Unit 1: Fluids
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/10
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The substances which can flow. This property applies to liquids and gases. We can't tell that solids can flow due to their high atomic forces of attraction.
Last updated 5:52 PM on 4/4/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
11 Terms
1
New cards
Density
\________ is a positive scalar quantity.
2
New cards
Density
Mass per unit volume of a substance is defined as density.
3
New cards
Buoyancy
If a body is fully or partially immersed in a fluid, it experiences an upward force due to the fluid called buoyant force, and the phenomenon is called buoyancy.
4
New cards
The Volume Flow Rate
It is the volume of fluid that passes through a particular point per unit of time.
***f = Av***
* f = volumetric flow rate
* A = cross-sectional area
* v = flow velocity v
***f = Av***
* f = volumetric flow rate
* A = cross-sectional area
* v = flow velocity v
5
New cards
Bernoulli’s Effect
At comparable heights, the pressure is lower where the flow speed is greater.
6
New cards
Air Flow
The air on the bottom has greater pressure and pushes up on the wing giving the airplane lift force
7
New cards
Pressure
Pressure is defined as the magnitude of the normal force acting per unit surface area.
***P = F/A***
* P is pressure
* F is force
* A is the area
***P = F/A***
* P is pressure
* F is force
* A is the area
8
New cards
Pressure units
* Pascal (Pa) 1 Pa = 1 N/m^2
* Practical units: atm, bar, torr
* Practical units: atm, bar, torr
9
New cards
Hydrostatic pressure
It is the pressure due to the liquid.
10
New cards
Continuity equation
The density of the fluid is constant.
***A1V1 = A2V2***
* A1 and A2 (cross-sectional areas)
* V1 and V2 (flow velocities)
***A1V1 = A2V2***
* A1 and A2 (cross-sectional areas)
* V1 and V2 (flow velocities)
11
New cards
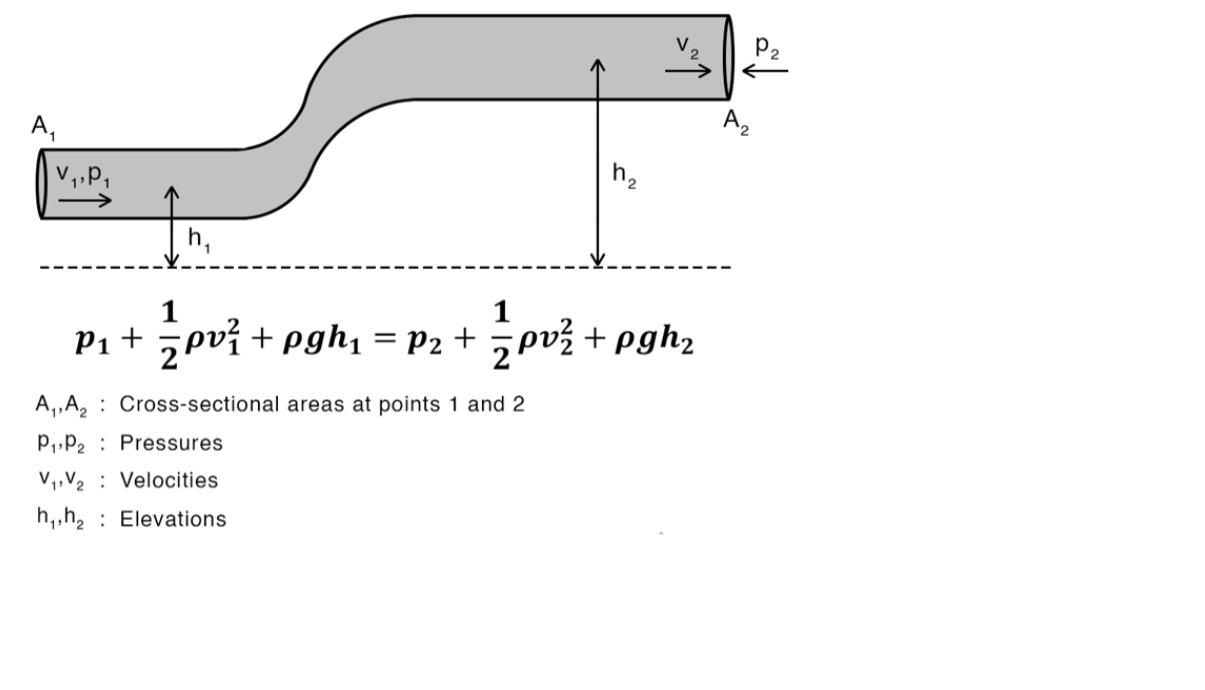
Bernoulli’s Equation (Conservation of energy in liquids)
* fluid is incompressible.
* fluid’s viscosity is negligible.
* fluid is streamlined.
* the equation is very similar to the conservation of energy with total mechanical energy.
* fluid’s viscosity is negligible.
* fluid is streamlined.
* the equation is very similar to the conservation of energy with total mechanical energy.