Menstrual cycle (+ Overview)
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
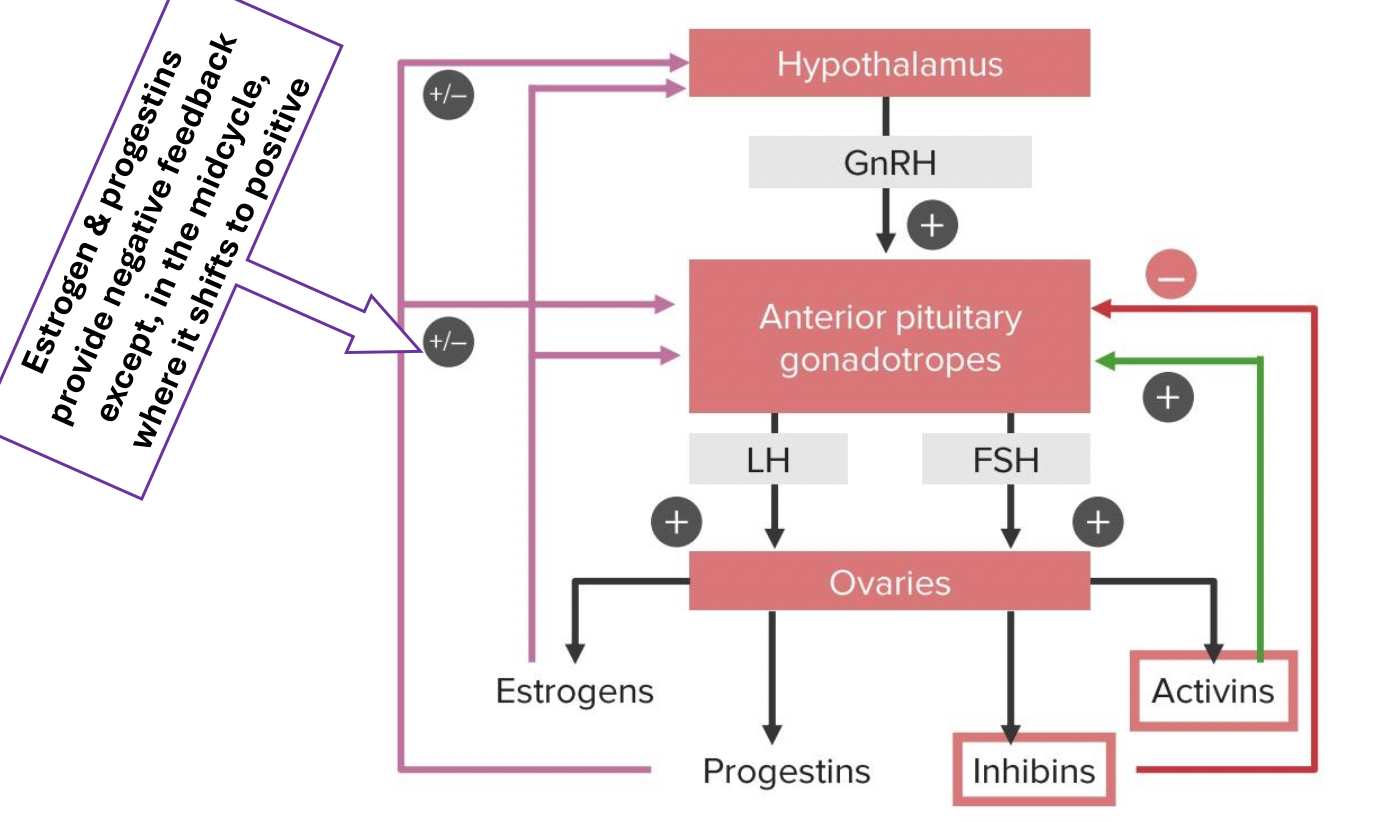
HPG axis : What feedback does Activin, Inhibins, Progestins, Estrogens give and where (include midcycle)?
