module 1: genes, genome, and the tree of life
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
69 Terms
what is “genetics”?
study of genome sequence variation
what is “genome”?
the complete set of “inherited” instructions that contribute to the traits of an organism (DNA, RNA, etc)
what is a gene?
a unit of inheritance
a piece of instructions that influences the inheritance of traits from one individual to the next
a specific region / locus of DNA that is transcribed into a single RNA molecule
the entire DNA sequence that’s needed to transcribe and encode an RNA (including regulatory sequences)
T/F: in recent years, nearly the entire genome is transcribed at low levels, and we’re still in the process of determining what all of the non-coding RNA actually does in the cell
TRUE
T/F: no gene works in isolation
TRUE: all genes are part of a complex regulatory network
what are alleles?
changes to specific DNA sequences / variants
what are examples of replication errors? (2)
environmental mutagens
reassortment / recombination
In a growing population of genomes with no selection pressure, the total number of alleles _______ every generation.
increases
how do we estimate origin of alleles?
by comparing alleles, tracing back.
what happens if an allele is advantageous to the organism?
it will always be outcompeted / changing
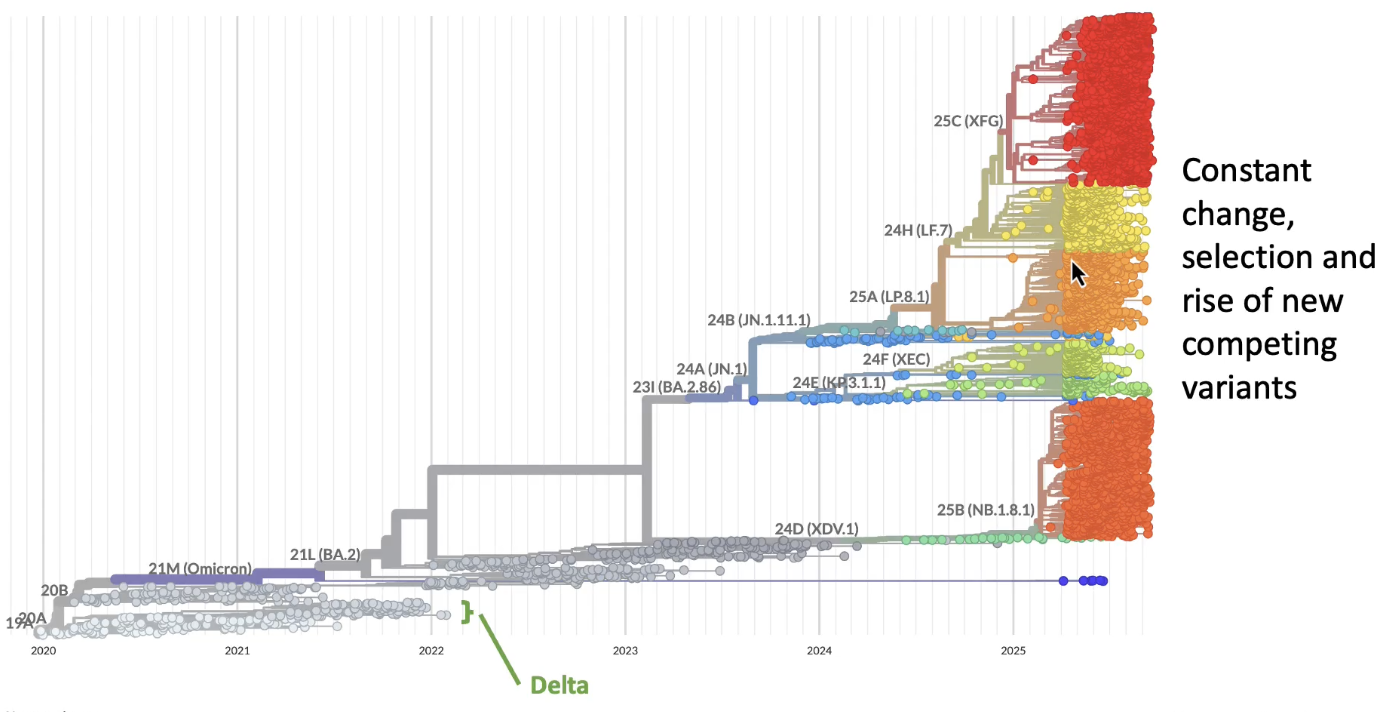
what are the consequences of constantly-changing genomes?
the genome of a zygote accumulates alleles as it divides during development
the fibroblast cells in your skin will have alleles not present in the zygote
these new alleles can lead to cancer
what are living fossils? what is an example of this?
living fossils contain “primitive features”
coelacanth were thought to be extinct when they were observed in the fossil
After being caught in the wild, they are actually cousins of us as tetrapods
Their genomes have also been changing over the past 390M years
how do we explain that even after constant change in alleles, some traits still remain?
