Everyday Memory and Memory Errors: Chapter 8 Overview
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Autobiographical Memory
Memory for specific life experiences, episodic and semantic.
Sensory Component
Visual experience aids forming and retrieving autobiographical memory.
Medial Temporal Lobe
Brain area involved in episodic memory processing.
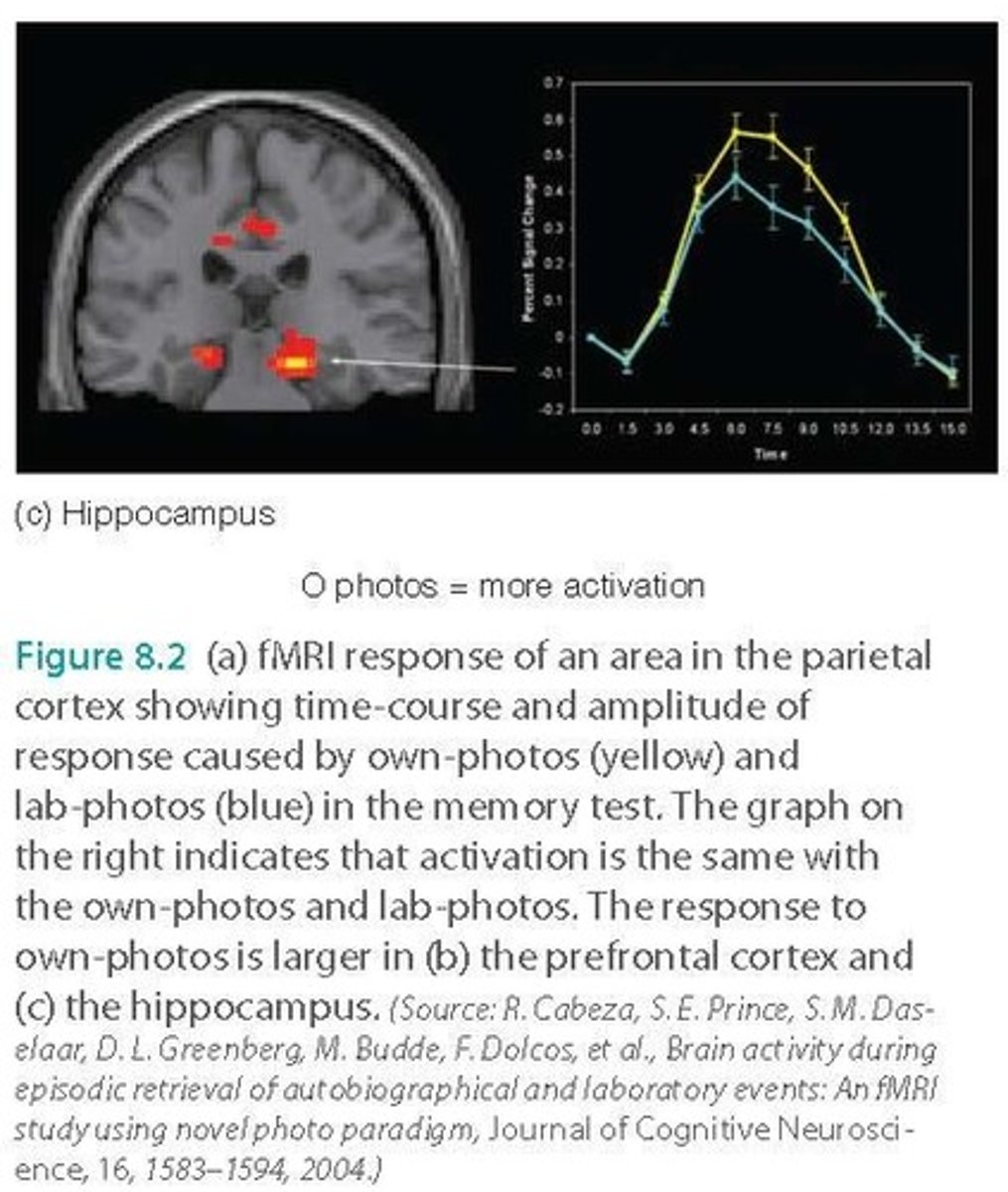
Prefrontal Cortex
Brain region associated with self-referential information.
Hippocampus
Critical for recollection and forming new memories.
Reminiscence Bump
Enhanced memory for events in adolescence and early adulthood.