Basic remember: Hypothalamus (+) → GnRH → Anterior Pituitary (+) → FSH & LH → Ovaries (+) → Estrogen , Progestins, Inhibins, Activins
Feedbacks
Progesterone and estrogen - feedback on hypothalamus and anterior pituitary (gonadotropes) = ↓ GnRH , ↓ FSH , ↓ LH
Inhibins give - feedback gonadotropes = ↓ FSH, ↓ LH
Activins give + feedback on gonadotropes = = ↑ FSH, ↑ LH
Midcycle
Mid- cycle high estrogen give + feedback = ↑ GnRH , ↑ LH
Mid cycle even progesterone give + feedback for LH but too small so negligible
Female hormones non preg, prego, lactating ?
Non preg = Estrogen , Progestins, Activins and inhibins
Prego = hCG, Estrogen, Progesterone, hPL, Relaxin
Lactating Female = Prolactin and oxytocin
Menstrual cycle : Define menstruation, menarche and menopause and what is duration of menses , cycle length and amount ml
Menstruation: The periodic discharge of blood, mucus and soughed endometrium at cyclic interval from menarche to menopause
Menarche : 1st menstrual cycle / menstrual bleeding 10-16 yrs (Avg:13 yrs)
Menopause: Permanent end of menstruation 45-55 yrs (Avg: 51 yrs)
Duration of menses : 5 (± 2 days)