some are more advantageous
what are extant species?
species that are NOT extinct
T/F: coelacanth is our ancestor
NO, we share a common ancestor, just like chimpanzees and humans, we diverged due to the instability of genomes
how do we get speciation?
with enough divergence in alleles
think of a tree (of life !!)
what is DNA world?
stores genetic information
very stable, but chemically inert (not static)
without other molecules… no life (biochemical activity)
what is protein world?
can catalyze chemical reactions
can alter other proteins (eg. prions)
‘protocells’ may have existed - concentrated proteins surrounded by lipid membranes
generally unstable - lack the ability to pass on genetic information
what is RNA world?
can store genetic info (in-between level of chemical stability)
can catalyze reactions: ribozyme = RNA enzyme
overtime:
RNA makes proteins
RNA makes a more stable template of self
gives rise to the central dogma: DNA → RNA → protein
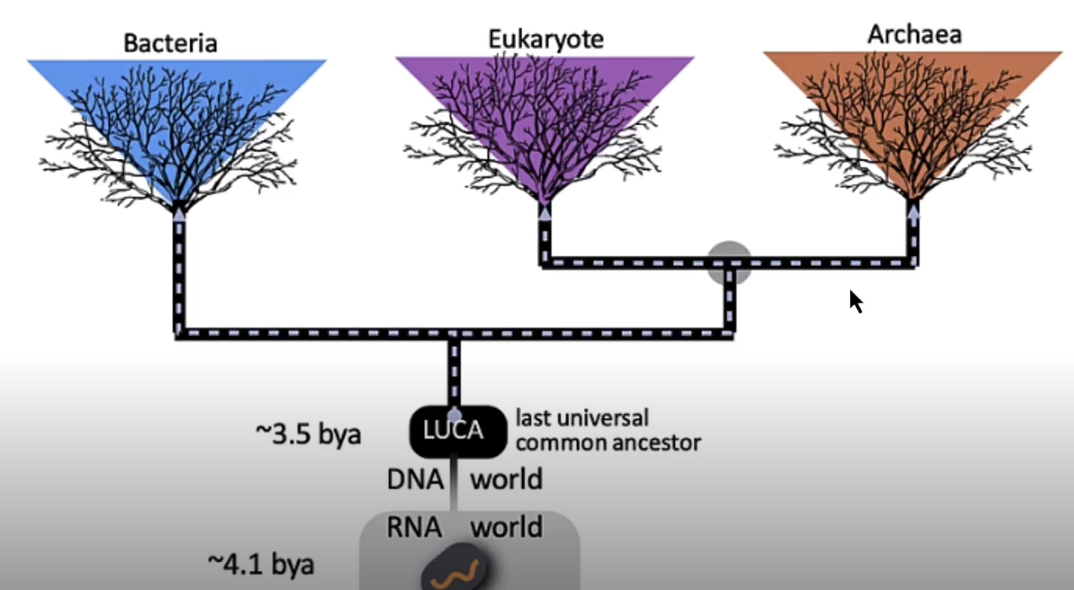
what is at the centre of the tree of life?
LUCA - last universal common ancestor (~3.5 billion years ago)wha
what are the three domains of the tree of life?
bacteria, eukaryote, archaea
but they can have cross-overs
what does genetics (study of sequence variation) tell us?
about history of life and its evolution
how inheritance works
the chemistry of life
what genes are required for a process or trait
why is it easier to analyze genome sequence from cells in a male rather than a female?
males only have one X chromosome, females have two.
