MMSC200 Exam 1 (ch. 1-6)
1/211
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
212 Terms
Rules of Medical terms
1) All medical terms MUST have a suffix
2) Most terms have at least one root(exceptions: apnea, anemia)
3)Some terms do not have a prefix or combining vowel, but they all do have a suffix (gastritis, hepatic)
4) Combining vowels are used to connect two roots or a root and suffix
5) Combining vowel taken out if suffix begins with vowel (encephalopathy)
6) Prefix can be attached to root without combining vowel (subhepatic)
combining vowel
connects roots to suffixes and roots to other roots
electrocardiogram
record of the electrical activity of the heart
subgastric
pertaining to below the stomach
Cell
fundamental unit of all living things
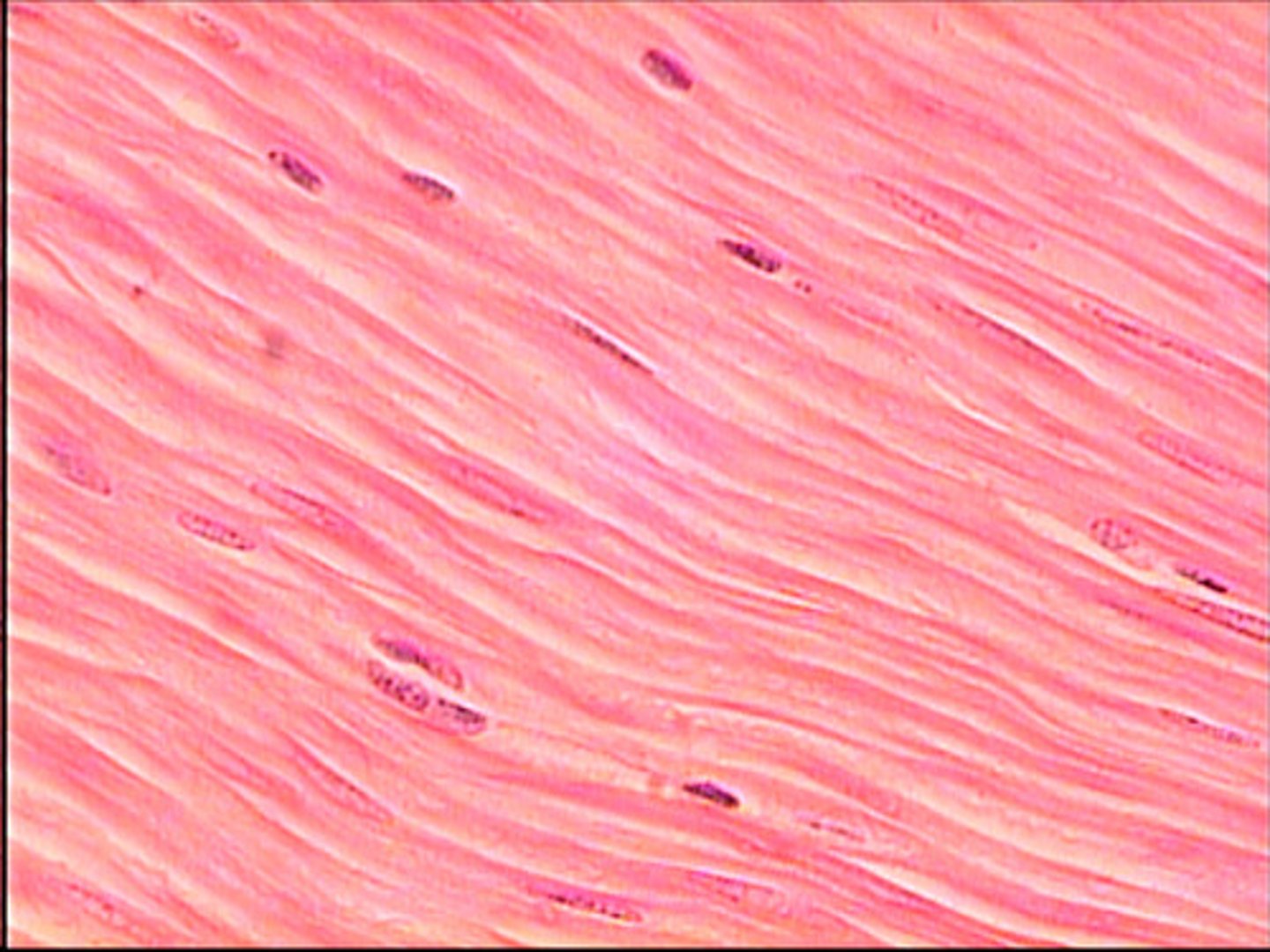
muscle cells
Shorten to cause movement of the body. They move the skeleton, heart, and internal organs
