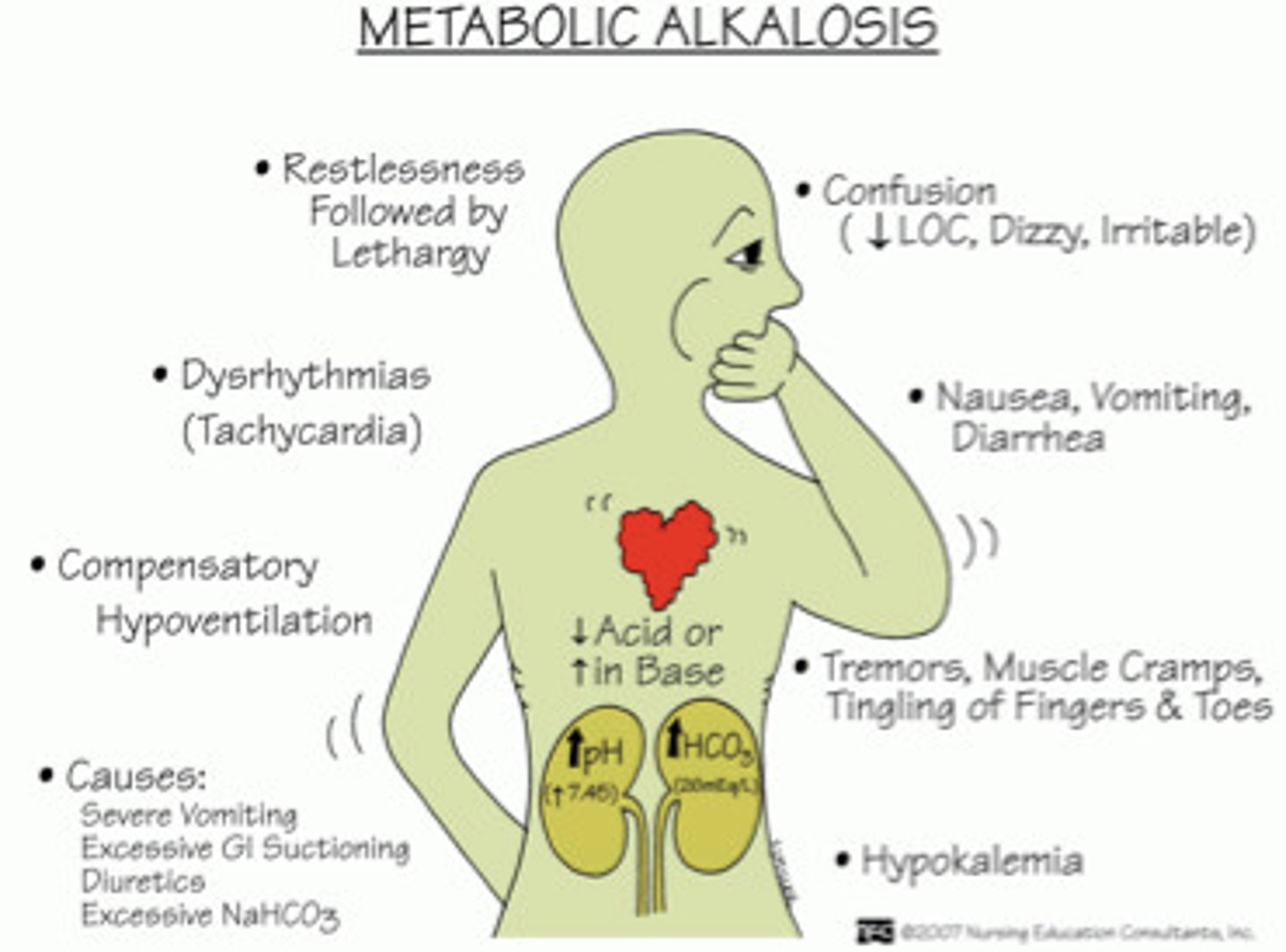
-High HCO3- metabolic alkalosis
-Low PaCO2 respiratory alkalosis
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Respiratory acidosis
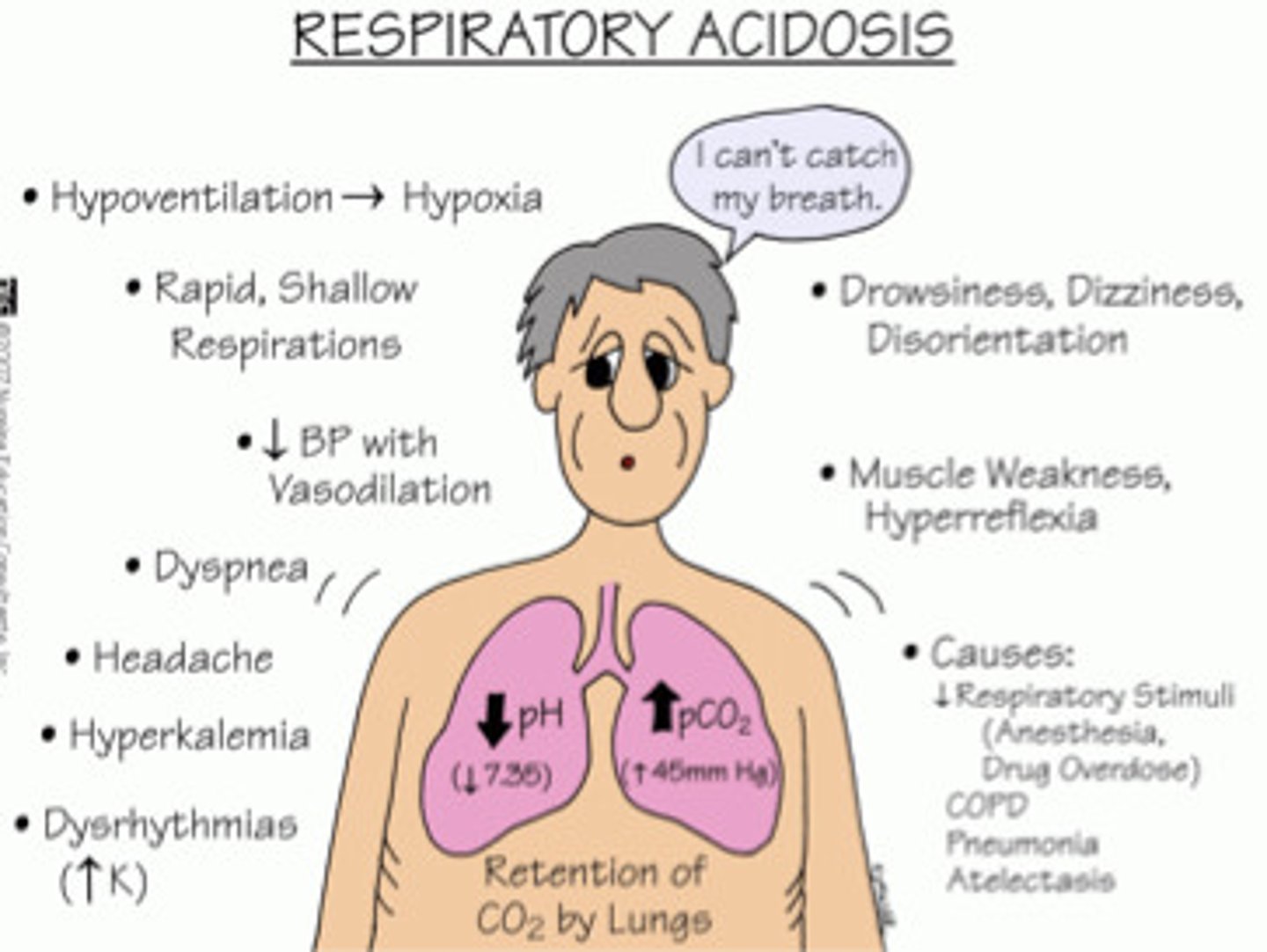