Cycle length : 21 - 35 days (Avg : 28 days)
Amount: 30 - 80 ml
Components of Menstrual cycle
Pre-ovulation
Ovarian cycle --> (Menstrual and) Follicular phase
Uterine/endometrial cycle --> Menstrual phase (period) and Proliferative phase
Ovulation
Ovarian cycle --> Ovulation
Uterine/endometrial cycle --> End of proliferative phase
Post-ovulation
Ovarian cycle --> Luteal phase
Uterine/endometrial cycle --> Secretory phase
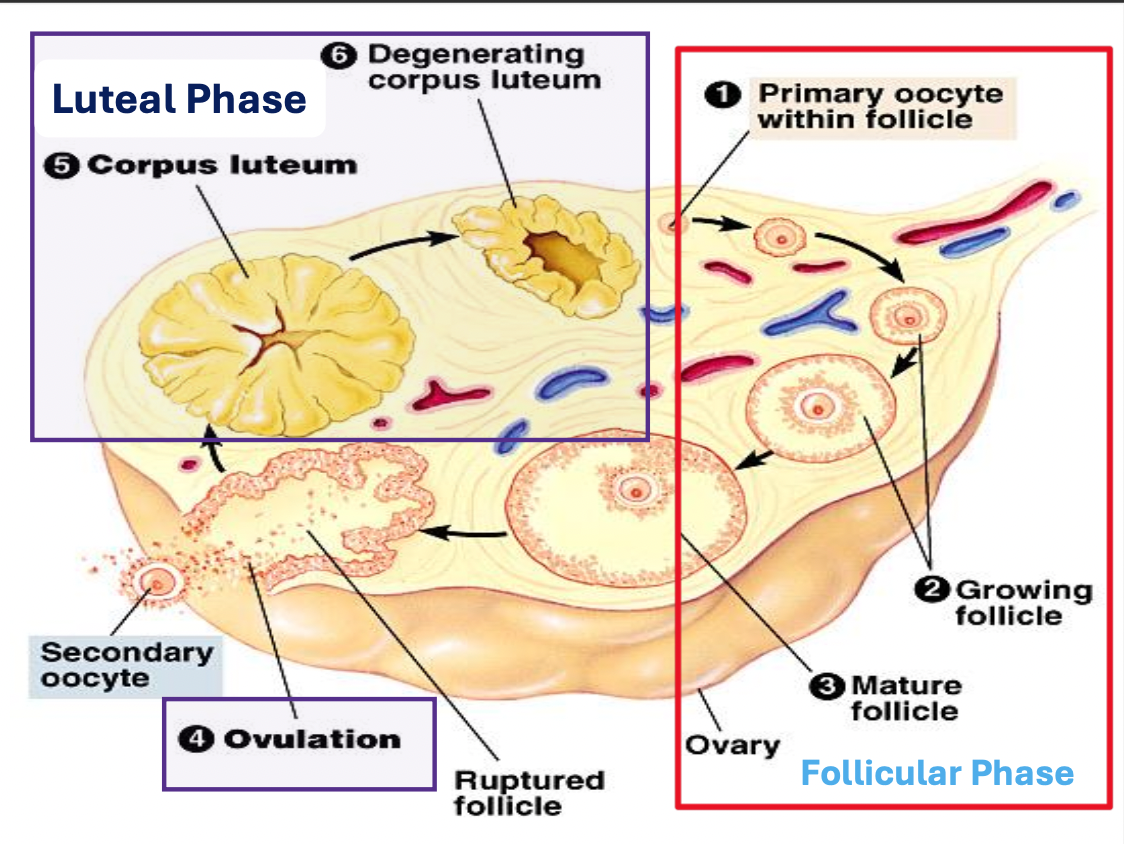
Ovarian cycle (recap)
Follicular phase
Low levels of estrogen and progesterone cause pituitary to secrete FSH
FSH cause egg to mature into follicle (ovary)
Follicle secrete estrogen which causes uterine lining (endometrium) to thicken
Ovulation
Estrogen production inhibits FSH production
Pituitary secretes LH (LH surge) causes follicle to burst and release mature egg into Fallopian tube
Luteal phase
Burst follicle turns yellow & becomes corpus luteum which produces progesterone to maintain thick uterine lining
LH production decreases
Menstrual phase
If fertilisation doesn’t occur corpus luteum disintegrates