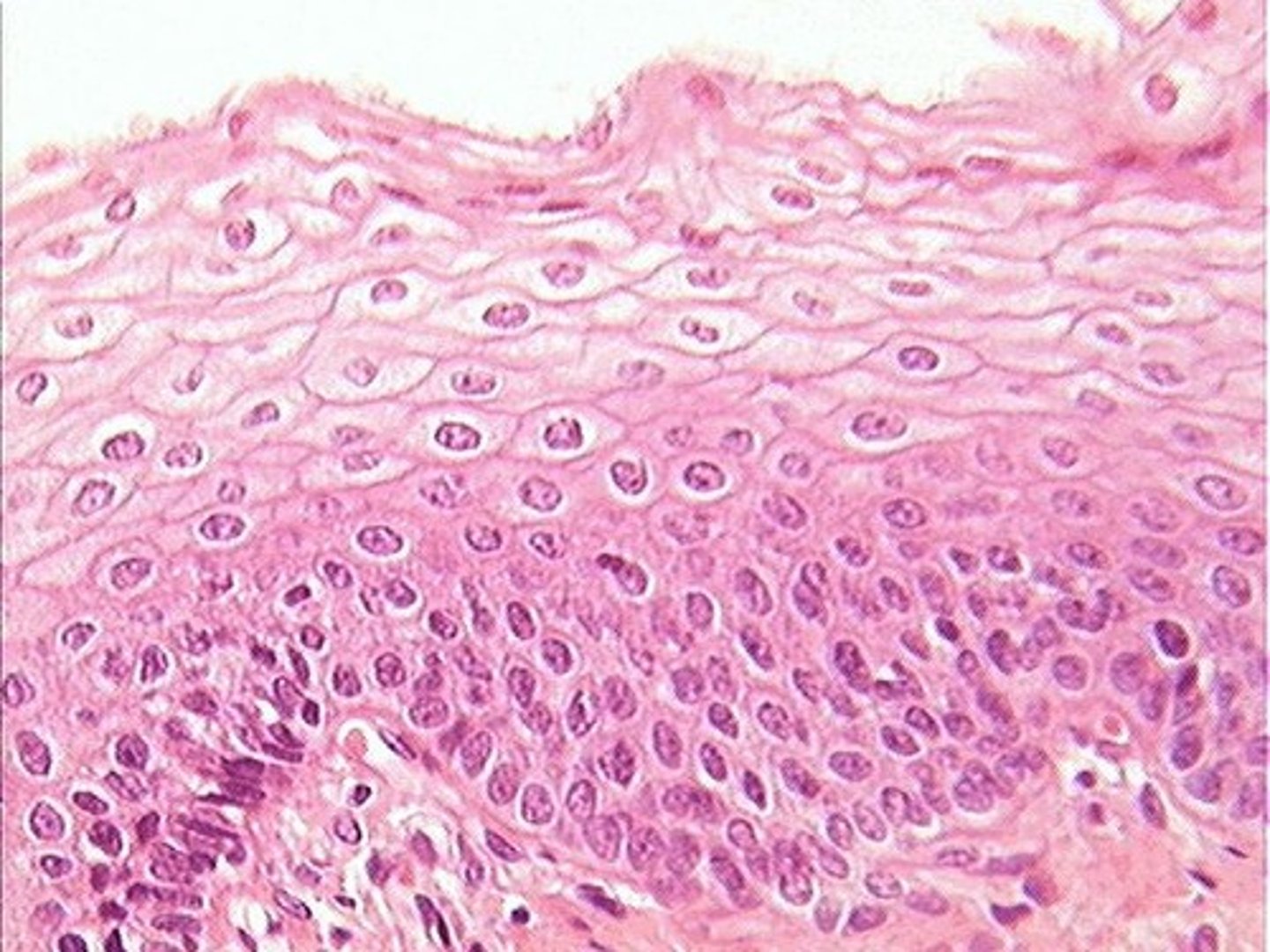
epithelial cells
skin cells that cover the outside of the body and line the internal surfaces of organs
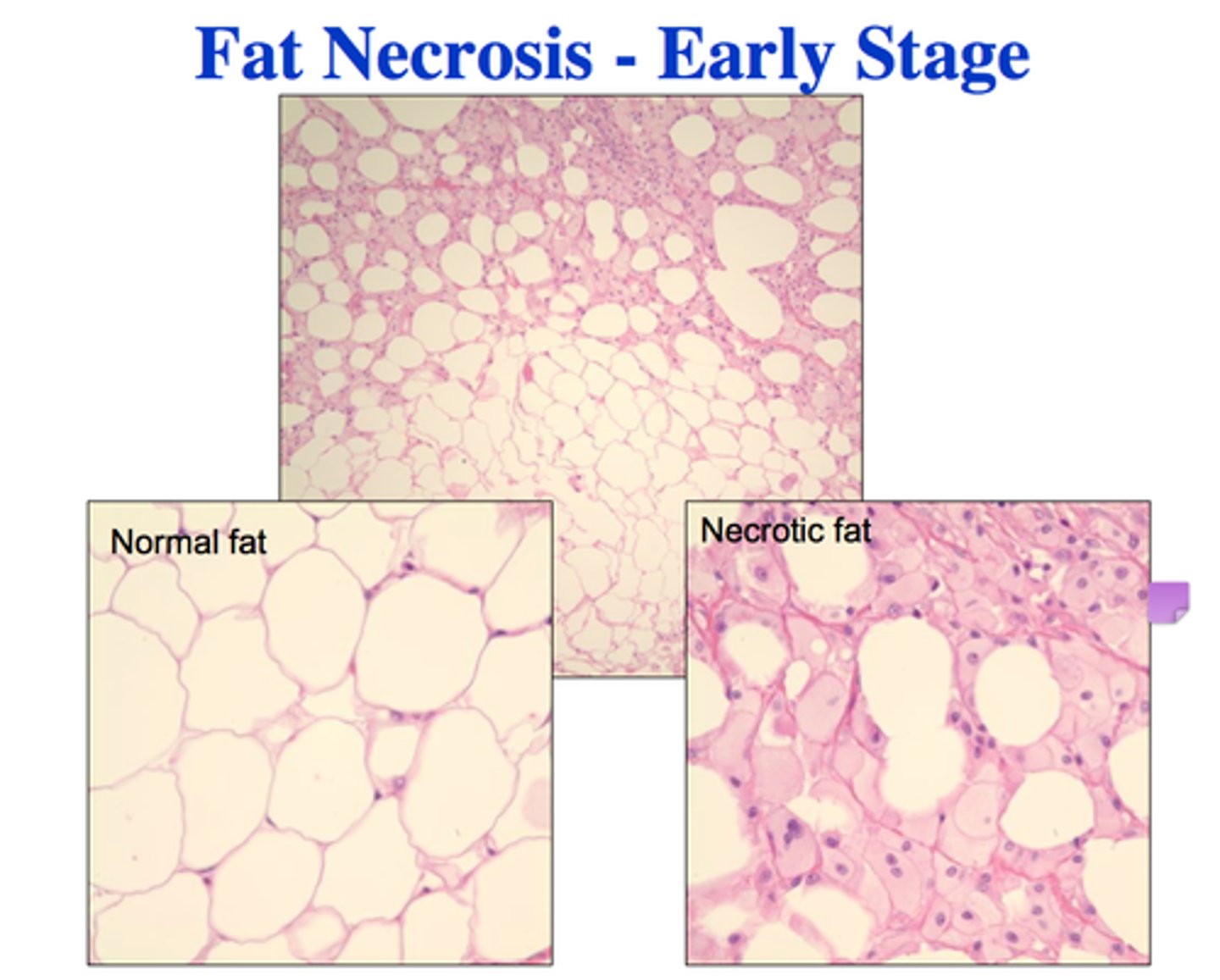
fat cells
store nutrients
4 types of tissues of the body
epithelial, connective, muscular, nervous
connective tissue
A body tissue that provides support for the body and connects all of its parts
epithelial tissue
A body tissue that covers the surfaces of the body, inside and out(made of cells closely packed)
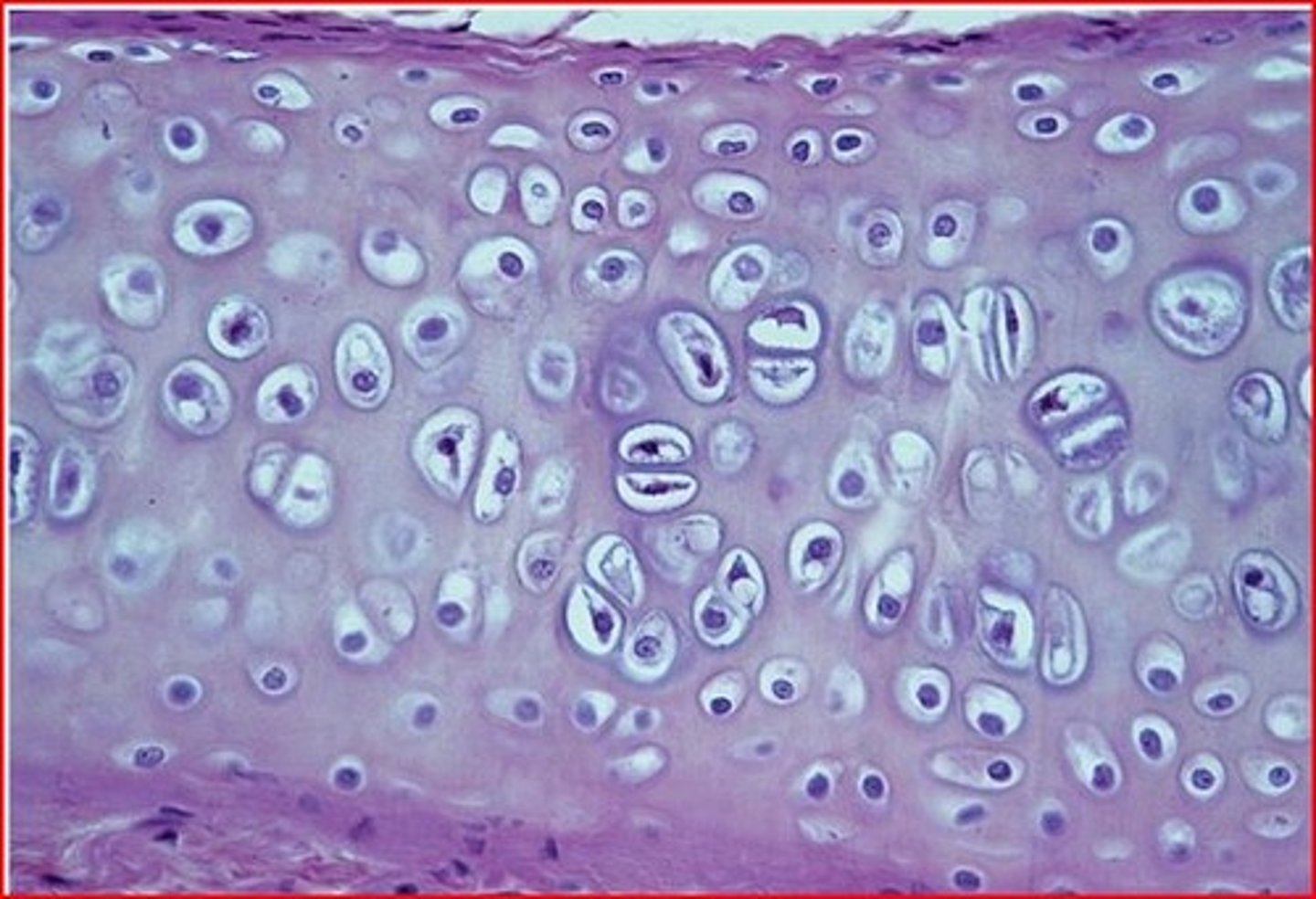
Cartilage
A connective tissue that is more flexible than bone and that protects the ends of bones and keeps them from rubbing together.
histologist
specialist in the study of tissues
body cavity
Body cavities are the spaces within the body that contain internal organs(viscera).
What organs does the cranial cavity hold?
brain and pituitary gland
What organs does the thoracic cavity hold?
