3.7.1 Inheritance
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
65 Terms
What is meant by the term 'genotype'? (1)
The genetic constitution of an organism e.g. Bb
What is meant by the term 'phenotype'? (1)
The expression of a genetic constitution and its interaction with the environment e.g. blue eyes
what is a gene
a sequence of bases on a DNA molecule that codes for a protein (polypeptide) which results in a characteristic.
What is meant by 'alleles'? (1)
Variations of a particular gene (same locus) → arise by mutation (changes in DNA base sequence)
How many alleles of a gene can be found in diploid organisms?
2 as diploid organisms have 2 sets of chromosomes (chromosomes are found in homologous pairs → one from each parent)
But there may be many (more than 2) alleles of a single gene in a population
define locus
the fixed position of a gene
What are the different types of alleles? (3)
- Dominant
- Recessive
- Co-dominant
What are dominant alleles?
- The allele that is always expressed in a phenotype when present in the genotype
- Always denoted in capital letters
What are recessive alleles?
- The allele is only expressed when 2 present in the genotype (homozygous recessive)
- Always denoted in lowercase
What are co dominant alleles?
Both alleles expressed / contribute to phenotype (if inherited together)
What is a homozygous genotype? (2)
- Where both alleles in the genotype are the same
- E.g. BB (homozygous dominant) or bb (homozygous recessive)
In a diploid organism, what are the possible states of the alleles at a specific locus?
- Homozygous
- Heterozygous
What is a heterozygous genotype? (2)
- Where both alleles in the genotype are different to each other
- E.g. Bb
how many alleles for each gene do diploid cells have
2
how many alleles for each gene do haploid cells have
1
What are genetic diagrams used for
to predict the genotypes and phenotypes of the offspring produced if two parents are crossed (bred).
what is monohybrid inheritance
inheritance of one phenotypic characteristic coded for by a single gene
what is the F1 generation.
The first set of offspring
what is the phenotypic ratio
ratio of different phenotypes in the offspring.
Genetic diagrams allow you to predict the phenotypic ratios in F1 and F2 offspring.
what is the usual ratio for monohybrid inheritance of 2 heterozygous parents
3 : 1
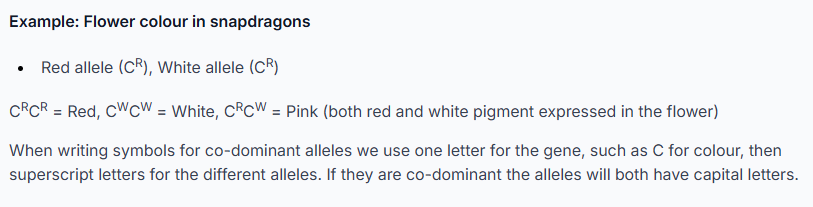
How is co-dominance shown?
the main gene as a normal capital letter (C) and then the alleles as superscript capitals, because neither is recessive.
what is an example of codominance and how is this written and expressed
Describe what is meant by 'multiple alleles' (3)
- Where there are more than two alleles of a particular gene in a population gene pool
- However, only two alleles can be present in a genotype
- E.g. There are 3 different alleles for the blood group gene (I^A , I^B and I^O)
what is the notation for multiple alleles
capital letter for the gene with superscript for the different alleles
For example, IA , IO IB
what is dihybrid inheritance
the inheritance of two characteristics, which are controlled by different genes.
Each of the two genes will have different alleles.