Respiratory alkalosis
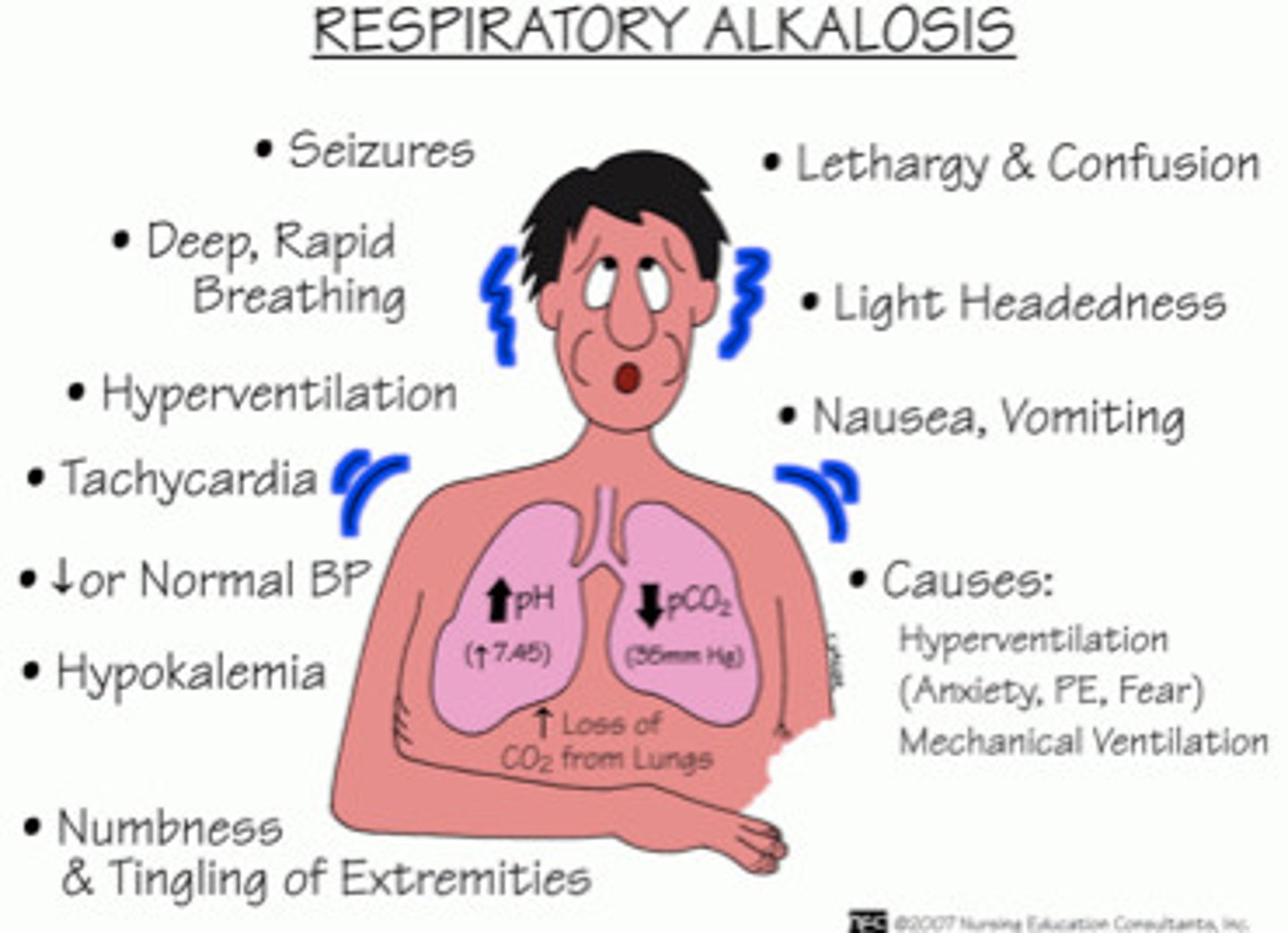
Fully compensated
-pH normal
-PaCO2 & HCO3 abnormal
Partially compensated
-All 3 values will be abnormal (pH, PaCO2, HCO3)
Uncompensated
-pH and one other value is abnormal (PaCO2, HCO3)
Pulse oximetry based on 2 physical principles
-presence of pulsatile signal generated by arterial blood
-fact that oxyhemoglobin and reduced Hb have different absorption spectra
Pulse ox is most reliable
-in 90's