Lecture 6 - EYES
1/43
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
44 Terms
Canadian's top concern
- too much screen time
- too much exposure to sun/UV rays
- environmental factors such as wildfires smoke, and pollution
most common eye problems
- vision changes
- itchy eyes
- dry eyes
- infection
- glaucoma
- cataracts
general survey of eyes
- skin
- anatomy
- movement
- behaviours
skin general survey
- color
- rasges/tags
- oozing
anatomy general survey
- as expected symmetry
- placement and presence
- lashes
- color
movement general survey
should by symmetrical and appropriate
Eye health history
- visual difficulty
- refraction errors
- pain
- photophobia
- strabismus
- diplopia
- redress, swelling discharge
- medications
- chronic illness
- surgical history
- allergies
- use of glasses/contact lenses
- self care
- community connections/resources
refraction errors
- myopia
- hyperopia
- presbyopia
- astigmatism
photophobia
sensitivity to light
strabismus
altered extra ocular movements
diplopia
double vision
self-care
- eye protection
- vision loss effect
- ADLs
community connections/resources accessed
want to ensure that patient have the ability to access the optometrist
conjuctiva (expected)
clear, some small blood vessels
sclera (expected)
white
anisocoria
unequal size of patient's pupils

anisocoria characteristics
can be harmless and 20% of population has genetic variation
when is anisocoria dangerous
can be dangerous, especially if presenting after trauma
miosis
small or constricted pupils
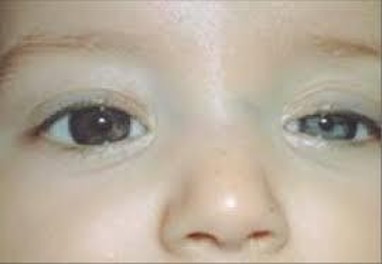
charecteristics of miosis
small pupil in one eye and dilated in other can indicate trauma
mydriasis
dilated pupils
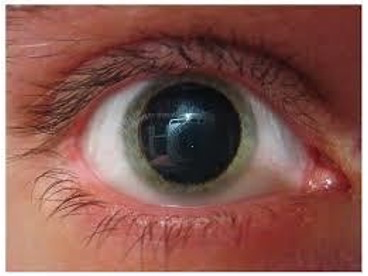
mydriasis characteristics
- can be normal after eye drops
- may indicate brain injury
arcus senalis
discolouration around cornea
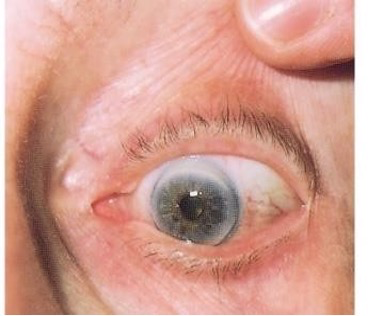
arcus senalis charecteristics
- cholesterol deposits around eyes
- mostly in older adults, big concern if in younger populations
pupillary light response
- should respond symmetrically and as expected when light sources is introduced look for both direct and consensual response - look at both eyes that light is shown in and the opposite eyes
what does light response
indicates neural response
visual acuity
- test for macular function
- macula gives risk to the majority of optic nerve fivers
- ability to accommodate to see far and near
Snellen's test for
visual acuity and distance
snellen's test
distance from chart (always 20 feet)/distances that someone with expected visions would stand from the chart to read that line
normal vision
20/20
legal blindness is best corrected vision
20/200
better test
(20/<20) can occur
jaeger test
near vision
jaeger test distance from eyes
14 inches from eyes
- read the smallest letter
other eye testing
colour blindness test
extraocular muscles and movements
test if eyes response to requested movements in an appropriate manner
eye movement
should be symmetrical in manner
tests of extra ocular muscles
- cardinal direction
- corneal reflection
- cover test
cardinal direction
one of the four compass points: north, south, east, west
corneal reflection
Shine penlight in front of patient, reflection of light on corneas should be symmetrical
Hypotropia
eye turns down
Hypertropia
eyes turn up
Exotropia
Eyes turn out
Esotropia
Eyes turn in