Progesterone secretion decreases causing uterine lining to detach from uterine wall
Tissue, egg , and blood are discharged from body
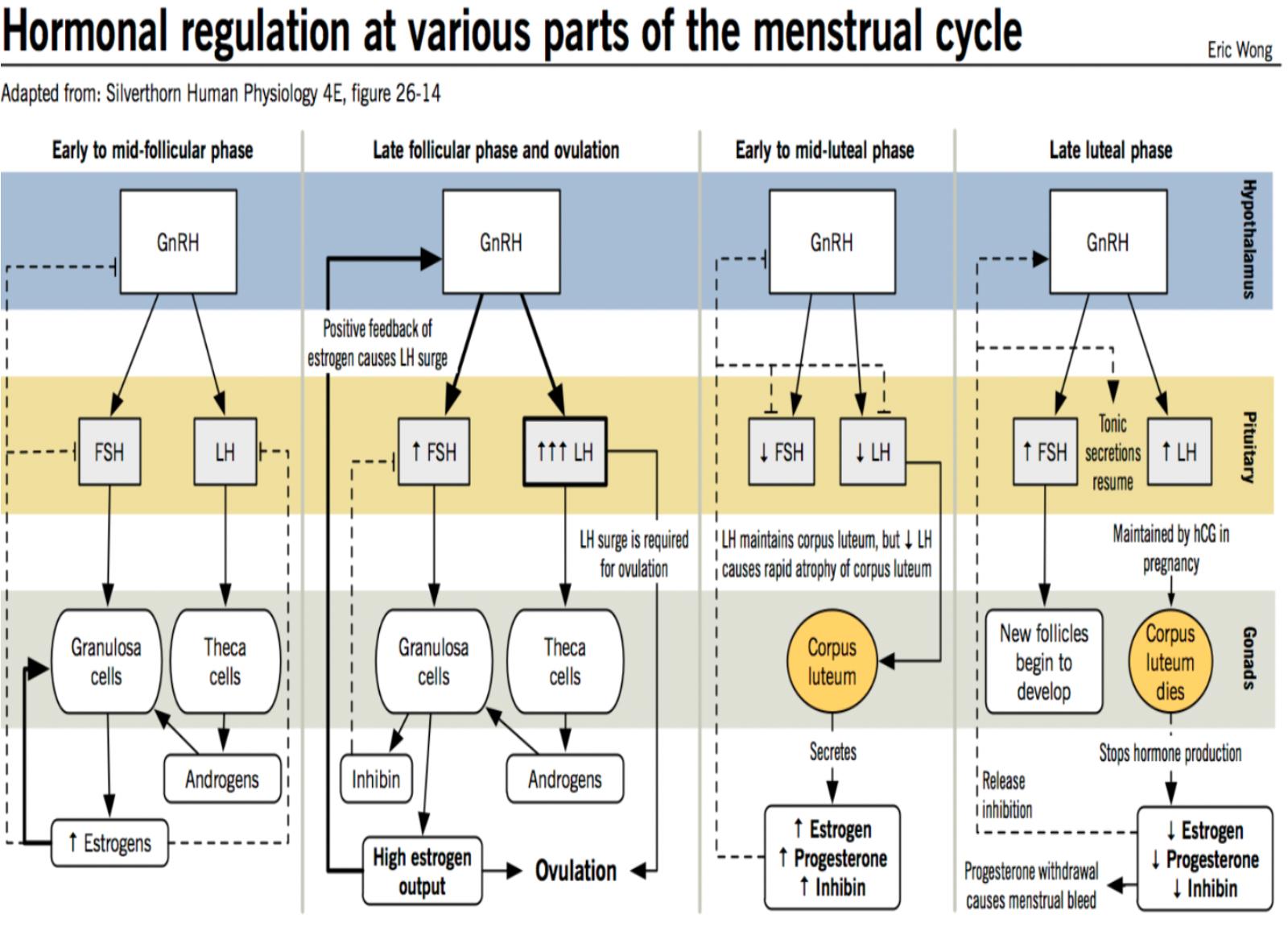
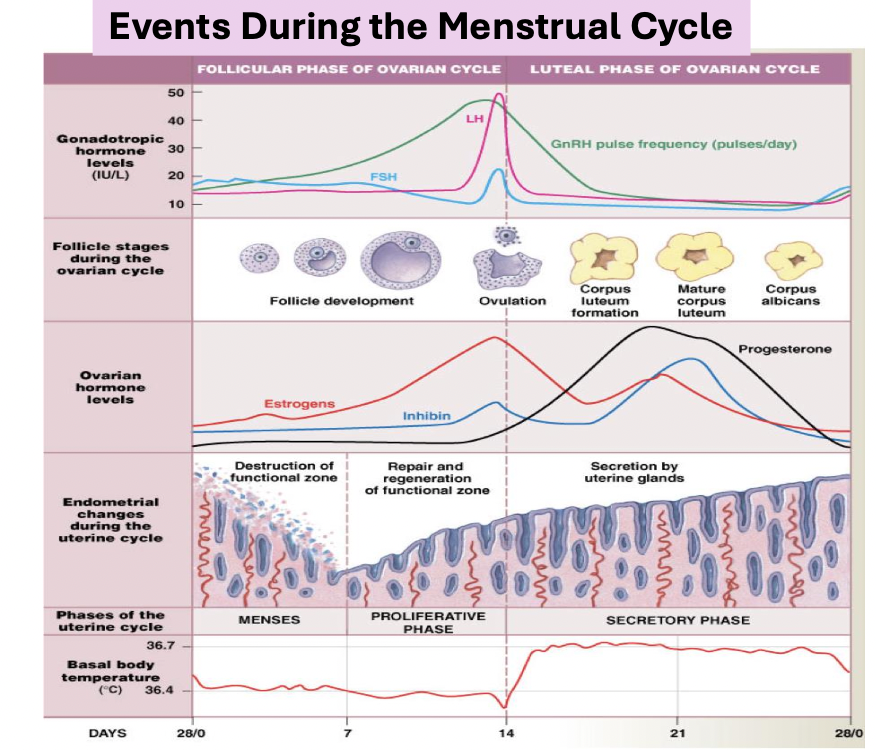
Hormonal regulations at various parts of menstrual cycle
Hormonal regulations at various parts of menstrual cycle
1. Early–Mid Follicular Phase
GnRH → FSH → stimulates Granulosa cells → Converts androgens into estrogen
GnRH → LH (basal level) → stimulates theca cells → secretes androgens
Result : ↑ Estrogen , mild FSH inhibition by inhibin from granulosa cells.
Feedback: Low-moderate estrogen → - feedback on GnRH, LH,FSH
Late Follicular Phase & Ovulation
High sustained estrogen → switch to + feedback on hypothalamus and pituitary
→ LH surge (6 - 10 fold increase) + small FSH rise
LH surge → Ovulation (follicle rupture)
Granulosa cells produce inhibin and more estrogen just before rupture
End Result: Ovulation + Formation of corpus luteum
Early–Mid Luteal Phase
Corpus luteum forms → secretes ↑ progesterone, ↑ estrogen, ↑ inhibin.
High hormones → - feedback → ↓ GnRH, ↓ FSH, ↓ LH (prevents new follicles).
