Energy, Work and Power Exam 2
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
What is newtons first law?
a body at rest remains at rest or if in motion remains in motion at a constant velocity unless acted on by a net external force
What are some characteristics of a force?
push or pull
acts on an object
requires an agent
a vector (magnitude and direction)
True or False: Forces from bodies outside of the system can impart a change in the motion of the object.
True
What type of force can slow down objects due to its roughness?
Friction
What equation do you use if you are calculating drag/air force if object is moving at a constant?
D (drag) = m (mass) x g (gravity)
What equation defines Newtons 2nd Law?
Fnet=m (mass) x a (acceleration)
What is Newtons 2nd Law?
All accelerating objects must be subject to a non-zero net force, and all forces subject to a non-zero net force must experience acceleration
What equation do you use if you are calculating drag/air force if object is accelerating with thrust force and drag?
Fthrust - D (drag) aka Fnet = m x a
What relationship does mass and acceleration have according to Newtons 2nd law?
the have an inverse relationship; a=1/m
To find acceleration in a Newtons 2nd law problem, use equation:
a= Fnet/m
What units are the SI units of N (newtons)?
kg x m/s²; weight x acceleration
True or False: In Newtons 2nd law of motion, a net force on an object is responsible for its acceleration?
True
Acceleration is a ________ quantity.
vector (magnitude and direction)
What is Newtons 3rd law?
Whenever one body exerts a force on a second body, the first body experiences a force that is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force that it exerts.
what is thrust force?
a mechanical force that pushes or accelerates a mass in one direction, creating an equal force in the opposite direction
If the force supporting a load is perpendicular to the surface of contact between the load and its support, this force is defined to be a
Normal Force
Tension force is
is a force along the length of a medium, especially a force carried by a flexible medium, such as a rope or cable.
Use this equation when you have a perpendicular force (F⊥) is exerted at the middle of a flexible connector:
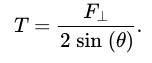
What is static friction?
when objects are stationary; the static friction is usually greater than the kinetic friction between the surfaces.
What is kinetic friction?
If two surfaces are in contact and moving relative to one another,
What is the equation for both static and kinetic friction?
F=μN
When finding the coefficient of kinetic friction when going down a slope use equation:
,𝑓k=𝜇kmgcos0º to find fk, then use 𝜇k=𝑓k/𝑁 to get answer
What is the name of the acceleration of uniform circular motion that points toward the center of the circular trajectory?
Centripetal acceleration Ac =v²/r
What is the direct relation to the centripetal acceleration equation?

What is the direct relation to the centripetal acceleration equation?

What is the centripetal acceleration equation in comparison to newtons 2nd law (centripetal force)?
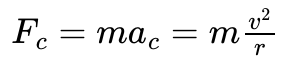
The magnitude of the mutual gravitational attraction between two objects of mass m and M is
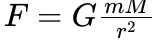
What is Keplers 1st law of planetary motion?
Each planet moves around the Sun in an orbit that is an ellipse, with the Sun at one focus of the ellipse.
What is Keplers 2st law of planetary motion?
The straight line joining a planet and the Sun sweeps out equal areas in space in equal intervals of time.
What is Keplers 3st law of planetary motion?
The square of a planet’s orbital period is directly proportional to the cube of the semimajor axis of its orbit.
What is newtons law of gravitation?
every particle in the universe attracts every other particle with a force along a line joining them.