Macromolecules
1/112
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
113 Terms
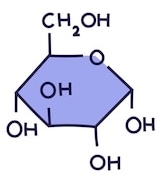
Name this monosaccharide
Glucose
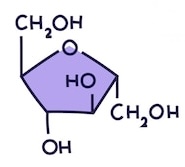
Name this monosaccharide
Fructose
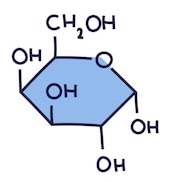
Name this monosaccharide
Galactose
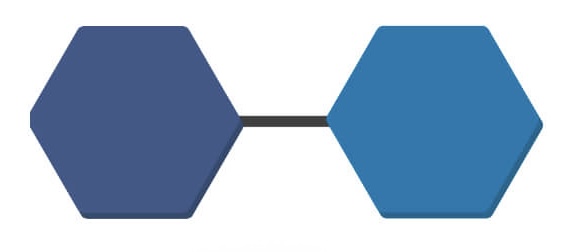
Name this structure
Monosaccharide
(one sugar)
Name this structure
Polysaccharide
(Many sugars)
Name this structure
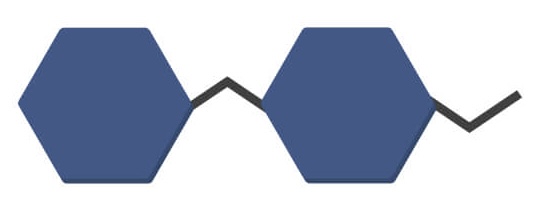
Disaccharide
(Two sugars)
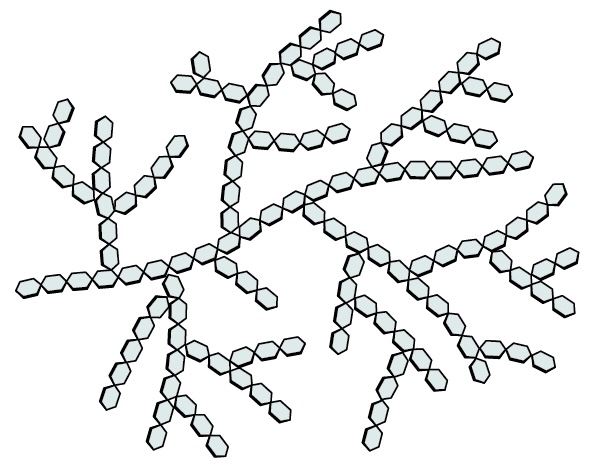
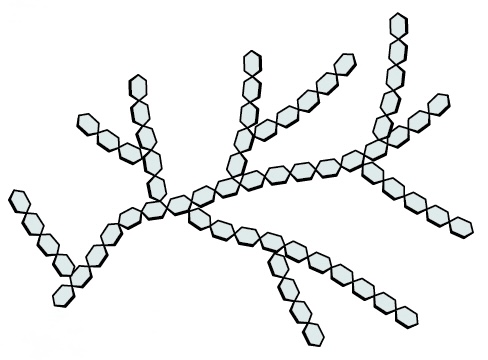
Name this polysaccharide
Glycogen
Highly branched chains
Name this polysaccharide
Cellulose
(Fiber)
Strands joined by hydrogen bonds
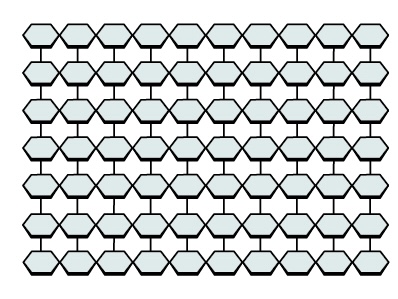
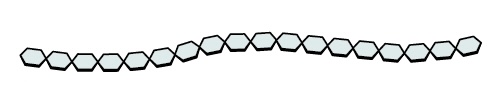
Name this polysaccharide
Starch
(Amylopectin)
Unbranched or slightly branched chains
Name this structure
Amylose
Unbranched starch
What type of bonds are used in carbohydrates?
Glycosidic linkages
What disaccharide is made with glucose and galactose?
Lactose
What disaccharide is made with glucose and glucose?
Maltose
What disaccharide is made with glucose and fructose?
Sucrose
What polymer is used in a carbohydrate?
Polysaccharide
What monomer is used in a carbohydrate?
Monosaccharide
Strands joined by peptide bonds
Peptidoglycan
What is the function of starch and where is it found?
Energy storage
It is found in plant cells
What is the function of glycogen and where is it found?
Energy storage
It is found in animal cells
What is the function of cellulose and where is it found?
Structural support
It is found in plant cell walls
What is the function of chitin and where is it found?