LH maintains corpus luteum function initially
Late Luteal Phase
If no pregnancy : Corpus luteum degenerates → Estrogen, ↓ Progesterone, ↓ Inhibin → release of pituitary inhibition → ↑ FSH → new follicle growth begins and progesterone withdrawal → menstrual bleeding
If pregnancy → hCG maintains corpus luteum → continues estrogen and progesterone secretion
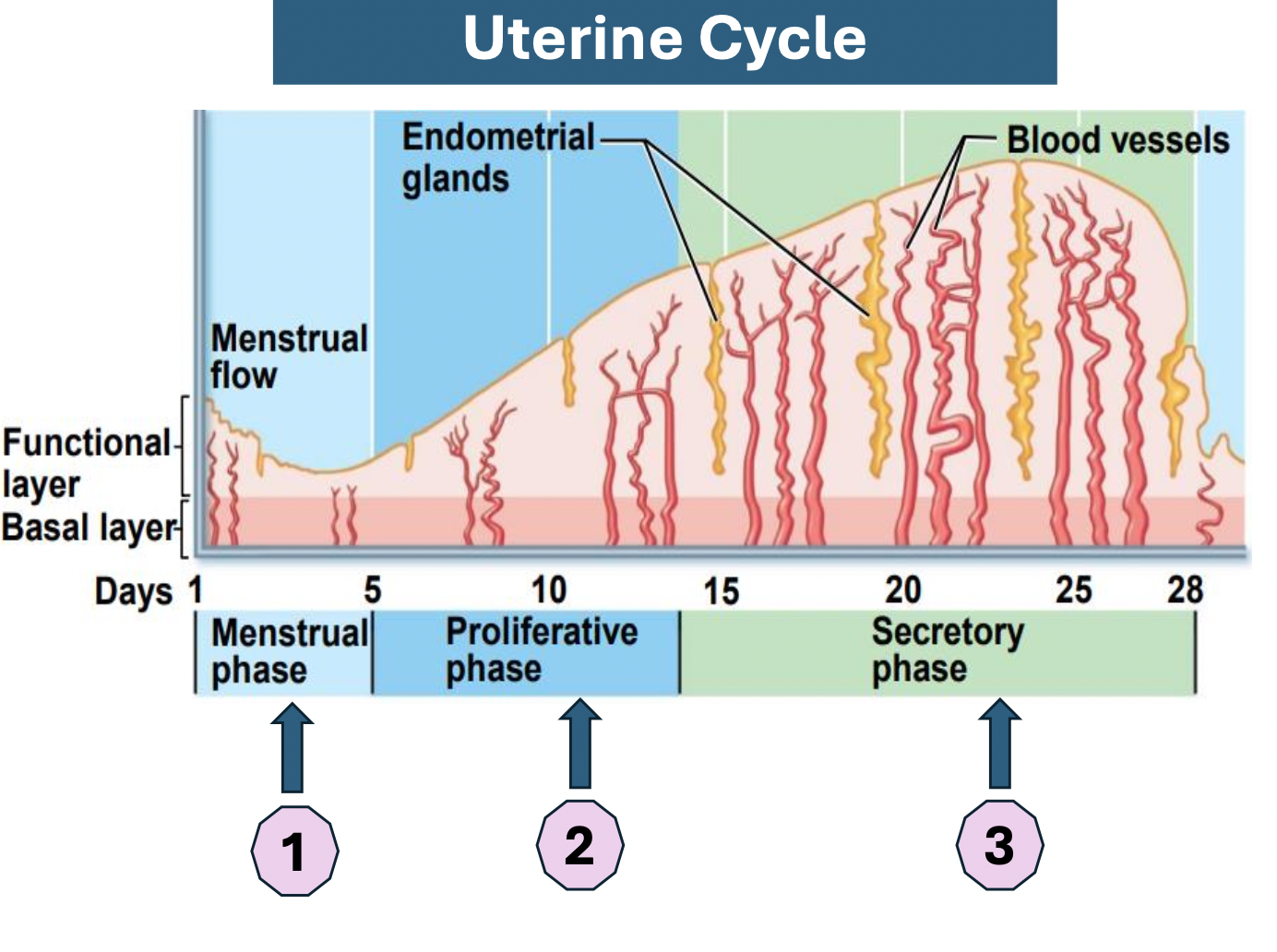
Uterine cycle : Describe Phases incl Days
Menstrual phase (Day 1-5)
Ovarian hormones at lowest levels
Functional layer sheds due to progesterone withdrawal and vasoconstriction of spiral arteries → these 2 factors can cause transient hypoxia
Proliferative phase (Day 6-14)
Estrogen levels rise
Vascular & endothelial tissue proliferation