there is only one copy of the region sequenced, so we don’t have to worry about potential allelic differences between the homologous X chromosomes
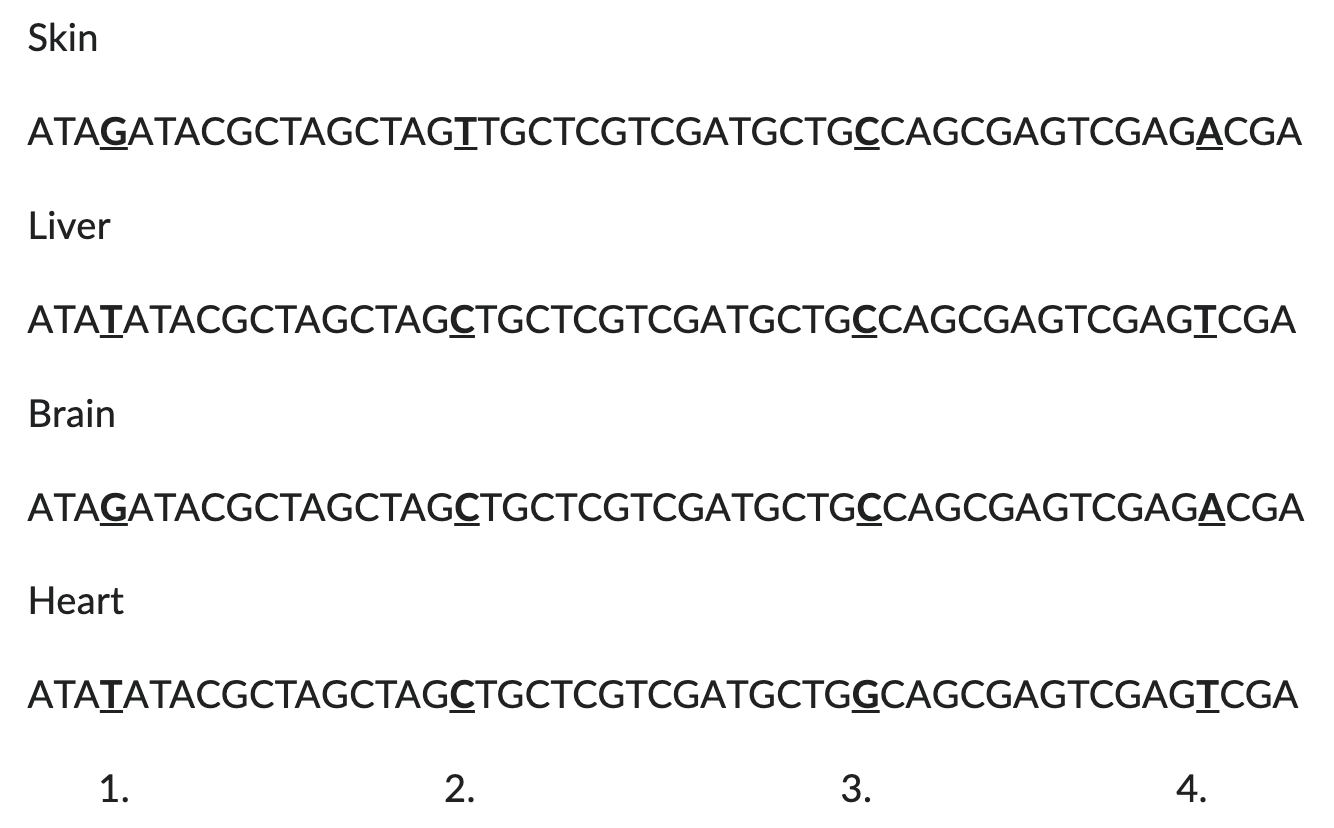
which pairs of cells share the most recent common ancestors with each other (eg. share the same lineage)?
skin and brain same except for one SNP
liver and heart same except one SNPskin and brain, liver and heart
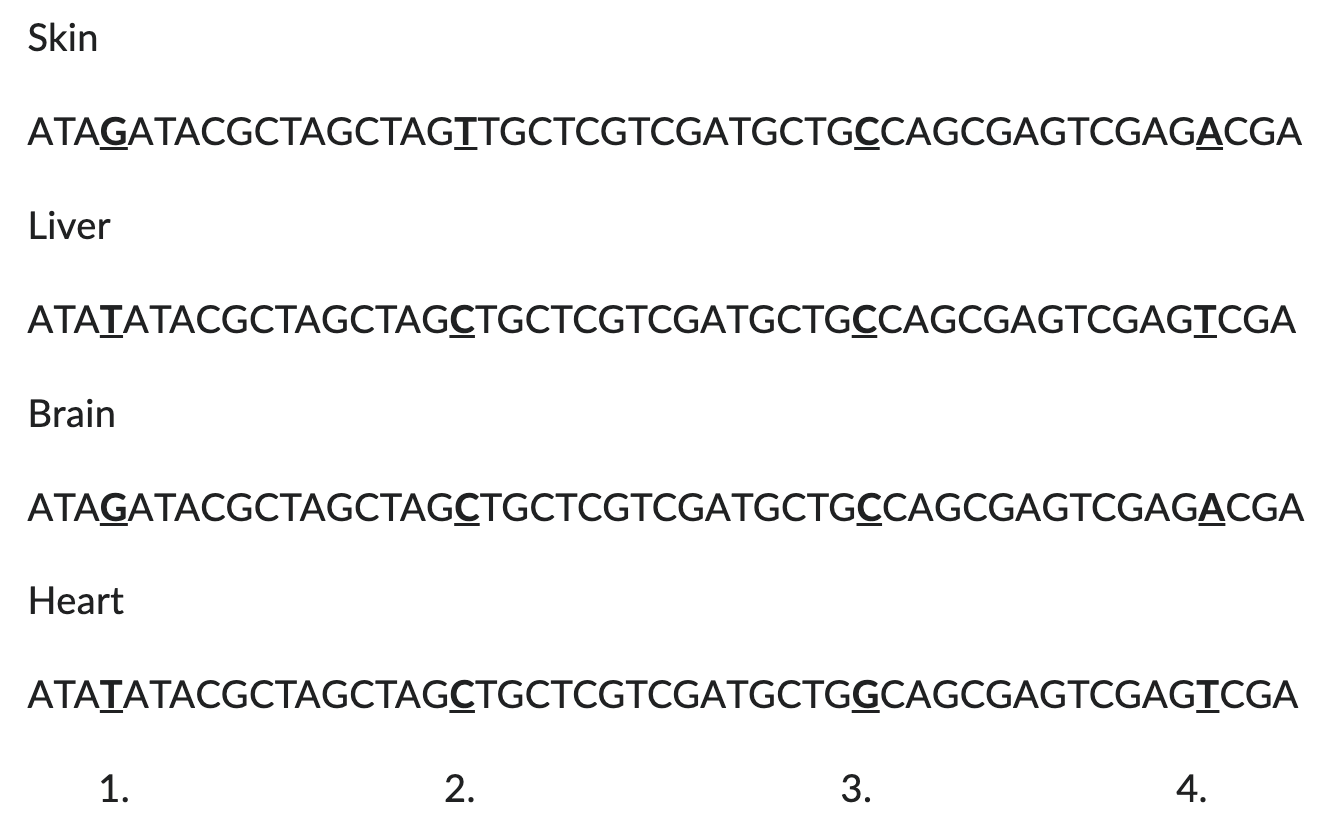
