URR CTLPathology 42% Liver
1/152
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
153 Terms
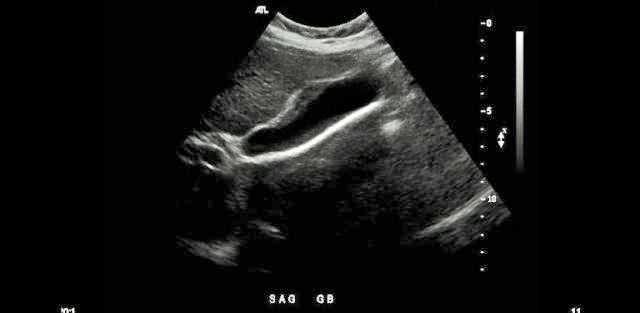
Which liver pathology is most commonly associated with the gallbladder pathology demonstrated on the image?
Hepatitis |
A patient presents with lower extremity edema and increased abdominal girth 2 weeks after a liver transplant. These findings are most suggestive of what complication?
|
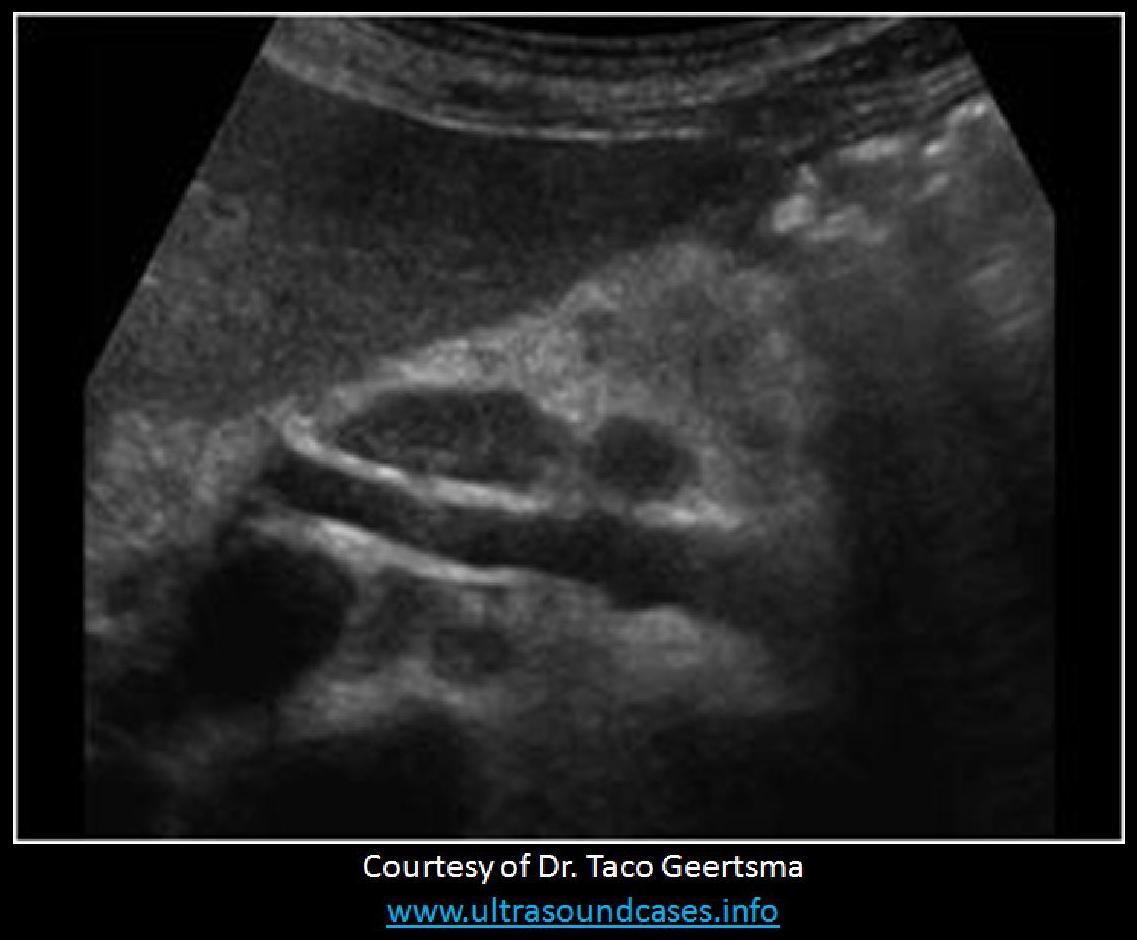
When reviewing a prior US exam for an upcoming follow up exam for the same patient, you come across an image labeled "sandwich sign"? What are they referring to?
lymphadenopathy surrounding the portal vein |
Which of the following describes the appearance of the liver in a patient in the later stages of cirrhosis caused by viral hepatitis?
|
Which of the following describes the most common Sonographic appearance of hepatoma?
Solid mass that may be more or less echogenic than liver parenchyma
Benign liver masses will usually demonstrate ultrasound contrast enhancement during the arterial and portal venous phases of imaging. Malignant masses will usually demonstrate:
contrast enhancement during the arterial phase of imaging |
If discovered in early stages, which of the following effects on the liver can be reversed
Fatty Infiltration |
Fulminant hepatitis is most commonly caused by:
|
What liver complication is associated with cholangitis, diverticulitis and osteomyelitis?
pyogenic abscess |
A mass that presents with a bull's eye appearance within the liver tissue is most likely __________________.