Lungs, heart, esophagus, trachea, bronchial tubes
What organs does the abdominal cavity contain?
digestive organs
stomach, small and large instestine, spleen, pancreas, liver, gall bladder
What organs does the pelvic cavity contain?
urinary bladder, reproductive organs, rectum, parts of intestines
Spinal Cavity holds
spinal cord, nerves of spine
cranial cavity
contains the brain
thoracic cavity
contains heart and lungs, pleural cavity and mediastinum
Mediastinum
space between the lungs
abdominopelvic cavity
abdominal cavity and pelvic cavity
peritoneum
-a multilayered membrane that protects and holds the organs in place within the abdominal cavity
-covers visceral organs
9 regions of abdominopelvic cavity
right hypochondriac, epigastric, left hypochondriac, right lumbar, umbilical, left lumbar, right inguinal, hypogastric, left inguinal
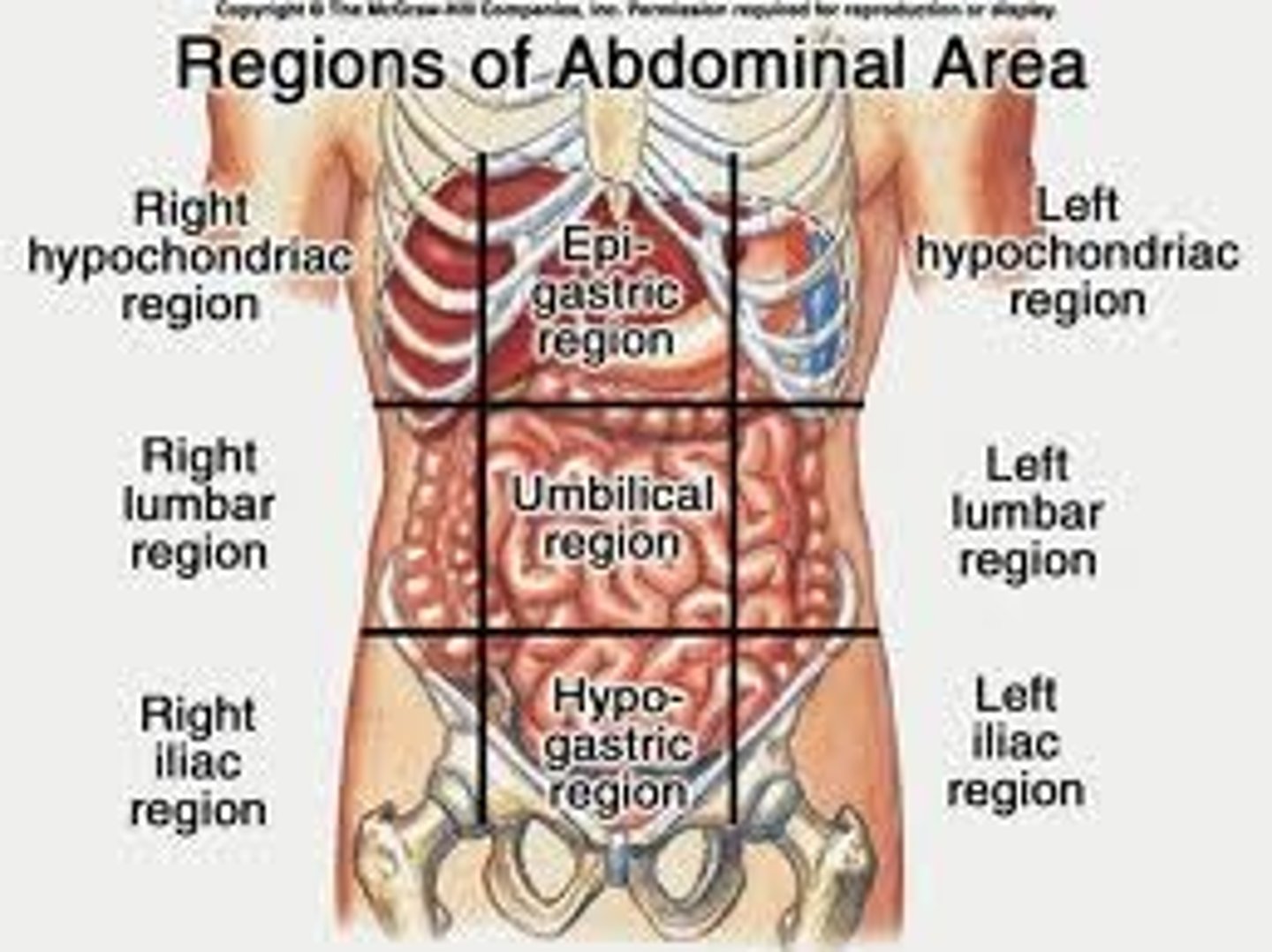
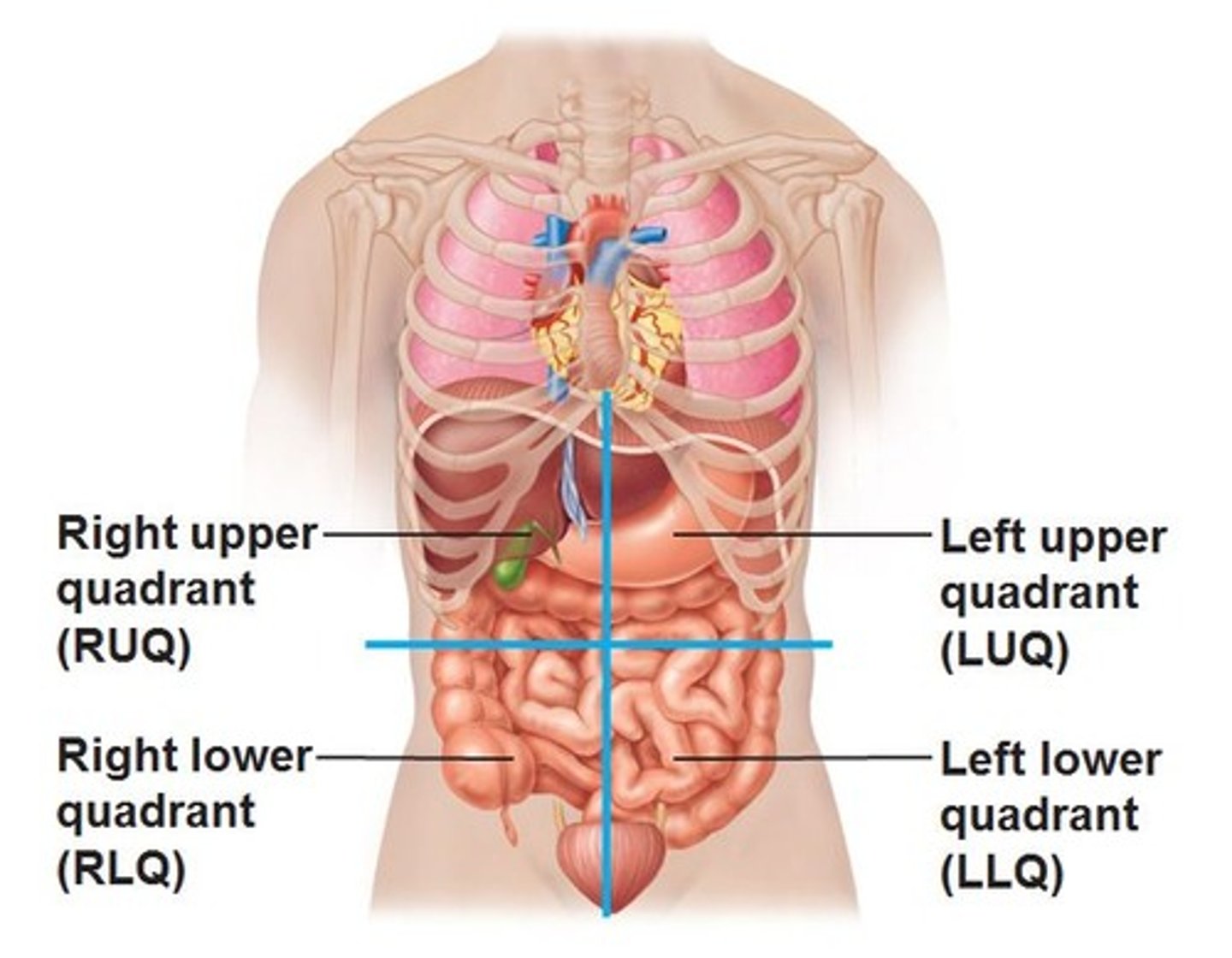
4 quadrants of abdominopelvic cavity
right upper, left upper, right lower, left lower