at the second and third position, what would the sequence most likely have been in the zygote?
2 = C
3 = C
the zygote would be the origin for all of the tissues, so we are looking for the least amount of changes / the most common sequences. It must also match with the lineages. C is most common for 2nd position and C is also most common for third position, and the Cs are shared in both lineages.
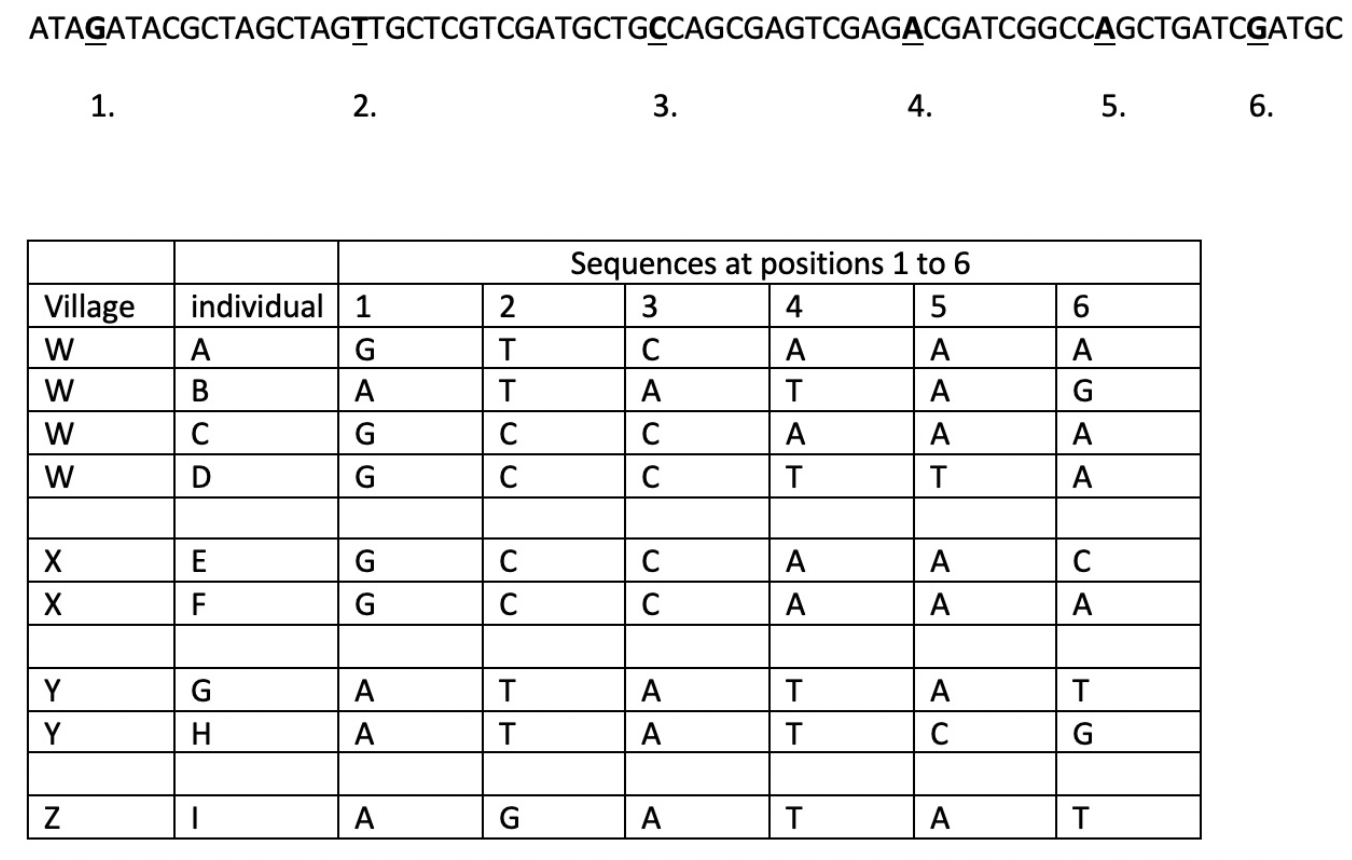
which individual in village W has the virus that’s most similar to the infections in village X?