Endometrial stromal cells (ESCs) produce VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)
Endothelial cells express Angiopoietin 2 → ↑ Angiogenesis
Glands enlarge and ↑ number of spiral arteries
↑ synthesis of endothelium receptors
Secretory phase (Day 15-28)
Rising progesterone levels in granulosa. cells stimulate →
Endometrial stromal cells to express Angiopoetin 1
Growth & coiling of spiral arterioles
Uterine glandular secretory activity
If no fertilisation: ↓ progesterone and ↓estradiol levels → spiral arteries kinking & spasm, gland regression, endometrium necrosis → menstruation
Fertilisation: Secretory activity maintained
Events during menstrual cycle and physiological changes (incl pics)
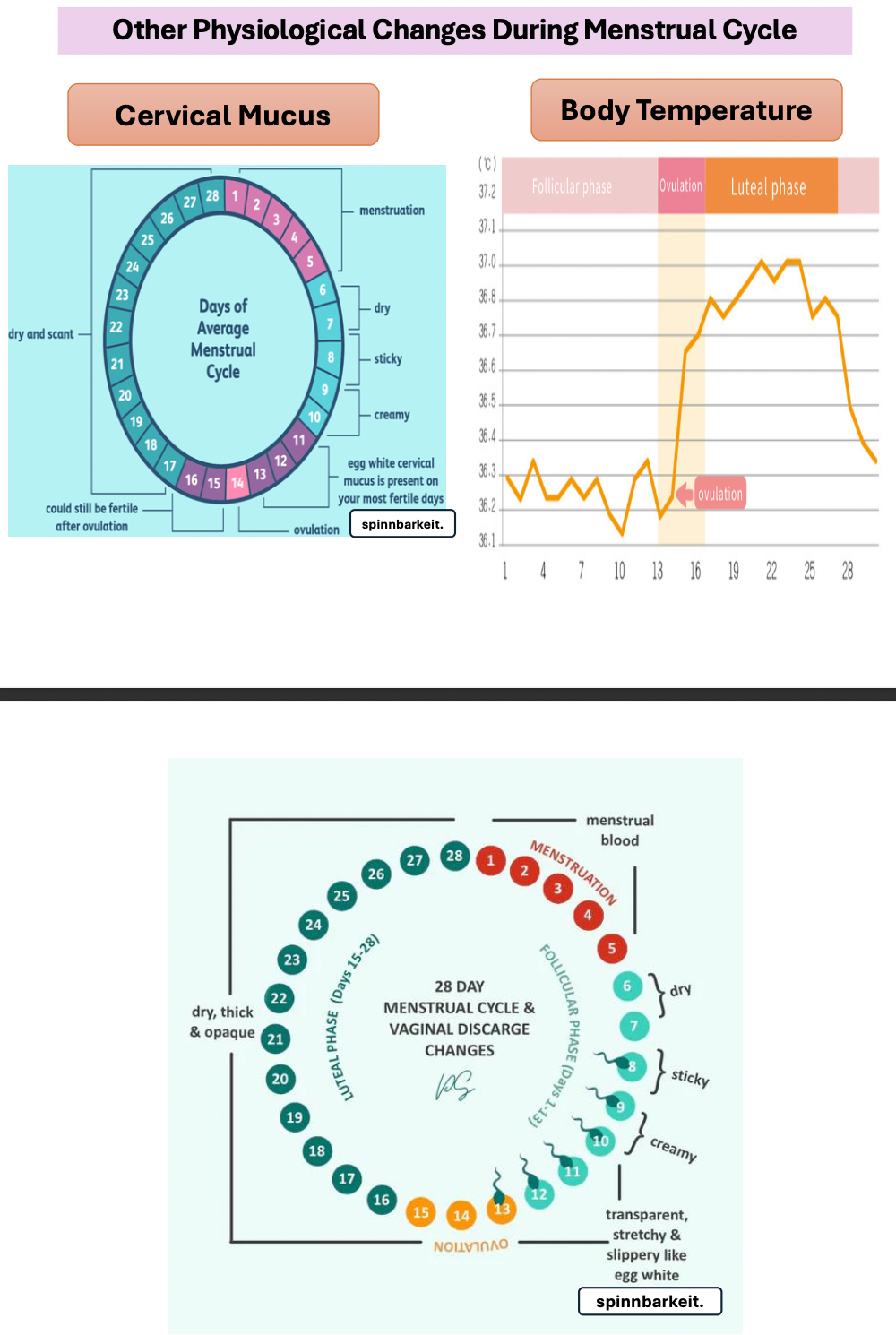
Physiological menstrual change:
Body temp increase (due to progesterone after ovulation) , Cervical mucus
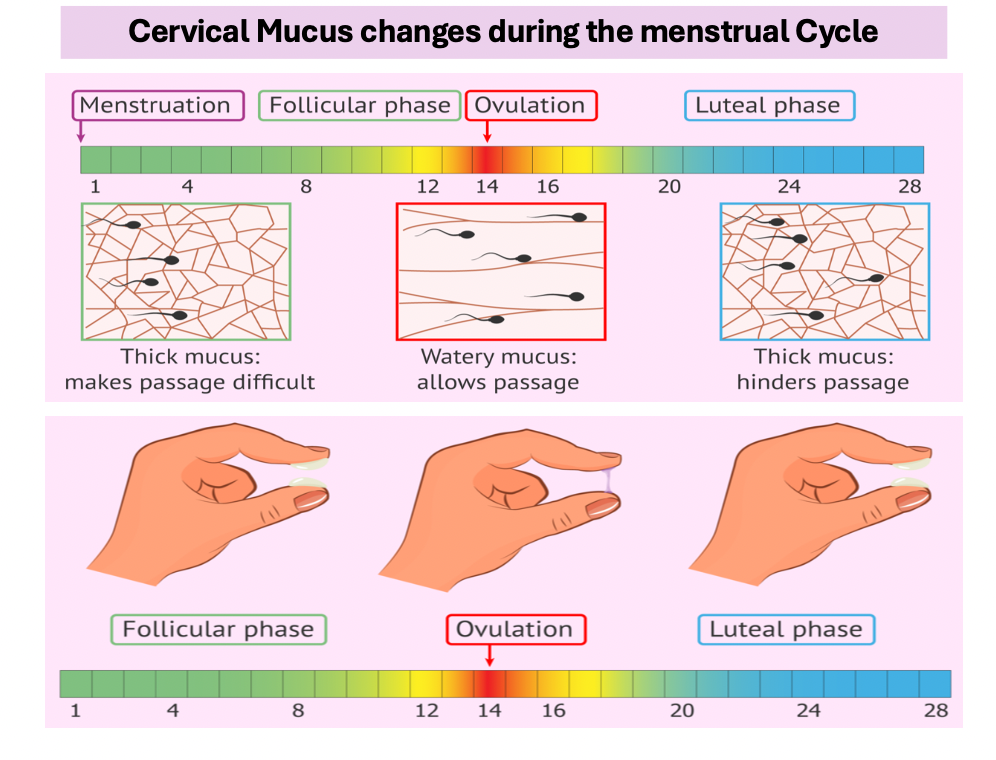
Cervical mucus change during menstrual cycle
Menstruation/ Follicular = Thick mucus so passage difficult
Ovulation = Water mucus so allows passage
Luteal phase = Thick mucus hinder passage
Disorders of menstrual Cycle (Define Amenhorrea (1ry & 2ry) , Menorrhagia, Hypomenorrha, Metrorrhagia , Oligomenorrhea , Dysmenorrhea)
Amenhorrea : Absence of menstrual period of female in reproductive age
Primary : Period never occurs
Secondary: Cycle cease after normal period
Menorrhagia : Excessive bleeding during menstruation
Hypomenorrhea: Scanty or little bleeding
Metrorrhagia : Bleeding between cycle
Oligomenorrhea : Reduced period frequency
Dysmenorrhea : Painful periods