|
The most common parasitic infection in humans is:
schistosomiasis |
A TIPS shunt is placed into the liver circulation to alleviate portal HTN. What two vessels are usually connected
|
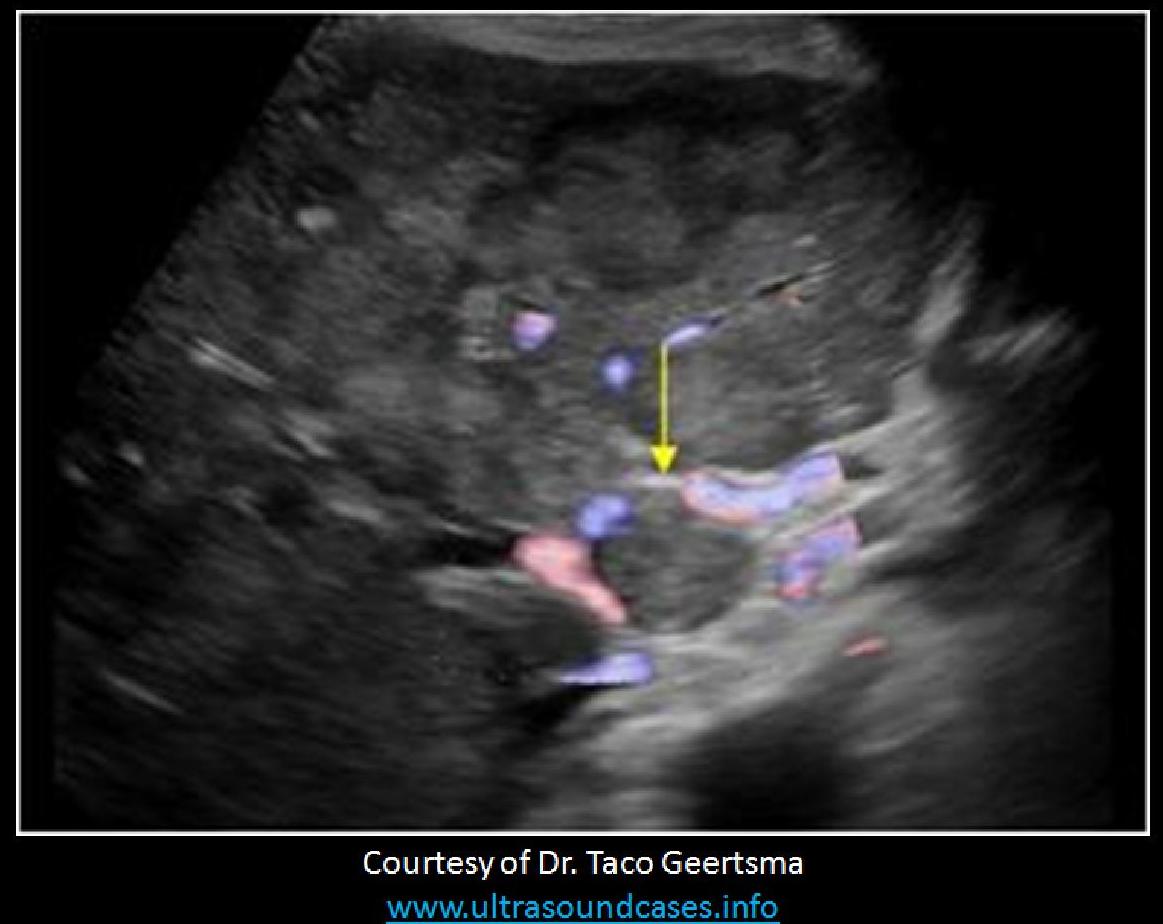
What is the yellow arrow pointing to?
|
Which of the following statements is true regarding the sonographic appearance of fatty infiltration?
As fatty infiltration increases in the liver, the portal vein branches become more difficult to visualize.
Which of the following vessels will be abnormally dilated with significant portal HTN?
|
Reye Syndrome will demonstrate features on liver ultrasound that are similar to:
steatosis |
Periportal cuffing is a sign of:
|
Which of the following is true regarding a liver hemangioma?
A hemangioma is composed of an abnormal concentration of vascular tissues within the liver.
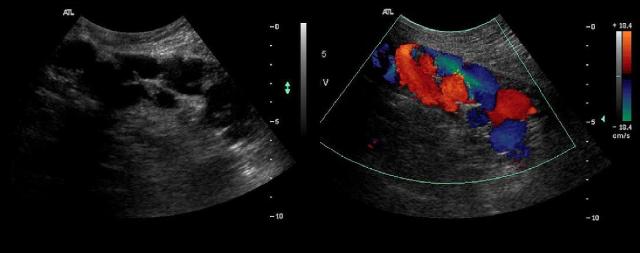
Longitudinal images are presented of the anterior abdomen just superior to the umbilicus. What is the most common cause of the abnormality seen on the images?
|
A patient presents with abdominal pain for 3 months following a missionary trip to India. Lab values demonstrate normal LFTs. The US exam demonstrates a 3cm cyst with septations in the right lobe of the liver. These findings are most consistent with:
hydatid disease |
A patient presents for a follow up ultrasound due to Budd Chiari syndrome. Which of the following is an expected finding on the exam?
thrombosis of the hepatic veins with hepatic congestion |
A patient presents with splenomegaly and multiple, small, tortuous vessels are visualized in the porta hepatis area of the liver. These vessels most likely represent
Cavernous transformation |
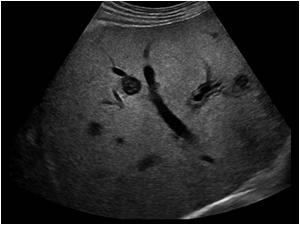
If this is a transverse view of the liver, where is the liver mass located?
anterior right |
While performing ultrasound on the liver, a transverse view reveals a hyperechoic triangular structure in the inferior left lobe. The hyperechoic structure demonstrates an anechoic center that fills with color when Doppler is applied. Which of the following best describes the finding identified on the image?