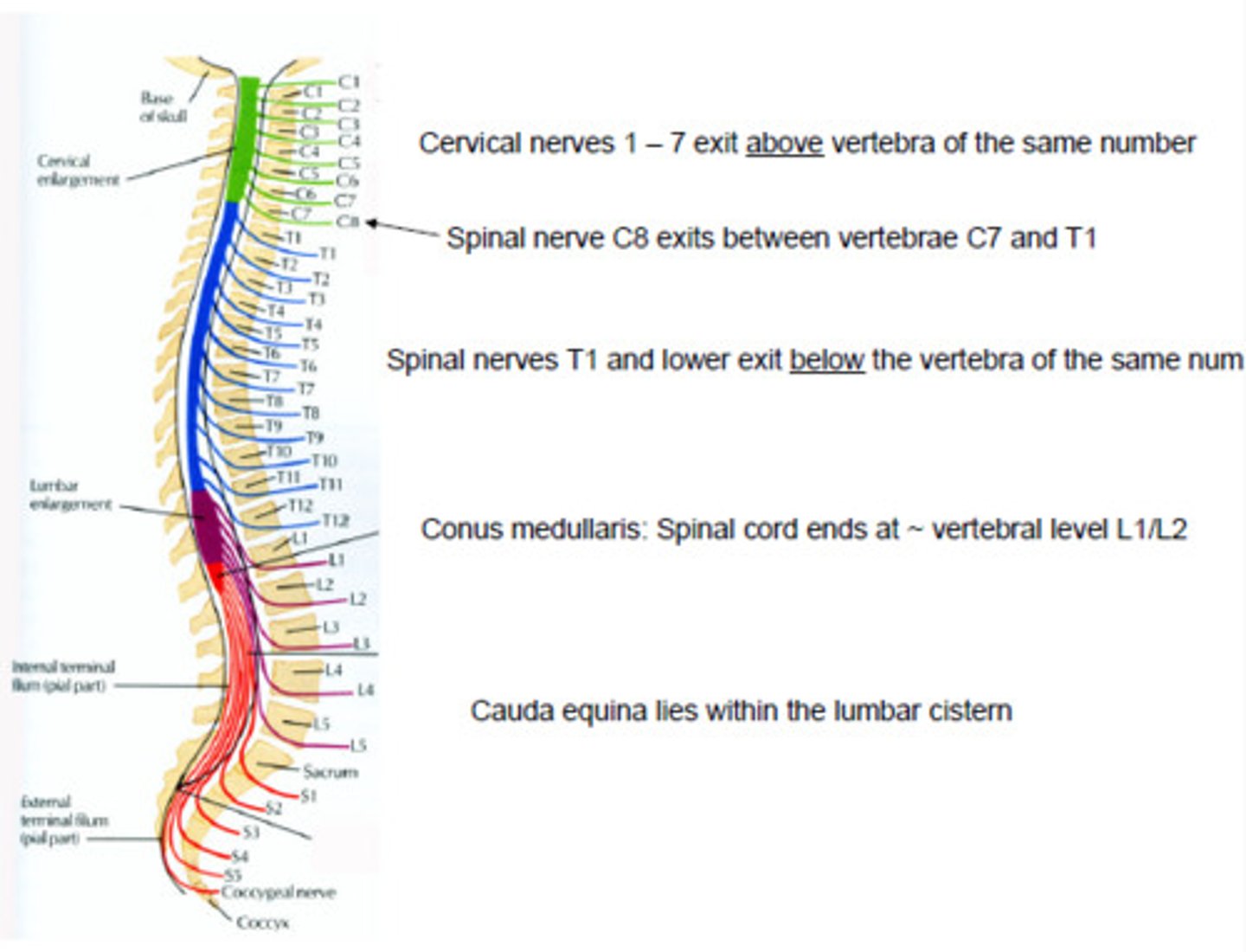
spinal cavity
spinal column and disc, pelvic bones
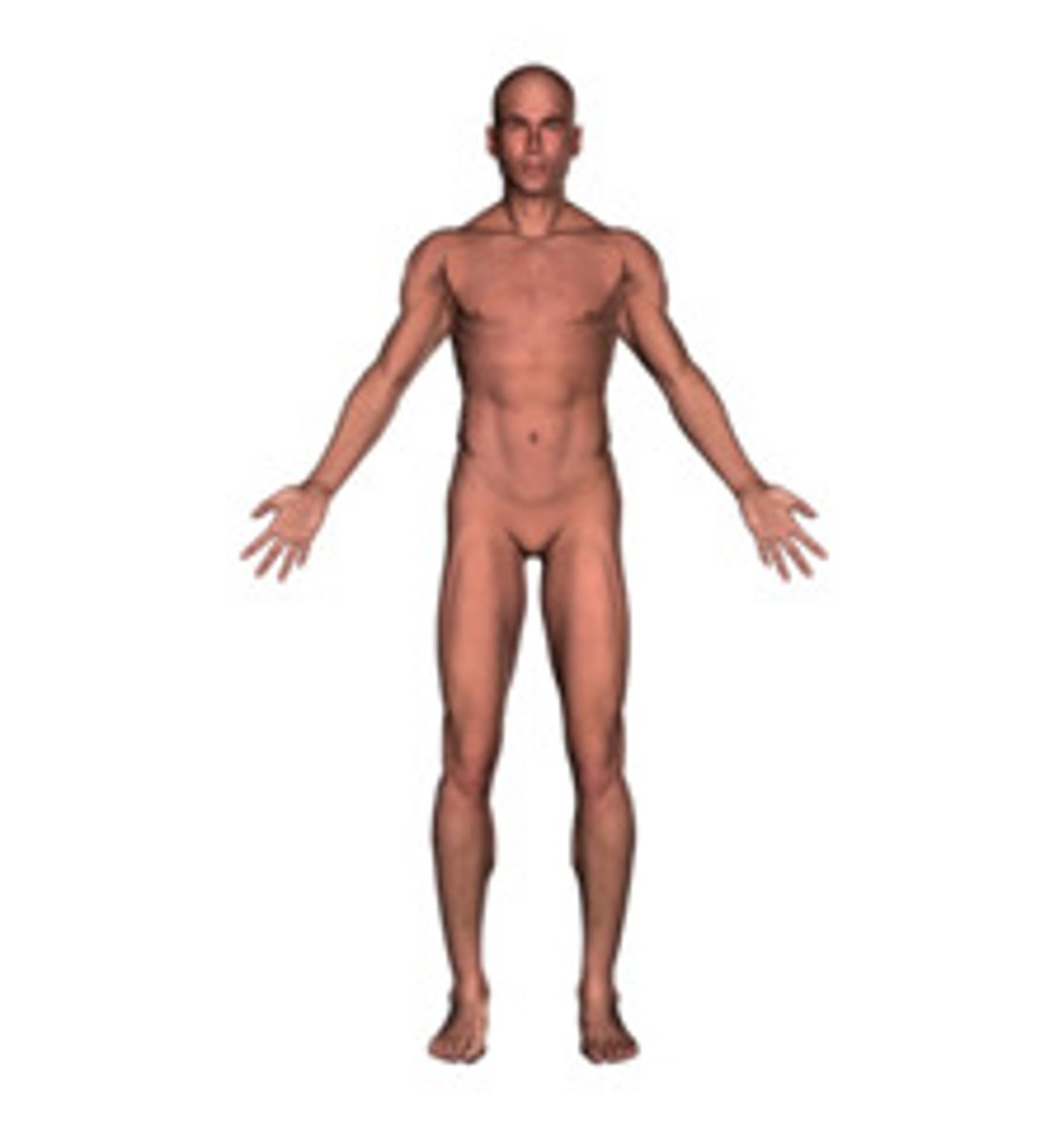
Proper Anatomical Position
Standing erect, palms forward, feet forward
Anterior(ventral)
front
Posterior(dorsal)
back
deep
away from the surface
superficial
near the surface
Proximal
Closer to the point of attachment
Distal
away from the point of attachment
Superior
above
Inferior
away from the head
Caudal
toward the tail or inferior end
Cephalic
pertaining to the head
lateral
away from the midline
Medial
toward the midline
unilateral
pertaining to one side
anteroposterior
from front to back
posteranterior
from back to front
frontal plane of the body
coronal
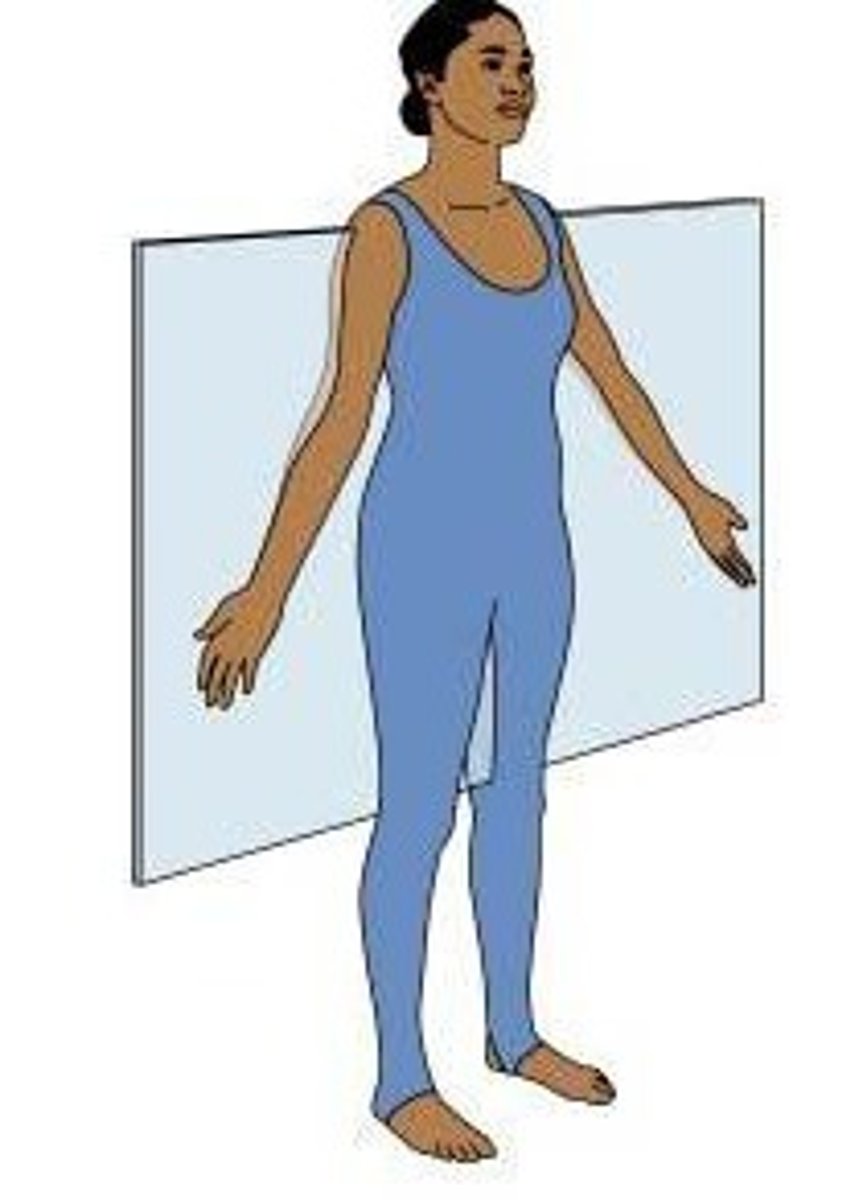
sagittal plane
divides body into left and right
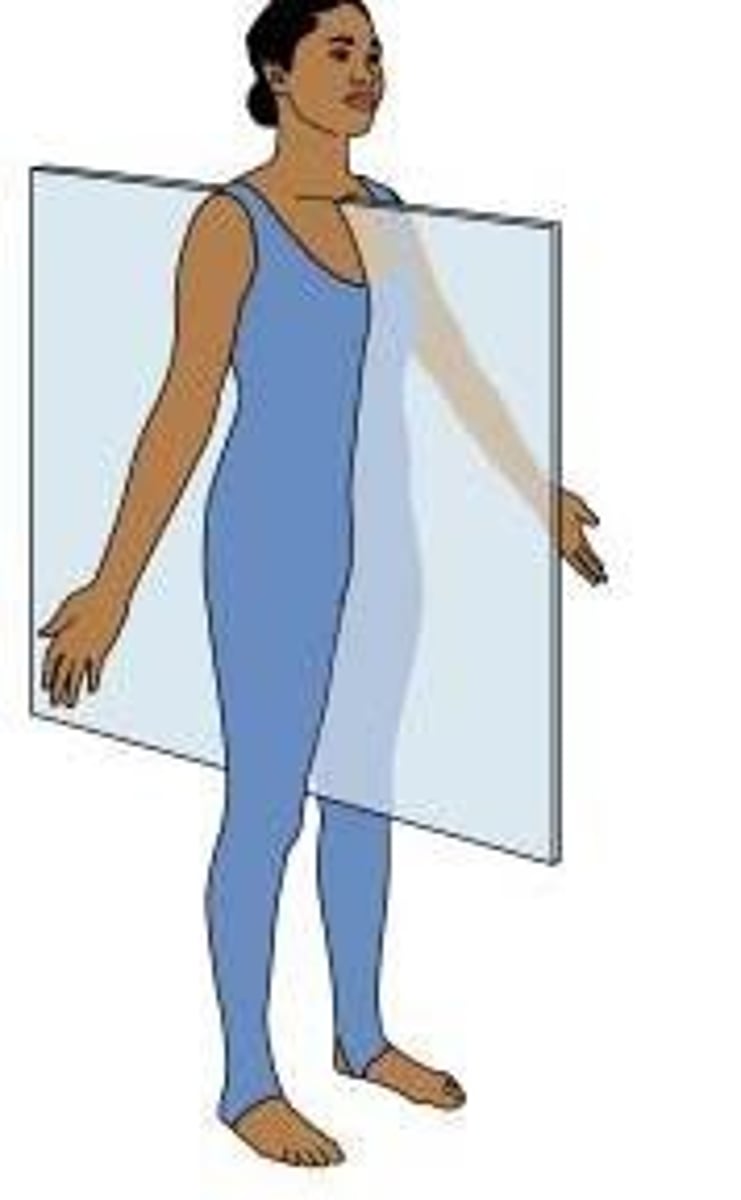
transverse plane
horizontal division of the body into upper and lower portions
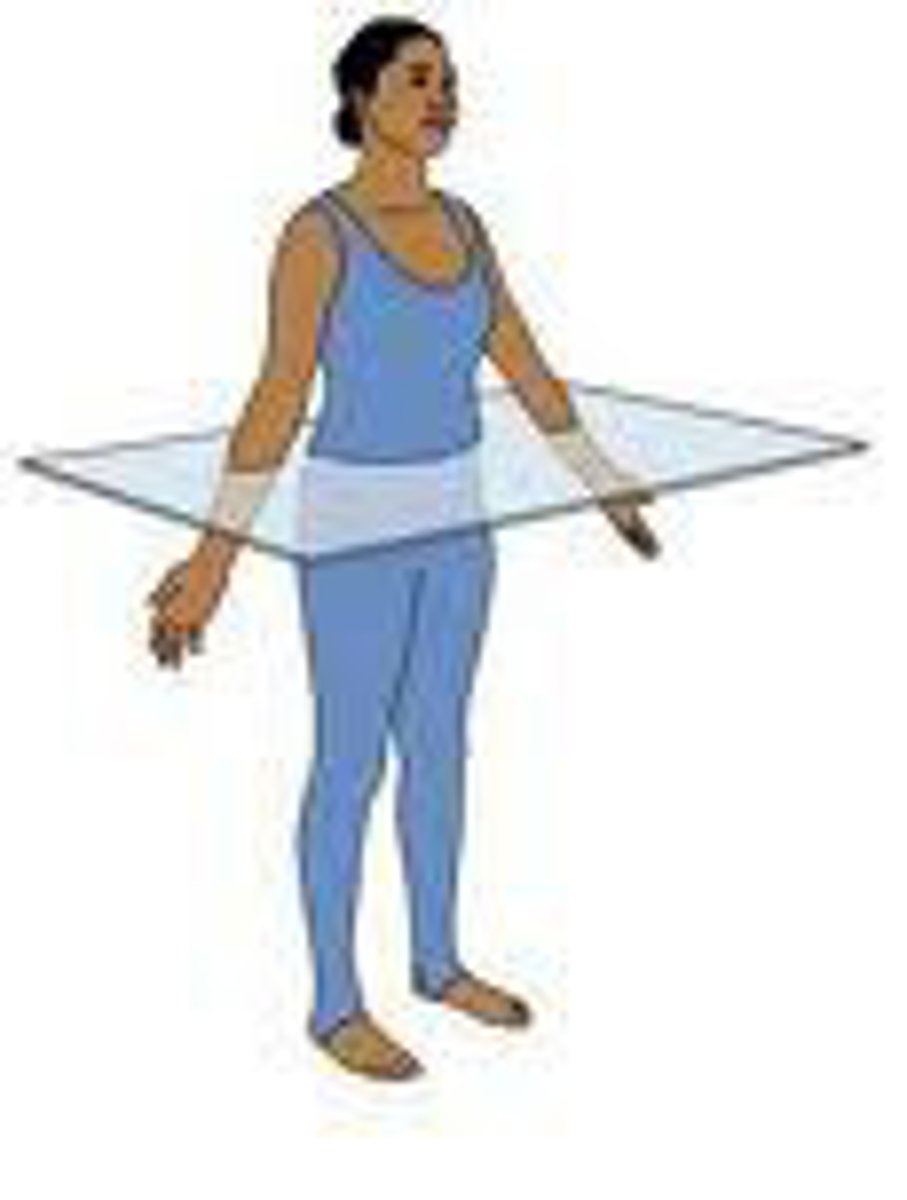
supine position
lying on back, facing upward