C
(GCCAAA) has no difference from F
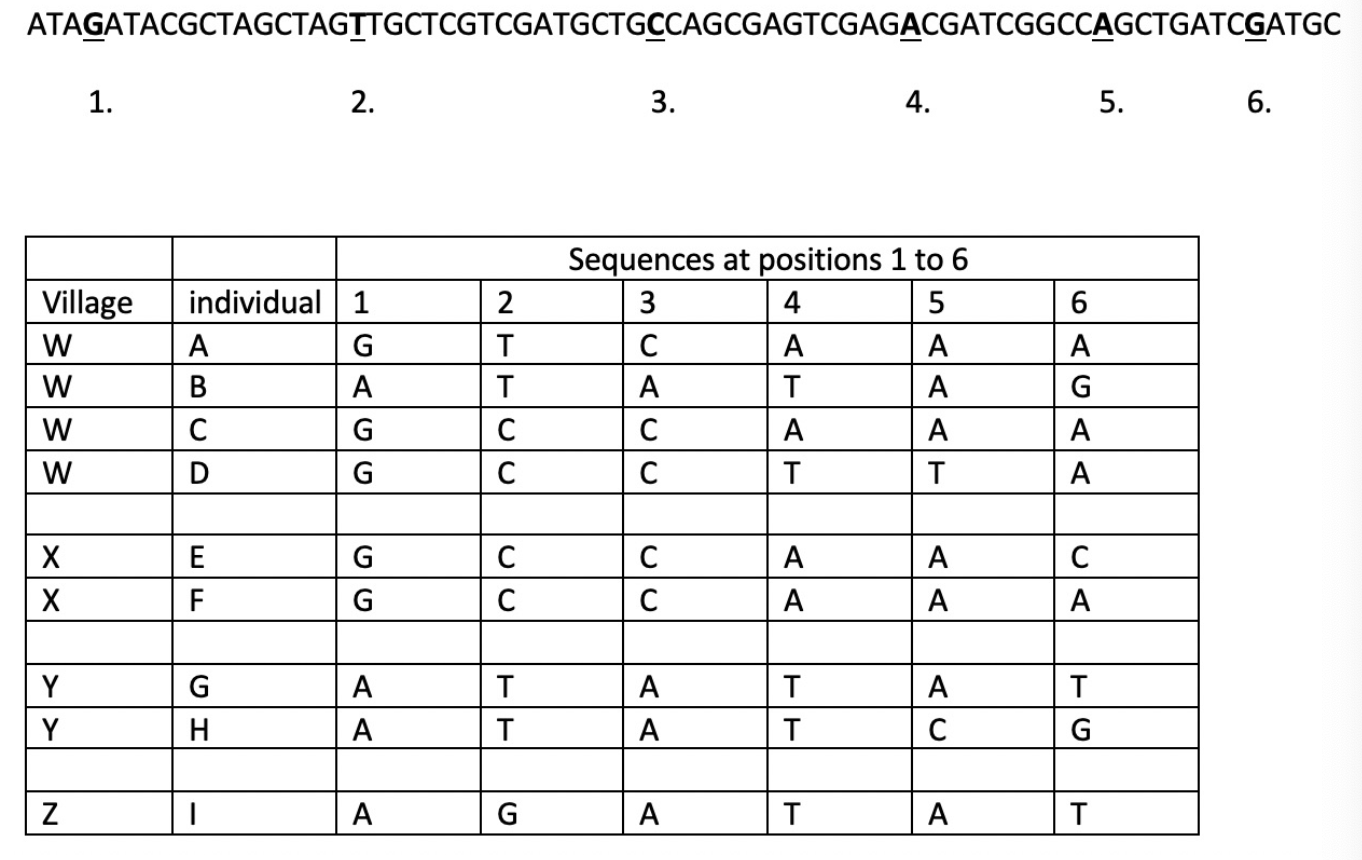
which individual in village W has the virus that’s most similar to the infection in village Y?
