Annelids
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
16 Terms
What are annelids?
Annelids are segmented worms that belong to the phylum Annelida, characterized by their elongated bodies divided into ring-like segments.
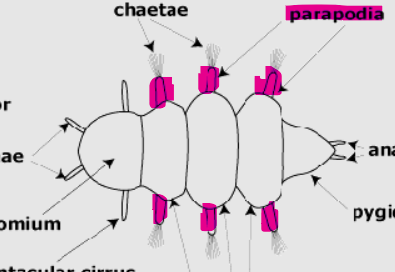
What are chaetae? What are they used for?
Chaetae are bristle-like structures found on the bodies of annelids, primarily used for locomotion and grip in the soil or water.

What are parapodia? What do they do?
Parapodia are paired, fleshy protrusions found on the bodies of certain annelids.
They bear chaetae and function in locomotion, respiration, and sometimes feeding
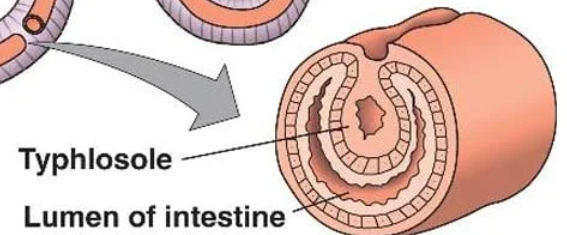
What is a typhlosole? What does it do?
An internal fold of the intestine in certain annelids.
This increases surface area for nutrient absorption.
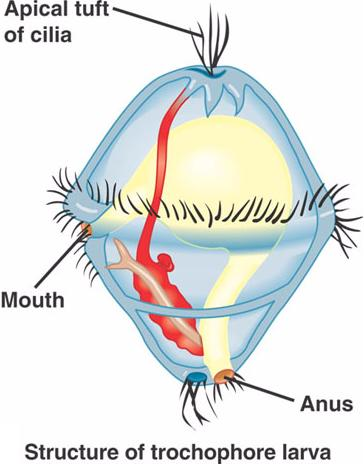
What is a trochophore?
A free-swimming larval stage in the life cycle of many marine annelids and mollusks, characterized by a band of cilia for locomotion and feeding
What is a detritivore?
An animal which feeds on dead organic material, especially plant detritus.
What is an oligochaete? What are some important characteristics?
Oligochaetes are a class of annelids that include earthworms and freshwater worms
Characterized by:
A segmented body
A reduced number of chaetae
A lack of distinct parapodia.
Important detritivore
What is a polychaete? What are some important characteristics?
Polychaetes are a class of annelids that include marine worms
Characterized by:
Numerous chaetae
Well-developed parapodia
Divided into errant (mobile predators) and sedentary (tube-dwellers, filter feeders)
What are hirudinea? What are some important characteristics?
Hirudinea are a class of annelids known as leeches.
Characterized by:
No chaetae
Segments are fused into a functional unit
Anterior and posterior suckers
What is an errant polychaete? What are some examples?
Errant polychaetes are active, free-moving marine worms often recognized for their predatory behavior.
Examples:
Nereis
Fireworms
Bobbit worm
Aphrodite
What are sedentary polychaete? What are some examples?
Sedentary polychaetes are marine worms that remain in one place, often living in tubes or burrows.
Examples:
Sabellids (feather dusters)
Serpulids (Christmas tree worms)
Terebellids (spaghetti worms)
Lugworms
Parchment worms
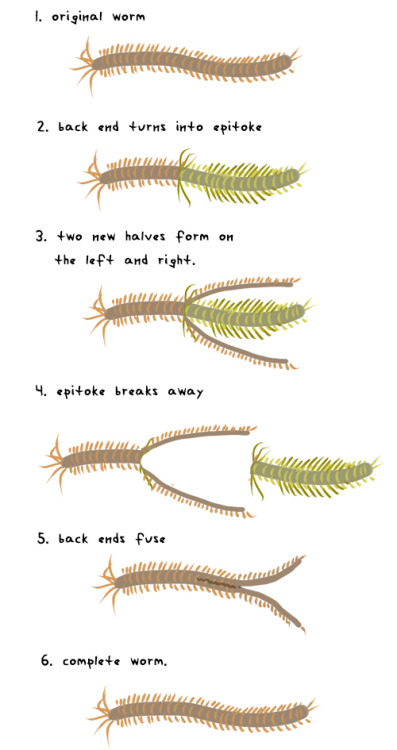
What is epitoky?
Epitoky is a reproductive phenomenon in certain polychaetes where a portion of the worm transforms into a specialized free-swimming form (epitoke), often for breeding purposes.
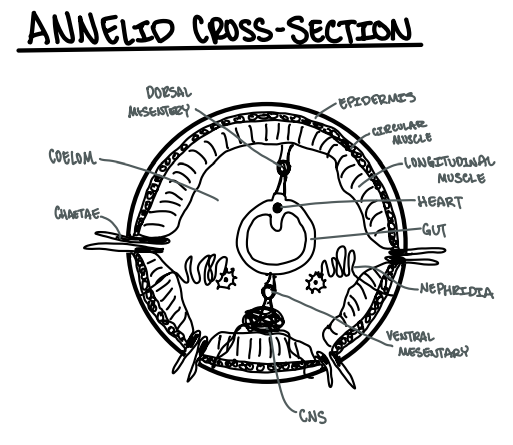
Draw a generic annelid cross-section
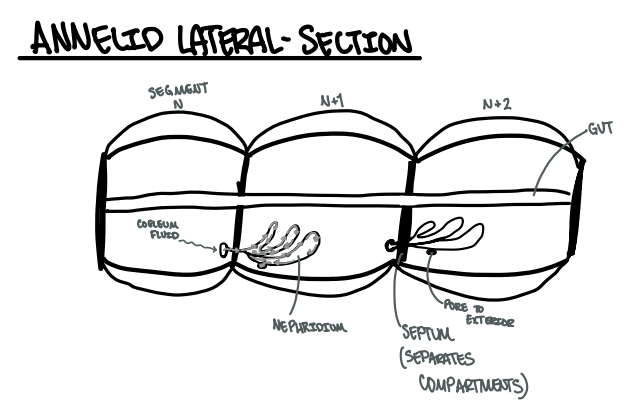
Draw a generic annelid lateral section (showing segmentation and nephridia function)
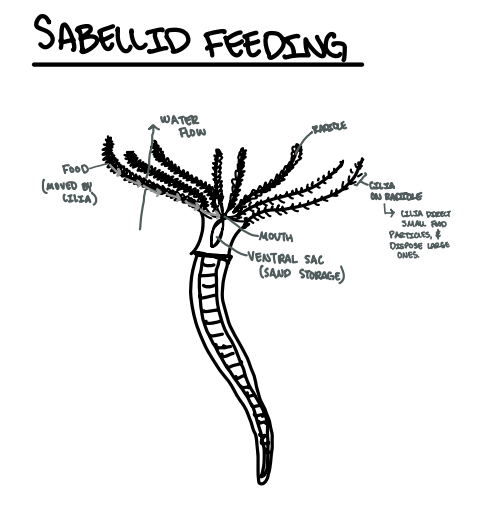
Explain filter feeding and particle sorting in a Sabellid (feather duster) worm
Radioles (crown tentacles) extend into the water column.
Cilia on radioles create feeding currents.
Particles are captured on mucus-coated cilia.
Particle sorting:
Large particles → rejected
Medium particles → used for tube-building
Small particles → transported to mouth for ingestion
Filtered water exits the crown
Draw a depiction of the filter feeding and particle sorting in a Sabellid (feather duster) worm