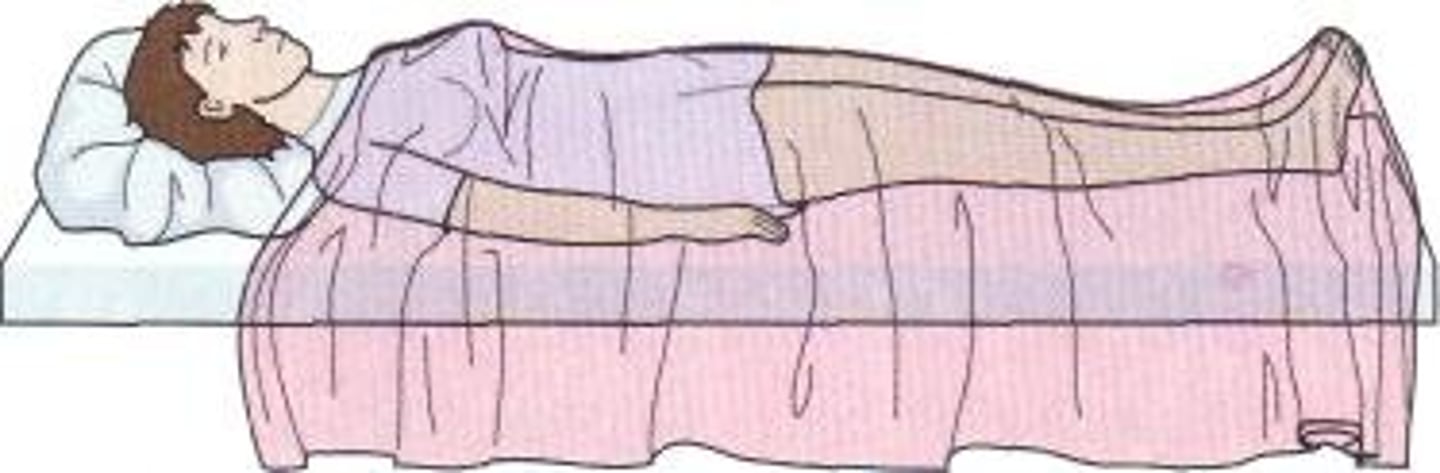
prone position
lying face down
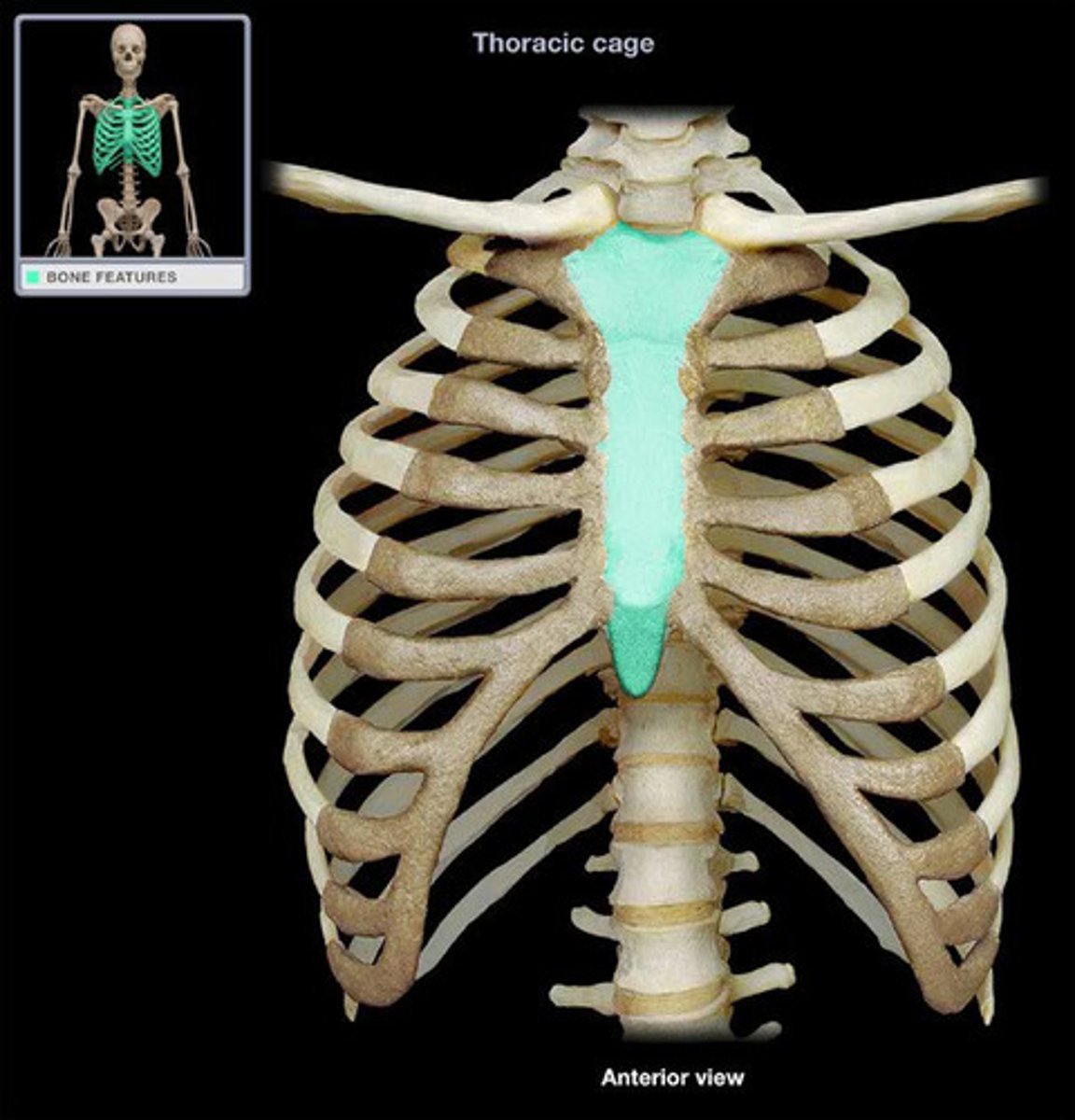
Sternum
breastbone, connects ribs via cartilage forming rib cage that protects the heart, lungs, and major blood vessels
hernia
Protrusion of an organ through the wall of the cavity that normally contains it
hiatal hernia
protrusion of a part of the stomach upward through the opening in the diaphragm
inguinal hernia
the protrusion of a small loop of bowel through a weak place in the lower abdominal wall or groin
omphalocele
herniation at the umbilicus
amniocentesis
the sampling of amniotic fluid using a hollow needle inserted into the uterus, to screen for developmental abnormalities in a fetus.
Streptococcus
berry-shaped (bacterium) in twisted chains
Anemia
A condition in which the blood is deficient in red blood cells, in hemoglobin, or in total volume.
-algia, -dynia
pain
-cele
hernia
-centesis
surgical to remove fluid
-cyte
cell
-emia
blood condition
-genesis
condition of producing, forming
-ectomy
removal; excision
-tomy
incision, cutting into
-stomy
creating or installing an new opening
nephrectomy
surgical removal of a kidney
kindly incision
nephrotomy
kidney new opening
nephrostomy
adenoids
mass of lymphatic tissue in the nasopharynx
adenoidectomy
excision of the adenoids
-trophy
development
-malacia
softening
-megaly
enlargement
-oma
tumor
acromegaly
enlargement of the extremities(hands, feet)
splenomegaly
enlargement of the spleen (if spleen is removed, other organs can carry out its functions)
Achondroplasia
A form of human dwarfism caused by a single dominant allele; the homozygous condition is lethal
blepharoptosis
drooping eyelid
laparoscopy
visual examination of the abdomen(minimally invasive)
Ischemia
Lack of blood supply
erythrocyte
red blood cell
Thrombocytes(platelets)
clotting cells
leukocytes
white blood cells
Granulocytes
A group of leukocytes containing granules in their cytoplasm; neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils.