B
it only has one difference from H
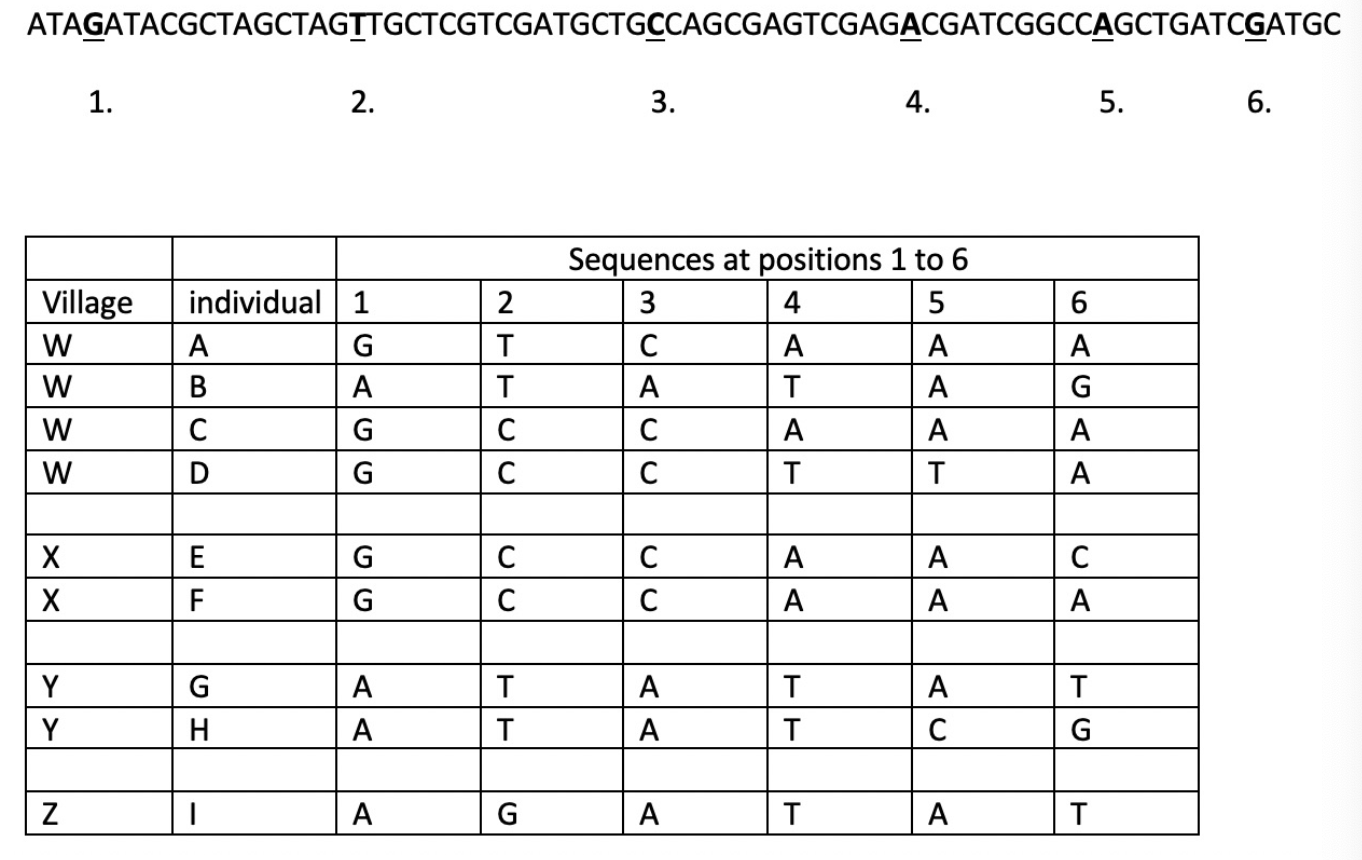
the infection in village Z most likely came from village _____ .
Y
individual I has only one difference from G
what is synthetic biology?
multidisciplinary area of research that seeks to create new biological parts, devices, and systems.
are viruses living forms of life?
no, because they are dependent on a host cell for infection
T/F: we have genes from both bacteria and archaea
TRUE: alpha-proteobacteria for metabolism and archaea for information storage & processing
why does animal genome come from both bacteria and archaea?
endosymbiosis !!
the origin of mitochondria = the origin of ______
the origin of eukaryotes
when did endosymbiosis occur between archael and alpha-proteobacterial cells?
~1.8 billion years ago
how many organisms are involved in endosymbiosis?`
2 distinct organisms with 2 genomes
what are the 2 organisms that united in endosymbiosis? anaerobic or aerobic? what’s their metabolism mechanism?
archeae (anaerobic) metabolizes through fermentation
alpha-proteobacterium (aerobic) - performs cellular respiration
fermentation is very _____ at generating ATP from glucose. How many ATP molecules are made?