|
The Ultrasound Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (US LI-RADS) is used to assess patients at risk for:
|
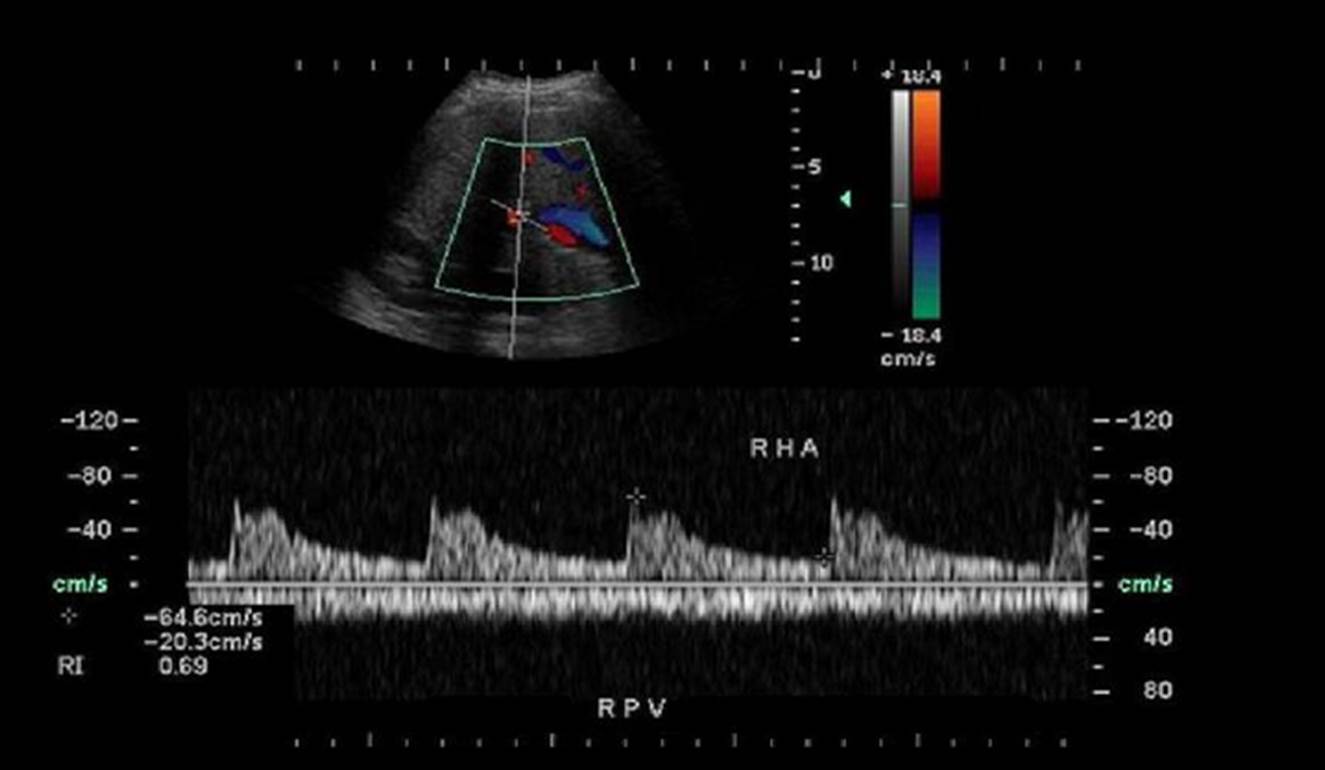
Which of the following statements is true regarding the Doppler evaluation of the liver vasculature displayed?
|
Portalization of the hepatic veins is a common finding in which of the following?
advanced cirrhosis |
Which type of liver abscess presents as a mass with the appearance described as a wheel within a wheel?
fungal |
Hepatic artery hypertrophy is a common finding with
|
Which of the following would indicate a normal Doppler evaluation of an intrahepatic shunt?
|
Which of the following Doppler parameters is most commonly used when evaluating the common hepatic artery in patient with a liver transplant?
Resistive index |
Which liver disorder leads to the sonographic appearance of hepatomegaly with decreased echogenicity and scattered bright portal reflections within the parenchyma?
|
Which of the following describes the Doppler appearance of liver transplant rejection?
High resistance flow in the hepatic artery |
A _____________ abscess is caused by bacteria and most commonly forms within the right lobe of the liver. A _______________ abscess is caused by a parasite and usually forms in the right dome of the liver causing elevation of the diaphragm.