Agranulocytes
A group of leukocytes without granules in their nuclei; lymphocytes, monocytes.
Neutrophils
A type of white blood cell that engulfs bacterial cells
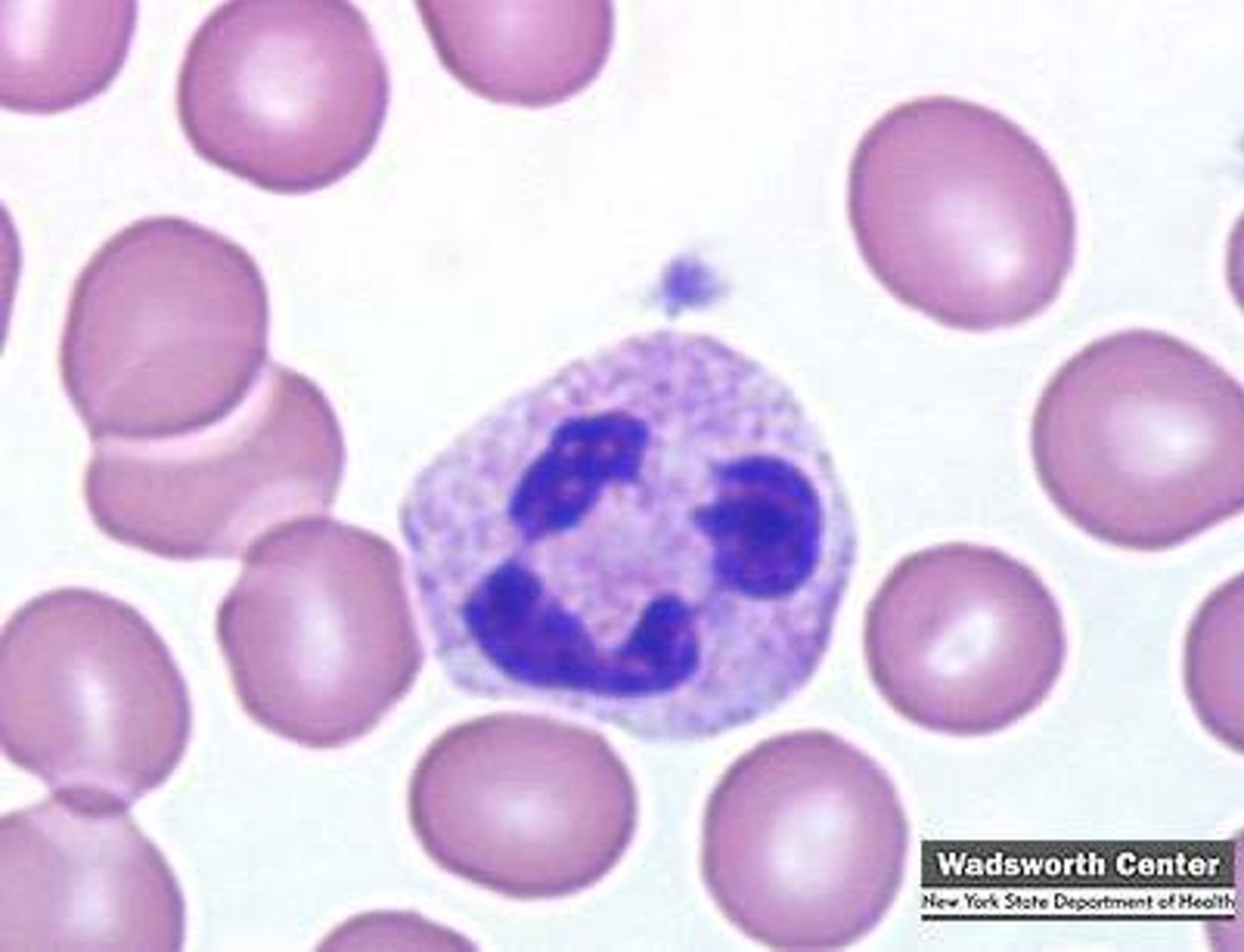
Eosinophils
defend against toxic compounds
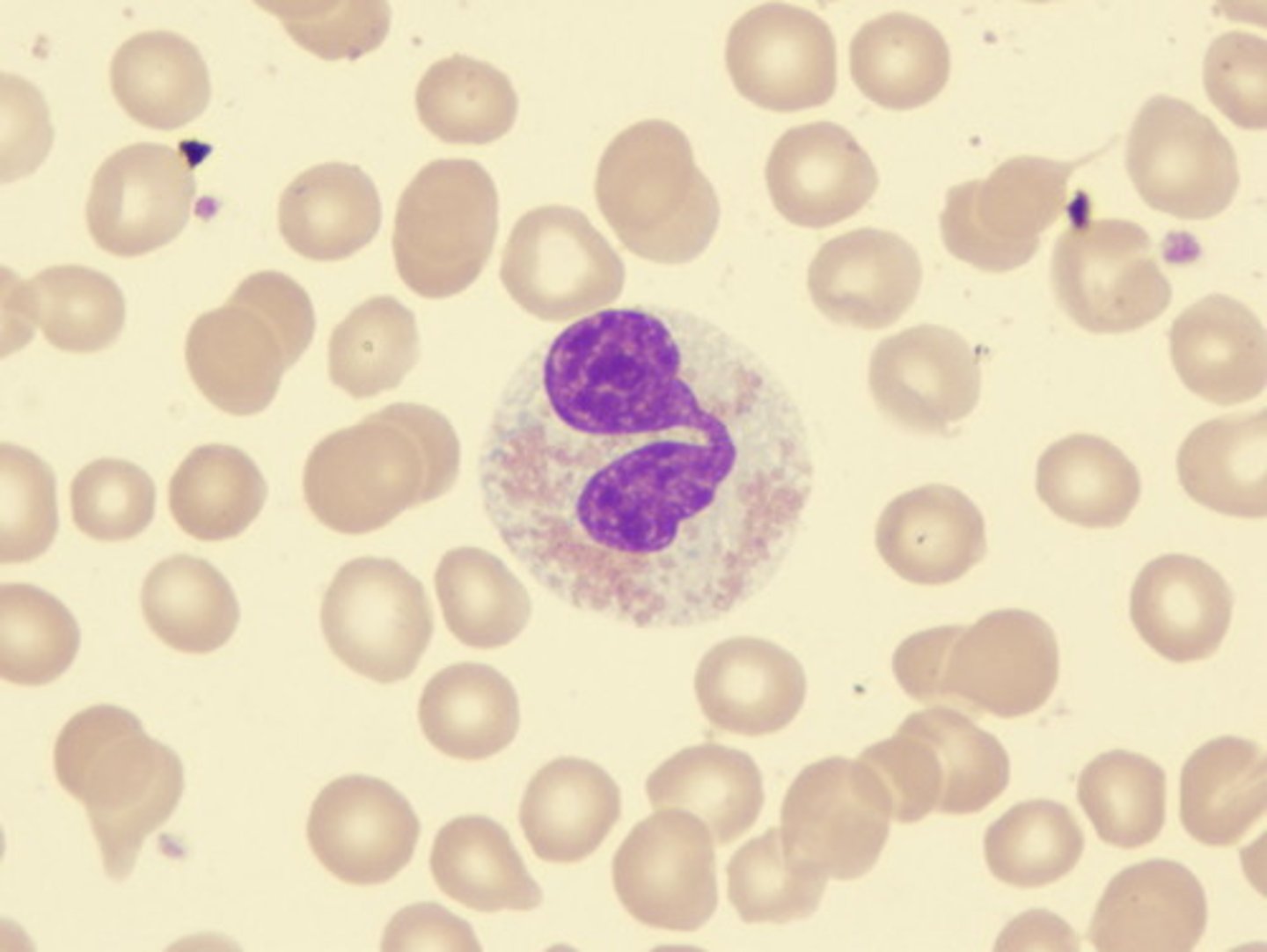
Basophils
release histamine
-act in allergic reactions
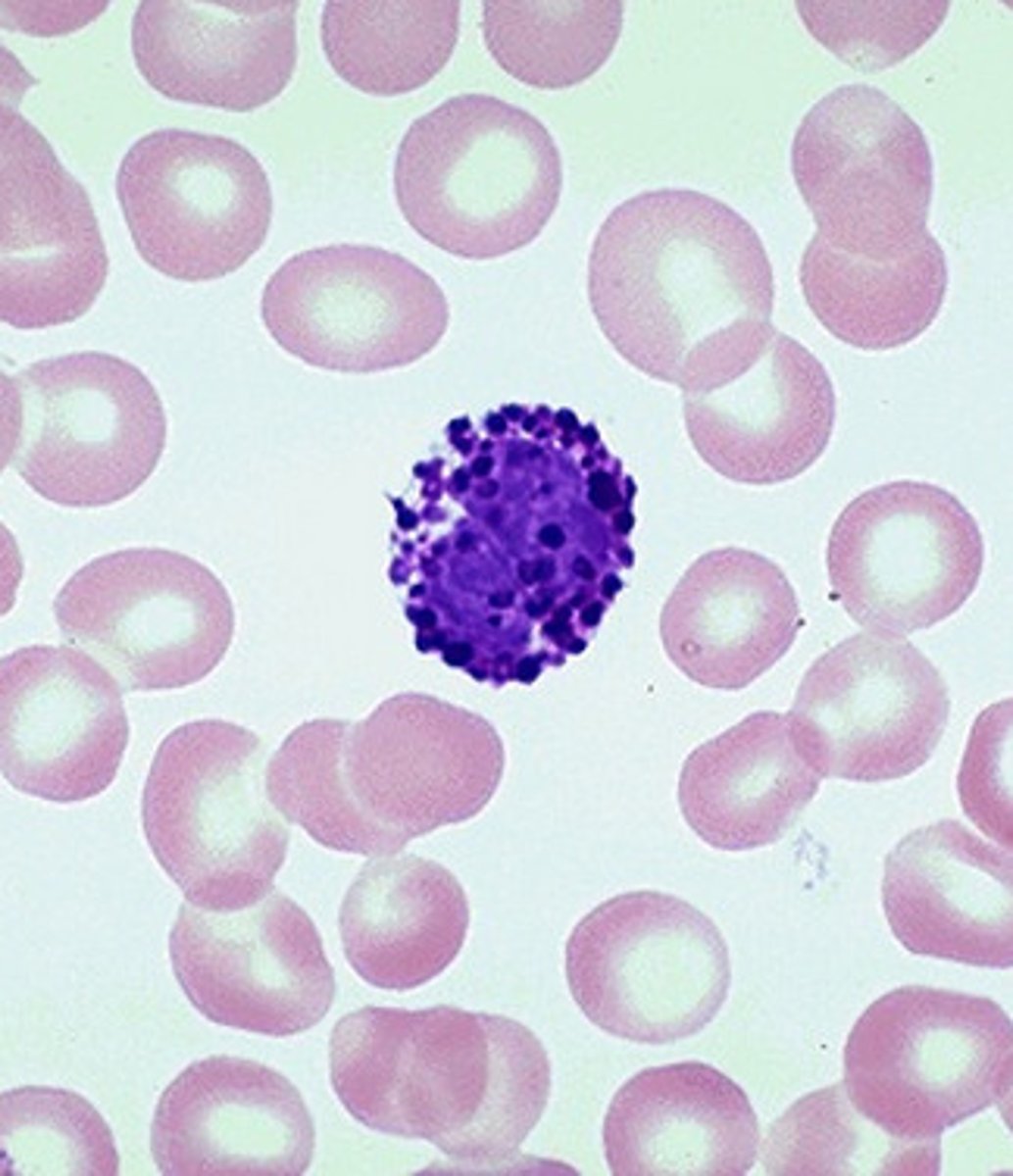
Monocytes
An agranular leukocyte that is able to migrate into tissues and transform into a macrophage.
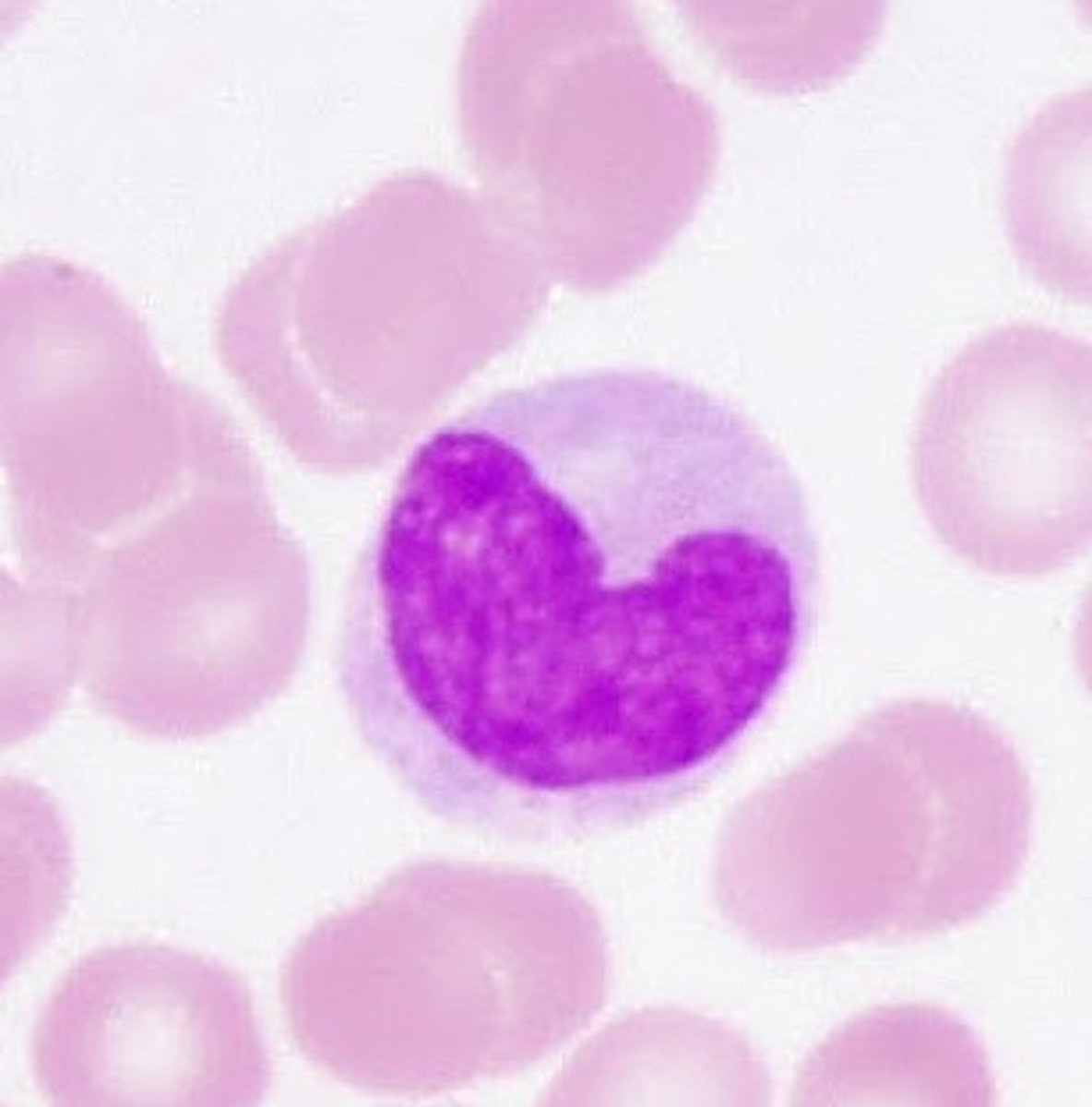
Lymphocytes
A type of white blood cell that make antibodies to fight off infections
Leukocytosis
increase in the number of white blood cells
-penia
abnormally decrease in cells (leukopenia, neutropenia)
ante
before, in front of
auto-
self
antibiotic
destroys or inhibits the growth of microorganisms like bacteria, fungi, parasites, viruses
Antigen
a toxin or other foreign substance that induces an immune response in the body, especially the production of antibodies.
antibody
A protein that acts against a specific antigen
autoimmune disorder
the body makes antibodies against its own healthy cells and tissues, causing inflammation and injury
Graves disease
Antibodies produced stimulate the production of thyroid hormones (hyperthyroidism)
juvenile diabetes
destroys pancreatic beta cells that produce insulin