POOR, each molecule of glucose that’s fermented through anaerobic fermentation → 2 ATP
how many ATP can one glucose molecule make in cellular respiration in the presence of oxygen?
30 ATP
T/F: mitochondria is the site of cellular respiration in eukaryotes.
TRUE
5 key steps of endosymbiosis
feeding (phagocytosis)
symbiosis
sharing
entrapment
transfer of control and genetic integration
what happens during the first stage of endosymbiosis? can all bacteria do this?
FEEDING
the archael cell (A) consumes the alpha-proteobacterial cell (B) through phagocytosis
NO, this complex process is not performed by all bacterial cells
what happens during the second stage:
During symbiosis, the bacterial cell remains undigested, it floats around the cytosol of cell A.
what happens at the 3rd stage?
During sharing, A & B cells develop a relationship where they share metabolites (eg. enzymatic functions)
this is the basis of their symbiotic relationship.
T/F: during stage 3: SHARING, B alpha-proteobacterial cell can still survive outside archeal cell A if released.
what are the exceptions?
TRUE, it would still be able to be a free-living organism !
but if B gets a random mutation and lose certain enzymatic functions, it wouldn’t be able to live as free-living.
what happens at stage 4?
ENTRAPMENT
cell B is now completely dependent on cell A
cell B already has its essential genes mutated
“if you don’t use it, you lose it !!”
their relationship strengthens
common genes can also be lost due to redundancy
what is an “evolutionary ratchet”? which cell type has become more complex?
a genetic change that increses the complexity of a biological system that’s hard to undo
loss of gene function - it’s impossible to undo the relationship, and the cell type is now more complex because it has acquired cell type B
what is the final stage?
GENE TRANSFER
in every endosymbiotic event
majority of cell type B is transferred into the nuclear genome of cell type A (host)
this gives cell type A better control of cell type B
only a few remnants remain of cell type B
what sets the stage for gene loss?
gene transfer - when the same genes are present in both cell types’ genomes
gene will be inactivated from the bacterial genome over time
what was the experimental evidence of gene transfer?
an active TRP1 was integrated into the mitochondrial genome - not functional, because mitochondria can’t express nuclear genes
then, inactivated the nuclear version of trp1 → inactivated trp1 allele → the starting cell can’t grow on medium that’s lacking tryptophan
the only way for the cell to be rescued is if the active trp1 migrates to the nuclear genome
what is the result of endosymbiosis? what benefits did it bring for eukaryotic cells?
cell type A and B become a single organism
almost all the endosymbiont genes are lost or transferred to host
gave eukaryotic cells a new source of energy production
gave rise to organelles (distinct genetic compartment) - bacterias don’t have
what genes are expressed in our mitochondrial genomes (remnants)? what do they have in common?
2 rRNAs
22 tRNAs
13 mRNAs for oxidative phosphorylation (part of the ETC in mitochondria)
they’re proteins embedded in the mitochondrial membrane
what is a genetic merger?
merging 2 genomes into 1
there’s still technically 2 genomes
why is mitochondria the powerhouse of the cell?
because the endosymbiotic event gave rise to mitochondria, giving the initial archael cells the ability to perform cellular respiration.
eg. yeast can carry out both anaerobic fermentative metabolism in the cytosol, aerobic cellular respiration in mitochondria via oxidative phosphorylation and ETC
where else has endosymbiosis also occurred?
plant and algal genomes !! - the breakdown of their genome has alpha-proteobacteria and archaeal genes and cyanobacteria
why do plants and algal genome contain cyanobacteria?
because of a second endosymbiosis that occurred to give rise to photosynthetic plants and algae.
what happened after the endosymbiosis of archaea and alpha-proteobacterium? about how long ago did this occur?
endosymbiosis of eukaryotic cell (with mitochondria) that engulfed a cyanobacterium (photosynthetic).
this happened ~1.5 billion years ago
T/F: the endosymbiosis of eukaryotic and cyanobacterium cell follows the same 5 stages of endosymbiosis
TRUE !!
what did the cyanobacterium cell become after endosymbiosis?
chloroplasts !!
they also have genomes
T/F: cyanobacterial genes are seen in both plant and algal nuclear genome.
