Memory & Thought (2.2a, 2.2b, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 2.7)
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
Cognition
all the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Metacognition
cognition about our cognition; keeping track of an evaluating our mental processes
Schemas
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
(assimilation —> interpreting new experiences into our current schemas, accommodation —> adapting our current schemas)
Convergent thinking vs divergent thinking
convergent —> narrowing the available problem solutions to determine the single best solution
divergent —> expanding the number of possible problem solutions; creative thinking that diverges in different directions
Prototype, concept
concept —> a mental grouping of similar objects, events, ideas, or people (BROAD category)
prototype —> a mental image or best example of a category (BEST example)
matching new items to a prototype provides a quick and easy method for sorting items into categories (as when comparing featured creatures to a prototypical bird, such as a crow)
Executive functions
cognitive skills that work together, enabling us to generate, organize, plan, and implement goal-directed behavior
Problem Solving Strategy
Algorithm —> a methodical, logical rule or procedure that guarantees solving a particular problem. More reliable but slower
ex) following a recipe or solving a math problem
Heuristic —> — a mental shortcut— (rules of thumb or informal guidelines) used to make judgments and solve problems efficiently; faster but less reliable
ex) guessing a password based on common patterns rather than guessing random combinations
Intuition —> an effortless, immediate, automatic feeling or thought, as contrasted with explicit, conscious reasoning
Insight
a sudden realization of a problem’s solution; contrast with strategy-based solutions
Mental set
a tendency to approach a problem in one particular way, often a way that has been successful in the past
Obstacles to Problem Solving
confirmation bias —> a tendency to search for info that supports our preconceptions and ignore contradictory evidence
functional fixedness —> a cognitive bias that hinders problem-solving by limiting one's ability to see objects beyond their typical, intended uses
fixation —> the inability to see a problem from a new perspective; an obstacle to problem solving
Problems in decision making
intuition
representative heuristics —> judging the likelihood of events in terms of how well they seem to represent, or match, particular prototypes; may lead us to ignore other relevant information
availability heuristics —> judging the likelihood of events based on their availability in memory; if instances come readily to mind, we presume such events as common
overconfidence —> the tendency to be more confident than correct—to overestimate the accuracy of our beliefs and judgments.
framing —> the ay an issue is posed; how an issue is framed can significantly affect decisions and judgments
belief perseverance —> the persistence of one’s initial conceptions even after basis on which they were formed has been discredited
Recall, recognition, relearning
recall —> a measure of memory in which the person must retrieve information learned earlier, as on a fill-in-the-blank test
recognition —> a measure of memory in which the person identifies items previously learned, as on multiple-choice test
relearning —> a measure of memory that assesses the amount of time saved when learning material again
Memory processes
encoding —> Transforming information so that the nervous system can process it.
Auditory/Acoustic: repeating out loud ,or mentally repeating to yourself
Visual: attempting to keep a mental picture
Semantics: the meaning of the encoding itself
storage —> the process of retaining encoded information over time
retrieval —> the process of getting information out of memory storage
Parallel processing
processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
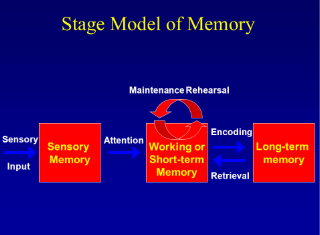
Memory stages
Sensory Memory – fraction of a second (iconic-visual images) (echoic-auditory sounds)
Working Memory/Short Term Memory (STM) — 1 minute
Long Term Memory (LTM)—Unlimited capacity — remember it forever
Central executive
a memory component that coordinates the activities of the phonological loop and visuospatial sketchpad
Sensory Memory
Very brief storage of memory immediately following initial reception of stimulus
Two types
Iconic (visual)
Echoic (auditory)
Important!
Prevents you from being overwhelmed
Gives you some decision time
Continuity and stability
Lasts for up to a couple seconds
Working Memory / Short-Term Memory
Limited in capacity to about 7 items
Length of memory depends on how actively you rehearse information
What it does;
Maintenance rehearsal
Keeps information in working memory (repeat, repeat, repeat)
Chunking
Grouping
Mnemonics
Memory aids
Serial position effect (Primacy-recency effect)
We usually remember first and last things
Long-Term Memory
Relatively permanent
Limitless!
