CH6: TLD
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
30 Terms
The RCMP Blanket Exercise
Participants act as indigenous peoples in Canada standing on blankets that represent the land (Canada) they reenact pre-contact, treaty making, colonization, and resistance manipulating the cloth to symbolize the impacts on indigenous people.
It's an effort to give them an experience and to give them a better understanding as to what has happened historically. Overall building empathy and using it as a reconciliation tool
What is the difference between Training and Development
Training→ focuses on the present and is designed to prepare employees for their current job. It makes low use of work experiences, and participation is usually required.
Development → focuses on the future and aims to prepare employees for changes and career growth. It makes high use of work experiences, and participation is generally voluntary
How does TLD link to strategy: Strategic goals
Workplace training and employee development are key ingredients in the competitiveness of firms and ultimately of national competitiveness.
Organizations identified their top three strategic goals for learning and development:
improving organizational performance
enhancing individual employee performance
developing organizational leaders.
How does TLD link to strategy: Learning Culture & Continuous learning
Learning culture: ongoing commitment to learning, support, and communication that moves the organization forward, while providing them a competitive edged —more likely to be agile and resilient as well as high-performing
Continuous learning: refers to a learning system that requires employees to understand the entire work system, acquire new skills, apply them on the job, and share what they have learned with other employees
Generative VS Non-generative AI
Generative AI creates new content where as Non-Generative AI optimizes existing data
Key Use Cases for AI Across the Learning Lifecycle
Onboarding : Chatbots that answer queries in real time
Training : Autogenerate training modules customized to employee
Continuous learning: Analyze progress, feedback, and performance metrics and recommend new courses or resources.
Performance support: Chatbots help by giving advice, recommending resources, and acting as a virtual coach.
Risks of AI usage
Bias in AI models (misinformation & unfair practices)
Over-reliance on automated content (leading to unfair outcomes and depersonalized learning)
Quality control issues (Risk of outdated and/or incorrect information)
Upskilling & Reskilling
Increasing the skill sets of the workforce is a business imperative to keep the organization agile/adaptive and ensure employees stay relevant.