when is the ratio 9:3:3:1
dihybrid inheritance of 2 heterogenous alleles, without linkage or epistasis
how do you work out the gametes for dihybrid crosses
draw an expand the brackets type diagram
GAMETES ARE NOT THESE WHEN LINKED GENES

what are the gametes of monohybrid crosses
just single letters
What are the two sex chromosomes? (2)
- X
- Y
what is the probability of having male offspring and having female offspring
both 50%
What is the sex chromosome genotype of all females? (1)
XX
What is the sex chromosome genotype of all males? (1)
XY
Describe what is meant by 'sex-linked' genes (2)
- Where the alleles that code for a specific characteristic is located on a sex chromosome
- Usually the X chromosome (as Y chromosome is smaller and so has less genes)
why males are more likely to express a recessive X-linked allele
assuming males are XY and females are XX
males - only need one copy of the recessive allele to be expressed
females - both copies of the recessive allele are needed in order for it to be expressed
Why are sex linked conditions more common in males than females? (3)
- Males only contain one X chromosomes
- Females contain two X chromosomes
- X-linked disorders are always expressed in males (as they only have one X-chromosome)
What is are common examples of sex-linked disorders? (1)
- Colour blindness
- Haemophillia
- Which are both caused by a faulty recessive allele that is carried on the X chromosome
what is a carrier in regards to sex linked conditions
Females with one copy of the recessive allele
not expressed in the phenotype but that can be passed on to offspring.
how are sex linked conditions shown
X then the recessive allele in superscript and the other sex chromosome
For example,
Xᴴ = normal clotting
Xʰ = haemophilia
Males are written as XᴴY or XʰY.
Females are written as XᴴXᴴ, XᴴXʰ, or XʰXʰ.
what is an autosome
any chromosome that isnt a sex chromosome
what is autosomal linkage
Genes on the same chromosome different loci are inherited together
How does autosomal linkage affect inheritance of alleles
Two genes located on same autosome (non-sex chromosome)
So alleles on same chromosome inherited together → Stay together during independent segregation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis
New combinations of alleles can be created → crossing over between homologous chromosomes
The closer together the genes are on an autosome the less likely they will be split up by crossing over
why does autosomal linkage reduce variation
they’ll stay together during the independent segregation of chromosomes in meiosis I, and their alleles will be passed on to the offspring together, unless crossing over occurs
what does it mean for 2 genes to be more closely linked
The closer together two genes are on the autosome, the more closely they are said to be linked. This is because crossing over is less likely to split them up.
How many potential gamete combinations result from autosomal linked genes? (2)
- Result in two potential gamete combinations
- Rather than four (as previously considered in dihybrid inheritance)
what are the gametes in autosomal linkage
Each chromosome goes into a gamete as it is.
For example, if one chromosome has the genes with alleles G and L on it the gamete will be GL
EXAMPLE In fruit flies, the genes for body colour and for wing development are not on the sex chromosomes. The allele for grey body colour, G, is dominant to the allele for black body colour, g. The allele for long wings, L, is dominant to the allele for short wings, l.
A cross was carried out between flies with grey bodies & long wings (heterozygous for both genes) and flies with black bodies & short wings.
The result of this cross was 225 offspring with a grey body & long wings and 220 with a black body &short wings. Explain these results
The two genes are linked / autosomal linkage
No crossing over occurs / genes are close together
So only GL and gl gametes produced / no Gl and gL gametes produced / no Ggll and ggLl offspring produced
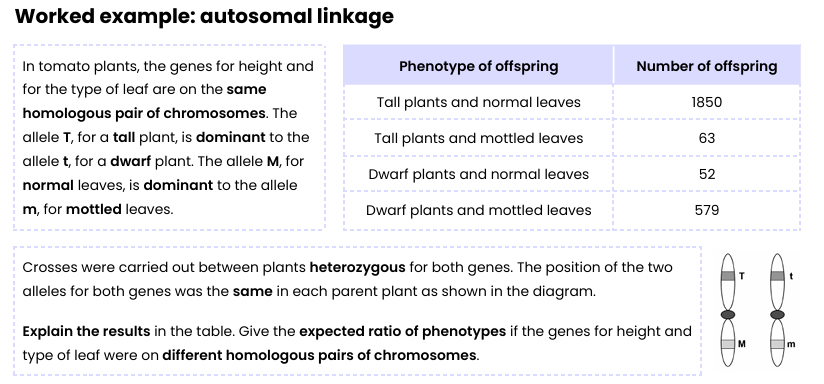
Example - Explain these results
Genes are linked (so mainly TM and tm gametes are produced)
Crossing over has occurred
So few Tm and tM gametes produced/ fewer tall, mottled and dwarf, normal offspring produced
If not linked (use punnett square)- 9:3:3:1(tall, normal : tall, mottled : dwarf normal : dwarf, mottled)
What type of cross pattern should be used for autosomal linked genes? (1)
Monohybrid pattern rather than a dihybrid pattern
(What this means is that when approaching questions related to autosomal linked genes, you should treat the question as if you were asked about a monohybrid pattern (4 box punnet square) rather than a dihybrid inheritance (16 box punnet square)
would you expect the typical dihybrid phenotypic ratio in autosomal linkage
no
phenotypic ratio is more likely to be that expected for a monohybrid cross between two heterozygous parents (3 : 1) because the two autosomally-linked alleles are inherited together. This means that a higher proportion of the offspring will have their parents’ (heterozygous) genotype and phenotype.