Structural support
It is found in fungal cell walls and insect and crustacean exoskeletons
What is the function of peptidoglycan and where is it found?
Structural support
It is found in bacterial cell walls
What is the most abundant natural biopolymer?
Cellulose
Four major functions of carbohydrates in cells
Energy storage (short term)
Structural molecules made from glucose
Used to build complex molecules
Cell identity markers
What macromolecule has the chemical structure CH2O?
Carbohydrates
They have a 1:2:1 ratio of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen
What is the most common monosaccharide?
Glucose
Define dehydration synthesis
A chemical reaction that joins two molecules together by removing water.
Define hydrolysis
A chemical reaction that breaks down larger molecules into smaller ones using water.
Define cellular respiration
The process of converting chemical energy in food into a usable form of energy for organisms.
Monomer
A small unit that joins with others to form a polymer.
Polymerization
The process of joining small molecules to form a large molecule.
Polymer
A large molecule made of repeating units.
Macromolecule
A very large molecule.
What have 3-7 carbons and are named by carbon number?
Monosaccharides
•Trioses (3) •Pentoses (5) •Hexoses (6)
Isomer
A molecule that has the same chemical formula as another molecule, but with a different arrangement of atoms in space, leading to distinct structural properties and potentially different functions within the organism.
How are disaccharides formed?
Dehydration synthesis
Hydroxyl group
A functional group in chemistry consisting of one oxygen atom covalently bonded to one hydrogen atom. -OH
Glycogenolysis
When glycogen breaks down to release glucose.
Lipids
Non-polar, hydrophobic molecules, including fats, oils, waxes, phospholipids, and steroids.
Triglycerides
•Glycerol + 3 fatty acids
•Energy storage
•Non-polar (hydrophobic)
•3 carbons connected to 3 hydroxyl groups
Phospholipids
•Glycerol + 2 fatty acids + phosphate group
•Form cell membranes
•Amphipathic (charged)
•Most abundant lipid in the cell
Saturated fatty acid
•Single bonds between carbons
•Saturated with hydrogen atoms
•Usually solid at room temperature (butter, lard)
•Forms plaque in arteries
Unsaturated fatty acid
•At least 1 double bond between carbons
•For 1 double carbon bond, 2 hydrogen atoms are removed
•Usually liquid at room temperature (olive oil, canola oil)
•Helps lower blood cholesterol
Steroids
•Fused ring structure
•Hydrophobic
•Signaling molecules; cell communication
-Progesterone
-Estrogen
-Testosterone
-Cortisol
What is the most common steroid?
Cholesterol
Cholesterol
•Found in cell membranes = fluidity
•Precursor to hormones, vitamin D, and bile salts
•Absorbs fats
•Necessary for body function
Trans fats
Unsaturated fat where the hydrogen atoms on the carbon chain are positioned opposite each other, creating a straighter molecular structure, making them behave more like saturated fats
Four major functions of lipids
Energy storage (long term)
Protection and insulation for organs
Structural
Hormones
What monomer is used in a lipid?
Fatty acids
What polymers are used in lipids?
Triglycerides
Phospholipids
What type of bonds are used in lipids?
Ester bonds

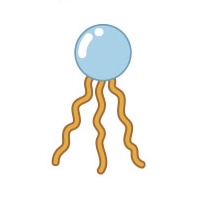
Name this structure
Phospholipid
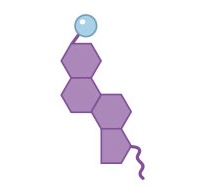
Name this structure
Triglyceride
Name this structure
Steroid (cholesterol)
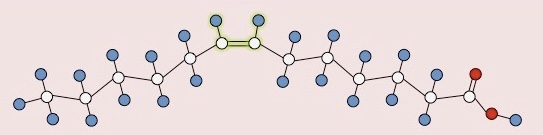
What type of fatty acid is this?
Unsaturated fatty acid (cis double bond)
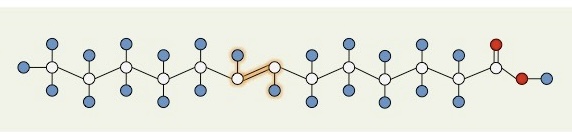
What type of fatty acid is this?
Unsaturated fatty acid (trans double bond)
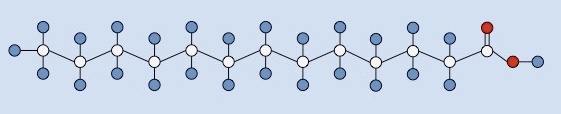
What type of fatty acid is this?
Saturated fatty acid
Define amphipathic
A compound that possesses both hydrophobic and hydrophilic parts.