|
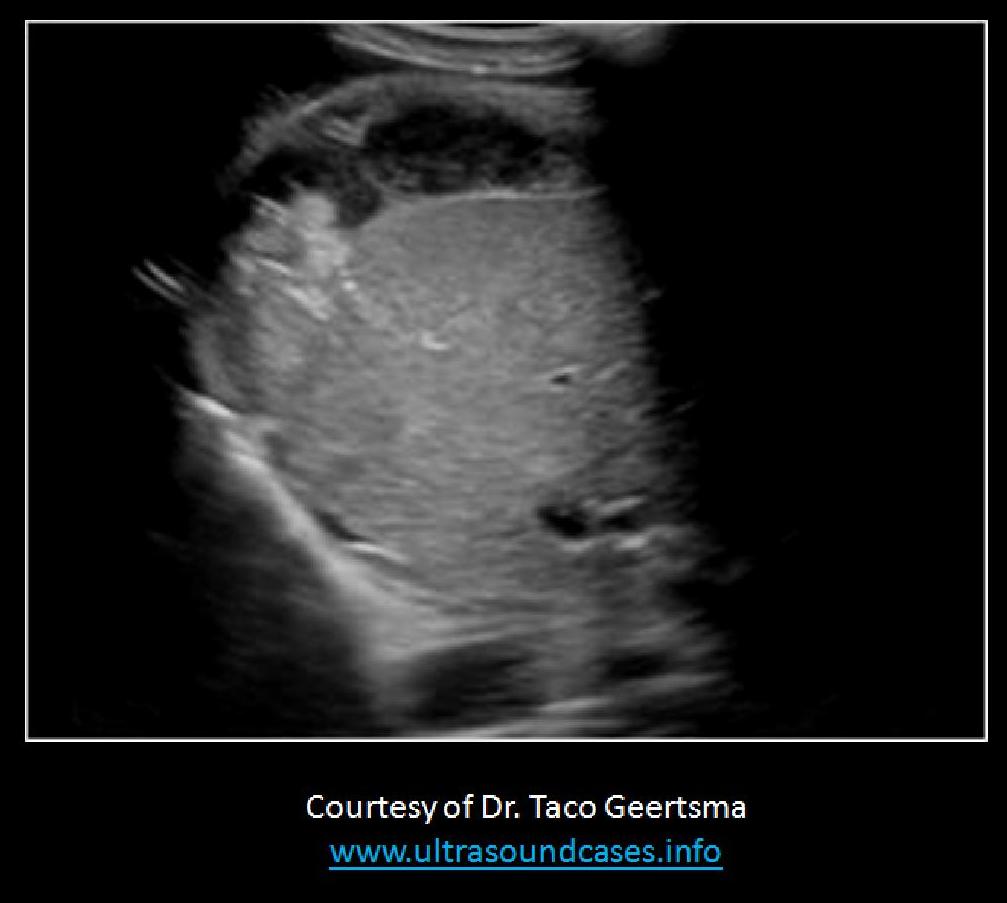
The findings on the transverse view of the RUQ are most consistent with:
subcapsular hematoma of the liver |
A patient presents with a history of hepatitis C and you identify a solid liver mass with a hypoechoic halo, This finding is most consistent with:
|
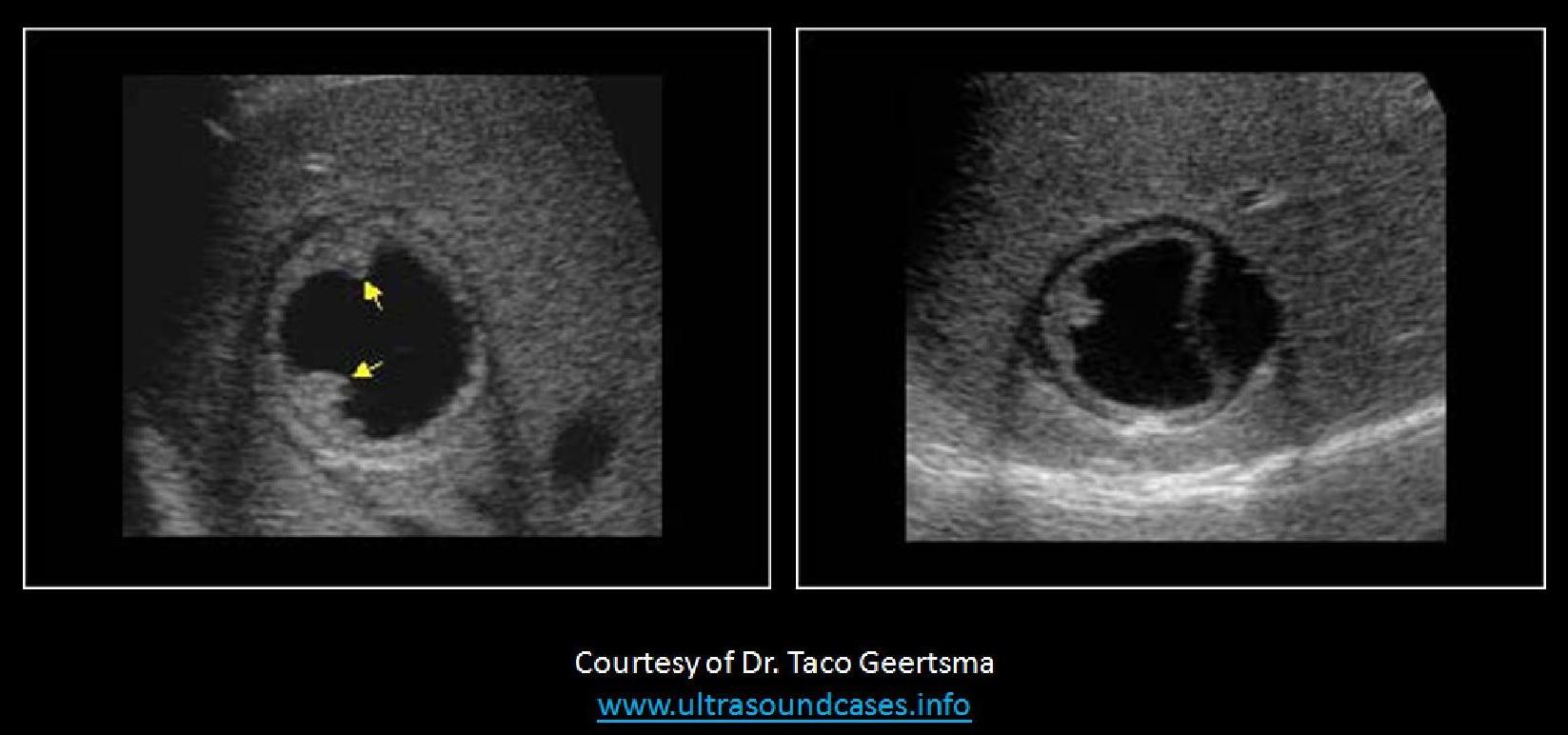
A 40yr old female patient presents with increasing RUQ pain over the last month, beginning upon returning from a trip to Indonesia. The findings on her exam are most consistent with:
|
Portal thrombosis may lead to an accumulation of fluid in the abdomen called:
|
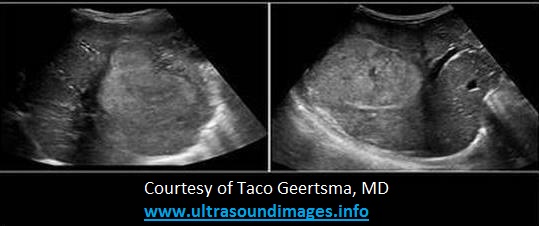
A 4yr old patient is referred for an abdominal ultrasound due to a palpable mass in the RUQ and jaundice. The image most likely represents which of the following findings?