What is an example of gamete production with autosomal linked genes? (3)
- If genes A and B, and a and b are linked
- The gametes each parent produces are AB and ab (linked together)
- Rather than AB, Ab, aB, and ab (not linked).
What is epistasis? (2)
- Occurs when two or more genes interact
- To contribute to a phenotype
- allele of one gene masks/supresses the expression of the alleles of other genes
Where can epistasis often occur? (3)
- In metabolic pathways
- That are controlled by enzymes
- Coded for by different genes
How does enzyme dependency affect metabolic pathways in the context of epistasis? (2)
- Each enzyme is dependent on the previous enzyme for its substrate
- If any one of these enzymes is non-functional, the pathway comes to a halt
would you get the expected dihybrid phenotypic ratio for epistatic genes
no
The phenotypic ratio you would expect to get from a dihybrid cross involving an epistatic allele depends on whether the epistatic allele is recessive or dominant.
Draw a table that shows the most common exam questions that related to pedigree diagrams (8)
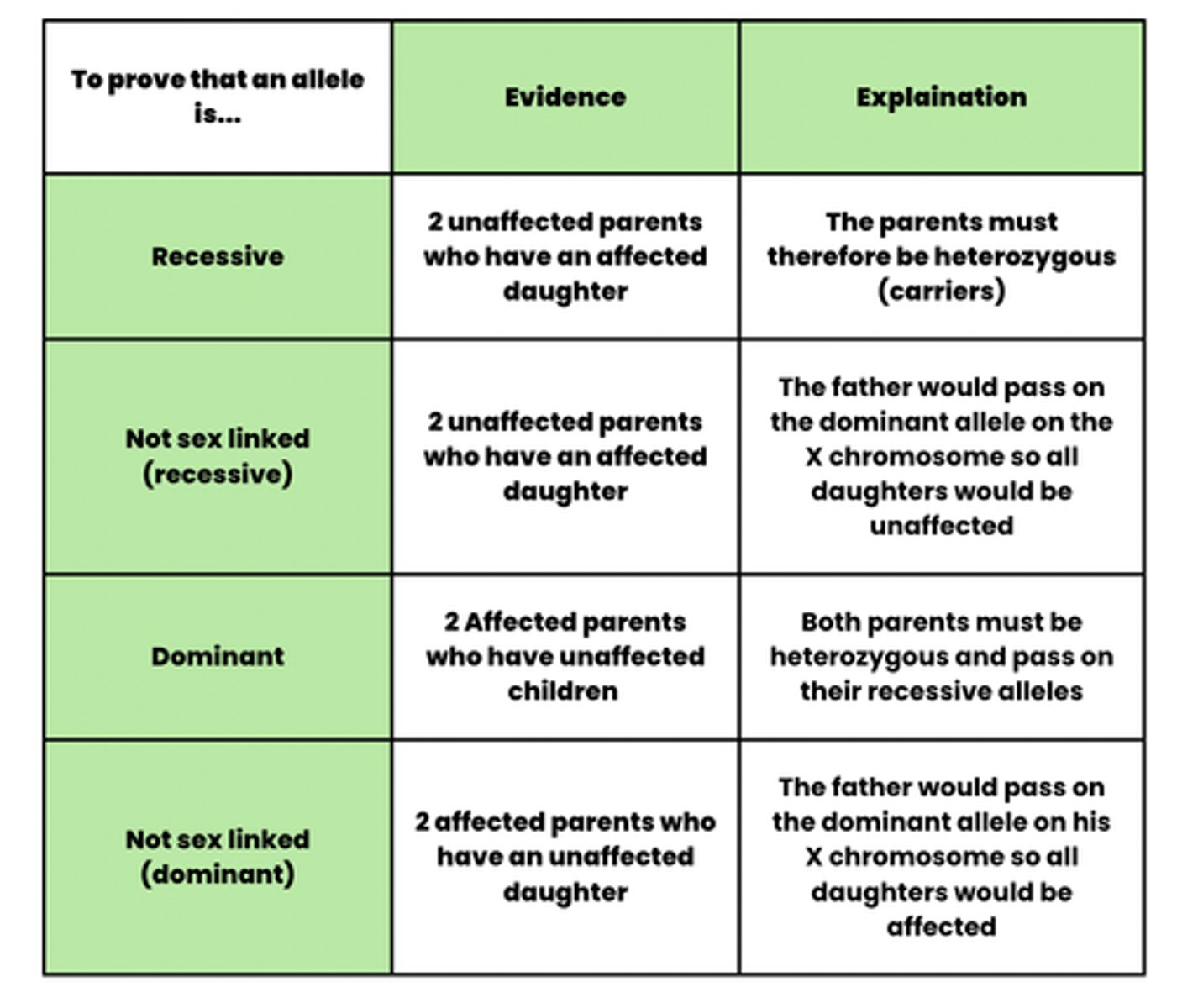
Explain the evidence from a pedigree diagram which would show that the allele for [named phenotype] is dominant
[Named phenotype] parents [n&n] have child [n] WITHOUT [named phenotype]
So both parents [n&n] must be heterozygous/carriers of recessive allele
If it were recessive, all offspring would have [named phenotype]
Explain the evidence from a pedigree diagram which would show that the allele for [named phenotype] is recessive
Parents [n&n] WITHOUT [named phenotype] have child [n] WITH [named phenotype] ●
So both parents [n&n] must be heterozygous/carriers of recessive allele
Explain the evidence from a pedigree diagram which would show that the allele for [named phenotype] on the X-chromosome is recessive
Mother [n] WITHOUT [named phenotype] has child [n] WITH [named phenotype]
So mother [n] must be heterozygous/carrier of recessive allele