TRUE !!
what are 3 organisms that resulted from cyanobacteria endosymbiotic event (primary)?
red algae, land plants, green algae
they all derived from the same endosymbiotic event
what are secondary chloroplasts?
chloroplasts that occurred as a result of a second endosymbiotic event observed in nature
what 2 cells are involved during secondary endosymbiosis?
a non-photosynthetic eukaryote (with no chloroplast) engulfing a eukaryote with chloroplast
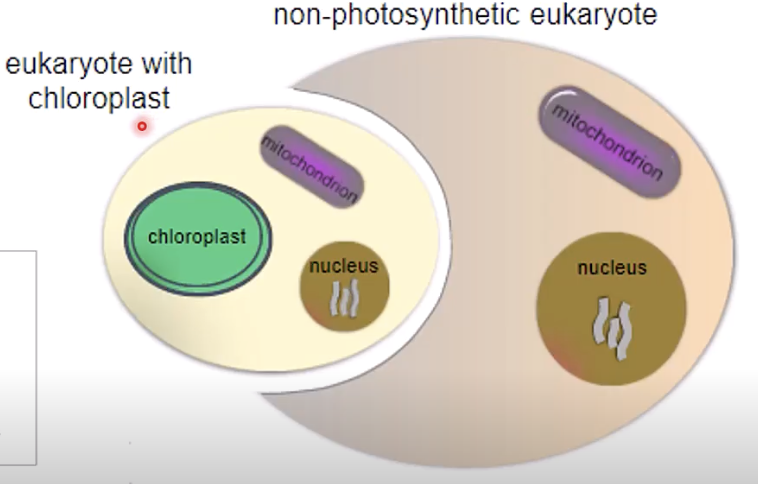
what happens to the mitochondria and nucleus during secondary emdosymbiosis (since the original cell already has them)
they are lost overtime and incorporated as membranes in the secondary chloroplast
the chloroplast has an extra membrane
what is the difference between a regular chloroplast and secondary chloroplast?
secondary chloroplasts have extra membranes
what are nucleomorphs? how many genomes do they have?
when the eukaryote with secondary chloroplast doesn’t fully lose its nuclear genome - incomplete integration
they have 4 genomes (mitochondria, nuclear (host), remnant nuclear, and chloroplast)
what are 2 examples of organisms that derived from secondary chloroplast endosymbiosis?
malaria parasite - Plasmodium
Dinoflagellates
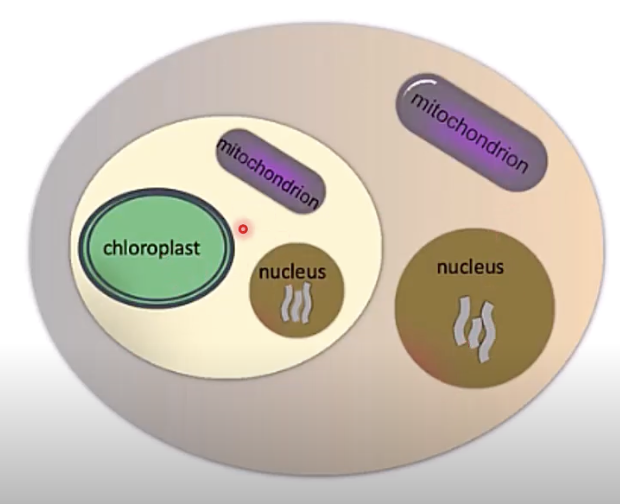
how many genomes are present?
5
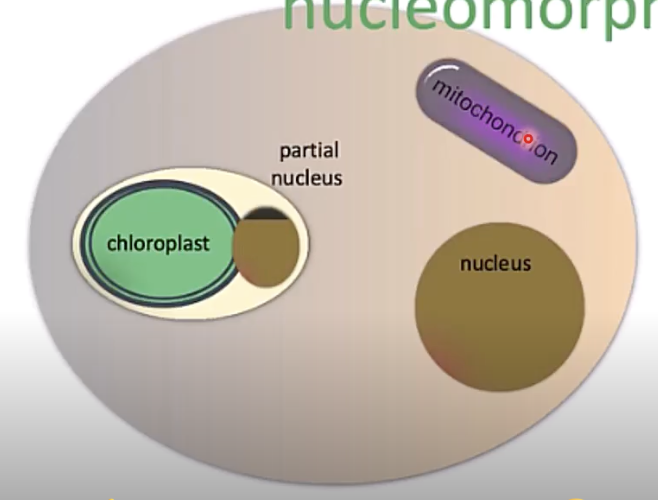
how many genomes ?
4
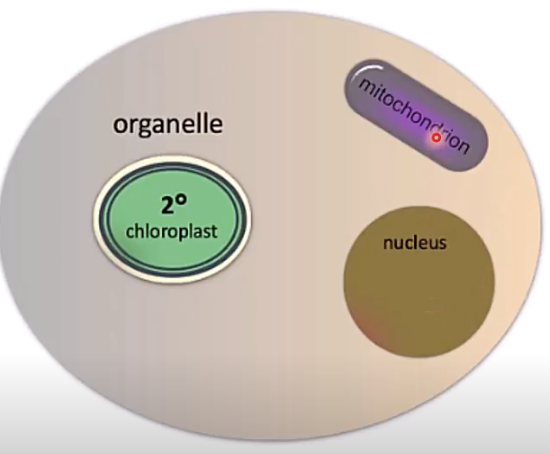
how many genomes?
3