|
Placement of a Linton or Warren shunt is a method used to:
|
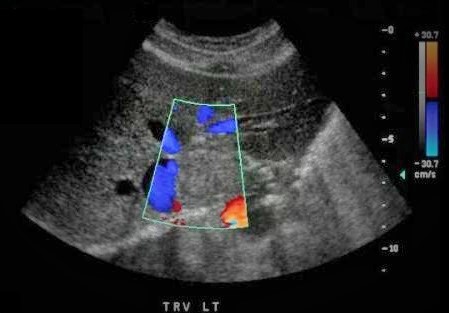
Which of the following statements is true regarding the image displayed?
There is a mass identified in the caudate lobe of the liver adjacent to the IVC.
Which type of liver abscess is caused by a parasite?
|
Which of the following findings indicates a failed transjugular intrahepatic shunt?
|
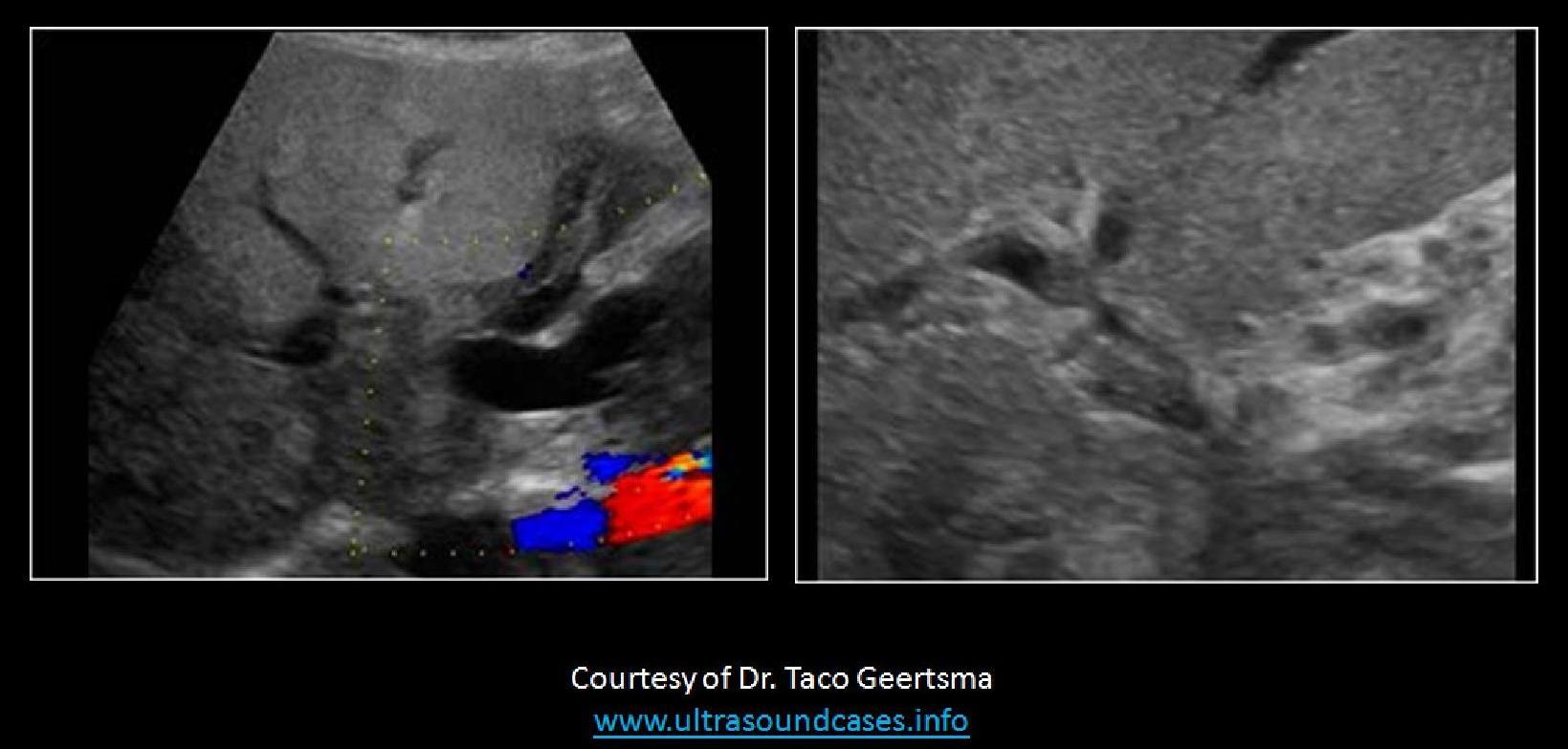
A 50yr old female presents with nausea, vomiting and increased levels of AFP in lab testing. Which of the following pathologies is demonstrated on the image displayed?
Klatskin tumor |
Contrast enhanced ultrasound is used to determine the outcome of tumor ablation in the liver. If the procedure was a success, what are the expected findings on the image?