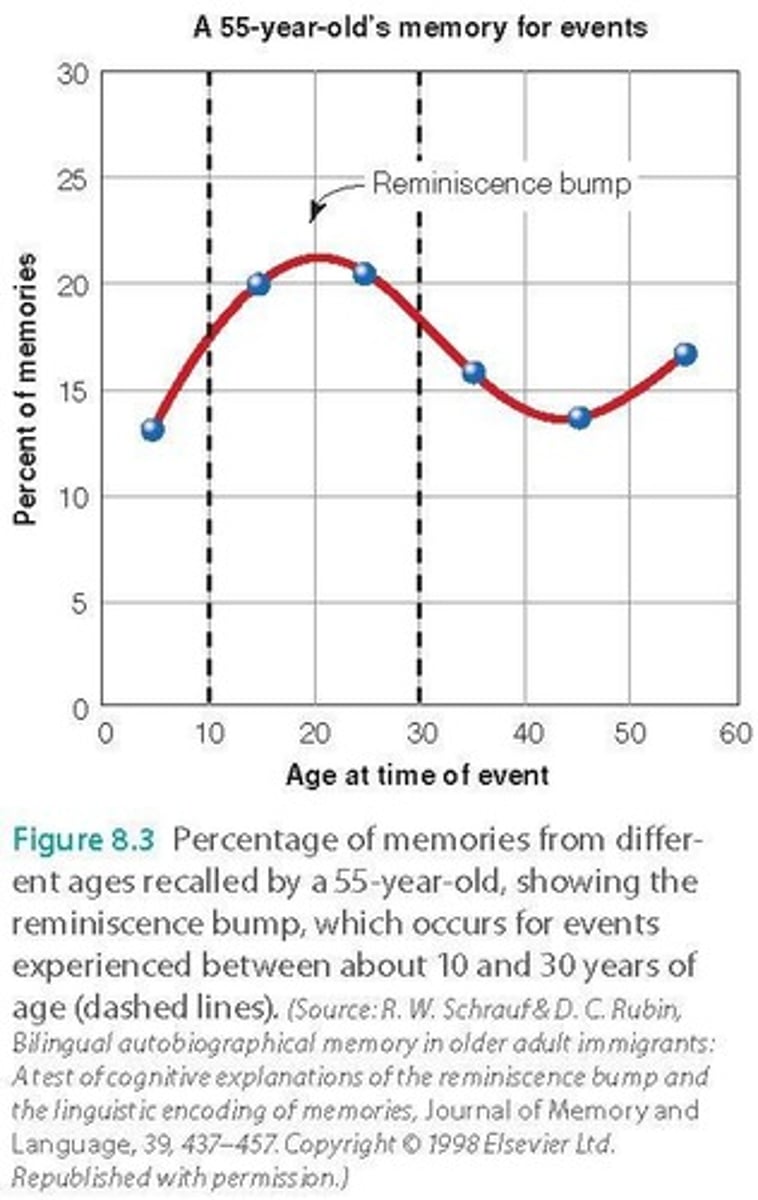
Self-Image Hypothesis
Memory is better for events shaping self-identity.
Cognitive Hypothesis
Better encoding during rapid change and stability periods.
Cultural Life-Script Hypothesis
Personal events easier to recall fitting cultural expectations.
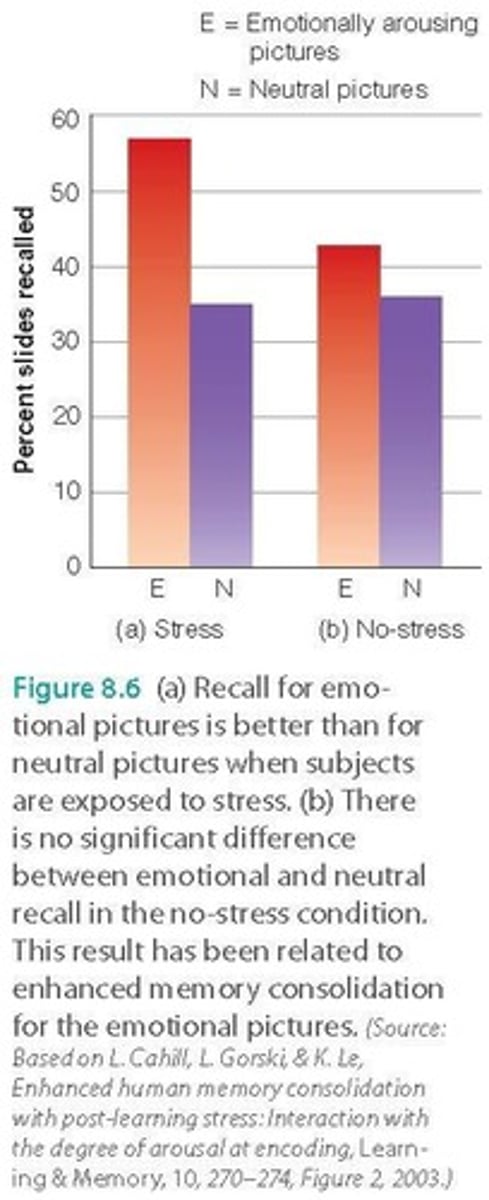
Memory for Emotional Stimuli
Emotional events remembered more vividly and easily.
Weapons Focus
Tendency to focus on weapons during a crime.
