34
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Herbivores
Are animals whose primary food source is plant-based
Carnivores
Are animals that eat other animals.• Obligate carnivores are those that rely entirely on animal flesh to obtain their nutrients• Facultative carnivores are those that also eat non-animal food in addition to animal food – but generally do best eating animals
Omnivores
Animals that eat both plant- and animal-derived food – and do well eating either
Incomplete Tracts “ Digestive Tracts”
single opening = Gastrovascular cavity
Ex: Planarian
Food enters through mouth and muscular pharynx• Wastes exit through mouth and muscular pharynx• Lacks specialized parts
Complete Tracts “Digestive Tracts”
two openings = Alimentary canal• Ex: Earthworm• Food enters through mouth• Wastes exit through anus
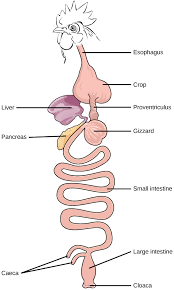
Birds “Vertebrate Digestive Systems”
crop, stores food
• Two stomachs: the proventriculus (enzymes) and the gizzard (grinding).
• One openings to excrete urine and feces = the cloaca
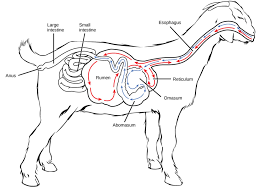
Ruminants
Four stomachs:
the rumen and the reticulum – contain prokaryotes and protists to digest cellulose fiber.
Cud is regurgitated chewed and swallowed in third stomach, the omasum – removes water.
Cud then passes onto the abomasum – enzymes produced by animal
Omnivores “ ADAPTATION TO DIET”
Variety of specializations•
Accommodate both vegetation and meat
Herbivores “ ADAPTATION TO DIET”
Incisors for clipping
Premolars and molars for grindin
Carnivores “ADAPTATIONS TO DIET”
Pointed incisors and enlarged canines
Shear off pieces small enough to swallow
Human Digestive Tract
complete (alimentary canal)
• Part of a tube-within-a-tube body plan
• Begins with a mouth and ends in an anus
• Digestion entirely extracellular
• Digestive enzymes are secreted by
• The wall of the digestive tract, or
• By nearby glands
Mouth “Human Digestive Tract”
• Three major pairs of salivary glands
• Saliva contains salivary amylase
• Salivary amylase initiates starch digestion
• Tongue is composed of striated muscle
• Mixes chewed food with saliva
• Forms mixture into bolus
Pharynx “ Human Digestive Tract”
• Where digestive and respiratory passages come together
• Soft palate closes off nasopharynx
• Epiglottis
• Covers opening into trachea
• Keeps food from air passages (most of the time)
Esophagus “Human Digestive Tract”
Takes food to stomach by peristalsis
Def. PERISTALSIS - Rhythmical contraction to move contents in tubular organ
Stomach “ Human Digestive Tract”
Stomach wall has deep folds
• Folds disappear as the stomach fills to an approximate volume of one liter
• Epithelial lining of the stomach has millions of gastric pits, which drain gastric glands
Pepsin
hydrolytic enzyme that acts on protein to produce peptides
Chyme
Food mixing with gastric juices become
Small intestine
• First segment is duodenum
• Chyme from stomach enters the duodenum
• Mixes with secretions from the liver and pancreas
Liver
Produces bile, which is stored in gallbladder
• Bile contains bile salts which break up fat into fat droplets via emulsification
•Helps maintain glucose concentration in blood by converting excess
Pancreas “ Small intestine”
Exocrine gland
• Produces pancreatic juice and digestive enzymes into the duodenum
Pancreatic amylase
digests starch to maltose
Trypsin
digest protein to peptides
Lipase
digests fat droplets to glycerol and fatty acids
Epithelial cells
intestine also produce enzymes
• These complete digestion of peptides and sugars
Mucous membranes of small intestine “ Absorption”
Has ridges and furrows that give it a corrugated surface
• Villi are ridges on the surface, which contain even smaller ridges, microvilli
• Greatly increase absorptive area
• Each villus contains blood capillaries and a lymphatic capillary (lacteal
Enzymes
Digestion of carbohydrates is performed by several
Amylase and Maltase
Starch and glycogen are broken down into glucose by
sucrase and lactase, respectively.
Sucrose (table sugar) and lactose (milk sugar) are broken down by
Protein Digestion
takes place in the stomach.
• The enzyme pepsin plays an important role in the digestion of proteins by breaking down the intact protein to peptides, which are short chains of four to nine amino acids.
Duodenum
other enzymes—trypsin, elastase, and chymotrypsin—act on the peptides reducing them to smaller peptides.
free amino acids.
Specifically, carboxypeptidase, dipeptidase, and aminopeptidase play important roles in reducing the peptides to
Lipid digestion
begins in the stomach with the aid of lingual lipase and gastric lipase.
• However, the bulk of lipid digestion occurs in the small intestine due to pancreatic lipase.
Large Intestine
Includes cecum, colon, rectum, and anal canal
• Larger in diameter, but shorter in length than small intestine
• Absorbs water, salts, and some vitamins
Cecum
has small projection – appendix
Colon
subdivided
Constipation:
feces are hardened because of excess water removal in the colon.
Diarrhea:
Not enough water is removed from the feces
Inorganic essential nutrients
Must be obtained from food.
They help in structure and regulation and are considered co-factors.
Vitamin A
Promotes eye health, helps form and maintain healthy skin, teeth, and bones
Vitamin D
helps the body absorb calcium, maintains strong bones
Vitamin E
Antioxidant, boost immune function
Vitamin K
aids in blood clotting
Vitamin B
Helps body produce energy, influence growth/ development
Vitamin C
boosts immune function, fights skin aging, antioxidant
Organic compounds
body is unable to produce, but are required for metabolic purposes
Antioxidants
• Cellular metabolism generates free radicals that carry extra electron
• Vitamins C, E, and A are believed to defend the body against free radicals
Type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease
often seen in people who are obese
Monosaccharides
• Glucose
• Fructose
Disaccharides
Lactose (milk sugar)
• Sucrose (table sugar)
Fiber
Includes various undigestible carbohydrates derived from plants
• Food sources rich in fiber include beans, peas, nuts, fruits, and vegetables
• Technically, fiber is not a nutrient for humans• Cannot be digested
• Soluble fiber combines with bile acids and cholesterol in the small intestine and prevents them from being absorbed
NUTRITION: LIPIDS
• Fat, oils, and cholesterol
• Essential for the storage and activity offat-soluble vitamins A, D, E and
• Provide energy, at nine calories per gram.
• fat storage is essential to protect your internal organs and to help insulate against cold temperatures
Saturated fats
solids at room temperature) usually come from animals• Butter and meats, such as marbled red meats and bacon, contain saturated fats• Palm oil and coconut oil are high in saturated fats