19) Metamorphic textures
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
lineation
alignment of elongate minerals to make a linear fabric
stretching of non platy (amphibole/feldspar)
end view doesn’t look stretched
rock cleavage
tendency of a rock to break along parallel surfaces
mostly for low grade meta rocks, slaty minerals
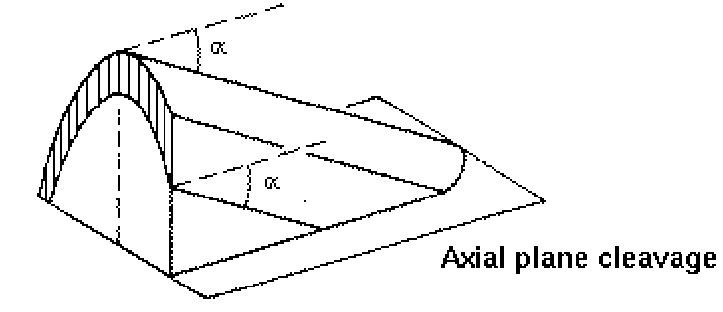
axial plane cleavage
alignment of platy minerals normal to the major compressive stress responsible for the folding, parallel to the axial plane
if stress is horizontal we expect to see vertical cleavage
granoblastic
like array of bubbles
no pore space or sediment between any of the grains
recrystallized textures
porphyroblastic
fast growing porphyroblasts grow bigger than rest of crystals
grew in solid state within a fine grain as a result of compression
usually euhedral
garnet and staurolite are common in metapelites
poikiloblastic
porphyroblasts with abundant inclusions
inclusions inside are older, then larger mineral grew around it
crenulation cleavage
small scale folding of an earlier formed metamorphic fabric causing ripple or wavy appearance (crenulation)
pressure shadows
halo of minerals surrounding a porphyroblast differing from the matrix
commonly quartz, coarser than matrix
deformation twins
result of metamorphism and stress
common in calcite, plagioclase, and pyrx
differ from igneous polysynthetic twinning bc aren’t as straight, tend to taper, and may only be found in part of the grain
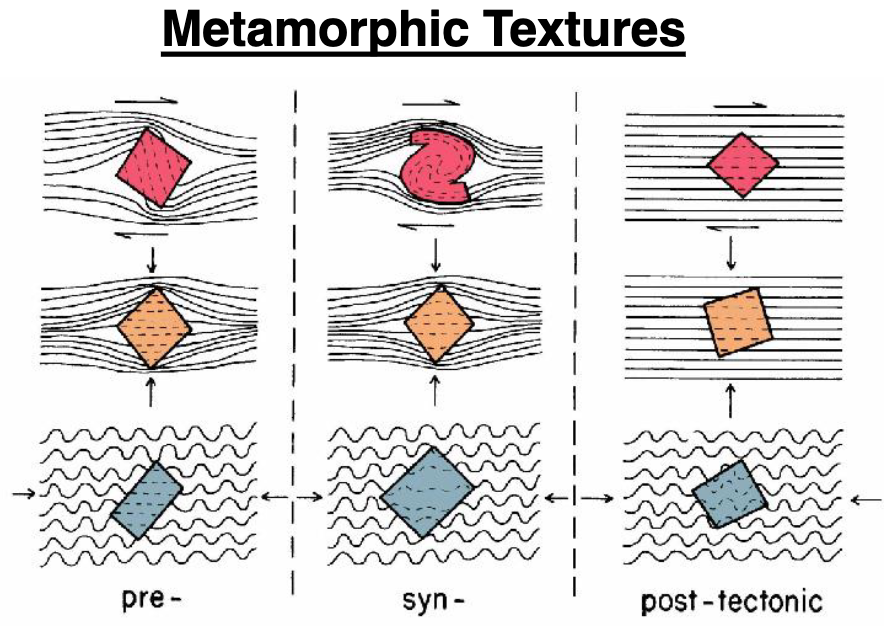
explain pre- syn- post- tectonic
porphyroblasts can grow at diff times during the history of the meta rock
porphs formed pre-tectonic will have foliation wrapped around them
porphs formed syn-tectonic will have foliation semi-wrapped around them, rotated
porphs formed post-tectonic will have foliation included in them
spiral is shear force syn-tectonic
details on migmatites
between igneous and meta rocks
form under extreme temp conds during prograde meta, partial melting
complicated folding
commonly occur within extremely deformed rocks expressing base of eroded mountain belts
light coloured leucosome within dark coloured melanosome
explain dynamic crystallization in fault zones
cataclasis: deformation of the rock caused by fracture and rotation of mineral grains
Ex: cataclastic breccia (formed in a fault)
comminution: breaking down into smaller size, crushing up, pulverizing
things at top are fairly easily eroded
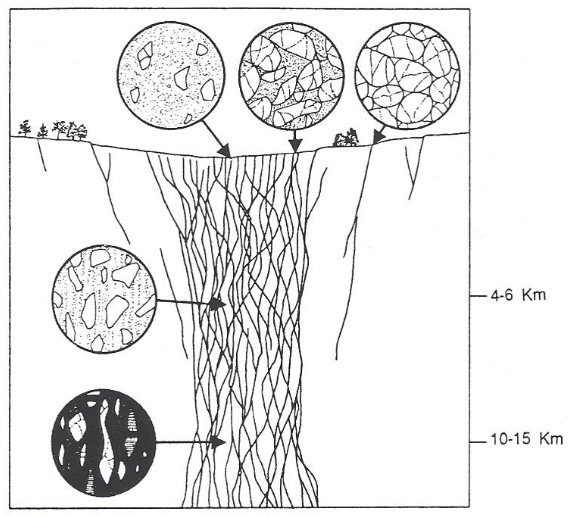
mylonite
ductile process, smearing out. parent rock is granite
protomylonite: not much grainsize reduction
ultramylonite: super finegrained, very smeared
porphyroclast
large mineral in finer grained matrix
clast older than matrix
relic of previous rock
occur in rock that have undergone shear
can be used to determine sense of shear
different from porphyroblast