Ch 5 Part 1: Sex determination & chromosomes (SEPT 24th)
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
Define sex
sex: one of two or more mating classes
-syngamy possible between different classes
define gender
gender: cultural norms sometimes associated with sex
-vary across cultures and through time
-relationship to inheritance is complicated
sexual organisms are often divided into mating types, what is it
-binary: male and female (may be mono or dimorphic)
-way more mating classes than that
what did nettie stevens observe
male beetles produce two distinct gametes differing by one chromosome
define heterogametic and homogametic
what are males known as
heterogametic: producing two kinds of gametes (X or Y)
homogametic: producing one kind of gamete (X only)
males produce two diff gametes, known as heterogametic
What did nettie stevens suspect
she suspected that the Y chromosome inhibited expression of the x chromosome resulting in male development.
Explain the Y-chromosome mechanism
(Sex determination in mammals)
-Y chromosome includes testis-determining factor
-initiates development of testes
-without TDF, gonads become ovaries
-XX: female
-XY: male
Define Aneuploidy
(Sex determination in mammals)
what is it lethal in
where is it not unusual to occur
what do dosage effects do
aneuploidy: Condition of having more or less than two homologous chromosomes for any chromosomes
-lethal for all autosomes except for Chr. 21
-not unusual at sex chromosomes
-dosage effects early in embryogenesis result in altered development
How does aneuploidy occur
an abnormal number of chromosomes, arises due to errors in cell division during meiosis or mitosis
Define non-disjunction
failure of chromosomes to segregate properly during anaphase I or II
Draw nondisjunction in meiosis I and meiosis II
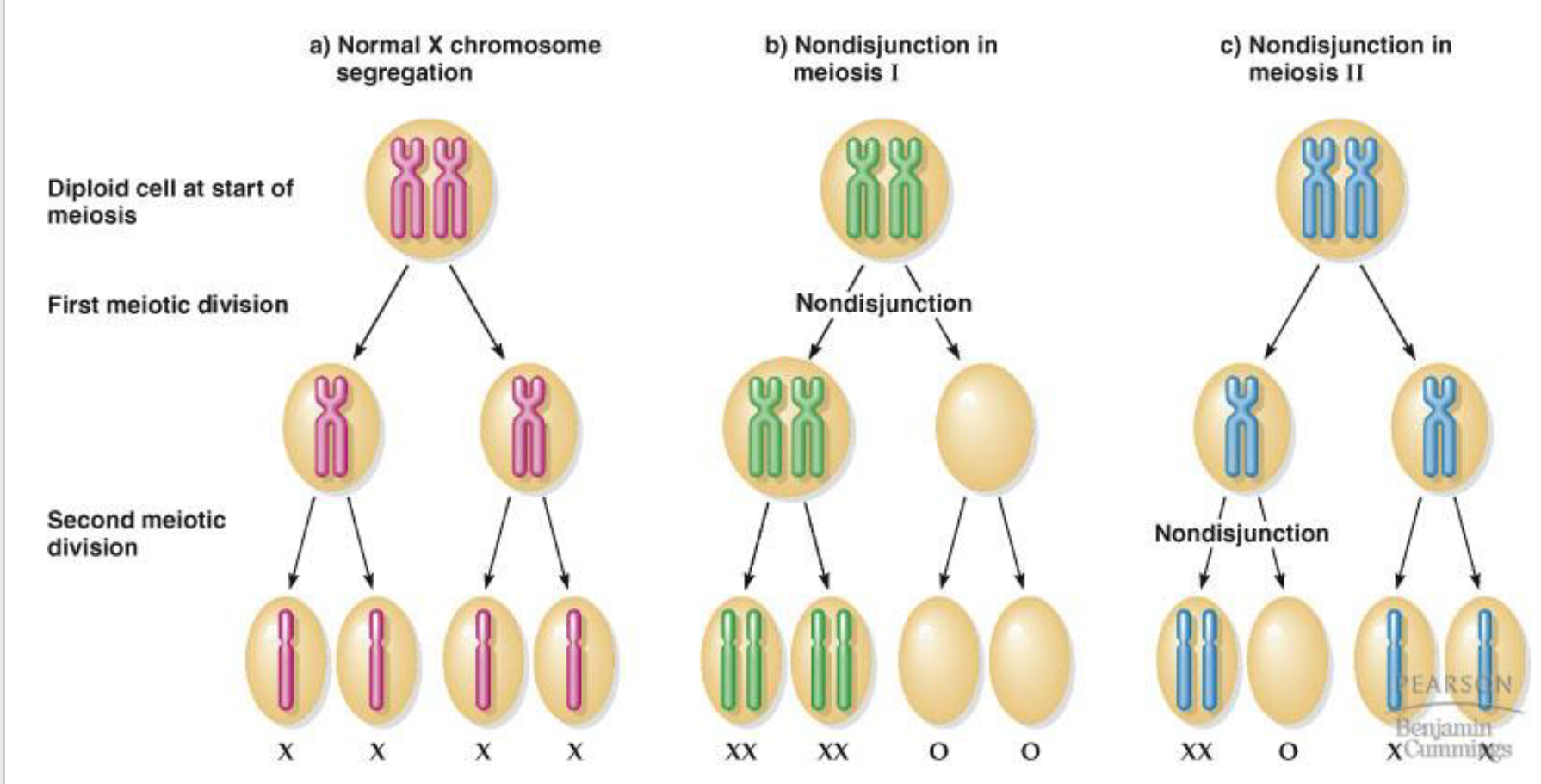
Define Primary non-disjunction
non-disjunction for an individual with a normal set of chromosomes (diploid)
Describe XO female, Turner syndrome
symptoms
how many die and when
how many in live births
-have 45 chromosomes
-Shorter than average, webbed neck, undeveloped breasts, immature sex organs, sterile
-reduced ability to interpret spatial relationships
-99% die before birth
-1 in 10,000 live births
Describe XXY male, Klinefelter Syndrome
symptoms
how many in live births
-have 47 chromosomes
-taller than average, breast development (gynecomastia), broad hips, small testes (hypogonadism), mostly infertile
-subnormal intelligence (rarely)
-often difficulty with verbal learning
-1 in 1,000 live births
Describe XYY male, Jacobs syndrome
symptoms
how many die and when
how many in live births
what did studies suggest about these XYY males
-have 47 chromosomes
-often unidentified due to very few phenotypic changes
-slightly taller on average than XY males
-Increased incidence of learning disorders
-Some evidence of delayed speech, decreased language skills
-~1 in 1,000 births
Some studies have suggested XYY males: are more likely to commit violent crimes
-focus on incarcerated XYY males
-most lack experimental controls
-confounded by higher likelihood of poverty
Describe XXX female, triple X syndrome
symptoms
how many die and when
how many in live births
-have 47 chromosomes
-often unidentified due to very limited phenotypic change
-slightly taller on average than XX females
-decreased fertility (slightly)
-delayed motor-skills and learning disorders (rarely)
-1 in 1,000 births