Upskilling : Learning new skills for the same or similar role, to prepare for future needs.
Reskilling: Learning new skills for a completely different role.
What would be the Core Skills on in 2030
Thinking smart, thinking creatively, using tech and data, staying resilient, leading others, and continuous learning.
Key employee considerations to attract and retain
Surveys have indicated:
(79% )that training opportunities are important when job searching
(94%) employees would stay with a company longer if their company invested in their career development
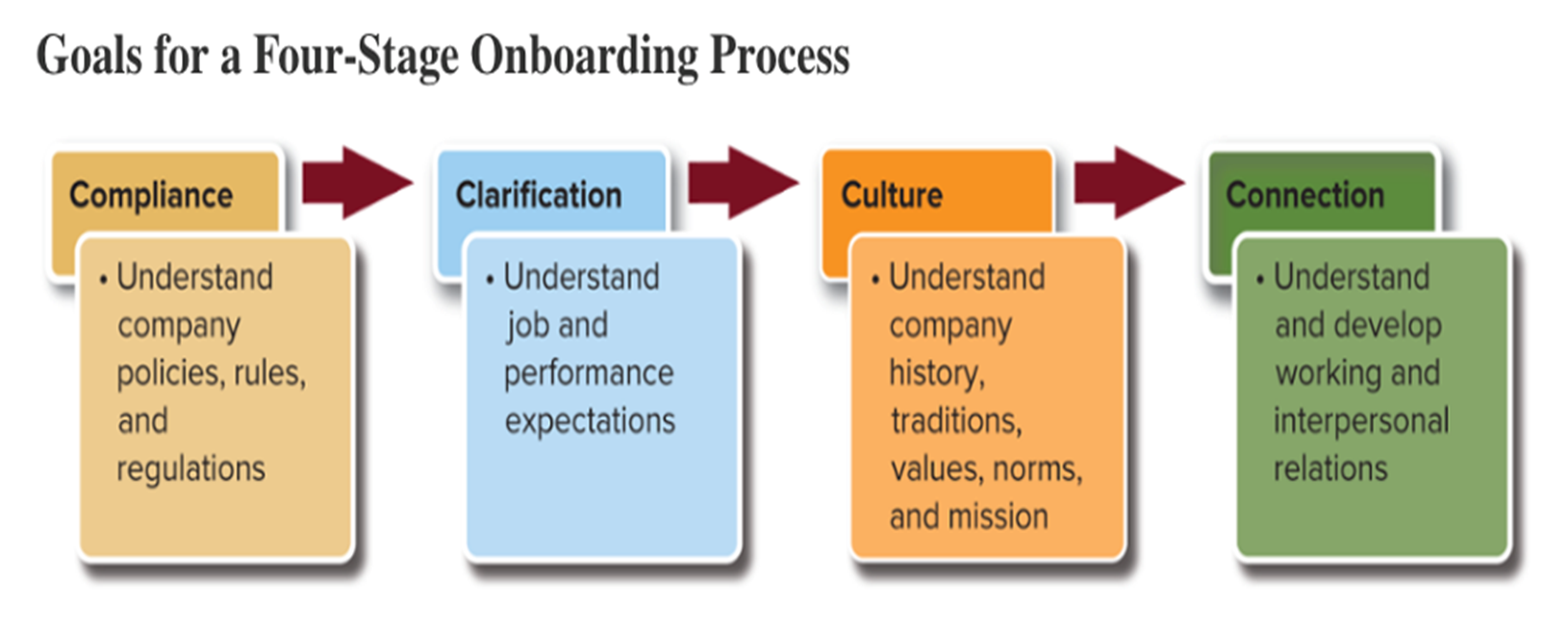
Goals for a four- safe onboarding & orientation process
Stages of instructional design (5)
assess needs for training
ensure readiness for training
plan training program
implement program
evaluate
all this is done while receiving feedback at each step.
(1) The Need Assessment Process
Understand why training might be needed through identifying reasons ( or triggers) that signal a potential skills gap.
Understanding the context (the 3 analyses) of why training is needed:
Organizational: The first step is to assess whether training is appropriate by considering the organization’s strategy, resources, and management support.
Person: Person analysis focuses on individual employees to determine whether training is the appropriate solution for their performance.
Causes for potential performance gaps, who needs training, and are employee readiness
Task: Identifies the tasks that training should emphasize while taking into consideration: job environment, time constrains, safety. and performance standards
Outcomes are the decisions you can confidently make once you understand the problem.
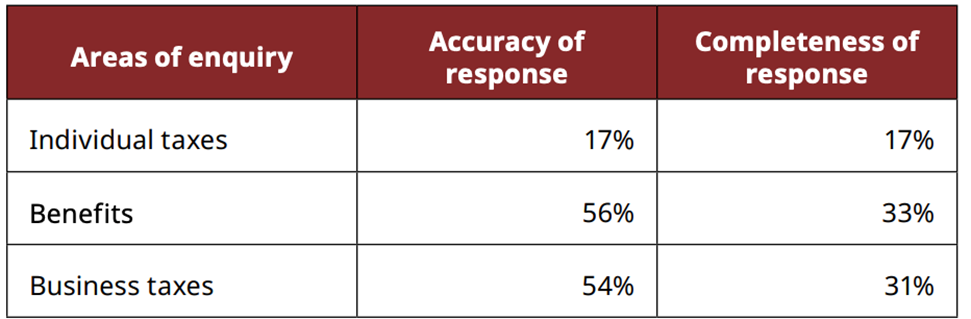
Canada Revenue Agency Contact centers
CRA contact centers often gave untimely, incorrect or incomplete information
A CRA chatbot (“Charlie”) was accurate only 33% of the time
Errors occurred across individual taxes, benefits, and business taxes
(2) Readiness for learning
Employee readiness for training depends on employees’ readiness characteristics: cognitive ability, motivation, and curiosity. It also accounts for work environment in which level of situational constraints ( money or time) and Social support become significant.
Skills needed in the Era of LLMs
Intelligent interrogation: The ability to write clear, specific prompts and use AI thoughtfully — often called “thinking with AI.”
Judgment integration: Using human judgment to decide where, when, and how to check, correct, or override AI outputs.
Reciprocal apprenticing: Knowing how to guide, correct, and train AI systems so they can handle more complex tasks in the future.