Knowledge, skills, experiences
Phonological loop
a memory component that briefly holds auditory information
Visuospatial sketchpad
a memory component that briefly holds information about object’s appearance and location in space
Long-term potentiation (LTP)
an increase in a nerve cell’s firing potential after brief, rapid stimulation; a neural basis for learning and memory
Encoding - shallow processing and deep processing
shallow processing: maintenance rehearsal
deep processing: elaborative rehearsal
Chunking
organzing items into familiar, manageable units; often occurs automatically
Implicit verses Explicit memories
Implicit memory (nondeclarative/procedural memory)
Independent of conscious recollection (unconscious in the cerebellum)
Includes procedural memory
example : Clive Wearing’s ability to play piano
Explicit memory (declarative memory)
Facts and experiences that one can consciously know and “declare”
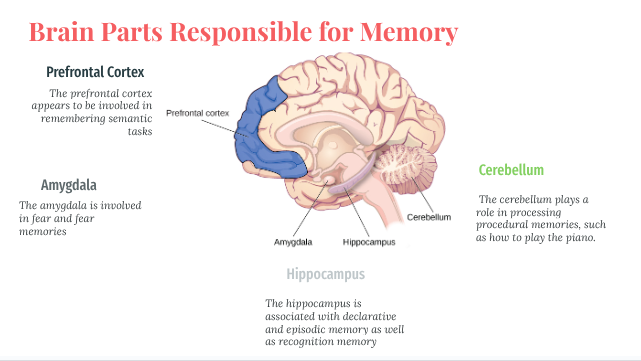
Hippocampus
Semantic memories and episodic memories
Hierarchies
Memory Tricks
Mnemonic devices —> memory aids, especially those techniques that use vivid imagery and organizational devices
Method of Loci —> memory aid in association of something with a location
Spacing Effect (distributed practice)
rehearsal —> practicing something outloud can help with memory aid
Testing Effect
enhanced memory after retrieving, rather than simply rereading, information. Also regerred to a retrieval practice effect or test-enhanced learning
Spacing Effect
the tendency for distributed study or practice to yield better long-term retention than is achieved through massed study or practice
Semantic Memory (hippocampus) and Episodic Memory (limbic system)
Semantic and episodic memories are both types of declarative memory, but they serve different purposes and rely on different brain regions.
Semantic memory, involving facts and general knowledge, is primarily stored in the neocortex,
Episodic memory, involving personal experiences and specific events, is formed and stored in the hippocampus and surrounding medial temporal lobe structures within the limbic system.
Brain Parts Responsible for Memory
State-Dependent Memory
You recall information more easily when you are in the same physiological or emotional state (mood congruent) or physical setting (context) you were when you originally encoded the info
Memory consolidation
the process by which newly formed memories, initially stored in the hippocampus, are transformed into more stable, long-term memories.
This involves strengthening memory traces, making them resistant to interference, and integrating them into pre-existing memory networks, often occurring during sleep
Flashbulb Memories
A clear memory of an emotionally significant moment or event.
Amygdala
Retrieval
Retrieval cues: the best retrieval cues come from associations we form when we encode a memory (little bits of information like passwords and open memories)
Context
State Dependent: when we learn in one state it may be more early recalled when we are again in that state (state of excitement or tension)
Serial Position (primacy effect vs. recency effect)
Priming (associations): the activation often unconsciously, of a particular associations in memory
Serial Position (primacy effect vs. recency effect)
our tendency to recall best the last items in a list initially (a recent effect) and the first items in a list after a delay (a primacy effect)
Mood Congruent Memory (state-dependent)
the tendency to recall experiences that are consistent with one’s current good or bad mood
Encoding specificity principle
memory recall is most effective when the conditions present during encoding (learning) are similar to the conditions present during retrieval (recall)
the more closely the encoding and retrieval contexts match, the better the memory retrieval will be
Interleaving
a retrieval practice strategy that involved mixing the study of different topics
studying by mixing together topics rather than blocking them out in groups
Anterograde amnesia vs. retrograde amnesia
anterograde magnesia —> an inability to form new memories (more common)
retrograde amnesia —> an inability to remember information from one’s past
Encoding failure
the inability to properly store information in long-term memory, leading to a later inability to recall it
This happens when the brain fails to create a memory link because information was not properly encoded, or when encoding was disrupted by factors like inattention or interference
Storage decay
the weakening or fading of memories
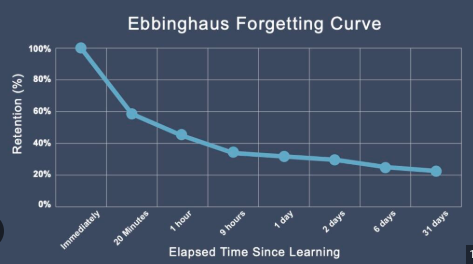
Forgetting Curve—Ebbinghaus
the course of forgetting is initially rapid, then levels off with time
Interference (proactive and retroactive)
Blocking of a memory by a previous or subsequent memory
Proactive interference: old memory blocks a new memory
Retroactive interference: New memory blocks an earlier memory
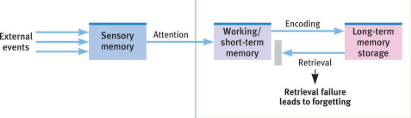
Retrieval failure
a type of forgetting where information, though stored in long-term memory, cannot be accessed or retrieved when needed
This happens due to the absence of sufficient retrieval cues or the interference of other information.
Repression (Freud)
in psychoanalytic theory, the basic defense mechanism that banishes from consciousness anxiety—arousing thoughts, feelings, and memories
Reconsolidation
a process in which previously stored memories, when retrieved, are potentially altered before being stored again
Confabulation and Eyewitness Testimony (Loftus)
Reconstructed false memory is caused by “source amnesia,” framing the question and “misinformation effect” (occurs when a memory has been corrupted by misleading information)
Several factors can influence the accuracy of eyewitness memory, including stress, time elapsed, misleading information, and suggestive questioning —> we automatically replace orginal info with new info rather than what's the truth
Deja Vu
the eerie sense that “I’ve experienced this before”
cues from current familiarity of a situation may unconsoiusly trigger retrieval of an earlier experience