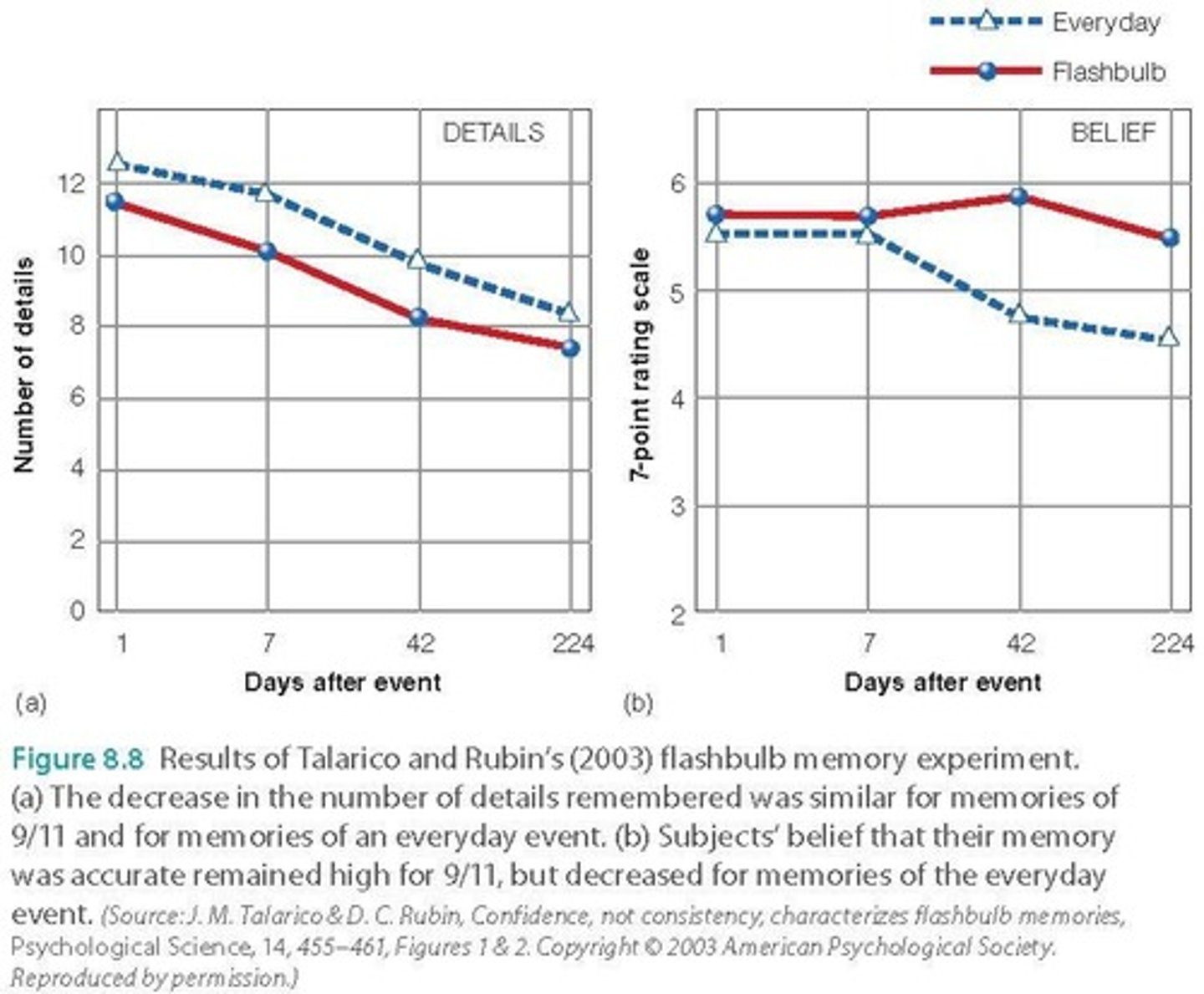
Flashbulb Memories
Vivid memories of shocking, significant events.
Narrative Rehearsal Hypothesis
Repeated exposure can distort memory accuracy.
Constructive Nature of Memory
Memory combines actual events with personal knowledge.
Source Monitoring Error
Misidentifying the origin of a memory.
Cryptoamnesia
Unconscious plagiarism due to source misrecognition.
Episodic Memory
Memory for specific events and experiences.
Semantic Memory
Memory for facts and general knowledge.
Memory Consolidation
Process of stabilizing memories after acquisition.
Emotional Consolidation
Emotion enhances memory retention over time.
Brain Activation
Increased neural activity during memory retrieval.
Significant Life Events
Memorable events impacting personal life narratives.
Memory Over the Lifespan
Patterns of memory retention throughout life stages.
Memory Inaccuracy
Memories can change and become less detailed.
Recollection
Active retrieval of specific details from memory.
Memory Errors
Mistakes in recalling or recognizing past events.