No contrast enters the lesion during the cardiac cycle |
About 50% of all primary tumors that metastasize to the liver are drained through the:
Portal vein |
What is caput medusae?
tortuous vessels around the umbilicus caused by portal HTN |
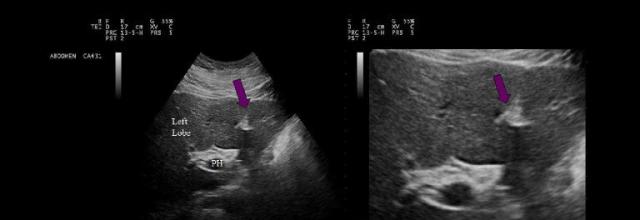
Which of the following liver abnormalities is commonly associated with the recanalization of the vessel within the structure indicated by the purple arrows?
|
If tardus parvus waveforms are identified in the intrahepatic artery waveforms of a transplant, this finding is _______________________. If biphasic waveforms are identified in the right and left hepatic arteries, the finding is _________________________.
suspicious for hepatic artery stenosis, suspicious for organ rejection
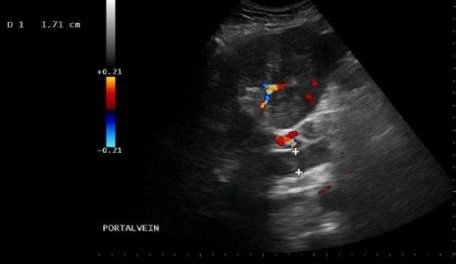
Which of the following statements is true regarding the displayed ultrasound image?
The PV is abnormally dilated at 17mm and is filled with mildly echogenic thrombus.
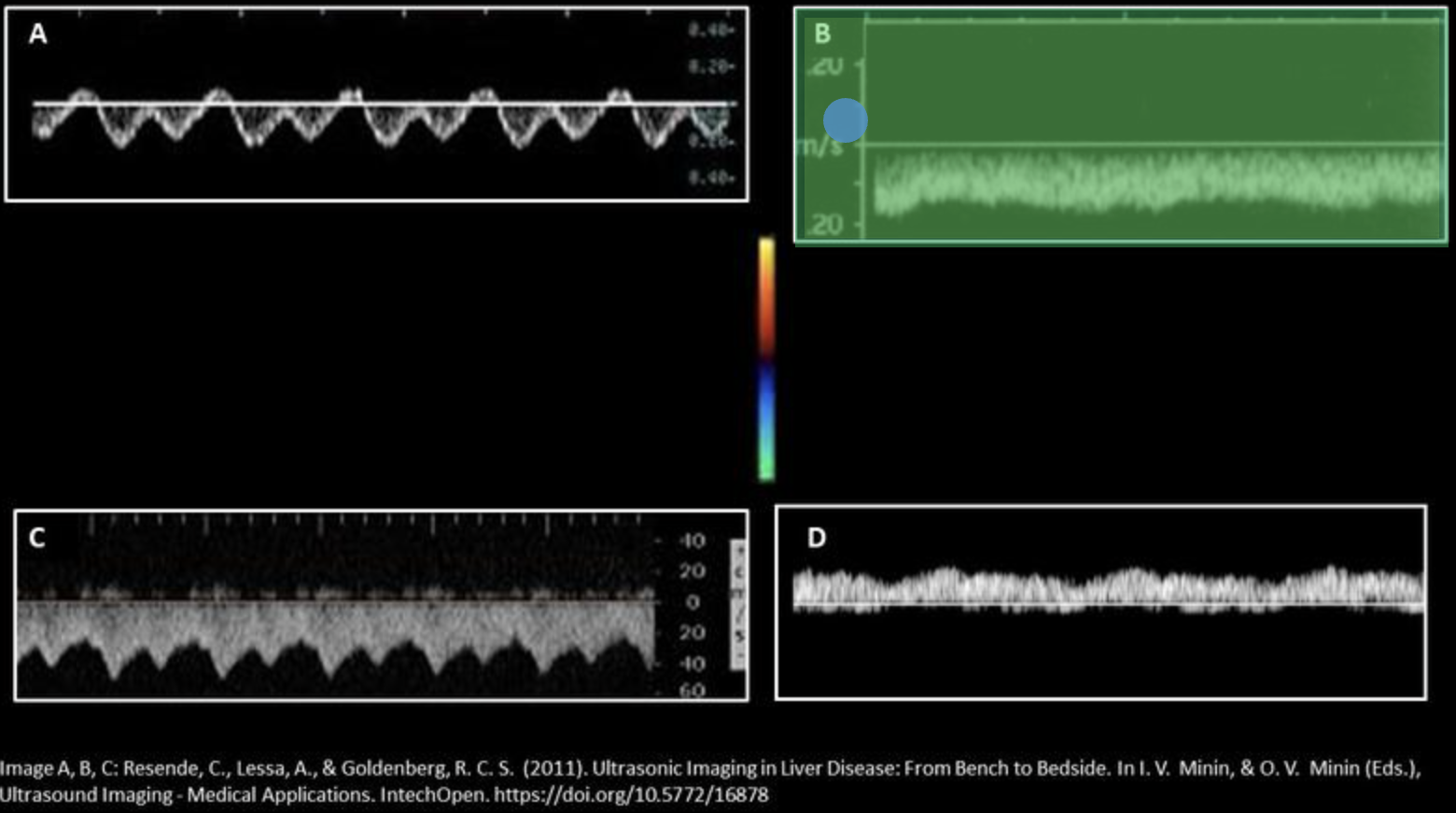
Which waveform represents hepatic vein flow in a patient with advanced cirrhosis? Use your mouse to position your cursor over the correct waveform and click to set the answer.