Explain the evidence from a pedigree diagram which would suggest that [named recessive phenotype] is caused by a gene on the X chromosome
Only males tend to have [named recessive phenotype]
Explain the evidence from a pedigree diagram which would show that the gene for [named phenotype] is not on the X chromosome
[Named phenotype] father [n] has daughter [n] WITHOUT [named phenotype]
Father [n] would pass on allele for [named phenotype] on X chromosome so daughter [n] would have [named phenotype]
OR
[Named phenotype] mother [n] has son [n] WITHOUT [named phenotype]
Mother [n] would pass on allele for [named phenotype] on X chromosome so son [n] would have [named phenotype]
when can the chi squared test be used
When determining if observed results are significantly different from expected results (frequencies)
Eg. comparing the goodness of fit of observed phenotypic ratios with expected ratios
Data is categorical (can be divided into groups eg. phenotypes)
what is the aim of chi squared
to determine if there is a statistical difference between the expected and observed ratios from the results of a genetic cross
To see whether the results support the expected results of a theory, a null hypothesis must be made. The observed outcome will support or reject the null hypothesis.
How to calculate a chi-squared value
O= frequencies observed
E= frequencies expected (multiply total n with each expected ratio as a fraction)

How may a chi squared value be analysed
Number of degrees of freedom = number of categories - 1 (eg. 4 phenotypes = 3 degrees of freedom)
Determine critical value at p = 0.05 (5% probability) from a table
If x2 value is [greater / less] than critical value at p < 0.05 Difference [is / is not] significant so [reject / accept] null hypothesis
As there is [less / more] than 5% probability that difference is due to chance
why may the actual ratio not be the same as the expected ratio
Fusion / fertilisation of gametes is random
Autosomal linkage / epistasis / sex-linkage
Small sample size -> not representative of whole population
Some genotypes may be lethal (cause death)