(3) Plan & Design Training program ( names its aspects)
1. Effective learning objectives
Learning objectives clearly state what employees must be able to do after training. Effective objectives include:
Expected behavior – what the employee will do
Level or quality of performance – how well it must be done
Conditions – under what circumstances the task is performed
Measurable standards – criteria used to evaluate success
Required resources – tools, time, or support needed to meet the standard
2. In-house or contracted out
Decides who will deliver the training:
In-house training uses internal staff and resources
Contracted out training uses external vendors or experts
3. Choose training methods
Types of training methods: Presentation Methods
Presentation methods involve learners receiving information from an instructor or learning materials such as lectures, videos, or workbooks. They are best for delivering facts, and comparing alternatives.
Types of training methods: Hands-on Methods
Hands-on methods actively involve learners in practicing skills through activities such as on-the-job training, simulations, or role-plays. They help learners apply knowledge to real job situations and improve skill performance.
Types of training methods: Group or Team-Building Methods
Group or team-building methods focus on learning through interaction, discussion, and shared experiences. They help build teamwork, improve communication, and strengthen interpersonal relationships. These methods are especially useful for developing collaboration and managing team performance.
Training delivery methods based on company size
Larger organizations use more virtual, blended, and technology-based training methods, while smaller organizations rely more on traditional classroom and online approaches.
(3) Implementing the training program
when implementing the program it is important to consider:
Principles of learning (understanding the various way that people learn)
creating value for the learner
positive learner experience
Link theory & practice
The goal of implementing id Transfer of learning: It ensures employees apply the knowledge, skills, and behaviours learned in training to their actual job, making training effective and improving performance.
Ways to support the implementation of TLD
Microlearning: Microlearning delivers training in short, focused modules that are easy to access, reduce time away from work, and improve retention during training rollout.
Community of practice: Groups who work together, learn from each other, and develop common understanding of how to get work done
Micro credentials
Stacked set of micro learnings that accelerate learners’ skills in a specific area
Inuit Holistic Lifelong Learning Model
The Inuit Holistic Lifelong Learning Model views learning as a lifelong, community-based process that integrates Indigenous and Western knowledge while supporting the social, cultural, environmental, and personal well-being of individuals and communities.
Inuit Learning Principles & beliefs
We learn with Elders, Knowledge Keepers, teachers, and community members.
We practice Tunnganarniq by being open, welcoming, kind, and inclusive. This encourages learners to be friendly, use humour within learning spaces.
We make decisions together as a team and share our ideas, fostering collaboration, creative thinking and problem solving.
We show our learning in different ways and receive helpful feedback to grow.
Measuring Results of Training (5)
Trainee satisfaction (learner reaction)
New skills and/or knowledge acquired
Transfer of learning (behaviour change/use of skills)
Performance improvements (individual/organization)
Return on investment
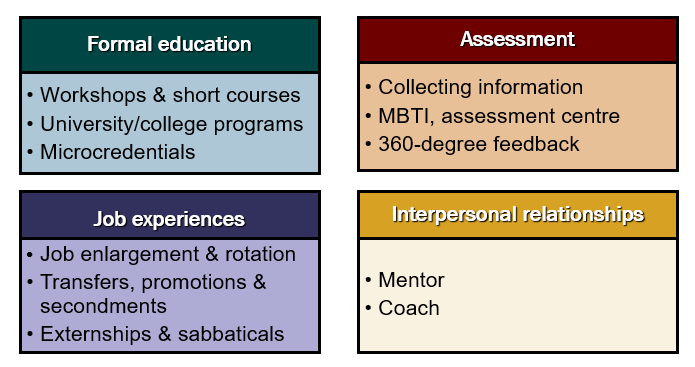
4 Approaches to Development
Career management process
1. Data Gathering
We collect information about skills, strengths, and areas to improve.
This focuses on what is needed to be successful and uses different ways to measure learning.
2. Feedback
We talk about what the information shows.
Feedback is private, respectful, and focuses on strengths, successes, and areas to grow.
3. Goal Setting
We decide what to work on next.
Goals are clear and specific, and support comes from teachers, coaches, mentors, or leaders.
4. Action Planning & Follow-Up
We make a plan and take action.
Progress is checked, plans are adjusted if needed, and we make sure goals are realistic.
High-Potential Employees
High-potential employees are strong performers chosen for their achievements and growth potential, and are given advanced developmental experiences , with guidance from senior leaders to develop future leadership skills.