***the color map displayed applies to all displayed Doppler tracings.
A vascular condition of the liver seen in women who take oral contraceptives is:
Budd Chiari Syndrome |
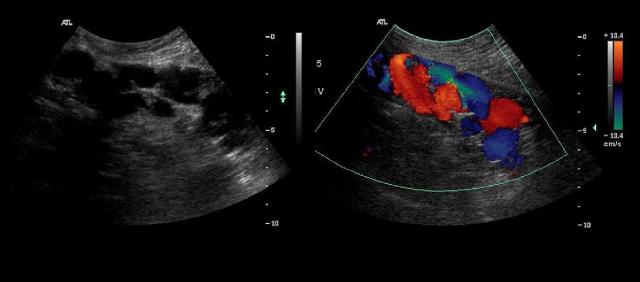
A patient presents for a liver ultrasound due to a history of cirrhosis. While scanning in the subcostal sagittal plane, just to the left of midline, you obtain the images displayed below. Which of the following best describes the findings?
|
Which of the following describes the sonographic appearance of hepatic candidiasis?
mass formation is described as a wheel within a wheel pattern |
__________________ is the most common malignant liver mass found in children.
Hepatoblastoma |
Shear wave elastography can be used to assess the liver. Which of the following correctly describes the results of an abnormal exam?
higher values indicate liver fibrosis |
The most common benign liver tumor is:
Cavernous hemangioma |
What usually causes an echinococcal cyst in the liver?
|
A cyst within a cyst (daughter cyst) is a classic sign of:
Hydatid cyst or Echinococcal cyst |
A patient is referred for a RUQ scan with a 4yr history of treatment for AIDS. The liver demonstrates diffuse presentation of multiple calcifications of different sizes, with and without shadowing. These findings are most consistent with:
|
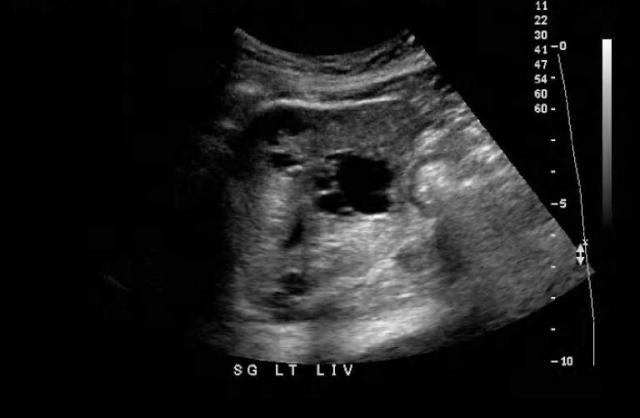
Which of the following organs can be involved in this multi-organ syndrome and can also display the same abnormality seen here in the liver?
|
The most common finding with congestive hepatomegaly is:
|
__________________ can lead to air within the portal venous system and ___________________ can lead to air
Ulcerative colitis, an ERCP |
Hypoalbuminemia associated with cirrhosis leads to
gallbladder and bowel wall thickening
Which of the following sonographic characteristics is associated with Budd Chiari syndrome?
|
A patient presents with increasing RUQ pain and vomiting after a recent liver biopsy. An irregular mass with internal debris and an overall heterogeneous appearance is noted in the right lobe. The mass also demonstrates several echogenic foci with ringdown artifact. These findings are most suggestive of:
|
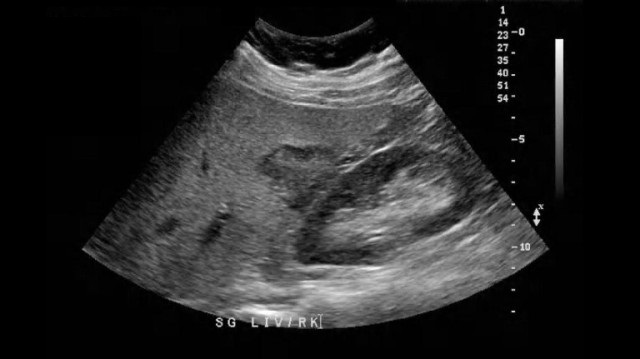
A 65yr old male presents with a history of cirrhosis, RUQ pain, and recent weight loss over the last 6 months. Lab testing indicates abnormal LFTs and increased alpha-fetoprotein. The image displayed is most suggestive of?
Hepatocellular carcinoma |
______ should be suspected in an infant with a large hepatic hemangioma and unexplained thrombocytopenia .
Kasabach-Merritt syndrome
A portal vein diameter that is greater than or equal _____________ indicates portal HTN.
13mm
Which of the following is true regarding a liver hemangioma?
Color Doppler is not usually helpful in evaluating this highly vascular mass.
If a liver transplant patient has an interposition anastomosis, how does this affect your evaluation?f
|
The hormone changes with pregnancy have been associated with the enlargement of what type of liver mass?
hemangioma |
A liver ultrasound demonstrates a hyperechoic mass with smooth borders and posterior enhancement in the posterior right lobe. These findings are most suggestive of:
cavernous hemangioma
A patient presents with a history of RUQ pain. He currently uses anabolic steroids. The exam demonstrates multiple irregular areas of varied echogenicity throughout the liver parenchyma. No internal flow is documented in these areas on color Doppler evaluation. These findings are most suggestive of:
peliosis hepatis |
Which of the following describes the expected waveform from the hepatic vein in a patient with cirrhosis?
|
Which of the following correctly describes how contrast enhanced ultrasound can be used to differentiate benign and malignant masses?