What part of a phospholipid is hydrophobic?
The fatty acid tails
What part of a phospholipid is hydrophilic?
The phosphate grouped head
What forms a bilayer in cell membranes?
Phospholipids
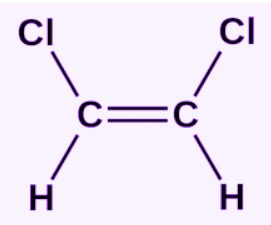
Identify this bond
Cis bond
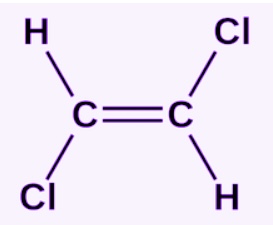
Identify this bond
Trans bond
What is the molecular formula for glucose, galactose, and fructose?
C6H12O6
Amino acids are composed of a central carbon atom bonded to what?
•Amino group
•Carboxyl group
•R-group
•Hydrogen atom
How many common amino acids are there?
20
What type of bonds are used in proteins?
Peptide bonds
What monomer is used in protein?
Amino acids
What polymers are used in protein?
Proteins
Polypeptides
How are amino acids separated from each other?
Hydrolysis
What are called the “building blocks” of proteins?
Amino acids
What is a carbon-nitrogen backbone, also known as a peptide backbone?
A chain of carbon and nitrogen atoms
What is a short stretch of amino acids called?
Polypeptide
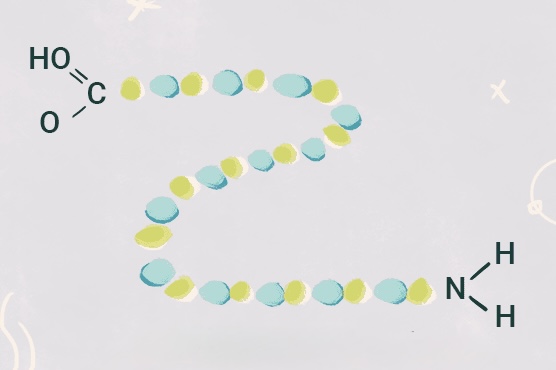
What protein structure is this?
Primary structure
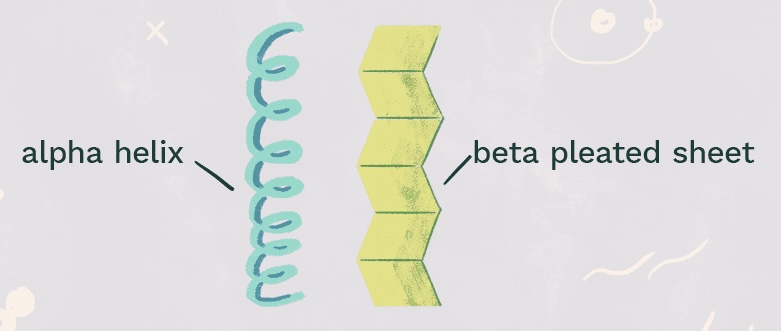
What protein structure is this?
Secondary structure

What protein structure is this?
Tertiary structure

What protein structure is this?
Quaternary structure
What type of bonds do R groups with opposite charges make?
Ionic bonds
What type of bonds do amino acids with polar side chains make?
Hydrogen bonds
What happens between cysteine side chains when they interact?
Disulfide linkages
What is responsible for catalyzing a biochemical reaction?
Enzymes
What are the chemical reactants that bind to an enzyme called?
Substrates
Where does the substrate bind to on the enzyme?
Active site
When an enzyme binds to its substrate and changes shape, what process is this?
Induced fit
What type of protein coordinates the activity of different body systems?
Hormones
What type of protein protects the body from foreign pathogens?
Defense proteins
What type of protein makes up the cytoskeleton?
Structural proteins
What type of protein affects muscle contraction?
Contractile proteins
What type of protein catalyzes chemical reactions?
Enzymes
What type of protein carries substances in the blood?
Transport proteins
Define denaturation
When a protein loses its shape because of heat, pH changes, or exposure to chemicals.
What is the N terminal?
A free amino group (NH2)
What is the C terminal?
A free carboxyl group (COOH)
The shape of a protein determines its _____.
Function
Match the definition with its structure:
Linear sequence of amino acids
Primary structure
Match the definition with its structure:
Folding into alpha-helices or beta-sheets
Secondary structure
Match the definition with its structure:
3D shape of a single protein chain
Tertiary structure
Match the definition with its structure:
Arrangement of multiple protein chains
Quaternary structure
What polymers are used in nucleic acid?
DNA
RNA
What monomer is used in nucleic acid?
Nucleotides