Benign nodules usually demonstrate isovascular enhancement while malignant tumors usually demonstrate hypervascular enhancement
___ is the most common cause for micronodular cirrhosis and ________ is the most common cause of macronodular cirrhosis.
Alcohol consumption, chronic viral hepatitis
A 6 month old female is referred for an abdominal ultrasound due to suspected Kasabach-Merritt syndrome. What are you looking for on the exam?
|
Which of the following is true regarding a transjugular intrahepatic shunt?
|
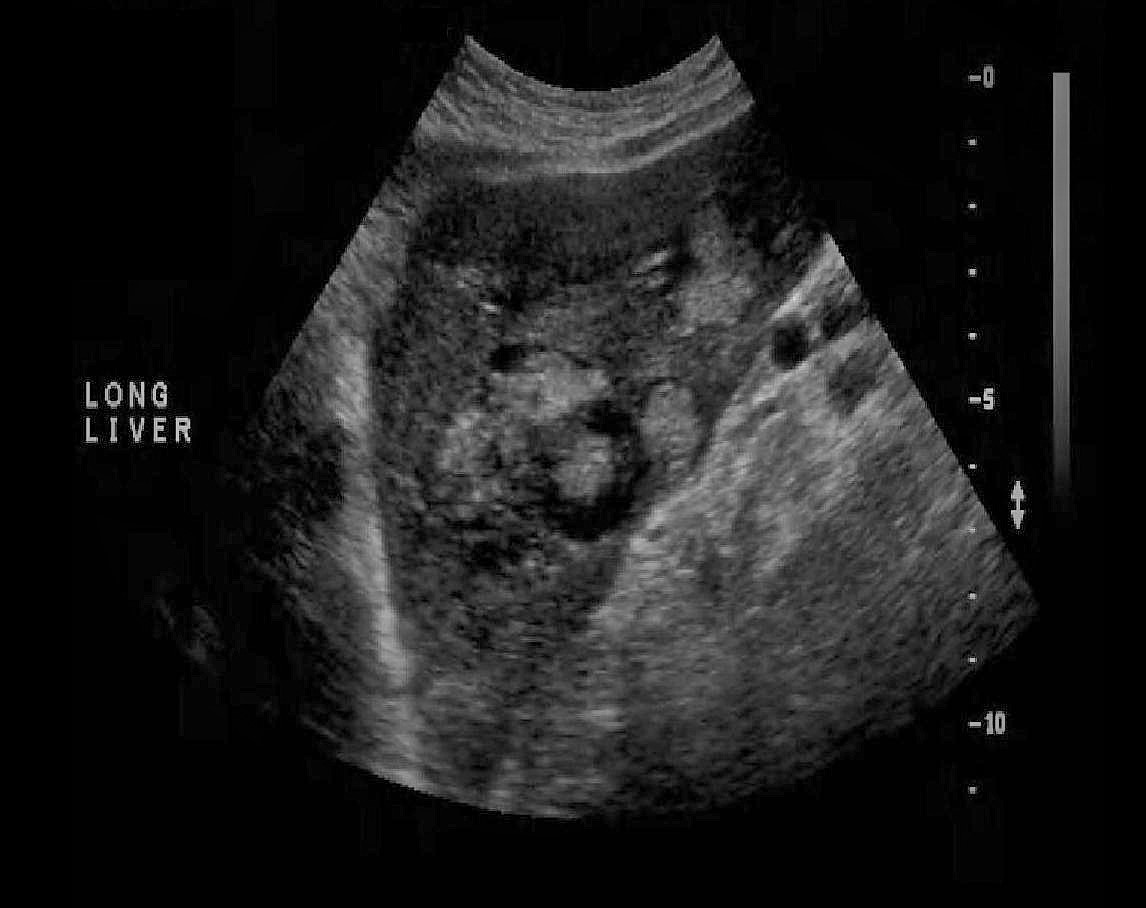
A patient presents with a recent history of gastric carcinoma diagnosis. The image most likely demonstrates which of the following abnormalities?
metastatic lesions |
The most frequently involved organ in metastatic disease is the:
|
Which of the following is a potential collateral pathway formed in patients with cirrhosis?
blood moves from the superior rectal vein to middle rectal vein |
_____ is the most common liver malignancy, while ______ is the most common primary liver malignancy.
|
The ___________lobe of the liver does not normally atrophy with chronic Budd Chiari Syndrome.
caudate
Which of the following findings will indicate hepatomegaly is present?
When the right lobe is rounded inferiorly and extends below the lower pole of the right kidney, the liver is considered enlarged.
High-intensity transient signals (HITS) are seen on the Doppler evaluation of a patient with:
portal venous gas |
What type of liver infection/abscess is commonly associated with immunocompromised patients?
candidiasis |
A 43-year-old female with a history of hepatitis C presents with jaundice, increased abdominal girth and pain. The most probable US finding in the liver will be:
|
A patient presents with a history of AIDS and recent pneumocystis carinii infection. What changes to the liver do you expect to see on the ultrasound exam?
diffuse echogenic foci throughout the liver tissue |
A 10 yr old presents for an abdominal ultrasound with a palpable RUQ mass. He has no history of liver disease and alpha-fetoprotein levels are normal. You identify a 9cm mass in the right lobe that demonstrates punctate calcifications and a central scar. These findings are most suggestive of?
|
___ usually presents as multiple target lesions in the liver.
Metastasis |
A patient is referred for an abdominal ultrasound after a CT demonstrated a possible mass near the fundus of the gallbladder. The ultrasound demonstrates mild hepatomegaly with a mild diffuse increase in echogenicity. The area in question appears hypoechoic to the surrounding tissues. These findings are most suggestive of:
|
What is the most common cause of a hepatic abscess in the US?
|
Which of the following describes the sonographic appearance of focal nodular hyperplasia?
A single mass <5cm with a central scar and prominent central and radial vascularity.
A contrast enhanced ultrasound examination is performed on a patient with suspected hepatocellular carcinoma. What are the expected findings if the exam is positive for HCC?
|
Schistosomiasis is an ________ cause of portal HTN. Budd Chiari syndrome is an ___________ cause of portal HTN
|
A patient presents for a liver ultrasound. A 5cm mass is identified at the porta hepatis of the liver. How will this affect the IVC position in the abdomen?
|
Which of the following is the most common cause for intrahepatic cholestasis?
hepatitis
What is the most common liver malignancy identified on ultrasound?
metastatic tumor |
The primary finding that differentiates liver mass formation from steatosis is:
steatosis will demonstrate normal vessel course through affected areas, while mass formation displaces vasculature